Combating the Emerald Ash Borer: How Illinois Uses Remote Sensing for Forest Health Monitoring
“The Emerald Ash Borer has spread to over 30 U.S. states since its discovery in Michigan in 2002.”
In the heart of America’s heartland, a silent invader has been wreaking havoc on our beloved ash trees. The emerald ash borer (EAB), scientifically known as Agrilus planipennis, has become a formidable threat to our nation’s forests, particularly in states like Illinois, Michigan, and Tennessee. As we delve into this pressing issue, we’ll explore how innovative technologies, including those offered by Farmonaut, are revolutionizing our approach to emerald ash borer management and forest health monitoring.
The Emerald Menace: Understanding the Threat
The emerald ash borer, an exotic beetle native to Asia, first made its unwelcome appearance in the United States near Detroit, Michigan, in 2002. Since then, this invasive species has spread like wildfire across the nation, leaving a trail of devastation in its wake. The adult beetles may be small, measuring only about half an inch in length, but their impact on our ash trees has been nothing short of catastrophic.

The EAB’s destructive power lies in its larvae, which feed on the inner bark of ash trees, disrupting the tree’s ability to transport water and nutrients. This feeding frenzy creates distinctive S-shaped galleries beneath the bark, eventually girdling the tree and causing its demise. The speed at which these beetles can decimate ash populations is alarming, with infested trees often dying within 2-4 years of initial infestation.
The Spread of EAB: A National Crisis
From its initial discovery in Michigan, the emerald ash borer has rapidly expanded its range. Today, EAB infestations have been confirmed in numerous states, including:
- Illinois
- Ohio
- Indiana
- Maryland
- Pennsylvania
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Missouri
- Minnesota
- New York
- Tennessee
- Virginia
This widespread distribution has put millions of ash trees at risk, threatening not only our forests but also urban and suburban landscapes where ash trees are common street and park trees.
Illinois: A Case Study in EAB Management
Illinois, with its vast expanses of woodlands and urban forests, has been particularly hard-hit by the emerald ash borer. The Illinois Department of Natural Resources (IDNR) has been at the forefront of the battle against this invasive pest, implementing a multi-faceted approach to forest health monitoring and EAB management.
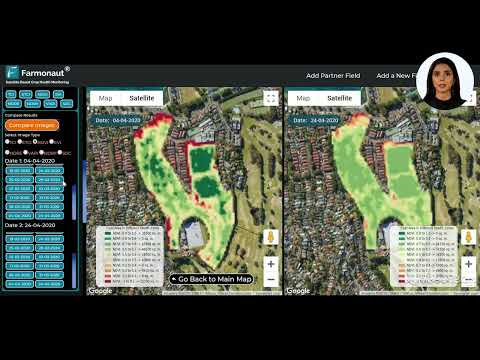
One of the most innovative tools in Illinois’ arsenal is the use of remote sensing in forestry. This technology, similar to that offered by Farmonaut, allows for early detection and monitoring of EAB infestations across large areas of forest land.
How Remote Sensing is Changing the Game
Remote sensing technology, including satellite imagery and aerial surveys, has revolutionized our ability to detect and monitor EAB infestations. Here’s how it works:
- Early Detection: Remote sensing can identify changes in tree canopy health before they’re visible to the naked eye, allowing for early intervention.
- Large-Scale Monitoring: Satellite imagery enables forest managers to monitor vast areas of woodland efficiently, something that would be impossible with ground surveys alone.
- Precision Mapping: By combining remote sensing data with GIS technology, foresters can create detailed maps of EAB spread and predict future infestation patterns.
- Resource Allocation: With accurate data on infestation locations and severity, resources for control measures can be allocated more effectively.
Farmonaut’s advanced satellite-based farm management solutions are at the forefront of this technological revolution. While primarily focused on agricultural applications, the principles behind Farmonaut’s precision agriculture technology can be adapted for forestry use, offering powerful tools for tree disease identification and monitoring.
“Remote sensing technology can detect Emerald Ash Borer infestations up to 2 years earlier than traditional methods.”
The Role of GIS in Forest Management
GIS for forest management has become an indispensable tool in the fight against the emerald ash borer. By integrating remote sensing data with other geographical information, GIS allows forest managers to:
- Track the spread of EAB infestations over time
- Identify high-risk areas for proactive management
- Plan and implement targeted control measures
- Assess the effectiveness of management strategies
In Illinois, the use of GIS has been crucial in developing comprehensive EAB management plans. By mapping the location of ash trees, tracking infestation patterns, and predicting future spread, forest managers can make informed decisions about where to focus their efforts.
Innovative Approaches to EAB Control
While early detection is crucial, effective control measures are equally important in managing the emerald ash borer threat. Illinois and other affected states have implemented a range of strategies, including:
- Biological Control: Introduction of natural predators from the EAB’s native range in Asia
- Chemical Treatments: Insecticide applications to protect high-value ash trees
- Quarantines: Restrictions on the movement of ash wood products to slow the spread of EAB
- Public Education: Raising awareness about EAB and promoting early detection by citizens
These efforts, combined with advanced monitoring techniques, form a comprehensive approach to emerald ash borer management.
The Impact on Illinois Forests and Beyond
The emerald ash borer’s impact on Illinois forests has been profound. Ash trees, once a common sight in both urban and rural landscapes, have been decimated in many areas. This loss has far-reaching consequences:
- Ecological Impact: Ash trees play a vital role in forest ecosystems, and their loss affects wildlife habitats and biodiversity.
- Economic Consequences: The cost of removing dead or dying ash trees and replacing them in urban areas is substantial.
- Aesthetic Changes: The loss of mature ash trees alters the character of many neighborhoods and natural areas.
However, the story is not all bleak. The crisis has spurred innovation in forest management techniques and fostered greater collaboration between states, federal agencies, and private sector partners like Farmonaut.

Farmonaut’s Contribution to Forest Health Monitoring
While Farmonaut’s primary focus is on agricultural applications, its technology has significant potential for adaptation to forestry needs. The company’s satellite-based monitoring systems and AI-driven analytics could be powerful tools in the fight against the emerald ash borer and other forest health threats.
Key features of Farmonaut’s technology that could benefit forest managers include:
- Real-time Monitoring: Regular satellite imagery updates allow for continuous monitoring of forest health.
- AI-powered Analytics: Advanced algorithms can detect subtle changes in vegetation health, potentially identifying EAB infestations early.
- User-friendly Interface: Farmonaut’s platform makes complex data accessible to forest managers of all technical levels.
- Integration Capabilities: The ability to integrate with existing GIS systems enhances the overall effectiveness of forest management efforts.
For more information on Farmonaut’s capabilities, visit their web application or explore their API for custom integrations.
The Future of Forest Health Monitoring
As we look to the future, the integration of advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut with traditional forestry practices holds great promise for more effective forest health monitoring and management. Some emerging trends include:
- Drone Technology: Complementing satellite imagery with high-resolution drone surveys for more detailed assessments.
- Machine Learning: Developing more sophisticated algorithms to predict EAB spread and identify at-risk areas.
- Citizen Science: Engaging the public in monitoring efforts through mobile apps and crowdsourcing platforms.
- Inter-state Collaboration: Enhancing data sharing and coordinated response efforts across state lines.
Comparative Analysis: EAB Impact and Detection Methods
| State | Estimated Ash Trees Affected | Primary Detection Method | Farmonaut’s Remote Sensing Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Michigan | Over 40 million | Visual surveys, purple prism traps | Satellite imagery for early detection of canopy changes |
| Illinois | Approximately 30 million | Aerial surveys, ground inspections | AI-powered analysis of vegetation health indices |
| Tennessee | Estimated 20 million | Trapping, branch sampling | Regular monitoring with high-resolution satellite data |
This table illustrates the scale of the EAB problem across different states and highlights how Farmonaut’s technology could enhance traditional detection methods. By providing more frequent and comprehensive data, remote sensing solutions like those offered by Farmonaut have the potential to significantly improve our ability to detect and respond to EAB infestations.
Sustainable Forest Management in the Face of EAB
Sustainable forest management has become more critical than ever in light of the emerald ash borer threat. This approach involves balancing the ecological needs of the forest with economic considerations and social benefits. Key aspects of sustainable management in the context of EAB include:
- Diversification: Planting a variety of tree species to create more resilient forests
- Proactive Management: Implementing preventive measures in high-risk areas
- Adaptive Strategies: Flexibility in management approaches based on monitoring data
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in forest conservation efforts
Farmonaut’s technology can support these efforts by providing the data needed to make informed decisions about forest management strategies.
The Role of Public Awareness and Education
Combating the emerald ash borer is not just a task for forest managers and scientists; it requires a concerted effort from the public as well. Education and awareness campaigns play a crucial role in:
- Helping citizens identify signs of EAB infestation
- Encouraging responsible wood transport practices to prevent spread
- Promoting the importance of tree diversity in landscaping
- Fostering a sense of stewardship for our forests and urban trees
By leveraging technology like Farmonaut’s mobile apps, public agencies can engage citizens in forest health monitoring efforts, creating a more comprehensive surveillance network.
Economic Implications and Cost-Share Programs
The economic impact of the emerald ash borer on states like Illinois has been substantial. Costs associated with tree removal, replacement, and treatment have strained budgets at both the state and local levels. To address this, various cost-share programs have been implemented, including:
- USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) programs
- Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP)
- State-level grants for municipalities and private landowners
These programs aim to offset the financial burden of EAB management and encourage proactive forest health practices.
The Intersection of Technology and Traditional Forestry
As we continue to battle the emerald ash borer, the integration of advanced technology with traditional forestry practices becomes increasingly important. This synergy allows for:
- More efficient resource allocation
- Improved accuracy in pest detection and monitoring
- Enhanced decision-making capabilities for forest managers
- Greater adaptability in the face of changing environmental conditions
Farmonaut’s platform exemplifies this integration, offering powerful tools that complement on-the-ground expertise.
Looking Beyond EAB: Broader Applications of Remote Sensing in Forestry
While our focus has been on the emerald ash borer, the applications of remote sensing and GIS in forestry extend far beyond this single pest. These technologies are invaluable for:
- Wildfire Management: Early detection and monitoring of forest fires
- Biodiversity Assessment: Tracking changes in forest composition and structure
- Carbon Sequestration: Estimating forest carbon stocks and changes over time
- Land Use Planning: Informing decisions about forest conservation and development
As we continue to face environmental challenges, tools like those offered by Farmonaut will become increasingly crucial in our efforts to protect and manage our forest resources.
Conclusion: A United Front Against the Emerald Ash Borer
The battle against the emerald ash borer in Illinois and across the United States is far from over. However, with the integration of advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, combined with traditional forestry practices and public engagement, we are better equipped than ever to face this challenge.
As we move forward, continued innovation in forest health monitoring, invasive species detection, and sustainable forest management will be crucial. By leveraging the power of remote sensing, GIS, and AI-driven analytics, we can work towards a future where our forests are more resilient, diverse, and better protected against threats like the emerald ash borer.
The story of Illinois’ fight against the EAB serves as both a cautionary tale and a beacon of hope. It reminds us of the fragility of our forest ecosystems and the importance of vigilance. At the same time, it showcases the power of innovation and collaboration in addressing complex environmental challenges.
As we continue this journey, let us remain committed to protecting our forests, embracing new technologies, and working together to ensure the health and vitality of our woodlands for generations to come.
FAQ Section
- Q: What is the emerald ash borer?
A: The emerald ash borer (EAB) is an invasive beetle native to Asia that feeds on and kills ash trees. - Q: How does remote sensing help in detecting EAB infestations?
A: Remote sensing technology can detect changes in tree canopy health before they’re visible to the naked eye, allowing for early detection and intervention. - Q: What role does Farmonaut play in forest health monitoring?
A: While primarily focused on agriculture, Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring and AI-driven analytics can be adapted for forestry use, offering powerful tools for tree disease identification and monitoring. - Q: How can individuals help in the fight against EAB?
A: Individuals can help by learning to identify signs of EAB infestation, reporting suspicious trees to local authorities, and following guidelines for proper wood transportation to prevent the spread of the pest. - Q: Are there any successful cases of EAB eradication?
A: While complete eradication has proven challenging, many areas have successfully managed EAB populations through a combination of early detection, targeted treatments, and biological control methods.
For more information on Farmonaut’s solutions and how they can be applied to forest health monitoring, visit our web application or explore our API developer documentation.
Download our mobile apps for on-the-go access to powerful monitoring tools:
Farmonaut Subscriptions