Effective Peach Twig Borer Control: Monitoring, Trapping, and Scouting Strategies for Orchard Protection
As orchard managers and fruit growers, we understand the critical importance of protecting our valuable peach trees from devastating pests. One of the most notorious culprits threatening peach orchards is the peach twig borer (Anarsia lineatella). In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective strategies for monitoring, trapping, and scouting to control peach twig borer infestations and safeguard your orchard’s health and productivity.
Understanding the Peach Twig Borer
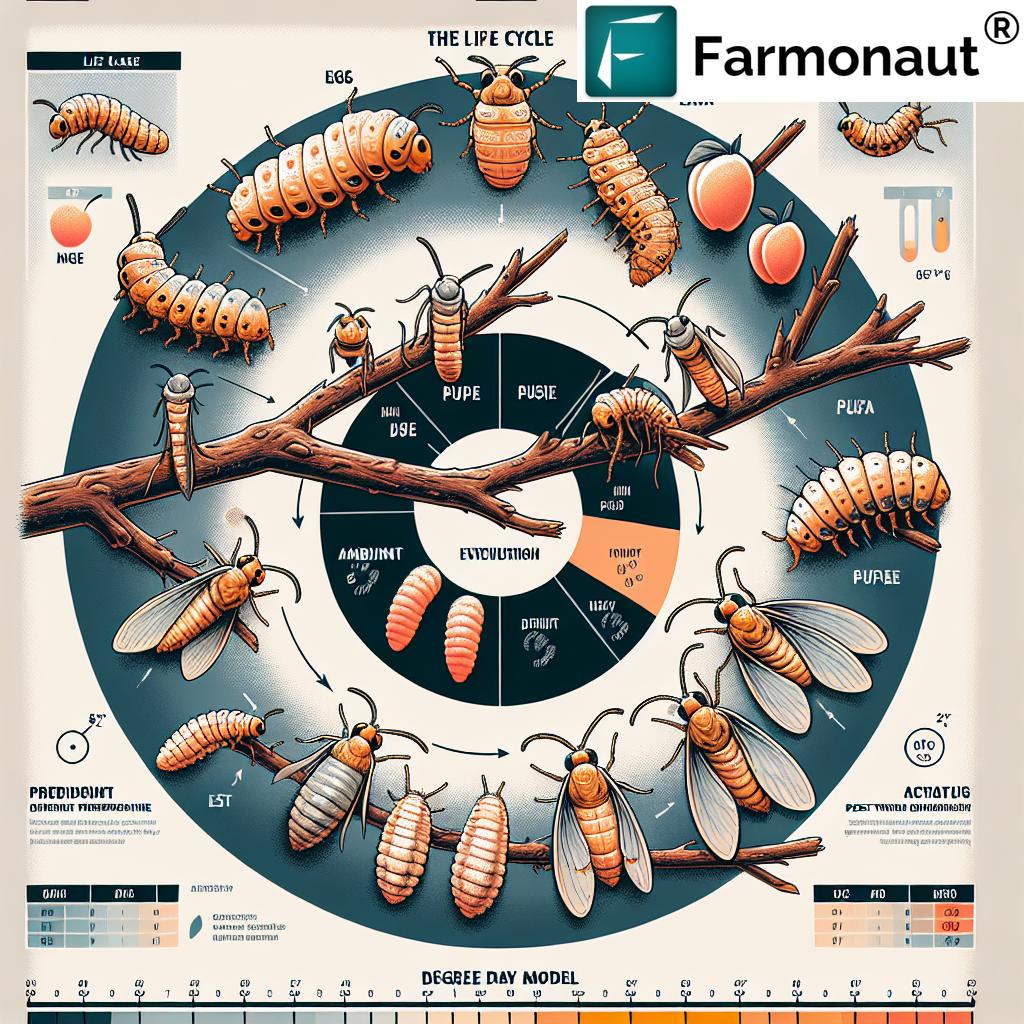
Before diving into control methods, it’s crucial to understand the life cycle and behavior of the peach twig borer. This knowledge forms the foundation for implementing effective management strategies.
Life Cycle and Behavior
- Eggs: Adult moths lay tiny, oval eggs on twigs, leaves, and fruit.
- Larvae: Upon hatching, larvae bore into new shoots or fruit, causing significant damage.
- Pupae: Larvae pupate in bark crevices or on the ground.
- Adults: Moths emerge and begin the cycle anew, with multiple generations per season.
Damage Caused by Peach Twig Borers
Peach twig borers can cause extensive damage to peach trees and other stone fruit crops:
- Wilting and dying of new shoots
- Stunted tree growth
- Fruit damage, leading to unmarketable produce
- Weakened overall tree health
Monitoring and Detection Techniques
Early detection is key to effective peach twig borer control. We’ll explore various monitoring techniques to help you stay ahead of potential infestations.
1. Visual Scouting
Regular visual inspection of your orchard is crucial for early detection of peach twig borer activity:
- Examine new growth for signs of wilting or dying twigs
- Look for small entry holes on shoots and fruit
- Check for frass (insect excrement) near entry points
- Inspect bark crevices for overwintering larvae
2. Pheromone Traps
Pheromone traps are an effective tool for monitoring adult moth populations:
- Place traps in the orchard before bud break
- Use sticky traps baited with peach twig borer pheromone
- Check traps weekly and record moth catches
- Use catch data to time control measures accurately
3. Degree Day Modeling
Degree day models help predict pest development and optimize treatment timing:
- Track local temperature data
- Calculate degree days using a lower threshold of 50°F (10°C)
- Use degree day accumulations to predict key events in the pest’s life cycle
- Time control measures based on model predictions
4. Satellite-Based Monitoring with Farmonaut
At Farmonaut, we’ve revolutionized pest monitoring through advanced satellite technology:
- High-resolution satellite imagery for comprehensive orchard coverage
- Regular updates to detect early signs of stress or damage
- AI-powered analysis to identify potential infestation hotspots
- Integration with weather data for accurate degree day calculations
Learn more about our satellite monitoring services at Farmonaut App.
Trapping Strategies for Peach Twig Borer Control
Trapping serves dual purposes: monitoring pest populations and reducing adult moth numbers. Let’s explore effective trapping strategies:
1. Pheromone-Based Mass Trapping
- Deploy a higher density of pheromone traps throughout the orchard
- Use large, sticky traps to maximize catch potential
- Replace lures and clean traps regularly for optimal performance
- Monitor and record trap catches to assess population trends
2. Light Traps
- Set up light traps to attract and capture night-flying moths
- Use UV or black light sources for best results
- Position traps away from trees to avoid attracting pests to the crop
- Empty and maintain traps regularly
3. Combination Trapping
For maximum effectiveness, consider combining different trap types:
- Use both pheromone and light traps for comprehensive coverage
- Experiment with trap placement to optimize catch rates
- Analyze data from multiple trap types to gain a fuller picture of pest activity
Scouting Techniques for Early Detection
Regular scouting is essential for identifying peach twig borer infestations before they become severe. Here are some effective scouting techniques:
1. Systematic Orchard Inspection
- Develop a regular scouting schedule, especially during critical growth stages
- Divide the orchard into sections for thorough coverage
- Inspect a representative sample of trees in each section
- Record observations and track changes over time
2. Shoot Strike Counts
- Examine new shoots for signs of borer entry
- Look for wilting or dying branch tips
- Count and record the number of affected shoots per tree
- Use this data to assess infestation levels and treatment efficacy
3. Fruit Inspection
- Regularly check developing fruit for signs of damage
- Look for small entry holes and frass on fruit surfaces
- Monitor fruit drop and examine fallen fruit for borer activity
- Estimate the percentage of affected fruit to gauge infestation severity
4. Bark Examination
- Inspect tree bark, especially in winter, for overwintering larvae
- Look for small chambers or hibernacula in bark crevices
- Use this information to predict spring emergence and plan early-season controls
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approach
An integrated approach combining multiple control strategies is most effective for managing peach twig borer populations:
1. Cultural Controls
- Prune and destroy infested shoots to reduce pest numbers
- Maintain orchard sanitation by removing fallen fruit and debris
- Encourage natural predators through habitat management
- Use proper irrigation and fertilization practices to promote tree health
2. Biological Controls
- Introduce or conserve natural enemies like parasitic wasps
- Apply microbial insecticides such as Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)
- Use pheromone mating disruption techniques to reduce pest reproduction
3. Chemical Controls
When necessary, judicious use of insecticides can be part of an IPM program:
- Time applications based on monitoring data and degree day models
- Choose selective insecticides to minimize impact on beneficial insects
- Rotate insecticide classes to prevent resistance development
- Follow all label instructions and local regulations
4. Technological Integration
Leverage technology to enhance your IPM strategy:
- Use Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring to detect early signs of stress or damage
- Implement precision spraying techniques guided by satellite data
- Utilize weather APIs for accurate degree day calculations and spray timing
Explore our API offerings at Farmonaut API and API Documentation.
Seasonal Management Timeline
A year-round approach is necessary for effective peach twig borer control. Here’s a seasonal timeline to guide your management efforts:
Spring (Pre-bloom to Petal Fall)
- Set up pheromone traps before bud break
- Begin degree day calculations
- Scout for overwintering larvae emerging from bark
- Apply dormant or delayed dormant sprays if necessary
- Monitor shoot strikes as new growth begins
Early Summer (Fruit Development)
- Continue monitoring pheromone traps and updating degree day models
- Scout for first generation larval damage on shoots and fruit
- Implement mating disruption if planned
- Apply targeted insecticide treatments based on monitoring data
- Prune and destroy infested shoots
Mid to Late Summer (Pre-harvest)
- Monitor for subsequent generations of peach twig borer
- Continue fruit inspections, focusing on pre-harvest damage
- Apply pre-harvest treatments if necessary, observing pre-harvest intervals
- Maintain orchard sanitation by removing fallen fruit
Fall and Winter (Post-harvest)
- Conduct post-harvest evaluations of pest damage
- Remove and destroy any remaining mummified fruit
- Plan for next season’s IPM strategy based on this year’s data
- Perform winter pruning to remove potential overwintering sites
- Consider winter sanitation sprays to target overwintering larvae
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Pest Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping orchardists leverage cutting-edge technology for more effective pest management. Our satellite-based monitoring system offers several advantages for peach twig borer control:
1. Early Detection of Stress Symptoms
- High-resolution satellite imagery captures early signs of tree stress
- AI algorithms analyze spectral data to identify potential infestation areas
- Early warning system allows for prompt intervention
2. Comprehensive Orchard Mapping
- Create detailed maps of your orchard’s health status
- Identify patterns of infestation spread
- Target scouting and treatment efforts to high-risk areas
3. Integration with Weather Data
- Access precise, localized weather information
- Improve accuracy of degree day calculations
- Optimize timing of control measures based on weather patterns
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
- Collect and analyze historical pest data
- Identify trends and patterns in pest activity
- Make informed decisions about long-term pest management strategies
To experience the benefits of our technology firsthand, download the Farmonaut app:
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs. Satellite-Based Monitoring
To illustrate the advantages of modern technology in peach twig borer management, let’s compare traditional scouting methods with Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring approach:
| Method | Coverage | Frequency | Early Detection | Labor Required | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Scouting | Limited to sampled areas | Weekly or bi-weekly | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Pheromone Traps | Localized to trap locations | Weekly checks | Good for adult activity | Moderate | Good |
| Farmonaut Satellite Monitoring | Complete orchard coverage | Multiple times per week | Excellent | Low | Excellent |
As demonstrated in the table, Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring offers significant advantages in coverage, frequency, early detection, and cost-effectiveness, making it an invaluable tool for efficient orchard management.
Case Studies: Successful Peach Twig Borer Management
While we don’t provide specific case studies, we can share general insights from successful peach twig borer management programs:
Integrated Approach Success
Orchards that implement a comprehensive IPM strategy, combining cultural practices, biological controls, and targeted chemical applications, consistently report lower peach twig borer populations and reduced crop damage.
Technology-Enhanced Monitoring
Growers utilizing advanced monitoring tools, including satellite imagery and weather-based modeling, have achieved more precise treatment timing and reduced overall pesticide use.
Community-Wide Management
Coordinated efforts among neighboring orchards, such as area-wide mating disruption programs, have shown promising results in managing peach twig borer populations on a larger scale.
Future Trends in Peach Twig Borer Management
As we look to the future, several emerging trends and technologies promise to further enhance our ability to manage peach twig borer infestations:
1. Precision Agriculture
- Increased use of drones for high-resolution orchard mapping and pest detection
- Development of AI-powered image analysis for automated pest identification
- Integration of IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of orchard conditions
2. Biological Control Advancements
- Research into new, more effective strains of microbial insecticides
- Exploration of novel natural enemies for peach twig borer control
- Development of habitat management strategies to boost beneficial insect populations
3. Genetic Technologies
- Ongoing research into pest-resistant peach varieties
- Potential development of genetically modified insects for population control
- Advanced molecular techniques for rapid and accurate pest identification
4. Climate Change Adaptation
- Refinement of predictive models to account for changing climate patterns
- Development of management strategies adapted to shifting pest life cycles
- Research into the impact of climate change on pest-predator relationships
Conclusion
Effective management of peach twig borer requires a multifaceted approach combining traditional practices with modern technology. By integrating comprehensive monitoring, strategic trapping, regular scouting, and data-driven decision-making, orchardists can significantly reduce the impact of this devastating pest.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to empowering growers with the tools and insights needed to protect their orchards and optimize productivity. Our satellite-based monitoring system, coupled with advanced analytics and user-friendly apps, provides a powerful solution for modern orchard management.
As we continue to face challenges such as climate change and evolving pest pressures, staying informed and adaptable will be key to success. By embracing innovative technologies and sustainable practices, we can ensure the long-term health and productivity of our peach orchards.
FAQs
Q: How often should I scout my orchard for peach twig borer?
A: We recommend scouting at least weekly during critical periods, such as spring shoot growth and fruit development. Increase frequency if pest pressure is high or weather conditions are favorable for pest activity.
Q: Can peach twig borers be controlled organically?
A: Yes, organic control methods include cultural practices like pruning infested shoots, using pheromone mating disruption, and applying approved organic insecticides like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
Q: How accurate are degree day models for predicting peach twig borer activity?
A: Degree day models can be quite accurate when used with local weather data. However, they should be used in conjunction with field observations and trap monitoring for best results.
Q: What are the signs of peach twig borer damage on fruit?
A: Look for small entry holes, often near the stem end of the fruit, accompanied by frass (insect excrement) or gummy exudates. Cutting into suspected fruit may reveal internal tunneling.
Q: How can Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring help with peach twig borer management?
A: Our satellite monitoring provides early detection of tree stress, comprehensive orchard mapping, and integration with weather data for improved pest management decisions. It allows for targeted scouting and more efficient use of control measures.
Q: Is it necessary to use chemical controls for peach twig borer?
A: While an integrated approach using multiple control methods is ideal, chemical controls may be necessary in cases of severe infestation or when other methods prove insufficient. Always use pesticides judiciously and in accordance with local regulations.
Q: How do I get started with Farmonaut’s orchard monitoring services?
A: You can begin by downloading our app and setting up an account. Our team will guide you through the process of mapping your orchard and accessing our satellite monitoring services.
Ready to revolutionize your orchard management? Subscribe to Farmonaut today: