Organic Pest Control: Protecting Fruits and Crops from Marmorated Stink Bugs and Other Pentatomidae Species
In the world of agriculture, protecting our crops and fruits from pests is an ongoing challenge. At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of maintaining healthy harvests while minimizing the use of harmful chemicals. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective organic methods for controlling one of the most notorious agricultural pests: the marmorated stink bug and its relatives in the Pentatomidae family.
Understanding the Pentatomidae Family
The Pentatomidae family includes various species of stink bugs, which are known for their shield-shaped bodies and distinctive odor when disturbed. Among the most problematic genera are:
- Halyomorpha halys (Brown marmorated stink bug)
- Euschistus species (Brown stink bugs)
- Nezara viridula (Southern green stink bug)
- Oebalus pugnax (Rice stink bug)
These insects pose a significant threat to a wide range of crops and fruits, including peach, apple, soybean, and rice.
The Impact of Stink Bugs on Agriculture
Stink bugs, particularly the brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys), can cause extensive damage to crops. These pests use their piercing-sucking mouthparts to feed on plant tissues, leading to various symptoms of crop damage:
- Discolored spots on fruits and vegetables
- Deformed or stunted fruit growth
- Reduced yield in grain crops like rice
- Transmission of plant pathogens
The economic impact of these pests can be substantial, affecting both small-scale farmers and large agricultural operations.
Organic Control Methods for Stink Bugs
At Farmonaut, we advocate for organic pest control methods that are environmentally friendly and sustainable. Here are some effective strategies for managing stink bug populations:
1. Cultural Control
- Crop rotation to disrupt pest life cycles
- Proper sanitation and removal of crop residues
- Use of trap crops to lure pests away from main crops
- Adjusting planting dates to avoid peak pest activity
2. Physical Barriers
- Installing row covers or netting to protect vulnerable crops
- Using sticky traps to capture adult stink bugs
- Implementing pheromone traps for monitoring and mass trapping
3. Biological Control
- Encouraging natural predators like birds, spiders, and parasitic wasps
- Using entomopathogenic fungi as a biological pesticide
- Introducing predatory insects like the samurai wasp (Trissolcus japonicus)
4. Organic Pesticides
While we prioritize non-chemical methods, certain organic insecticides can be effective when used judiciously:
- Neem oil
- Pyrethrin-based sprays
- Kaolin clay
- Diatomaceous earth
It’s crucial to use these products in compliance with organic certification standards and local regulations.
Innovative Monitoring Techniques
Effective pest control begins with thorough monitoring. At Farmonaut, we leverage cutting-edge technology to enhance pest detection and management:
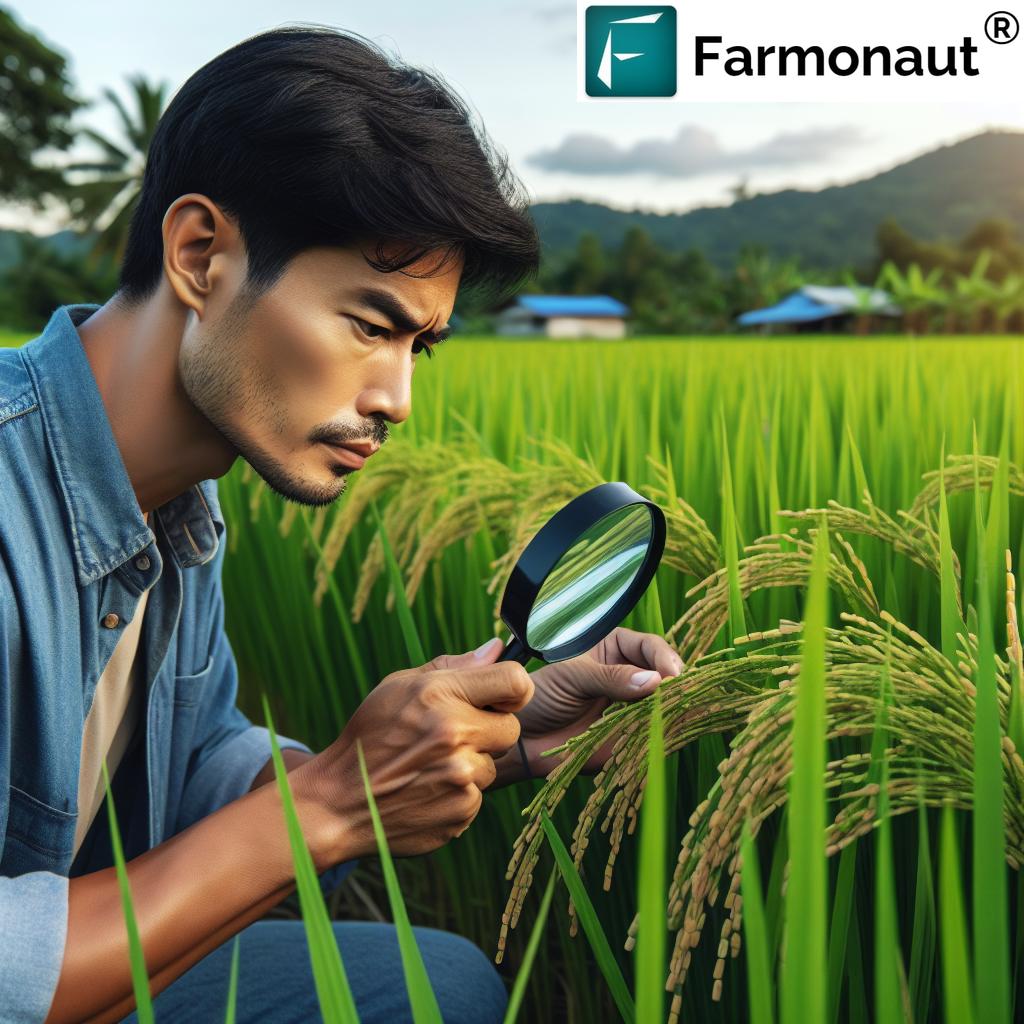

Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system provides farmers with real-time insights into vegetation health, helping to identify potential pest infestations early. By analyzing multispectral imagery, we can detect changes in crop vigor that may indicate stink bug activity.
AI-Powered Advisory System
Our Jeevn AI advisory system integrates satellite data with weather forecasts and pest population models to provide personalized recommendations for pest management. This helps farmers make informed decisions about when and where to implement control measures.
Comparison of Monitoring Methods
| Method | Accuracy | Coverage Area | Frequency | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Field Scouting | High (for scouted areas) | Limited | Weekly/Biweekly | Low (labor-intensive) |
| Pheromone Traps | Medium | Localized | Continuous | Medium |
| Farmonaut Satellite Monitoring | High | Large-scale | Daily/Weekly | High |
As the table illustrates, our satellite-based system offers superior coverage and frequency compared to traditional methods, enabling more comprehensive and timely pest detection.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approach
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach that combines various control methods to effectively manage stink bug populations while minimizing environmental impact. This strategy involves:
- Prevention: Implementing cultural practices to reduce pest attraction and establishment
- Monitoring: Regular surveillance using both traditional and technological methods
- Threshold-based action: Applying control measures only when pest populations reach economically damaging levels
- Multiple control tactics: Utilizing a combination of biological, cultural, and chemical controls as needed
- Evaluation: Assessing the effectiveness of control measures and adjusting strategies accordingly
Protecting Specific Crops from Stink Bugs
Different crops may require tailored approaches for stink bug management. Here are some specific strategies for protecting common targets of Pentatomidae pests:
Fruit Trees (e.g., Peach, Apple)
- Regular monitoring of fruit for feeding damage
- Use of kaolin clay as a protective barrier on fruits
- Strategic pruning to improve air circulation and reduce hiding spots
- Bagging individual fruits for physical protection
Field Crops (e.g., Soybean, Rice)
- Early planting to avoid peak stink bug activity periods
- Use of trap crops around field perimeters
- Regular scouting, especially during pod and grain development stages
- Targeted application of organic insecticides when thresholds are reached
Vegetables (e.g., Tomatoes, Peppers)
- Installation of floating row covers during vulnerable growth stages
- Companion planting with repellent herbs like basil or mint
- Hand-picking of adults and egg masses in small-scale operations
- Use of pheromone traps for monitoring and mass trapping
Emerging Technologies in Stink Bug Control
At Farmonaut, we’re always exploring innovative solutions to enhance pest management. Some promising technologies for stink bug control include:
- Drone-based pest detection: Using UAVs equipped with multispectral cameras to identify pest hotspots in large fields
- Smart traps: Automated traps that use AI to identify and count captured insects, providing real-time data to farmers
- Precision application systems: GPS-guided sprayers that can apply organic pesticides only where needed, reducing overall chemical use
- Blockchain traceability: Implementing our blockchain-based system to track pest management practices and ensure compliance with organic standards
The Role of Weather in Stink Bug Management
Weather conditions play a crucial role in stink bug behavior and population dynamics. Our satellite-based weather monitoring system provides farmers with accurate, localized forecasts to inform pest management decisions:
- Temperature: Stink bugs are more active in warm weather, with increased feeding and reproduction
- Humidity: High humidity can favor the development of entomopathogenic fungi, a natural control agent
- Rainfall: Heavy rains can wash off organic pesticides, requiring reapplication
- Wind: Strong winds can affect the dispersal of adult stink bugs and the effectiveness of sprayed treatments
By integrating weather data with our crop monitoring system, we help farmers time their control measures for maximum effectiveness.
Organic Certification and Stink Bug Control
For farmers pursuing or maintaining organic certification, it’s essential to ensure that all pest control methods comply with relevant standards. Our platform can help track and document pest management practices, facilitating the certification process:
- Maintaining detailed records of monitoring activities and control measures
- Ensuring all inputs (e.g., organic pesticides) are approved for use in organic production
- Implementing buffer zones to prevent drift from neighboring conventional farms
- Regularly reviewing and updating pest management strategies to align with organic principles
Economic Considerations in Organic Stink Bug Management
While organic pest control methods can be more labor-intensive and potentially costlier in the short term, they offer significant long-term benefits:
- Reduced input costs for synthetic pesticides
- Premium prices for organic produce
- Improved soil health and biodiversity
- Increased resilience to pest outbreaks over time
Our cost-effective satellite monitoring and AI advisory services can help farmers optimize their pest management strategies, balancing effectiveness with economic efficiency.
Community-Based Approaches to Stink Bug Control
Effective management of mobile pests like stink bugs often requires coordination beyond individual farm boundaries. We encourage community-based approaches to pest control:
- Collaborative monitoring efforts across multiple farms
- Sharing of pest control resources and knowledge
- Coordinated planting and harvesting schedules to disrupt pest life cycles
- Community-wide implementation of trap crops or mass trapping programs
Our platform facilitates data sharing and collaboration among farmers, supporting these community-based initiatives.
Future Directions in Organic Stink Bug Management
As we continue to innovate in the field of agricultural technology, several promising areas of research could revolutionize organic stink bug control:
- Gene editing for pest resistance: Developing crop varieties with enhanced natural defenses against stink bugs
- Improved biological control agents: Identifying and cultivating more effective predators and parasitoids
- Advanced pheromone technologies: Creating more potent and specific attractants for monitoring and mass trapping
- Machine learning for pest prediction: Enhancing our AI systems to forecast pest outbreaks with greater accuracy
Conclusion
Managing stink bugs and other Pentatomidae pests in organic farming systems requires a multifaceted approach combining traditional wisdom with cutting-edge technology. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing farmers with the tools and knowledge needed to protect their crops sustainably.
By leveraging our satellite-based monitoring, AI advisory systems, and blockchain traceability solutions, farmers can implement more effective, targeted, and environmentally friendly pest management strategies. As we continue to innovate and collaborate with the agricultural community, we look forward to developing even more powerful solutions for organic pest control.
For more information on how Farmonaut can support your organic pest management efforts, visit our website or download our mobile app:
For developers interested in integrating our agricultural data into their own applications, check out our API documentation:
FAQs
- Q: What are the most common stink bug species affecting crops?
A: The most problematic species include the brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys), various Euschistus species, the southern green stink bug (Nezara viridula), and the rice stink bug (Oebalus pugnax). - Q: How can I identify stink bug damage on my crops?
A: Look for discolored spots on fruits and vegetables, deformed or stunted fruit growth, and reduced yield in grain crops. In severe cases, you may also notice wilting or death of plant tissues. - Q: Are there any natural predators of stink bugs?
A: Yes, natural predators include birds, spiders, predatory insects like assassin bugs, and parasitic wasps. Encouraging these beneficial organisms can help control stink bug populations. - Q: How effective are organic pesticides against stink bugs?
A: Organic pesticides can be effective when used as part of an integrated pest management strategy. Products like neem oil and pyrethrin-based sprays can provide control, but timing and coverage are crucial for success. - Q: Can Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring detect stink bug infestations?
A: While our satellite monitoring cannot directly detect individual insects, it can identify changes in crop health that may indicate pest activity. This early warning system allows farmers to investigate and take action promptly. - Q: How often should I monitor my crops for stink bugs?
A: Regular monitoring is key. We recommend weekly scouting during critical growth stages, supplemented by daily checks of our satellite-based crop health reports. - Q: Are there any crops that are resistant to stink bug damage?
A: While no crop is entirely resistant, some varieties show higher tolerance. Research is ongoing to develop more resistant cultivars through traditional breeding and genetic engineering techniques. - Q: How can I prevent stink bugs from overwintering in my farm structures?
A: Seal entry points in buildings, remove nearby woodpiles or debris that could serve as shelter, and consider using physical barriers like screens on vents and windows. - Q: Is it possible to eradicate stink bugs completely from my farm?
A: Complete eradication is unlikely due to the mobility and adaptability of stink bugs. The goal of organic management is to keep populations below economically damaging levels. - Q: How can Farmonaut’s blockchain technology help with organic pest management?
A: Our blockchain system can help track and verify pest management practices, ensuring compliance with organic standards and providing transparency throughout the supply chain.
Ready to take your organic pest management to the next level? Subscribe to Farmonaut’s advanced agricultural monitoring services: