California Wildfire Insurance Crisis: How Climate Change Is Reshaping Home Coverage in High-Risk Areas
“California’s FAIR Plan, the state’s last-resort insurance option, has seen a 180% increase in policies since 2018.”
We are witnessing a profound shift in California’s insurance landscape, one that is reshaping the very fabric of home coverage in high-risk areas. As climate change continues to fuel increasingly severe and frequent wildfires, the Golden State finds itself at the epicenter of an insurance crisis that threatens to upend long-standing norms in property protection.
In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the complexities of California’s wildfire insurance crisis, examining how recent events, particularly in Los Angeles and the affluent Pacific Palisades neighborhood, have intensified the challenges faced by homeowners, insurers, and policymakers alike. We’ll uncover the intricate web of factors contributing to this crisis and analyze the potential solutions being proposed to stabilize the market.
The Burning Issue: California’s Wildfire Insurance Dilemma
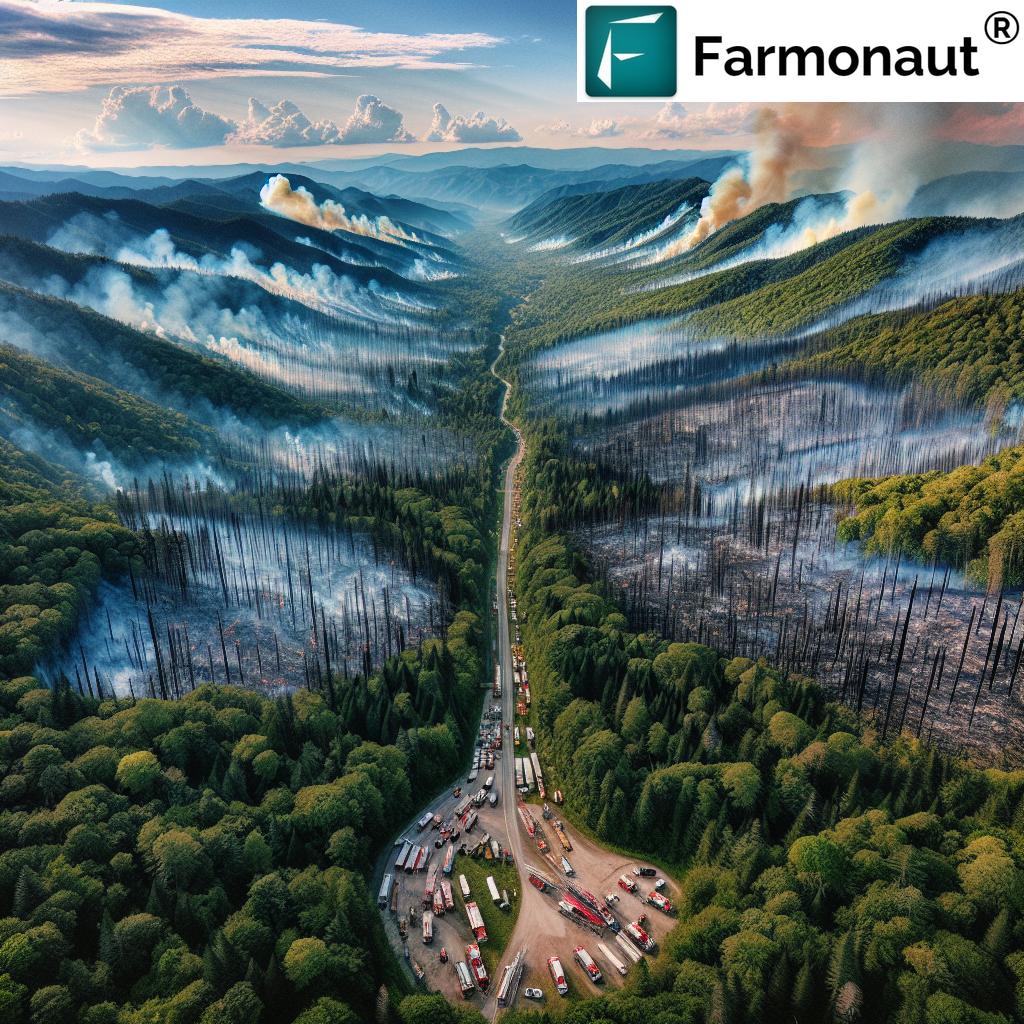
California’s wildfire insurance crisis is not a sudden development but rather the culmination of years of escalating risks and mounting losses. The recent fires that ravaged Los Angeles, including the destructive blaze in Pacific Palisades, have brought this issue into sharp focus, highlighting the precarious position of homeowners in fire-prone regions.
The crisis is characterized by a perfect storm of factors:
- Increasing frequency and severity of wildfires due to climate change
- Exodus of major insurers from high-risk areas
- Skyrocketing premiums for those who can still obtain coverage
- Growing reliance on the state’s FAIR Plan as a last resort
- Regulatory challenges in balancing consumer protection with market stability
As we navigate through these complexities, it’s crucial to understand how each element contributes to the overall crisis and what it means for California’s homeowners, especially those in vulnerable communities like Pacific Palisades.
Climate Change: The Catalyst of Crisis
At the heart of California’s insurance woes lies the undeniable impact of climate change. The state has experienced a dramatic increase in the frequency, intensity, and unpredictability of wildfires over the past decade. This trend has forced a reevaluation of risk models that have long underpinned the insurance industry.
Key climate-related factors exacerbating wildfire risks include:
- Prolonged droughts creating tinder-dry conditions
- Higher average temperatures extending fire seasons
- Changing wind patterns facilitating rapid fire spread
- Bark beetle infestations weakening forests and increasing fuel loads
These climate-driven changes have rendered many traditional risk assessment methods obsolete, leaving insurers scrambling to adapt their models and pricing strategies. The result? A seismic shift in how fire risk is evaluated and insured across California.
The Great Insurance Exodus
As the wildfire threat has intensified, we’ve witnessed a troubling trend: major insurers retreating from high-risk areas or exiting the California market entirely. In 2023 alone, seven of the twelve largest insurance companies either paused or limited new homeowners policies in the state.
The departure of industry giants like State Farm, which previously insured approximately 72,000 structures in California, has sent shockwaves through the market. This exodus has left many homeowners, particularly those in fire-prone regions like the Pacific Palisades, struggling to find adequate coverage.
The reasons behind this retreat are multifaceted:
- Unsustainable losses from recent wildfire seasons
- Difficulty in accurately pricing policies due to evolving risk landscapes
- Regulatory constraints on rate increases
- Challenges in obtaining reinsurance for high-risk portfolios
As insurers pull back, the ripple effects are felt across California’s real estate market, with potential buyers hesitating to invest in areas where insurance is scarce or prohibitively expensive.
The FAIR Plan: California’s Insurance Safety Net
In the wake of the insurance industry’s retreat, California’s FAIR (Fair Access to Insurance Requirements) Plan has emerged as a critical lifeline for many homeowners. Originally designed as a last-resort option, the FAIR Plan has seen its role expand dramatically in recent years.
“In 2022, wildfires in California burned over 362,000 acres, causing $769 million in damages to insured properties.”
Key points about the FAIR Plan:
- Policies have doubled from 2020 to 2024
- Coverage is limited, with a cap of $3 million
- Often insufficient for high-value properties in affluent areas like Pacific Palisades
- Faces scrutiny over its ability to handle catastrophic events
While the FAIR Plan provides a crucial safety net, it’s not without its challenges. Many policyholders find themselves underinsured, particularly in high-value neighborhoods where property values far exceed the plan’s coverage limits.
Regulatory Response and Market Stabilization Efforts
In response to the escalating crisis, California’s lawmakers and regulatory bodies have been working to stabilize the insurance market and protect consumers. Recent initiatives include:
- Allowing insurers to factor current and future fire risks into pricing models
- Introducing legislation to permit the FAIR Plan to seek “catastrophe bonds” for liquidity
- Revising regulations to encourage insurers to re-enter the market
- Exploring the use of parametric insurance products for wildfire coverage
These regulatory changes aim to strike a delicate balance between ensuring insurance availability and allowing companies to price policies that reflect actual risk. However, the effectiveness of these measures remains to be seen, and many experts warn that they may lead to significant premium increases for homeowners.
The Impact on Homeowners and Communities
The insurance crisis has far-reaching implications for California’s homeowners, particularly those in high-risk areas like Pacific Palisades, Hollywood Hills, and inland communities. The effects are multifaceted:
- Skyrocketing premiums for those who can still obtain coverage
- Decreased property values in fire-prone regions
- Increased reliance on inadequate FAIR Plan coverage
- Potential for underinsurance in the event of a catastrophic loss
- Challenges in obtaining mortgages without adequate insurance
These impacts are reshaping the real estate landscape in California, potentially altering long-term development patterns and community compositions in vulnerable areas.

Innovative Solutions and Future Outlook
As California grapples with this crisis, innovative solutions are emerging that could reshape the future of wildfire insurance. Some promising developments include:
- Parametric insurance products that pay out based on predefined triggers
- Use of advanced satellite technology and AI for more accurate risk assessment
- Community-based insurance pools to spread risk more effectively
- Integration of wildfire mitigation efforts into insurance pricing models
These innovations could pave the way for a more resilient and adaptable insurance market in the face of ongoing climate challenges.
The Role of Technology in Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Advancements in technology are playing an increasingly crucial role in addressing California’s wildfire insurance crisis. Sophisticated satellite imaging, artificial intelligence, and data analytics are revolutionizing how insurers assess and price wildfire risk.
For instance, companies like Farmonaut are leveraging cutting-edge satellite technology to provide real-time data on vegetation health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. While Farmonaut’s primary focus is on agricultural applications, the principles behind their technology have significant potential for wildfire risk assessment.
Key technological advancements in wildfire risk assessment include:
- High-resolution satellite imagery for detailed terrain and vegetation analysis
- Machine learning algorithms for predicting fire behavior and spread
- IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of environmental conditions
- Advanced weather modeling for more accurate fire weather forecasts
These technologies not only help insurers more accurately price policies but also assist homeowners and communities in implementing effective wildfire mitigation strategies.
The Economic Ripple Effect
The wildfire insurance crisis extends far beyond individual homeowners, creating a ripple effect throughout California’s economy. Some of the broader economic implications include:
- Potential decreases in property tax revenues for fire-prone communities
- Shifts in real estate development patterns away from high-risk areas
- Increased costs for businesses operating in vulnerable regions
- Strain on state resources as more residents rely on the FAIR Plan
These economic challenges require a holistic approach that considers not just insurance regulation but also urban planning, forest management, and climate change mitigation strategies.
Comparative Analysis: California vs. Other At-Risk States
While California’s wildfire insurance crisis is particularly acute, it’s not the only state grappling with climate-related insurance challenges. A comparative analysis reveals:
| Factor | California | Colorado | Oregon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Climate Risk | Wildfires | Wildfires, Floods | Wildfires, Coastal Flooding |
| Insurance Market Status | Severe Crisis | Emerging Challenges | Growing Concerns |
| State-Backed Insurance Program | FAIR Plan | Limited Options | In Development |
| Regulatory Approach | Aggressive Intervention | Moderate Regulation | Proactive Planning |
This comparison highlights the unique challenges faced by California while also demonstrating the growing need for climate-resilient insurance solutions across multiple states.
The Path Forward: Balancing Protection and Sustainability
As we look to the future of wildfire insurance in California, it’s clear that a multifaceted approach is necessary to address this complex crisis. Key components of a sustainable solution may include:
- Continued regulatory reform to encourage market participation while protecting consumers
- Investment in advanced risk assessment technologies and methodologies
- Enhanced collaboration between insurers, regulators, and climate scientists
- Increased focus on community-wide wildfire mitigation efforts
- Exploration of public-private partnerships to spread risk more effectively
The path forward will require innovation, collaboration, and a willingness to adapt to the realities of a changing climate.
Conclusion: Adapting to a New Reality
California’s wildfire insurance crisis serves as a stark reminder of the profound ways in which climate change is reshaping our world. As we’ve explored throughout this analysis, the challenges facing homeowners, insurers, and policymakers in high-risk areas are complex and multifaceted.
While the situation remains fluid, it’s clear that traditional approaches to property insurance are no longer sufficient in the face of escalating wildfire risks. The future of home coverage in California and other vulnerable regions will likely involve a combination of innovative insurance products, advanced risk assessment technologies, and proactive mitigation strategies.
As we navigate this new reality, it’s crucial that all stakeholders—from individual homeowners to large insurers and government agencies—work together to develop sustainable solutions. Only through collaboration, innovation, and a shared commitment to resilience can we hope to address the challenges posed by California’s wildfire insurance crisis and create a more secure future for communities in high-risk areas.
FAQs: California Wildfire Insurance Crisis
- Q: Why are insurance companies leaving California?
A: Insurers are retreating due to unsustainable losses from wildfires, difficulties in pricing risk accurately, and regulatory constraints on rate increases. - Q: What is the California FAIR Plan?
A: The FAIR Plan is California’s last-resort insurance option for homeowners who cannot obtain coverage in the traditional market, offering limited coverage up to $3 million. - Q: How is climate change affecting wildfire insurance in California?
A: Climate change is increasing wildfire frequency and severity, making risk assessment more challenging and leading to higher premiums and reduced coverage availability. - Q: What options do homeowners have if they can’t get traditional insurance?
A: Options include the FAIR Plan, surplus lines insurers, and potentially new parametric insurance products as they become available. - Q: How are California lawmakers addressing the insurance crisis?
A: Lawmakers are revising regulations to allow more accurate risk pricing, exploring catastrophe bonds for the FAIR Plan, and considering new insurance models to stabilize the market.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
For more information on Farmonaut’s innovative agricultural solutions, visit our API page or check out our API Developer Docs.
Download our mobile apps: