Mastering Black Spot Fungus Control in Roses: A Comprehensive Guide
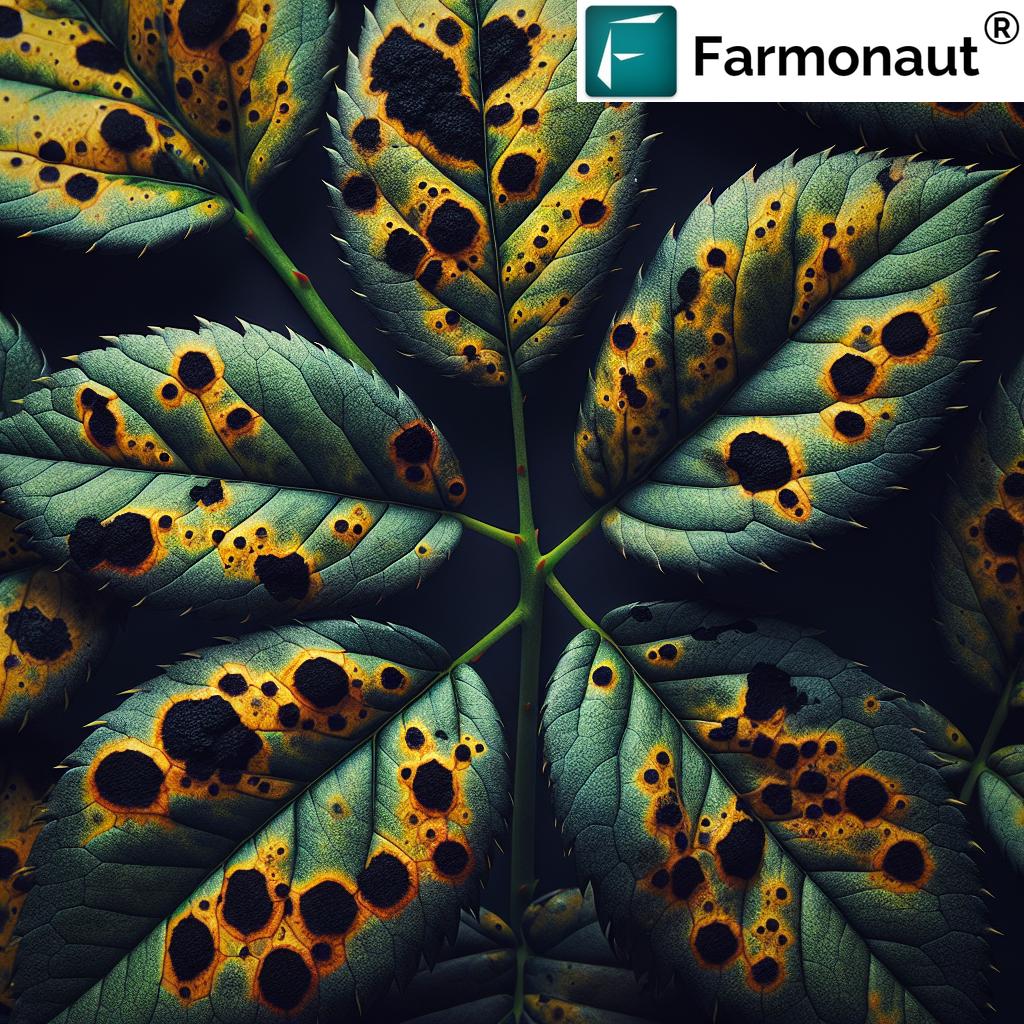

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on controlling black spot fungus in roses. As passionate horticulturists and agricultural experts, we at Farmonaut understand the challenges that rose enthusiasts and commercial growers face when dealing with this persistent fungal disease. In this blog post, we’ll delve deep into the world of black spot, scientifically known as Diplocarpon rosae, and provide you with expert insights on how to protect your beloved roses from this troublesome fungus.
Understanding Black Spot Fungus: The Enemy of Rose Lovers
Black spot is one of the most common and destructive diseases affecting roses worldwide. Caused by the fungus Diplocarpon rosae, this disease can quickly turn a beautiful rose garden into a sorry sight if left unchecked. Let’s break down the key aspects of this fungal menace:
- Appearance: Characterized by circular black spots on leaves, ranging from tiny specks to large blotches
- Spread: Thrives in warm, humid conditions, especially during rainy seasons
- Impact: Causes premature defoliation, weakening the plant and reducing bloom quality
- Lifecycle: Overwinters on fallen leaves and dormant canes, ready to strike again in spring
The Seasonal Cycle of Black Spot Fungus
Understanding the seasonal cycle of black spot is crucial for effective control. Here’s how the disease progresses throughout the year:
- Spring Awakening: As temperatures rise, dormant spores become active
- Early Summer Spread: Warm temperatures and increased humidity promote rapid fungal growth
- Late Summer Peak: The disease reaches its peak, causing significant damage if left untreated
- Fall Survival: The fungus prepares to overwinter on fallen leaves and in dormant canes
- Winter Dormancy: The fungus remains inactive but viable, ready for the next season
Factors Influencing Black Spot Development
Several factors contribute to the development and spread of black spot in roses. Understanding these can help us implement more effective control measures:
- Weather conditions: High humidity and temperatures between 60-80°F (15-27°C) are ideal for fungal growth
- Rain and irrigation practices: Excessive moisture on leaves promotes spore germination
- Air circulation: Poor air flow around plants creates a humid microclimate favorable for the fungus
- Plant susceptibility: Some rose varieties are more resistant to black spot than others
- Garden hygiene: Fallen leaves and debris can harbor spores, leading to reinfection
Preventive Measures: Your First Line of Defense
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to black spot. Here are some proactive steps you can take to protect your roses:
- Choose resistant varieties: Opt for rose cultivars known for their resistance to black spot
- Proper spacing: Plant roses with adequate space between them to improve air circulation
- Smart irrigation: Water at the base of the plant and avoid overhead watering to keep leaves dry
- Mulching: Apply a layer of mulch to prevent spores from splashing onto leaves
- Regular pruning: Remove and destroy infected leaves and canes promptly
- Fall cleanup: Thoroughly clean up fallen leaves and debris before winter to reduce overwintering spores
Effective Control Strategies for Black Spot
When prevention isn’t enough, it’s time to take action. Here are some effective control strategies to combat black spot:
- Fungicides: Apply appropriate fungicides as a preventive measure or at the first sign of infection
- Organic treatments: Consider using neem oil, potassium bicarbonate, or sulfur-based products for organic control
- Cultural practices: Improve air circulation by pruning and avoid overhead watering
- Sanitation: Regularly remove and destroy infected leaves and canes
- Nutritional support: Ensure proper fertilization to boost plant health and resistance
The Role of Technology in Black Spot Management
At Farmonaut, we believe in harnessing the power of technology to revolutionize agricultural practices. Our satellite-based monitoring system offers unprecedented advantages in managing black spot and other rose diseases:
| Feature | Traditional Methods | Farmonaut Satellite System |
|---|---|---|
| Early Detection | Visual inspection, often after symptoms appear | Advanced spectral analysis for pre-symptomatic detection |
| Coverage Area | Limited to manually inspected areas | Large-scale monitoring of entire rose fields |
| Accuracy | Dependent on human expertise, prone to errors | High-precision AI-driven analysis |
| Cost-effectiveness | Labor-intensive and time-consuming | Efficient, scalable, and cost-effective for large areas |
Our technology allows for early detection of stress patterns that may indicate black spot infection, even before visible symptoms appear. This early warning system enables growers to take preventive action, potentially saving entire crops from devastating outbreaks.
To learn more about how our satellite monitoring system can revolutionize your rose cultivation practices, visit Farmonaut’s App.
Implementing an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approach
An Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach is crucial for long-term control of black spot. This strategy combines various methods to manage the disease effectively while minimizing environmental impact:
- Regular monitoring: Use both visual inspections and advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring
- Cultural controls: Implement proper spacing, pruning, and sanitation practices
- Biological controls: Encourage beneficial organisms that may help suppress the fungus
- Chemical controls: Use fungicides judiciously and only when necessary
- Resistant varieties: Gradually replace susceptible roses with resistant cultivars
The Impact of Climate Change on Black Spot Management
As weather conditions become more unpredictable due to climate change, managing black spot in roses is becoming increasingly challenging. Here’s how climate change is affecting black spot management:
- Extended growing seasons: Longer periods of favorable conditions for fungal growth
- Increased rainfall: More frequent rain events can lead to higher infection rates
- Temperature fluctuations: Unpredictable temperatures can stress plants, making them more susceptible
- New disease patterns: Changing climate may alter the typical seasonal cycle of the fungus
To adapt to these changes, growers need to be more vigilant and proactive in their management strategies. This is where Farmonaut’s advanced monitoring systems can provide invaluable assistance, offering real-time data on weather conditions and plant health.
Innovative Solutions for Commercial Rose Growers
For commercial rose growers, managing black spot on a large scale requires innovative solutions. Farmonaut offers cutting-edge tools to streamline this process:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring: Get real-time insights into your rose fields’ health status
- AI-powered disease prediction: Anticipate black spot outbreaks based on environmental data and plant stress indicators
- Precision irrigation management: Optimize watering schedules to minimize leaf wetness and reduce fungal spread
- Automated alerts: Receive notifications when conditions are favorable for black spot development
To explore how these tools can transform your rose cultivation practices, check out our API services for seamless integration with your existing systems.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Black Spot Management
While we don’t include specific case studies or success stories, it’s worth noting that many rose growers have significantly improved their black spot management through a combination of traditional methods and modern technology. The key takeaways from successful growers include:
- Early adoption of resistant varieties
- Implementation of strict sanitation practices
- Utilization of advanced monitoring technologies
- Continuous education and adaptation of management strategies
The Future of Black Spot Control in Roses
As we look to the future, several exciting developments are on the horizon for black spot management in roses:
- Gene editing: Development of more resistant rose varieties through advanced genetic techniques
- Nanotechnology: Potential use of nanoparticles for more effective and targeted fungicide delivery
- AI-driven pest management: Further integration of artificial intelligence in predicting and managing disease outbreaks
- Sustainable biocontrols: Discovery and development of new, environmentally friendly biological control agents
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these technological advancements, continually improving our services to meet the evolving needs of rose growers worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How quickly can black spot spread in a rose garden?
A: Black spot can spread rapidly under favorable conditions. In warm, humid weather, it can infect new leaves within 24-48 hours of spore contact.
Q: Can black spot fungus affect other plants besides roses?
A: While Diplocarpon rosae primarily affects roses, similar fungi can cause leaf spot diseases in other plants. However, the specific black spot fungus that affects roses is host-specific.
Q: Is it possible to completely eradicate black spot from my rose garden?
A: Complete eradication is challenging, but with diligent management practices and the use of resistant varieties, you can significantly reduce its impact and maintain healthy roses.
Q: How often should I apply fungicides to prevent black spot?
A: The frequency of fungicide application depends on various factors, including the product used, weather conditions, and disease pressure. Generally, applications every 7-14 days during the growing season are recommended, but always follow the product label instructions.
Q: Can pruning help control black spot in roses?
A: Yes, proper pruning can significantly help control black spot by improving air circulation and removing infected plant material. It’s an essential part of any integrated disease management strategy for roses.
Conclusion: Embracing Technology for Better Rose Health
Managing black spot in roses requires a multifaceted approach combining traditional horticultural practices with cutting-edge technology. By understanding the disease cycle, implementing preventive measures, and leveraging advanced monitoring tools like those offered by Farmonaut, rose enthusiasts and commercial growers alike can significantly improve their control over this persistent fungal threat.
We invite you to explore how Farmonaut’s innovative solutions can transform your approach to rose cultivation and disease management. Visit our website or download our app to get started:
For developers interested in integrating our powerful API into their own applications, check out our API documentation.
Together, we can cultivate healthier, more beautiful roses while pushing the boundaries of agricultural technology. Here’s to a future where black spot is no longer a threat to our beloved roses!