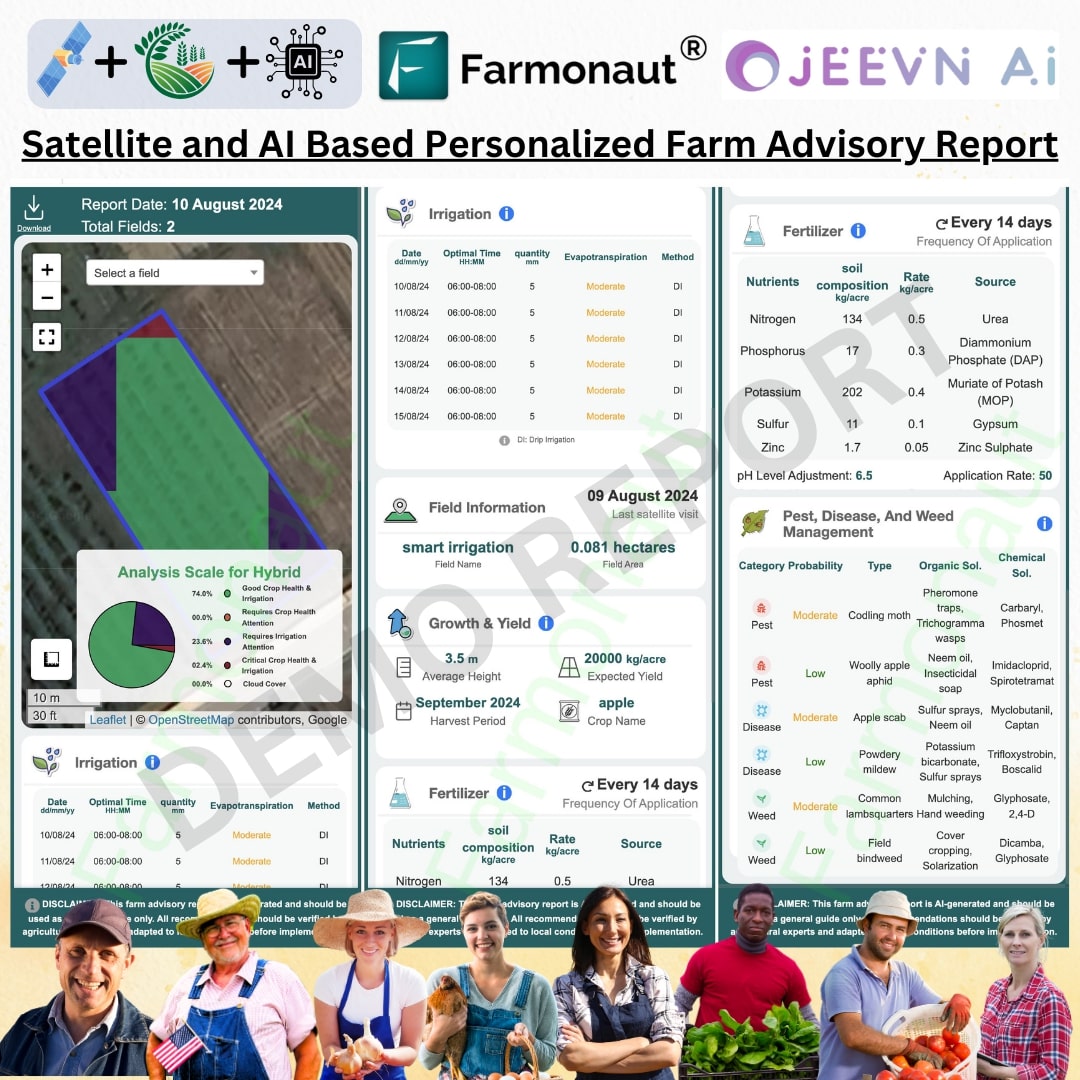
Organic and Chemical Powdery Mildew Control: Effective Fungicides and Treatments for Grapevines and Fruit Crops
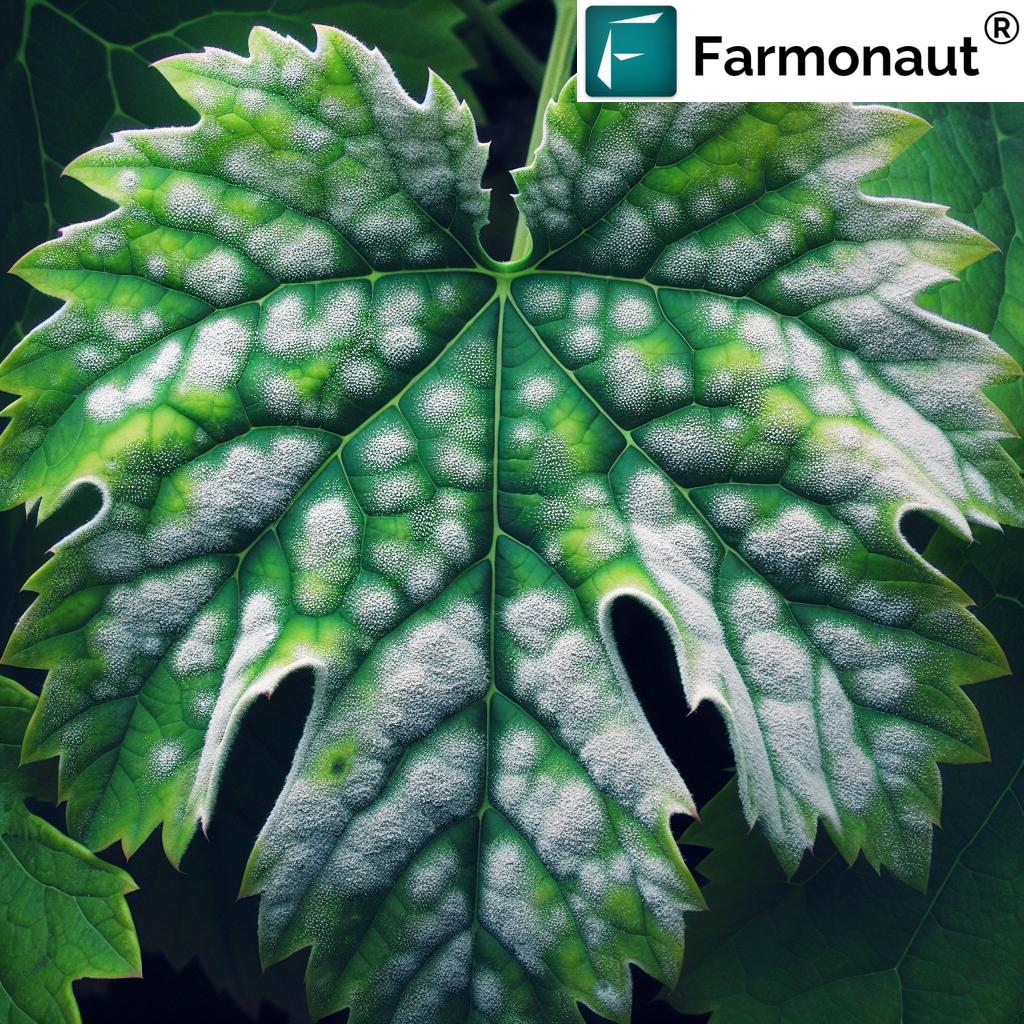

Powdery mildew is a persistent and devastating fungal disease that affects numerous crops, particularly grapevines and other fruit-bearing plants. As agricultural experts at Farmonaut, we understand the challenges farmers face in combating this resilient pathogen. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore both organic and chemical methods for powdery mildew control, focusing on effective fungicides and treatments that can help protect your valuable crops.
Understanding Powdery Mildew: A Persistent Threat to Grapevines and Fruit Crops
Powdery mildew is caused by various species of fungi belonging to the order Erysiphales. This disease is characterized by a white, powdery growth on the surface of leaves, stems, and fruit. In grapevines, it’s primarily caused by the fungus Erysiphe necator (formerly known as Uncinula necator).
The infestation typically begins with small, circular white spots on the upper surfaces of leaves. As the disease progresses, these spots expand and coalesce, eventually covering entire leaf surfaces, young shoots, and developing fruit. Severe infections can lead to reduced photosynthesis, stunted growth, and significant yield losses.
The Impact of Powdery Mildew on Grape Production
For grapevines, powdery mildew can be particularly devastating. It affects both table and wine grapes, causing:
- Reduced fruit quality and yield
- Increased susceptibility to other pathogens
- Altered wine flavors in infected grapes
- Weakened vine health and winter hardiness
Early detection and control are crucial for minimizing the impact of powdery mildew on grape production. This is where advanced technology, such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring system, can play a pivotal role.
Traditional vs. Advanced Detection Methods: A Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Powdery Mildew Detection | Farmonaut Satellite System |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Visual inspection by field scouts | Multispectral satellite imagery analysis |
| Coverage | Limited to accessible areas | Entire vineyard, including hard-to-reach areas |
| Early Detection | Often detects visible symptoms | Can detect stress before visible symptoms appear |
| Frequency | Dependent on labor availability | Regular updates based on satellite pass frequency |
| Data Analysis | Manual, subject to human error | AI-powered, consistent and objective |
| Treatment Planning | General recommendations | Precise, zone-specific treatment plans |
| Cost Efficiency | Labor-intensive and costly for large areas | Cost-effective for monitoring large vineyards |
| Integration with Other Data | Limited integration capabilities | Integrates with weather data and historical patterns |
As evident from the comparison, Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers significant advantages in early detection, comprehensive coverage, and data-driven decision-making for powdery mildew management in vineyards.
Effective Fungicides for Powdery Mildew Control
The control of powdery mildew often requires a combination of cultural practices and the judicious use of fungicides. Here, we’ll explore both chemical and organic options for treatment.
Chemical Fungicides
Chemical fungicides have long been a mainstay in powdery mildew management. Some effective options include:
- Sulfur-based fungicides: One of the oldest and most widely used fungicides for powdery mildew control. Sulfur works by inhibiting spore germination and fungal growth.
- Sterol Inhibitors (DMIs): These systemic fungicides, such as myclobutanil and tebuconazole, disrupt the fungal cell membrane formation.
- Strobilurins (QoIs): Fungicides like azoxystrobin and pyraclostrobin interfere with fungal respiration.
- Benzimidazoles: Compounds like thiophanate-methyl target fungal cell division.
While these chemical options can be highly effective, it’s crucial to rotate between different modes of action to prevent the development of fungicide resistance.
Organic Fungicides and Treatments
For growers seeking organic solutions, several options are available:
- Sulfur: Also used in organic production, sulfur remains one of the most effective organic fungicides against powdery mildew.
- Potassium bicarbonate: This compound alters the pH on the leaf surface, creating an inhospitable environment for the fungus.
- Neem oil: Derived from the neem tree, this natural fungicide also has insecticidal properties.
- Milk sprays: Some organic growers have found success using diluted milk as a fungicide.
- Biological controls: Certain beneficial microorganisms, such as Bacillus subtilis, can be used as biocontrol agents against powdery mildew.
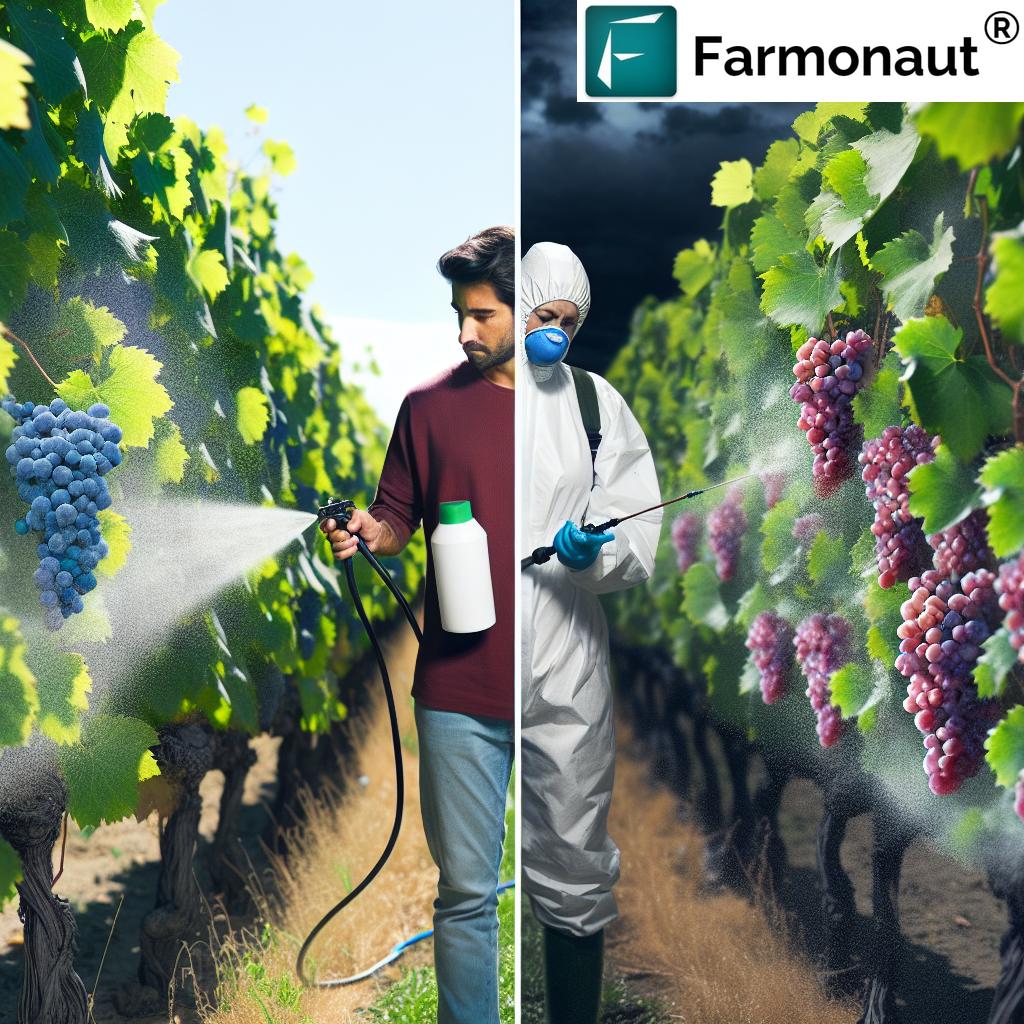

Application Techniques for Optimal Fungicide Efficacy
The effectiveness of fungicides, whether chemical or organic, largely depends on proper application techniques. Here are some key considerations:
Timing of Application
Timing is crucial for effective powdery mildew control. We recommend:
- Beginning applications at the first sign of disease or when conditions are favorable for disease development.
- Following a regular spray schedule, typically every 7-14 days, depending on disease pressure and weather conditions.
- Using Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system to detect early signs of stress in grapevines, allowing for timely interventions.
Coverage and Spraying Techniques
Proper coverage is essential for effective fungicide performance:
- Ensure thorough coverage of all plant surfaces, including the undersides of leaves.
- Use appropriate spraying equipment and nozzles for optimal droplet size and distribution.
- Consider using electrostatic sprayers for improved coverage and reduced drift.
Water Quality and Mixing
The quality of water used for mixing fungicides can affect their efficacy:
- Use clean water with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0 for most fungicides.
- Add adjuvants or surfactants as recommended to improve fungicide performance.
- Mix fungicides according to label instructions, paying attention to compatibility when tank-mixing multiple products.
Integrated Pest Management for Powdery Mildew Control
While fungicides play a crucial role in powdery mildew management, an integrated approach is often the most effective strategy for long-term control. This includes:
Cultural Practices
- Proper pruning and training to improve air circulation and reduce humidity within the canopy.
- Avoiding excessive nitrogen fertilization, which can promote succulent growth more susceptible to powdery mildew.
- Removing and destroying infected plant material to reduce inoculum levels.
Resistant Varieties
Planting resistant grape varieties can significantly reduce the need for fungicide applications. Some varieties with good resistance to powdery mildew include:
- Regent
- Traminette
- Norton
- Marquette
Environmental Management
Powdery mildew thrives in specific environmental conditions. Managing these conditions can help suppress disease development:
- Avoid overhead irrigation, which can increase humidity and promote disease development.
- If using irrigation, water early in the day to allow foliage to dry quickly.
- Use row orientation and spacing to maximize sunlight exposure and air movement through the vineyard.
Monitoring and Forecasting
Regular monitoring is crucial for effective powdery mildew management. Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring system offers advanced capabilities for early detection and targeted control:
- Multispectral imagery analysis to detect plant stress before visible symptoms appear.
- Integration with weather data to predict favorable conditions for disease development.
- AI-powered advisory system for optimized fungicide application timing and frequency.
To learn more about how Farmonaut’s technology can enhance your powdery mildew management strategy, visit our application page or explore our API solutions.
Sanitation and Hygiene Practices
Sanitation plays a crucial role in preventing the spread and recurrence of powdery mildew. Implementing good hygiene practices in your vineyard or orchard can significantly reduce disease pressure:
- Clean and disinfect pruning tools between uses to prevent the spread of spores.
- Remove and destroy infected plant material, including leaves, fruit, and pruned canes.
- Maintain a clean orchard floor by removing fallen leaves and fruit, which can harbor overwintering spores.
- Clean and sanitize trellises, stakes, and other support structures between growing seasons.
The Role of Biological Control Agents
Biological control agents are becoming increasingly popular in both organic and integrated pest management programs. These living organisms can help suppress powdery mildew without the use of synthetic chemicals:
Bacillus-based Products
Bacillus subtilis and other Bacillus species have shown promise in controlling powdery mildew:
- These beneficial bacteria compete with the pathogen for space and nutrients on the leaf surface.
- Some strains produce antifungal compounds that directly inhibit powdery mildew growth.
- Regular applications of Bacillus-based products can provide ongoing protection and may reduce the need for chemical fungicides.
Other Beneficial Microorganisms
In addition to Bacillus, other microorganisms have shown potential for powdery mildew control:
- Ampelomyces quisqualis: A hyperparasite that attacks powdery mildew colonies.
- Trichoderma species: Fungi that can colonize plant surfaces and outcompete pathogens.
- Streptomyces lydicus: A beneficial bacterium that produces antifungal compounds.
Advanced Technologies in Powdery Mildew Management
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of integrating advanced technologies into agricultural practices. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system offers several advantages for powdery mildew management in grapevines and other crops:
Early Detection and Precision Monitoring
- Multispectral imagery analysis can detect subtle changes in plant health, allowing for early intervention before visible symptoms appear.
- Regular monitoring provides a comprehensive view of vineyard health, enabling targeted treatments and reducing unnecessary fungicide applications.
Data-Driven Decision Making
- Integration of satellite imagery with weather data and historical disease patterns for accurate risk assessment.
- AI-powered advisory system provides personalized recommendations for fungicide application timing and product selection.
Efficient Resource Management
- Precise identification of affected areas allows for targeted treatments, reducing overall fungicide use and environmental impact.
- Optimization of labor and equipment resources through data-driven planning and execution of disease management strategies.
To explore how Farmonaut’s technology can revolutionize your powdery mildew management approach, visit our Android app or iOS app.
Resistance Management Strategies
The development of fungicide resistance is a growing concern in powdery mildew management. Implementing effective resistance management strategies is crucial for maintaining the long-term efficacy of fungicides:
Fungicide Rotation
- Rotate between fungicides with different modes of action to reduce selection pressure on pathogen populations.
- Use the Fungicide Resistance Action Committee (FRAC) codes to guide rotation decisions.
- Avoid using single-site fungicides exclusively; incorporate multi-site fungicides like sulfur into the rotation.
Tank Mixing
- Combine fungicides with different modes of action in tank mixes to provide multiple layers of protection.
- Ensure compatibility between mixed products and follow label recommendations for tank mixing.
Limiting Exposure
- Restrict the number of applications of any single fungicide class per season.
- Use fungicides preventatively rather than curatively when possible.
- Integrate non-chemical control methods to reduce overall fungicide use.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainable Practices
As we strive for effective powdery mildew control, it’s crucial to consider the environmental impact of our management practices. Sustainable approaches can help protect both your crops and the surrounding ecosystem:
Reduced Chemical Use
- Implement precision agriculture techniques, such as those offered by Farmonaut, to optimize fungicide applications and reduce overall chemical use.
- Consider incorporating more organic and biological control methods into your management strategy.
Water Conservation
- Use efficient irrigation systems to minimize leaf wetness and reduce conditions favorable for powdery mildew development.
- Implement water-conserving spray technologies to reduce waste and runoff during fungicide applications.
Biodiversity Promotion
- Maintain or establish natural habitats around vineyards to support beneficial insects and natural enemies of powdery mildew.
- Use cover crops to improve soil health and potentially suppress disease through increased microbial diversity.
Economic Considerations in Powdery Mildew Management
Effective powdery mildew control is not just about protecting your crops; it’s also about maintaining the economic viability of your operation. Consider the following economic factors when developing your management strategy:
Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Evaluate the costs of different fungicide programs against potential yield and quality improvements.
- Consider the long-term economic benefits of investing in resistant varieties or advanced monitoring technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite system.
Market Demands
- Be aware of market preferences for organic or low-residue grapes and adjust your management approach accordingly.
- Consider the potential premium for high-quality, disease-free fruit in your market.
Risk Management
- Assess the financial risks of potential crop losses due to powdery mildew and invest in appropriate insurance coverage.
- Diversify your management approach to mitigate risks associated with fungicide resistance or regulatory changes.
Future Directions in Powdery Mildew Control
As agricultural technology continues to advance, we anticipate several exciting developments in powdery mildew management:
Gene Editing and Resistant Varieties
- CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies may lead to the development of highly resistant grape varieties without compromising quality or yield.
- Continued traditional breeding efforts will likely produce new varieties with improved powdery mildew resistance.
Advanced Biological Controls
- Research into novel biocontrol agents, including engineered microorganisms, may provide new tools for organic and integrated pest management.
- Improved formulations and delivery systems for existing biological controls like Bacillus species may enhance their efficacy and ease of use.
Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Modeling
- AI-driven disease forecasting models, integrated with real-time environmental data, will enable increasingly precise timing of fungicide applications.
- Machine learning algorithms may identify subtle patterns in satellite imagery and other data sources, further improving early detection capabilities.
To stay at the forefront of these technological advancements in agricultural management, consider integrating Farmonaut’s cutting-edge solutions into your operations. Explore our API documentation to learn how our technology can be tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion
Effective management of powdery mildew in grapevines and other fruit crops requires a multifaceted approach, combining traditional practices with cutting-edge technologies. By integrating chemical and organic fungicides, cultural practices, biological controls, and advanced monitoring systems like those offered by Farmonaut, growers can achieve superior disease control while minimizing environmental impact and optimizing economic outcomes.
As we look to the future, the continued advancement of agricultural technologies promises even more precise, sustainable, and effective methods for combating powdery mildew and other crop diseases. By staying informed and adopting innovative solutions, growers can ensure the health and productivity of their vineyards and orchards for years to come.
To take the next step in revolutionizing your powdery mildew management strategy, consider subscribing to Farmonaut’s advanced crop monitoring services:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is powdery mildew, and why is it a concern for grape growers?
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects grapevines and many other plants. It’s a major concern for grape growers because it can significantly reduce yield and fruit quality, affecting both table grapes and wine production.
2. How can I identify powdery mildew in my vineyard?
Look for white, powdery spots on leaves, shoots, and fruit. As the disease progresses, these spots may cover entire leaf surfaces and cause leaf curling or distortion.
3. Are there any organic options for controlling powdery mildew?
Yes, organic options include sulfur-based products, potassium bicarbonate, neem oil, and biological control agents like Bacillus subtilis.
4. How often should I apply fungicides for powdery mildew control?
The frequency depends on disease pressure and weather conditions but typically ranges from 7 to 14 days. Using a monitoring system like Farmonaut can help optimize application timing.
5. Can powdery mildew develop resistance to fungicides?
Yes, powdery mildew can develop resistance to certain fungicides, especially if the same product or class of products is used repeatedly. It’s important to rotate fungicides and implement integrated management strategies.
6. How does Farmonaut’s technology help in managing powdery mildew?
Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system can detect early signs of plant stress, potentially indicating powdery mildew infestation before visible symptoms appear. This allows for timely and targeted interventions.
7. Are there grape varieties resistant to powdery mildew?
Yes, some grape varieties show better resistance to powdery mildew than others. Examples include Regent, Norton, and Marquette. However, even resistant varieties may require some level of management under high disease pressure.
8. How can I reduce the environmental impact of powdery mildew control?
Implement integrated pest management strategies, use precision agriculture techniques for targeted applications, consider organic alternatives, and maintain biodiversity in and around your vineyard.
9. What role does sanitation play in powdery mildew management?
Sanitation is crucial in reducing disease pressure. Remove and destroy infected plant material, clean tools and equipment, and maintain a clean orchard floor to reduce overwintering inoculum.
10. How can I stay updated on the latest powdery mildew management techniques?
Stay connected with agricultural extension services, attend industry workshops, and consider adopting advanced monitoring technologies like Farmonaut to access the latest in precision agriculture and disease management strategies.