Here’s a comprehensive blog post on the topic of cotton spotted bollworm, incorporating the requested keywords, images, and additional information about Farmonaut:

Combating the Cotton Spotted Bollworm: A Comprehensive Guide to Identification, Damage Assessment, and Management Strategies
As pioneers in agricultural technology, we at Farmonaut understand the critical challenges faced by cotton farmers worldwide. One of the most persistent threats to cotton cultivation is the cotton spotted bollworm, a destructive pest that can significantly impact crop yields and quality. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of the spotted bollworm in cotton, its lifecycle, the extent of damage it causes, and most importantly, how to effectively manage this pest using modern agricultural technologies and practices.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Cotton Spotted Bollworm
- Understanding the Lifecycle of the Spotted Bollworm
- Identifying Spotted Bollworm Damage in Cotton
- Economic Impact of Spotted Bollworm Infestation
- Traditional Management Strategies
- Modern Technological Approaches to Pest Management
- Farmonaut’s Role in Combating Spotted Bollworm
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Spotted Bollworm Control
- Future Outlook and Sustainable Practices
- FAQs
1. Introduction to the Cotton Spotted Bollworm
The cotton spotted bollworm, scientifically known as Earias vittella, is a notorious pest that plagues cotton crops across various regions of the world. This insect, belonging to the family Nolidae, is not just a menace to cotton but also affects other crops in the Malvaceae family. However, its impact on cotton is particularly severe, earning it the moniker “spotted bollworm of cotton.”
The spotted bollworm is characterized by its distinctive appearance:
- Adult moths have pale green or brown forewings with white spots
- Hindwings are white with brown margins
- Larvae are initially cream-colored, later developing a pinkish hue with dark spots
Understanding this pest is crucial for cotton farmers, as early detection and management can significantly reduce crop losses. At Farmonaut, we emphasize the importance of knowledge and technology in combating agricultural challenges like the spotted bollworm.
2. Understanding the Lifecycle of the Spotted Bollworm
To effectively manage the spotted bollworm in cotton, it’s essential to understand its lifecycle. This knowledge helps in timing interventions and implementing targeted control measures. The lifecycle of the spotted bollworm typically consists of four stages:
- Egg Stage: Female moths lay small, round, greenish eggs on various parts of the cotton plant, particularly on tender shoots, flower buds, and young bolls.
- Larval Stage: Upon hatching, larvae immediately begin feeding on plant tissues. This stage lasts about 10-14 days and is the most destructive phase.
- Pupal Stage: Mature larvae pupate within a silken cocoon, often in plant debris or soil. This stage lasts 7-10 days.
- Adult Stage: Adult moths emerge from pupae and live for about 7-10 days, during which they mate and lay eggs, continuing the cycle.
The entire lifecycle can complete in 3-4 weeks under favorable conditions, allowing for multiple generations within a single cotton growing season. This rapid reproduction rate underscores the importance of vigilant monitoring and timely intervention.
3. Identifying Spotted Bollworm Damage in Cotton
Recognizing spotted bollworm damage in cotton is crucial for early intervention. The damage caused by this pest can be extensive and varied, affecting different parts of the cotton plant at various growth stages. Here are key indicators of spotted bollworm infestation:
- Early Season Damage:
- Wilting and drooping of terminal shoots
- Presence of small holes in leaves and stems
- Shedding of young squares (flower buds)
- Mid to Late Season Damage:
- Circular holes in bolls, often with frass (insect excrement) visible
- Discoloration and premature opening of bolls
- Reduced boll size and weight
- Severe Infestation Signs:
- Extensive shedding of squares and young bolls
- Stunted plant growth
- Significant reduction in yield and fiber quality
At Farmonaut, our satellite-based crop monitoring system can help detect early signs of stress in cotton fields, potentially indicating pest infestations like spotted bollworm. Our advanced imagery analysis can highlight areas of concern, allowing farmers to investigate and take action promptly.
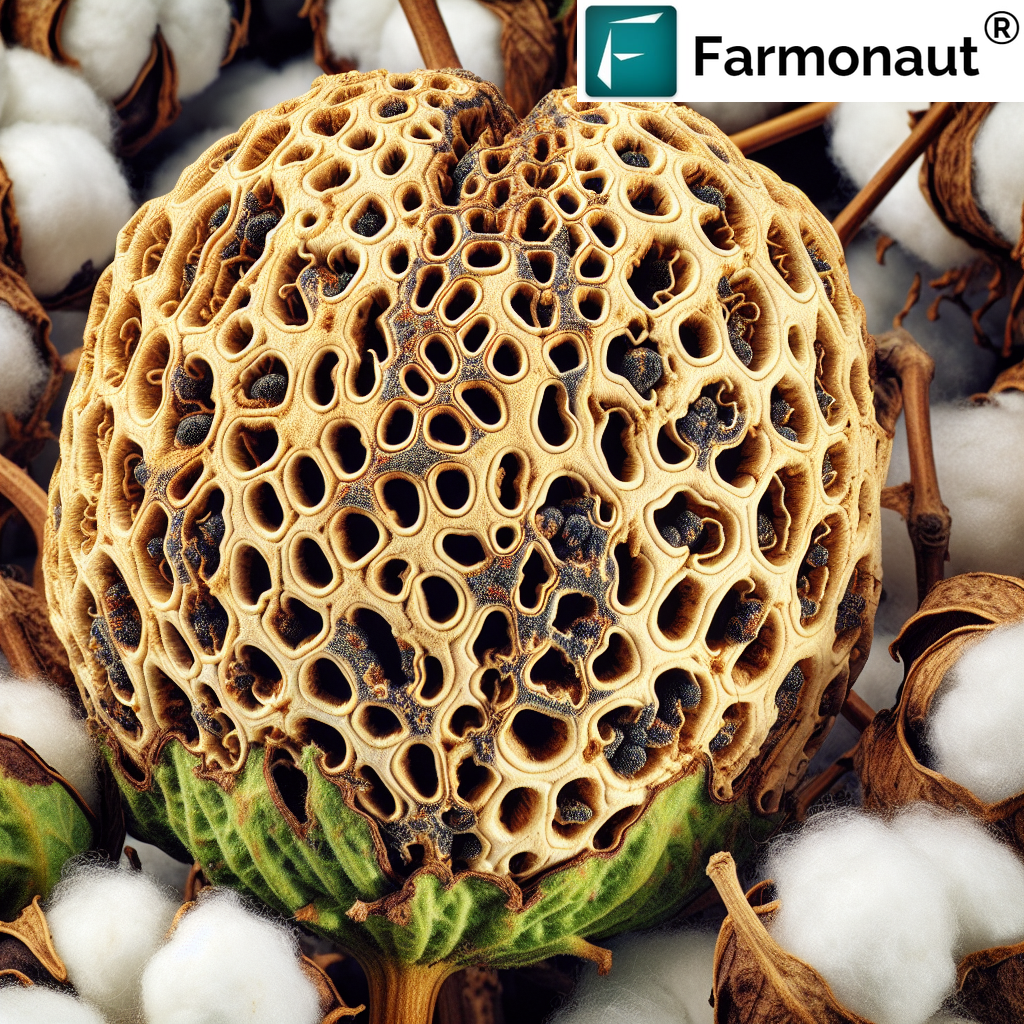

4. Economic Impact of Spotted Bollworm Infestation
The economic consequences of spotted bollworm damage in cotton can be substantial. This pest not only reduces yield quantity but also significantly impacts fiber quality, leading to:
- Reduced cotton yield, sometimes up to 50% in severe cases
- Lowered fiber quality, affecting market value
- Increased production costs due to pest management expenses
- Potential loss of export markets due to quality issues
According to various studies, global economic losses due to spotted bollworm and related pests in cotton can run into billions of dollars annually. This underscores the critical need for effective management strategies, which we at Farmonaut are committed to supporting through our advanced agricultural technologies.
5. Traditional Management Strategies
Historically, farmers have employed various traditional methods to combat the spotted bollworm of cotton. While these methods have their place, they often fall short in providing comprehensive protection, especially in large-scale commercial farming. Some traditional approaches include:
- Cultural Controls:
- Crop rotation to break pest cycles
- Early planting and harvesting to avoid peak pest periods
- Destruction of crop residues to eliminate overwintering sites
- Mechanical Controls:
- Hand-picking and destroying infested bolls
- Using pheromone traps to monitor pest populations
- Biological Controls:
- Encouraging natural predators like birds and beneficial insects
- Using microbial insecticides like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)
While these methods can be effective to some extent, they often require significant labor and may not be sufficient for large-scale operations. This is where modern technological approaches, including those offered by Farmonaut, come into play.
6. Modern Technological Approaches to Pest Management
In the fight against the cotton spotted bollworm, modern technology has revolutionized pest management strategies. These advanced approaches offer more precise, efficient, and environmentally friendly solutions. Some key technological advancements include:
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Platforms like Farmonaut use satellite imagery to detect crop stress, potentially indicating pest infestations early on. This technology allows for targeted interventions, reducing the need for broad-spectrum pesticide applications.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies help in predicting pest outbreaks based on historical data, weather patterns, and current field conditions.
- Precision Agriculture: GPS-guided equipment for precise pesticide application, minimizing wastage and environmental impact.
- Genetically Modified (GM) Cotton: Bt cotton varieties that are resistant to bollworms, though their effectiveness against spotted bollworm can vary.
- Remote Sensing: Using drones and satellites to assess crop health and identify potential pest hotspots.
At Farmonaut, we integrate many of these technologies into our comprehensive farm management solutions, providing farmers with powerful tools to combat pests like the spotted bollworm effectively.
7. Farmonaut’s Role in Combating Spotted Bollworm
Farmonaut’s advanced agricultural technology plays a crucial role in the management of pests like the spotted bollworm in cotton. Our satellite-based monitoring system offers several advantages:
- Early Detection: Our satellite imagery can detect changes in crop health before they’re visible to the naked eye, potentially indicating early stages of pest infestation.
- Precision Targeting: By identifying specific areas of concern, we enable farmers to focus their pest control efforts, reducing overall pesticide use.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Our AI-powered analytics provide insights that help farmers make informed decisions about pest management strategies.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regular satellite passes allow for ongoing assessment of crop health and pest pressure throughout the growing season.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Our platform can integrate with various farm management tools, creating a comprehensive pest management system.
To experience the benefits of Farmonaut’s technology in managing pests like the spotted bollworm, visit our application page or explore our API services.
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (100s to 1000s of acres) | Limited (10s to 100s of acres) | Very Limited (specific points) |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular (Every 3-5 days) | As needed (labor-intensive) | Continuous but localized |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High | Medium to High |
| Operational Complexity | Low (cloud-based) | High (requires skilled operator) | Medium (requires maintenance) |
| Data Analysis | Advanced AI and ML algorithms | Manual or semi-automated | Automated but limited scope |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited scalability | Moderate scalability |
8. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Spotted Bollworm Control
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that combines various strategies to manage pest populations effectively while minimizing environmental impact. For controlling the spotted bollworm of cotton, an IPM approach might include:
- Monitoring and Scouting: Regular field inspections and use of pheromone traps to track pest populations.
- Cultural Practices: Implementing crop rotation, adjusting planting dates, and maintaining field hygiene.
- Biological Control: Encouraging natural predators and using biopesticides when appropriate.
- Chemical Control: Judicious use of pesticides, preferably those with minimal impact on beneficial insects.
- Technological Integration: Utilizing Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring and AI-driven insights for precision pest management.
- Resistant Varieties: Planting cotton varieties that show resistance to spotted bollworm, where available.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of pest populations, control measures, and their effectiveness for future reference.
By integrating Farmonaut’s technology into an IPM strategy, farmers can achieve more effective control of spotted bollworm while promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
9. Future Outlook and Sustainable Practices
As we look to the future of cotton farming and pest management, several trends and innovations are shaping the way we approach challenges like the cotton spotted bollworm:
- Advanced Genetic Engineering: Development of new cotton varieties with enhanced resistance to pests, including spotted bollworm.
- Precision Agriculture: Further integration of AI, IoT, and satellite technology for ultra-precise pest detection and management.
- Biological Pest Control: Increased research into and use of natural predators and biopesticides.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Adapting pest management strategies to changing climate conditions that may affect pest populations.
- Sustainable Chemical Solutions: Development of more environmentally friendly and targeted pesticides.
At Farmonaut, we’re continually evolving our technology to meet these future challenges. Our commitment to sustainable agriculture drives us to develop solutions that not only combat pests like the spotted bollworm but also promote overall ecosystem health.
For the latest updates on our agricultural technology solutions, visit our website or download our app:
10. FAQs
Q1: How can I tell if my cotton crop is infested with spotted bollworm?
A1: Look for signs such as wilting terminal shoots, small holes in leaves and bolls, and premature opening of bolls. Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring can also help detect early signs of crop stress that may indicate infestation.
Q2: Are there any natural predators of the spotted bollworm?
A2: Yes, several natural predators can help control spotted bollworm populations, including parasitic wasps, predatory bugs, and some bird species.
Q3: How effective is Bt cotton against spotted bollworm?
A3: While Bt cotton is generally effective against many bollworm species, its efficacy against spotted bollworm can vary. It’s important to use Bt cotton as part of an integrated pest management strategy.
Q4: Can Farmonaut’s technology directly detect spotted bollworm infestations?
A4: Farmonaut’s satellite technology detects crop stress, which can indicate pest infestations. While it doesn’t directly identify specific pests, it provides valuable early warning signs that prompt further investigation.
Q5: How often should I monitor my cotton fields for spotted bollworm?
A5: Regular monitoring is crucial, especially during vulnerable crop stages. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can receive updates every 3-5 days, complementing your on-ground inspections.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you manage pests like the spotted bollworm in your cotton fields, please visit our API documentation or contact our support team.
Conclusion
Managing the cotton spotted bollworm requires a multifaceted approach combining traditional practices with modern technology. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing farmers with the tools and insights they need to combat this persistent pest effectively. By leveraging our satellite-based monitoring system, farmers can detect potential infestations early, implement targeted interventions, and minimize crop losses.
Remember, successful pest management is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, adaptability, and the right technological support. With Farmonaut by your side, you’re well-equipped to face the challenge of spotted bollworm and other agricultural pests.
To start leveraging the power of satellite technology in your pest management strategy, consider subscribing to Farmonaut:
Together, we can work towards more sustainable and productive cotton farming practices, ensuring a brighter future for agriculture worldwide.