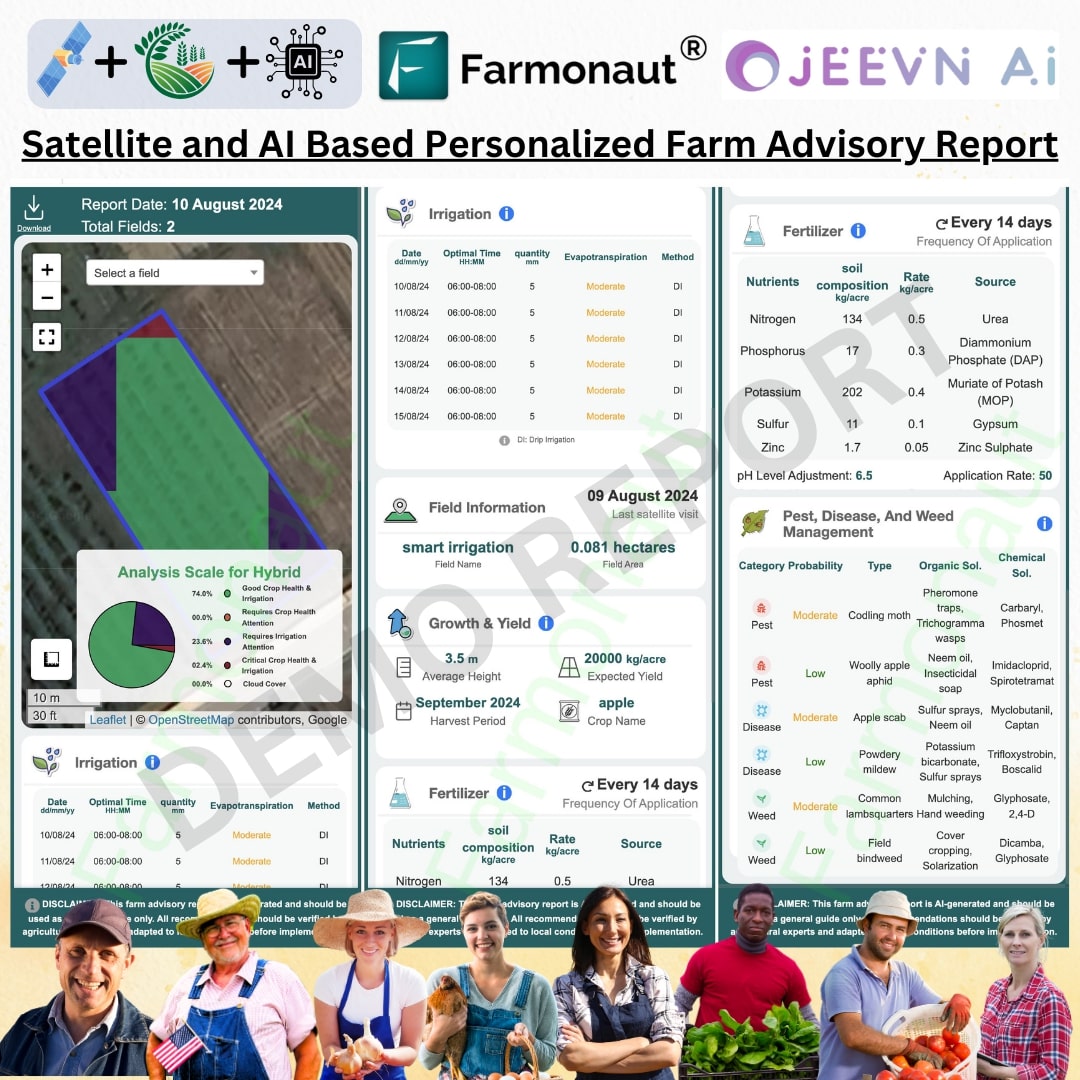
Understanding NDVI: What Does It Mean and How Can It Revolutionize Agriculture?
In the ever-evolving world of precision agriculture, one term that has gained significant importance is NDVI. But what does NDVI mean, and why is it so crucial for modern farming practices? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of NDVI, exploring its significance, interpretation, and how it’s revolutionizing the agricultural sector.
What is NDVI?
NDVI, or Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, is a simple yet powerful indicator used to assess the health and vigor of vegetation from satellite imagery. But what does NDVI mean in practical terms for farmers and agronomists?
At its core, NDVI is a measure of the difference between visible and near-infrared reflectance of vegetation cover. Healthy vegetation absorbs most of the visible light that hits it and reflects a large portion of the near-infrared light. Unhealthy or sparse vegetation, on the other hand, reflects more visible light and less near-infrared light.
The NDVI Formula
The NDVI is calculated using the following formula:
NDVI = (NIR – RED) / (NIR + RED)
Where:
- NIR = reflection in the near-infrared spectrum
- RED = reflection in the red range of the spectrum
This formula yields a value between -1 and 1, where higher values indicate healthier vegetation.
Interpreting NDVI Values: What Does NDVI Mean?
Understanding what NDVI means is crucial for interpreting the data effectively. Here’s a general guide to NDVI values:
- -1 to 0: Typically indicates water, ice, clouds, or barren areas
- 0 to 0.1: Rocks, sand, or snow
- 0.2 to 0.5: Sparse vegetation (shrubs, grasslands)
- 0.6 to 0.8: Dense vegetation (temperate and tropical forests)
- 0.8 to 1: Very dense, healthy vegetation
It’s important to note that these ranges can vary depending on the specific context and time of year. For instance, what might be considered a “high” NDVI value for a grassland might be “low” for a dense forest.
The Importance of NDVI in Agriculture
Now that we’ve answered the question “what does NDVI mean,” let’s explore why it’s so valuable in agriculture:
- Crop Health Monitoring: NDVI allows farmers to assess crop health across large areas quickly and efficiently.
- Early Stress Detection: By regularly monitoring NDVI, farmers can detect plant stress early, before it becomes visible to the naked eye.
- Yield Prediction: NDVI values correlate strongly with potential crop yields, helping farmers and agronomists make accurate yield predictions.
- Resource Optimization: By identifying areas of low NDVI, farmers can target their resources (water, fertilizers, pesticides) more effectively.
- Temporal Analysis: Comparing NDVI values over time allows farmers to track crop development and identify anomalies.
NDVI and Precision Agriculture
The integration of NDVI into precision agriculture practices has been a game-changer. At Farmonaut, we’ve harnessed the power of NDVI to provide farmers with unprecedented insights into their crops. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system uses NDVI and other vegetation indices to give farmers a comprehensive view of their fields’ health.
By leveraging NDVI data, we help farmers:
- Identify problem areas in their fields
- Make informed decisions about irrigation and fertilization
- Monitor crop growth stages
- Detect pest and disease outbreaks early
- Optimize harvest timing
Our Jeevn AI Advisory System takes this a step further by analyzing NDVI data along with other parameters to provide personalized recommendations for crop management.
Beyond NDVI: Other Vegetation Indices
While NDVI is undoubtedly one of the most widely used vegetation indices, it’s not the only one. At Farmonaut, we also utilize other indices to provide a more comprehensive picture of crop health:
- EVI (Enhanced Vegetation Index): Similar to NDVI but more sensitive to changes in areas of high biomass
- NDRE (Normalized Difference Red Edge): Particularly useful for assessing chlorophyll content in plants
- NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index): Helps in assessing plant and soil moisture content
By combining these indices with NDVI, we provide farmers with a multi-faceted view of their crops’ health and vigor.
NDVI and Climate Change
Understanding what NDVI means in the context of climate change is becoming increasingly important. NDVI data collected over long periods can provide valuable insights into how climate change is affecting vegetation patterns globally. This information is crucial for:
- Assessing the impact of climate change on agriculture
- Developing adaptive strategies for farmers
- Monitoring desertification and deforestation
- Studying changes in growing seasons and crop phenology
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers navigate these challenges by providing up-to-date NDVI data and AI-driven insights to adapt to changing climate conditions.
The Future of NDVI in Agriculture
As technology continues to advance, the applications of NDVI in agriculture are expanding. Some exciting developments include:
- Integration with IoT devices: Combining NDVI data with on-ground sensors for even more precise monitoring
- AI and Machine Learning: Developing more sophisticated algorithms to interpret NDVI data and predict crop outcomes
- Hyperspectral Imaging: Moving beyond traditional NDVI to capture more detailed spectral information
- Drone-based NDVI: Using drones for high-resolution NDVI mapping of smaller areas
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of these developments, constantly innovating to provide farmers with the most advanced and user-friendly tools for crop monitoring and management.
How Farmonaut Leverages NDVI
Our satellite-based farm management system utilizes NDVI and other vegetation indices to provide farmers with comprehensive insights into their crops’ health. Here’s how we leverage NDVI:
- Regular Monitoring: We provide frequent NDVI updates, allowing farmers to track changes in crop health over time.
- Anomaly Detection: Our AI algorithms analyze NDVI patterns to identify areas of concern in the field.
- Zone Management: NDVI data helps create management zones for precision application of inputs.
- Yield Forecasting: By analyzing historical NDVI data, we help farmers make more accurate yield predictions.
- Sustainability Tracking: NDVI trends can indicate the long-term sustainability of farming practices.
To experience the power of NDVI and other advanced farming tools, try Farmonaut today.
Farmonaut’s Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Monitoring
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large (Global) | Limited (Local) | Limited (Point-based) |
| Frequency of Data | Regular (Every few days) | On-demand (Manual flights) | Continuous |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High | Medium to High |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular (Equipment upkeep) | Regular (Sensor maintenance) |
| Scalability | Highly Scalable | Limited by equipment and manpower | Requires additional sensors for scaling |
| Weather Dependency | Moderate (Cloud cover can affect) | High (Cannot fly in bad weather) | Low |
| Data Processing | Automated (AI-driven) | Often requires manual processing | Automated but limited to sensor locations |
Practical Applications of NDVI in Various Agricultural Sectors
The versatility of NDVI makes it valuable across different agricultural sectors. Here’s how various stakeholders can benefit from understanding what NDVI means for their specific needs:
1. Row Crop Farming
- Identify variations in crop growth within fields
- Guide variable-rate applications of fertilizers and pesticides
- Monitor crop development stages for optimal harvesting
2. Orchard Management
- Assess tree health and vigor
- Detect early signs of disease or pest infestation
- Optimize irrigation schedules based on canopy density
3. Viticulture
- Monitor vineyard vigor and variability
- Guide selective harvesting for premium wine production
- Assess the impact of terroir on grape quality
4. Pasture Management
- Evaluate pasture quality and carrying capacity
- Guide rotational grazing practices
- Monitor the impact of drought on forage availability
5. Forestry
- Monitor forest health and detect areas of deforestation
- Assess the impact of forest fires and guide reforestation efforts
- Study long-term changes in forest ecosystems
Integrating NDVI with Other Data Sources
While NDVI is powerful on its own, its true potential is realized when combined with other data sources. At Farmonaut, we integrate NDVI with:
- Weather Data: Correlating NDVI trends with temperature, rainfall, and humidity data for more accurate predictions
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Combining NDVI with soil moisture data for optimized irrigation management
- Historical Yield Data: Using past yield information to refine NDVI-based yield predictions
- Pest and Disease Models: Integrating NDVI with pest pressure models for early warning systems
This multi-faceted approach provides a more comprehensive understanding of crop health and potential yields.
NDVI and Sustainable Agriculture
Understanding what NDVI means for sustainable agriculture is crucial in today’s environmentally conscious world. NDVI plays a significant role in promoting sustainable farming practices:
- Resource Optimization: By identifying areas of low plant vigor, farmers can target resources more efficiently, reducing waste and environmental impact
- Reduced Chemical Usage: Precision application of fertilizers and pesticides based on NDVI data minimizes chemical runoff
- Carbon Sequestration Monitoring: NDVI can help assess the carbon sequestration potential of agricultural lands
- Biodiversity Conservation: Monitoring natural vegetation using NDVI aids in biodiversity conservation efforts
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers adopt sustainable practices through our advanced NDVI-based monitoring and advisory systems.
NDVI and Precision Agriculture: A Case for Small-Scale Farmers
While NDVI and precision agriculture are often associated with large-scale farming operations, they can be equally beneficial for small-scale farmers. Here’s how:
- Cost-Effective Monitoring: Satellite-based NDVI monitoring eliminates the need for expensive on-ground sensors
- Improved Decision Making: Even on small plots, NDVI can guide more informed decisions about crop management
- Risk Mitigation: Early detection of crop stress through NDVI can be crucial for small farmers with limited resources
- Access to Technology: Platforms like Farmonaut make advanced NDVI analysis accessible to farmers of all scales
We believe in democratizing access to precision agriculture tools, ensuring that farmers of all sizes can benefit from understanding what NDVI means for their specific context.
The Role of NDVI in Climate-Smart Agriculture
As climate change continues to impact agriculture globally, NDVI is becoming an essential tool in climate-smart agriculture strategies:
- Adaptation: NDVI trends can help identify changing crop suitability zones, guiding farmers in adapting their crop choices
- Resilience: By monitoring vegetation health over time, NDVI helps in developing more resilient agricultural systems
- Mitigation: NDVI-based precision agriculture practices can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from farming activities
- Policy Making: Long-term NDVI data informs agricultural policies aimed at climate change mitigation and adaptation
At Farmonaut, we’re continuously refining our NDVI-based tools to help farmers navigate the challenges posed by climate change.
NDVI and Food Security
Understanding what NDVI means in the context of global food security is crucial. NDVI plays a vital role in addressing food security challenges:
- Early Warning Systems: NDVI-based crop monitoring can provide early warnings of potential food shortages
- Yield Forecasting: Accurate yield predictions based on NDVI help in better food supply chain management
- Land Use Optimization: NDVI data guides decisions on optimal land use for food production
- Drought Monitoring: NDVI is a key indicator in drought early warning systems, crucial for food security in vulnerable regions
Our commitment at Farmonaut extends beyond individual farm management to contributing to global food security through advanced NDVI-based monitoring systems.
The Future of NDVI: Emerging Technologies and Trends
As technology evolves, so does our ability to leverage NDVI for agricultural applications. Here are some exciting developments on the horizon:
- Hyperspectral NDVI: Moving beyond traditional red and near-infrared bands for more detailed vegetation analysis
- AI-Powered NDVI Interpretation: Advanced machine learning algorithms for more nuanced interpretation of NDVI data
- Real-Time NDVI: Developments in satellite technology may soon allow for near real-time NDVI monitoring
- NDVI and Big Data: Integrating NDVI with vast datasets for more comprehensive agricultural insights
- NDVI in Vertical Farming: Adapting NDVI principles for indoor and vertical farming systems
At Farmonaut, we’re always at the forefront of these technological advancements, ensuring our users have access to the most cutting-edge NDVI-based tools.
NDVI and Precision Livestock Farming
While NDVI is primarily associated with crop farming, it also has applications in livestock management:
- Pasture Management: NDVI helps in assessing pasture quality and guiding rotational grazing practices
- Forage Production: Monitoring NDVI of forage crops ensures optimal feed quality for livestock
- Carrying Capacity Assessment: NDVI data can help determine the optimal number of animals a pasture can support
- Wildlife Management: In extensive rangelands, NDVI aids in wildlife habitat assessment and management
Our platform at Farmonaut is versatile enough to support both crop and livestock farmers in leveraging NDVI for improved management practices.
NDVI in Urban Agriculture and Green Spaces
The application of NDVI isn’t limited to rural agriculture. Urban areas can also benefit from understanding what NDVI means for their green spaces:
- Urban Farming: NDVI can guide rooftop and community garden management in cities
- Park Management: City planners use NDVI to monitor the health of urban parks and green belts
- Heat Island Effect: NDVI helps in studying and mitigating urban heat island effects
- Green Infrastructure Planning: NDVI data informs decisions on where to implement green infrastructure in cities
While our primary focus is on agricultural applications, the principles of NDVI monitoring we’ve developed at Farmonaut can be adapted for urban green space management as well.
NDVI and Precision Fertilizer Application
One of the most impactful applications of NDVI is in guiding precision fertilizer application:
- Variable Rate Application: NDVI maps guide variable-rate fertilizer applications, ensuring each part of the field receives the optimal amount
- Nitrogen Management: NDVI is particularly useful in assessing crop nitrogen status, allowing for more precise nitrogen applications
- Reducing Environmental Impact: By optimizing fertilizer use, NDVI-guided applications help reduce nutrient runoff and environmental pollution
- Cost Savings: Precision application guided by NDVI can significantly reduce fertilizer costs for farmers
Our Jeevn AI system at Farmonaut integrates NDVI data with other parameters to provide precise fertilizer recommendations, helping farmers optimize their inputs while minimizing environmental impact.
NDVI and Water Management
Efficient water management is crucial in agriculture, and NDVI plays a significant role:
- Irrigation Scheduling: NDVI helps in determining when and where irrigation is needed most
- Drought Stress Detection: Early signs of water stress can be detected through changes in NDVI values
- Water Use Efficiency: By guiding precise irrigation, NDVI helps improve overall water use efficiency in agriculture
- Wetland Monitoring: NDVI is useful in monitoring wetland ecosystems and their impact on surrounding agricultural areas
At Farmonaut, we combine NDVI data with soil moisture information and weather forecasts to provide comprehensive water management advice to farmers.
NDVI in Organic Farming
Organic farmers can also benefit significantly from understanding what NDVI means for their operations:
- Crop Health Monitoring: NDVI helps organic farmers detect crop stress early, crucial when chemical interventions are not an option
- Biodiversity Assessment: NDVI can be used to monitor the health and diversity of non-crop vegetation in organic systems
- Cover Crop Management: NDVI guides the management and termination of cover crops in organic rotations
- Soil Health Indicators: Long-term NDVI trends can serve as indicators of improving soil health in organic systems
Our platform at Farmonaut is adaptable to various farming systems, including organic, ensuring that all farmers can leverage the power of NDVI regardless of their management approach.
NDVI and Crop Insurance
The insurance sector is increasingly recognizing the value of NDVI in crop insurance:
- Risk Assessment: NDVI data helps insurers assess crop health and potential risks more accurately
- Claim Verification: In the event of crop damage, NDVI provides objective data to verify claims
- Index-Based Insurance: NDVI is often used as a parameter in index-based insurance products
- Premium Calculation: Historical NDVI data can inform more accurate premium calculations for crop insurance
At Farmonaut, we work with insurance providers to leverage our NDVI data for more accurate and fair crop insurance products, benefiting both insurers and farmers.
NDVI in Agricultural Research
NDVI is a valuable tool in agricultural research, helping scientists:
- Crop Variety Trials: Assess the performance of different crop varieties under various conditions
- Climate Change Studies: Monitor long-term changes in vegetation patterns due to climate change
- Ecosystem Services: Study the role of agricultural lands in providing ecosystem services
- Crop Modeling: Improve crop growth models by incorporating NDVI data
Our extensive NDVI database at Farmonaut is a valuable resource for researchers looking to study long-term vegetation trends and patterns.
NDVI and Precision Harvesting
Understanding what NDVI means for harvest timing and quality is crucial for many farmers:
- Harvest Timing: NDVI trends can indicate optimal harvest times for maximum yield and quality
- Selective Harvesting: In crops like wine grapes, NDVI guides selective harvesting for premium quality
- Yield Estimation: Pre-harvest NDVI maps provide accurate yield estimates, helping in logistics planning
- Quality Zoning: NDVI can help identify zones of different crop quality within a field, allowing for segregated harvesting
Our AI-powered advisory system at Farmonaut integrates NDVI data with other parameters to provide precise harvest timing recommendations, helping farmers maximize both yield and quality.
FAQ: Understanding NDVI
Here are some frequently asked questions about NDVI and its applications in agriculture:
- Q: What does NDVI mean in simple terms?
A: NDVI is a measure of plant health and vigor based on how plants reflect light. Healthy plants reflect more near-infrared light and less visible light, resulting in higher NDVI values. - Q: How often should I monitor NDVI?
A: The frequency depends on your crop and goals, but typically, monitoring every 5-10 days during the growing season is beneficial. - Q: Can NDVI detect all types of plant stress?
A: While NDVI is excellent for detecting many types of stress, it may not catch all issues. It’s best used in combination with other monitoring methods. - Q: How accurate is NDVI for yield prediction?
A: NDVI can provide good yield estimates, especially when combined with historical data and other factors. However, it’s not 100% accurate and should be used as part of a broader predictive strategy. - Q: Can NDVI be used for all crop types?
A: NDVI is useful for most crops, but its effectiveness can vary. Some crops may benefit from other specialized vegetation indices. - Q: How does cloud cover affect NDVI measurements?
A: Clouds can interfere with satellite NDVI measurements. At Farmonaut, we use advanced algorithms to filter out cloud-affected data and provide clear, usable NDVI maps. - Q: Is NDVI useful for indoor or greenhouse farming?
A: While traditional satellite-based NDVI isn’t applicable indoors, the principles of NDVI can be applied using specialized sensors in controlled environments. - Q: How does Farmonaut’s NDVI monitoring compare to on-ground sensors?
A: Our satellite-based NDVI monitoring provides a broader view of your entire field, complementing on-ground sensors. It’s especially useful for detecting spatial variability across large areas. - Q: Can NDVI help in organic farming?
A: Absolutely! NDVI is particularly valuable in organic systems for early detection of crop stress and managing overall plant health without relying on chemical inputs. - Q: How does Farmonaut ensure the accuracy of its NDVI data?
A: We use high-resolution satellite imagery and advanced processing algorithms, validated against ground-truth data, to ensure the highest possible accuracy of our NDVI maps.
Conclusion: Embracing NDVI for Smarter Farming
Understanding what NDVI means and how to leverage it effectively can significantly transform agricultural practices. From improving crop health and yield to promoting sustainability and adapting to climate change, NDVI is a powerful tool in the modern farmer’s arsenal.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to making NDVI and other advanced agricultural technologies accessible to farmers of all scales. Our platform integrates satellite-based NDVI monitoring with AI-powered analytics and personalized recommendations, empowering farmers to make data-driven decisions and optimize their operations.
Whether you’re a small-scale organic farmer or managing large commercial operations, NDVI can provide valuable insights to improve your farming practices. By embracing NDVI and other precision agriculture tools, we can work together towards a more sustainable, productive, and resilient agricultural future.
Ready to harness the power of NDVI for your farm? Try Farmonaut today and experience the future of agriculture.
For developers interested in integrating our NDVI data into their own applications, check out our API documentation.
Download our mobile app to access NDVI data on the go:
For more detailed information on our satellite and weather API, visit our developer documentation.
Subscribe to Farmonaut
Join the Farmonaut community today and take your first step towards smarter, data-driven farming!