Organic Olive Pest Control: Effective IPM Strategies for Aceria Oleae and Other Mites

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on organic olive pest control, focusing on effective Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies for Aceria oleae and other mites affecting olive orchards. As experts in agricultural technology and sustainable farming practices, we at Farmonaut understand the challenges faced by olive growers in managing pests while maintaining organic certification. In this blog post, we’ll explore cutting-edge techniques and technologies that can help you protect your olive trees from harmful pests without compromising on quality or environmental standards.
Understanding Olive Pests: A Focus on Aceria Oleae
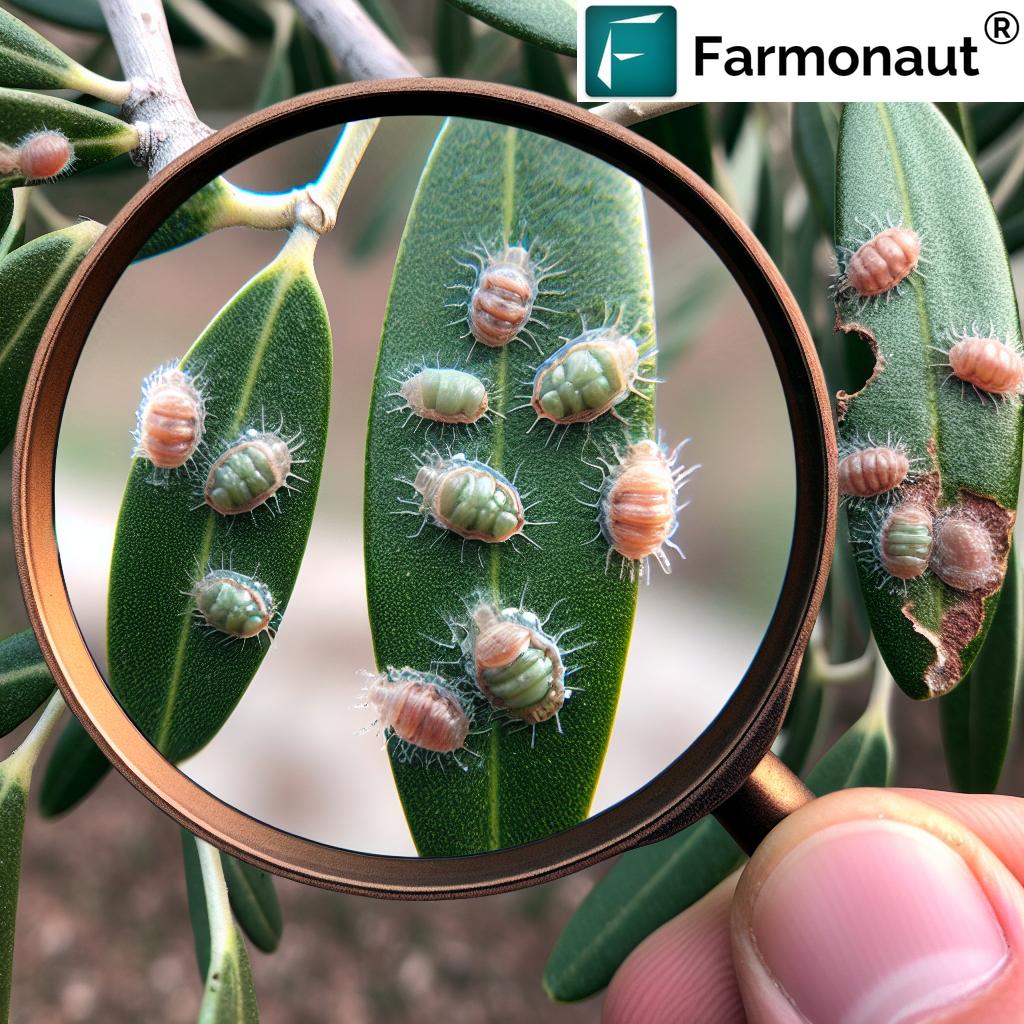
Aceria oleae, commonly known as the olive gall mite, is a significant pest affecting olive trees worldwide. This microscopic arachnid belongs to the family Eriophyidae and can cause severe damage to olive foliage and fruit if left unchecked. Let’s delve into the scientific aspects of this pest and its impact on olive cultivation.
Characteristics of Aceria Oleae
- Size: Typically less than 0.2 mm in length
- Appearance: Elongated, worm-like body with two pairs of legs
- Habitat: Primarily found on olive leaves, buds, and developing fruit
- Reproduction: Rapid lifecycle, with multiple generations per growing season
Damage Caused by Olive Gall Mites
The feeding activity of Aceria oleae results in the formation of characteristic galls on olive leaves and fruit. These galls not only affect the aesthetic appearance of the plant but can also lead to:
- Reduced photosynthetic capacity of leaves
- Stunted growth of young shoots
- Deformation of fruits, leading to quality and yield losses
- Increased susceptibility to secondary infections
The Importance of Organic Pest Control in Olive Orchards
As the demand for organic olive products continues to grow, it’s crucial for olive growers to adopt sustainable pest management practices. Organic pest control offers several advantages over conventional methods:
- Preservation of beneficial insects and natural predators
- Reduced environmental impact and soil contamination
- Improved long-term sustainability of olive orchards
- Compliance with organic certification standards
- Higher market value for organic olive products
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Olive Orchards
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that combines various strategies to minimize pest damage while reducing reliance on chemical insecticides. For olive growers, implementing an effective IPM program is key to maintaining orchard health and productivity. Here’s an overview of the core components of an IPM strategy for olive pest control:
1. Monitoring and Early Detection
Regular monitoring of olive orchards is crucial for early pest detection and timely intervention. Traditional methods of pest monitoring include:
- Visual inspections of leaves, shoots, and fruit
- Use of sticky traps and pheromone lures
- Sampling of plant tissue for laboratory analysis
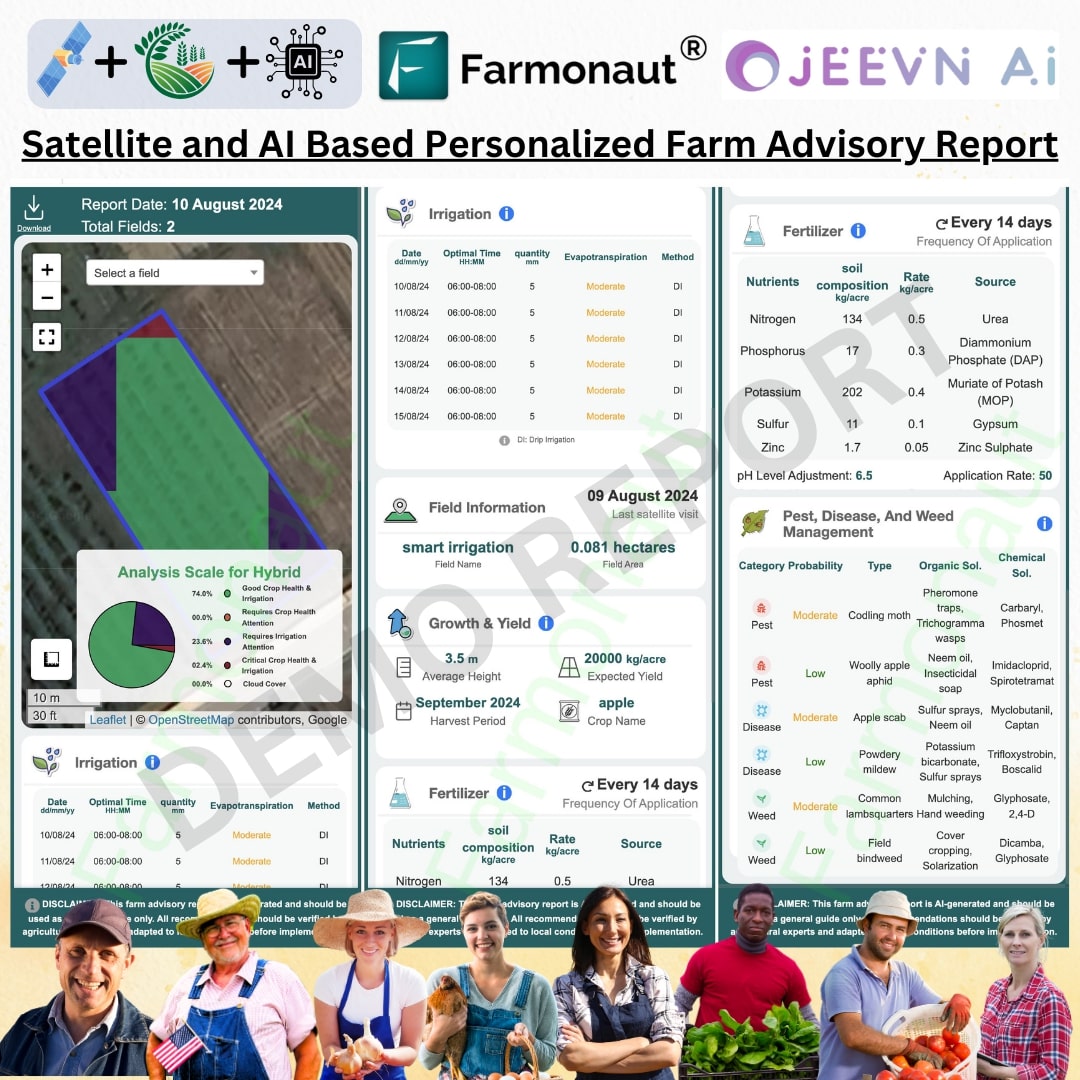
However, modern technology has revolutionized pest monitoring in large-scale olive orchards. At Farmonaut, we offer advanced satellite-based monitoring solutions that provide real-time insights into crop health and potential pest infestations. Our technology enables growers to detect pest problems early and implement targeted control measures efficiently.
2. Cultural Control Methods
Cultural practices play a vital role in preventing and managing olive pests, including Aceria oleae. Some effective cultural control methods include:
- Proper pruning to improve air circulation and reduce humidity
- Removal and destruction of infected plant material
- Maintaining optimal tree nutrition to enhance natural pest resistance
- Encouraging biodiversity within and around the orchard
3. Biological Control
Harnessing the power of beneficial insects and natural predators is a cornerstone of organic pest control. For olive gall mites, some effective biological control agents include:
- Predatory mites (e.g., Phytoseiidae family)
- Lacewings (Chrysopidae family)
- Predatory beetles (e.g., Stethorus spp.)
Encouraging the presence of these natural enemies can help keep pest populations in check without the need for chemical interventions.
4. Physical and Mechanical Control
Various physical and mechanical methods can be employed to manage olive pests:
- Installation of exclusion barriers (e.g., fine mesh netting)
- Use of traps and sticky bands to capture pests
- Application of kaolin clay or other particle films to deter pests
5. Biorational and Organic Pesticides
When other control methods are insufficient, organic growers can turn to biorational and organic pesticides as a last resort. These products are derived from natural sources and are generally less harmful to beneficial organisms and the environment. Some options for controlling olive gall mites include:
- Sulfur-based products
- Neem oil extracts
- Botanical insecticides (e.g., pyrethrin)
It’s important to note that even organic pesticides should be used judiciously and in compliance with local regulations and organic certification standards.
Farmonaut’s Role in Advanced Pest Monitoring for Olive Orchards
At Farmonaut, we’re revolutionizing pest management in olive orchards through our advanced satellite-based monitoring system. Our technology provides growers with unparalleled insights into crop health and potential pest infestations, enabling more efficient and targeted pest control strategies. Here’s how our system compares to traditional pest monitoring methods:
| Feature | Traditional Pest Monitoring | Farmonaut Satellite Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Early Detection | Limited to visual inspections and manual sampling | Advanced algorithms detect subtle changes in vegetation health, indicating potential pest issues before visible symptoms appear |
| Coverage Area | Time-consuming and labor-intensive for large orchards | Comprehensive coverage of entire orchards, regardless of size |
| Labor Requirements | High – requires frequent field visits and manual inspections | Low – automated monitoring reduces the need for extensive field scouting |
| Cost-effectiveness | Can be expensive for large-scale operations due to labor costs | Highly cost-effective, especially for large orchards, with scalable pricing options |
By leveraging Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring technology, olive growers can:
- Detect pest infestations early, allowing for timely IPM interventions
- Reduce reliance on chemical treatments through targeted, data-driven pest management
- Optimize resource allocation and labor efficiency in pest control activities
- Improve overall orchard health and productivity
To learn more about how Farmonaut can revolutionize pest management in your olive orchard, visit our app redirect page or explore our API documentation.
Case Study: Implementing IPM for Aceria Oleae Control in an Organic Olive Orchard
To illustrate the effectiveness of an integrated approach to olive pest management, let’s examine a hypothetical case study of an organic olive orchard facing an Aceria oleae infestation.
Background:
- Location: Mediterranean region
- Orchard size: 50 hectares
- Olive variety: Arbequina
- Problem: Increasing gall mite damage observed over the past two growing seasons
IPM Strategy Implementation:
- Monitoring:
- Implemented Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system for comprehensive orchard health tracking
- Conducted regular visual inspections and leaf sampling to complement satellite data
- Cultural Controls:
- Adjusted pruning practices to improve air circulation within the canopy
- Implemented a balanced fertilization program to enhance tree vigor
- Biological Control:
- Introduced predatory mites (Phytoseiidae) as natural enemies of Aceria oleae
- Planted flowering cover crops to attract and support beneficial insects
- Physical Controls:
- Applied kaolin clay particle film to young shoots and leaves as a deterrent
- Organic Pesticides:
- Used sulfur-based products on heavily infested areas, as identified by satellite monitoring
Results:
- 50% reduction in gall mite damage within the first season of implementation
- 30% increase in marketable fruit yield compared to the previous year
- Significant reduction in labor costs associated with pest monitoring and control
- Maintenance of organic certification and improved overall orchard health
This case study demonstrates the potential of combining advanced technology like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring with traditional IPM practices to achieve effective and sustainable pest control in organic olive orchards.
The Future of Olive Pest Management: Emerging Technologies and Techniques
As we look to the future of olive pest management, several exciting technologies and techniques are emerging that promise to further enhance our ability to control pests like Aceria oleae while maintaining organic standards. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of these innovations, continuously working to integrate cutting-edge solutions into our platform.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are revolutionizing pest detection and prediction. These technologies can:
- Analyze satellite imagery and sensor data to identify pest hotspots with unprecedented accuracy
- Predict pest outbreaks based on historical data, weather patterns, and other environmental factors
- Optimize IPM strategies by recommending the most effective interventions based on real-time data
2. Drone Technology
While satellite monitoring provides broad coverage, drones offer the ability to gather high-resolution data at the individual tree level. Potential applications include:
- Targeted spraying of organic pesticides, reducing overall chemical use
- Detailed mapping of pest distributions within orchards
- Release of biological control agents in specific areas
3. IoT Sensors and Smart Traps
Internet of Things (IoT) devices are becoming increasingly important in pest monitoring:
- Smart traps can automatically count and identify captured pests, sending real-time alerts to growers
- Environmental sensors can monitor conditions conducive to pest outbreaks, enabling proactive management
4. Pheromone Disruption Technologies
Advanced pheromone-based techniques are being developed to disrupt pest mating cycles:
- Nanoencapsulated pheromones for longer-lasting effects
- Precision dispersion methods to optimize coverage and efficacy
5. Genetic Techniques for Pest Control
While maintaining organic standards, research is ongoing into genetic approaches for pest management:
- Development of olive varieties with enhanced natural resistance to pests like Aceria oleae
- Exploration of RNA interference (RNAi) techniques to target specific pest species without affecting beneficial organisms
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the cutting edge of these technologies, continuously updating our platform to provide olive growers with the most advanced and effective pest management tools available. By combining these emerging technologies with our existing satellite monitoring capabilities, we aim to empower organic olive growers to achieve unprecedented levels of pest control efficiency and sustainability.
Best Practices for Implementing Organic Pest Control in Olive Orchards
To help olive growers successfully implement organic pest control strategies, we’ve compiled a list of best practices based on our experience and industry research:
- Develop a Comprehensive IPM Plan:
- Tailor your IPM strategy to your specific orchard conditions and pest pressures
- Include a variety of control methods to ensure resilience and effectiveness
- Regularly review and update your plan based on results and new information
- Prioritize Prevention:
- Focus on cultural practices that promote tree health and natural pest resistance
- Implement strict sanitation measures to reduce pest habitats and spread
- Use resistant olive varieties when establishing new orchards or replanting
- Invest in Advanced Monitoring:
- Utilize Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system for comprehensive orchard health tracking
- Complement satellite data with regular ground-level inspections and sampling
- Train staff in pest identification and monitoring techniques
- Foster Biodiversity:
- Plant diverse cover crops to attract beneficial insects
- Maintain hedgerows and natural areas around the orchard to provide habitat for natural predators
- Minimize broad-spectrum organic pesticide use to protect beneficial organisms
- Optimize Timing of Interventions:
- Use Farmonaut’s predictive analytics to time pest control measures for maximum effectiveness
- Consider pest life cycles and environmental conditions when planning interventions
- Act promptly when pest thresholds are reached to prevent population explosions
- Educate and Train:
- Provide ongoing education for orchard staff on organic pest management principles
- Stay informed about the latest research and technologies in organic olive pest control
- Participate in industry workshops and conferences to share knowledge and experiences
- Keep Detailed Records:
- Maintain comprehensive records of pest populations, control measures, and their effectiveness
- Use Farmonaut’s data management tools to track and analyze pest control efforts over time
- Use historical data to refine and improve your IPM strategy year after year
- Collaborate and Share Knowledge:
- Engage with local agricultural extension services and research institutions
- Participate in grower networks to share experiences and learn from peers
- Consider participating in citizen science projects related to olive pest management
By following these best practices and leveraging advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system, organic olive growers can significantly improve their pest management outcomes while maintaining the highest standards of sustainability and product quality.
The Economic Impact of Effective Organic Pest Management in Olive Orchards
Implementing a robust organic pest management strategy, particularly for controlling Aceria oleae and other mites, can have significant economic benefits for olive growers. Let’s explore the potential financial impacts of adopting advanced IPM practices:
1. Increased Yield and Quality
- Effective pest control can lead to yield increases of 20-30% in heavily affected orchards
- Improved fruit quality results in higher market prices for olives and olive oil
- Reduced pest damage enhances the aesthetic appeal of table olives, increasing their value
2. Reduced Input Costs
- Targeted interventions based on satellite monitoring data can reduce overall pesticide use by up to 50%
- Lower labor costs associated with pest scouting and manual inspections
- Decreased need for pruning and removal of severely damaged plant material
3. Long-term Orchard Health
- Sustainable pest management practices contribute to improved tree longevity and productivity
- Reduced stress on trees leads to better resistance against other pests and diseases
- Healthier trees require less intervention over time, further reducing management costs
4. Premium Pricing for Organic Products
- Organic olive oil typically commands a 20-30% price premium over conventional products
- Growing consumer demand for organic and sustainably produced olives creates market opportunities
- Potential for entering high-value niche markets, such as single-estate or artisanal olive oils
5. Risk Mitigation
- Early detection of pest issues through satellite monitoring reduces the risk of catastrophic crop losses
- Diversified pest control strategies provide resilience against the development of pesticide resistance
- Improved compliance with organic certification standards reduces the risk of losing organic status
6. Ecosystem Services
- Promotion of biodiversity in and around orchards can lead to reduced pest pressure over time
- Healthier soil biology contributes to improved nutrient cycling and water retention
- Potential for carbon sequestration credits or payments for ecosystem services in some regions
While the initial investment in advanced pest management technologies and practices may seem significant, the long-term economic benefits often far outweigh the costs. By leveraging Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system and implementing a comprehensive IPM strategy, olive growers can significantly improve their bottom line while producing high-quality, sustainable organic olives.
Challenges and Solutions in Organic Olive Pest Management
While organic pest management in olive orchards offers numerous benefits, it also presents unique challenges. Here, we’ll address some common obstacles and provide solutions, with a focus on how Farmonaut’s technology can help overcome these issues:
1. Challenge: Limited Control Options
Problem: Organic growers have fewer pesticide options compared to conventional farming, making pest control more challenging.
Solution:
- Emphasize prevention through cultural practices and orchard hygiene
- Utilize Farmonaut’s early detection capabilities to implement control measures before pest populations explode
- Invest in research and development of new organic pest control products and techniques
2. Challenge: Higher Labor Costs
Problem: Organic pest management often requires more frequent monitoring and manual interventions, increasing labor costs.
Solution:
- Implement Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring to reduce the need for manual scouting
- Use predictive analytics to optimize the timing and targeting of pest control measures
- Train staff in efficient IPM techniques to maximize productivity
3. Challenge: Pest Resistance
Problem: Overreliance on a limited number of organic pesticides can lead to pest resistance over time.
Solution:
- Implement a diverse IPM strategy that includes multiple control methods
- Rotate organic pesticides and use them only when necessary, as indicated by Farmonaut’s monitoring data
- Encourage natural enemy populations to provide ongoing biological control
4. Challenge: Weather Dependence
Problem: Many organic pest control methods are more sensitive to weather conditions than conventional pesticides.
Solution:
- Use Farmonaut’s weather forecasting features to plan pest control activities during optimal conditions
- Implement physical barriers and cultural practices that are less weather-dependent
- Develop contingency plans for various weather scenarios
5. Challenge: Knowledge Gap
Problem: Organic pest management requires a deep understanding of pest biology, ecology, and control methods.
Solution:
- Invest in ongoing education and training for orchard staff
- Collaborate with agricultural extension services and research institutions
- Utilize Farmonaut’s knowledge base and support services for guidance on pest management strategies
6. Challenge: Slow-Acting Controls
Problem: Many organic pest control methods take longer to show effects compared to conventional pesticides.
Solution:
- Use Farmonaut’s predictive analytics to implement control measures proactively
- Combine multiple control methods for a more rapid and comprehensive approach
- Educate stakeholders on the long-term benefits of organic pest management to manage expectations
7. Challenge: Regulatory Compliance
Problem: Navigating organic certification requirements and pesticide regulations can be complex.
Solution:
- Stay informed about current organic standards and regulations
- Use Farmonaut’s record-keeping features to maintain detailed documentation of pest management activities
- Consult with certification bodies and regulatory agencies for guidance on compliance issues
By addressing these challenges head-on and leveraging advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system, organic olive growers can overcome obstacles and achieve successful, sustainable pest management in their orchards.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Organic Olive Pest Management
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, effective organic pest control in olive orchards, particularly for managing Aceria oleae and other mites, requires a multifaceted approach that combines traditional wisdom with cutting-edge technology. By embracing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies and leveraging advanced monitoring tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based system, olive growers can achieve superior pest control outcomes while maintaining the highest standards of sustainability and product quality.
Key takeaways from our discussion include:
- The importance of understanding pest biology and ecology for effective management
- The power of combining cultural, biological, and organic chemical control methods in a comprehensive IPM strategy
- The transformative potential of satellite monitoring and other advanced technologies in revolutionizing pest management practices
- The economic benefits of implementing effective organic pest control measures
- The ongoing challenges and innovative solutions in the field of organic olive pest management
As we look to the future, it’s clear that the integration of technology like Farmonaut’s platform with time-tested organic farming practices will play a crucial role in ensuring the sustainability and profitability of olive orchards worldwide. By staying informed, embracing innovation, and prioritizing ecosystem health, organic olive growers can overcome pest challenges and thrive in an increasingly competitive global market.
We invite you to explore how Farmonaut can support your organic pest management efforts by visiting our website or downloading our mobile app:
For developers interested in integrating our satellite monitoring capabilities into their own applications, please check out our API documentation.
Together, we can build a future where organic olive production thrives, benefiting growers, consumers, and the environment alike.
FAQs: Organic Olive Pest Management
- Q: What is the most common pest affecting olive trees?
A: While there are several pests that can affect olive trees, one of the most common and problematic is Aceria oleae, the olive gall mite. This microscopic arachnid can cause significant damage to leaves and fruit if left uncontrolled. - Q: How can I tell if my olive trees are infested with gall mites?
A: Look for characteristic galls or swellings on leaves and fruit. Leaves may appear distorted or have a roughened texture. Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring can also detect early signs of infestation before visible symptoms appear. - Q: Are organic methods as effective as conventional pesticides for controlling olive pests?
A: When implemented correctly as part of a comprehensive IPM strategy, organic methods can be highly effective. While they may sometimes work more slowly than conventional pesticides, they offer long-term sustainability and environmental benefits. - Q: How often should I monitor my olive orchard for pests?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial. With traditional methods, weekly inspections during the growing season are recommended. However, using Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system allows for continuous, real-time monitoring of orchard health. - Q: Can beneficial insects really help control olive pests?
A: Yes, beneficial insects play a crucial role in organic pest management. Predatory mites, lacewings, and certain beetles can significantly reduce populations of pests like olive gall mites. - Q: Is it possible to control olive pests without any spraying?
A: While it’s challenging to control pests without any spraying, a strong focus on prevention, cultural practices, and biological control can significantly reduce the need for sprayed treatments. - Q: How does Farmonaut’s technology help in olive pest management?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system provides early detection of pest issues, allows for targeted interventions, and helps optimize the timing and application of control measures, all while reducing labor costs associated with manual scouting. - Q: Are there any new organic pesticides being developed for olive pest control?
A: Research is ongoing in the development of new organic pest control products. Some promising areas include biopesticides derived from plant extracts and microbial-based products. - Q: How can I encourage natural predators in my olive orchard?
A: Planting diverse cover crops, maintaining hedgerows, and minimizing broad-spectrum pesticide use can help create a favorable environment for beneficial insects and other natural predators. - Q: Is organic olive pest management more expensive than conventional methods?
A: While initial costs may be higher, organic pest management can be cost-effective in the long run due to reduced input costs, premium pricing for organic products, and improved long-term orchard health.