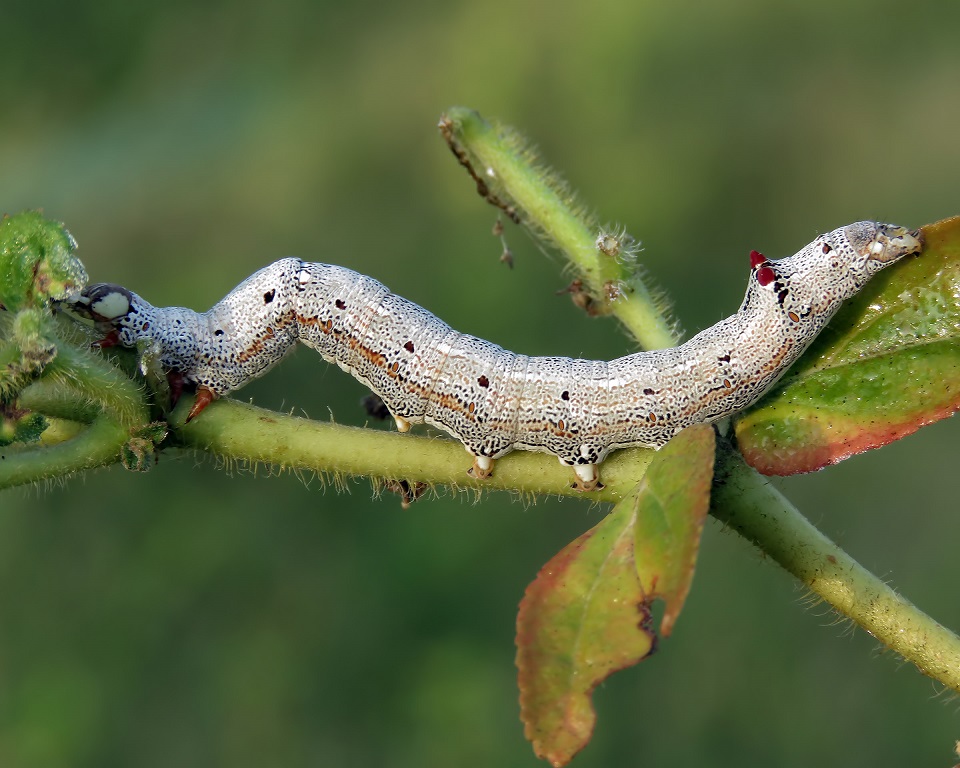
Achaea Janata - Castor Semilooper
Occurence
From field observations it is identified that the castor semilooper moths are found after the showers in the month of may, and the eggs are found only in the month of June/July.
Extent of Damage
The first and early second instar semiloopers scrape the epidermis of the leaf, whereas the late second instar larvae make holes, and fourth and the fifth instar larvae defoliate the whole plant in case of heavy infestation. The proboscis of the adult is adapted for piercing and sucking the juice of fruits. The adult semiloopers create large patches of decay in ripe banana, create brown circular area surrounding the puncture, and make them prematurely fall and rot.
Biology
a. Egg
Freshly laid eggs range in size from 0.85 mm to 0.9 mm in diameter and are light green in color and dome shaped with ridges all around and the lower surface is concave.
b. 1st instar
The 1st instar semilooper is transparent in color with a half green anterior. It measures around 0.8 cm. The duration of this stage lasts from 2 to 3 days.
c. Molting
The freshly molted semilooper has tender and pale skin and after molting, the larva eats its casted skin.
d. 2nd instar
The 2nd instar semilooper measures 0.65 to 0.87 cm and is covered with white powdery substance with black head.
e. Adult Moth
Adult moths are light brown and even sometimes deep grey in color with white and brown patches on the wings. They measure around 2.45 cm in length and 5.6 cm in wing span. Adult moths have long proboscis through which they suck the fruit juice.
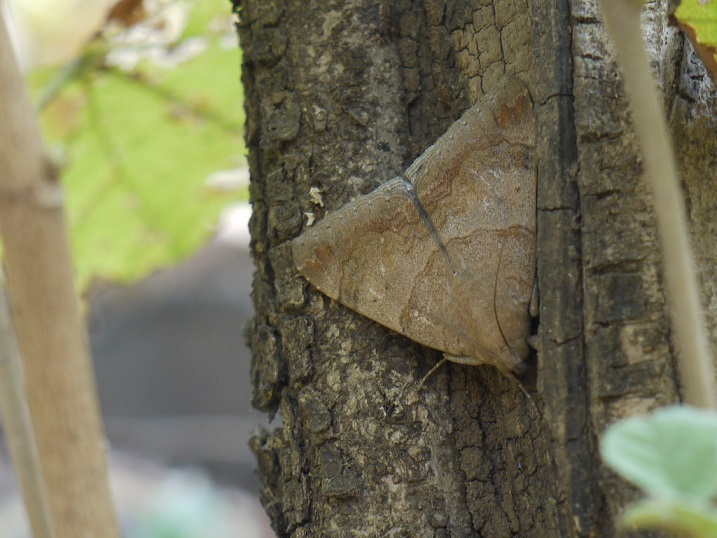

Natural enemies
The hymenopteran egg parasite of genus Telenomus is observed to keep castor semilooper in control. Similarly, branconid parasite Microplitis ephiusae is observed to be the natural control of the larvae. Field application of Bacillus thuringiensis spores have been found to be extremely lethal to the castor semilooper larvae.
Chemical Control Measures
1. Malathion can be sprayed thrice from flowering at three weeks interval. If a large number of semiloopers are observed, then spray 2ml/l of chloropyriphos in water.
Other Preventive Measures
It is recommended to build open space for birds which can feed on larvae. Once the harvest is ready, till the land to expose the semiloopers to predators.
We will keep posting about any such informative information on to our blogs, to help as many people as possible. Farmonaut is built upon a vision to bridge the technological gap between farmers and strives to bring state-of-the-art technologies in the hands of each and every farmer. For any queries/suggestions, please contact us at [email protected].
We have some more interesting articles coming up soon. Stay tuned!
Wait!!
Before that…
Follow us at:
Facebook: https://facebook.com/farmonaut
Instagram: https://instagram.com/farmonaut
Twitter: https://twitter.com/farmonaut
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/farmonaut/
Pinterest: https://in.pinterest.com/farmonaut/
Tumblr: https://farmonaut.tumblr.com/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCYWOOPPKATLgh4L6YRlYFOQ
AppLink: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.farmonaut.android
Website: https://farmonaut.com
Satellite Imagery: https://farmonaut.com/satellite-imagery
Satellite Imagery Samples: https://farmonaut.com/satellite-imagery-samples




