Oklahoma Forestry Services: Balancing Wildfire Prevention and State Employee Job Security
“Oklahoma’s forestry services manage prescribed burns for fire control and maintain water quality across thousands of acres annually.”
In the heart of the American Midwest, Oklahoma’s forests stand as silent sentinels, guardians of biodiversity and natural resources. However, recent events have thrust these verdant landscapes and the dedicated professionals who protect them into the spotlight of public discourse. As we delve into the complex interplay between wildfire prevention, state employee job security, and the future of Oklahoma’s Forestry Services, we find ourselves at a critical juncture that demands our attention and thoughtful consideration.
The Crucial Role of Oklahoma Forestry Services
Oklahoma Forestry Services plays a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance of our state’s ecosystems. From managing vast tracts of forested land to implementing critical wildfire prevention strategies, the department’s responsibilities are as diverse as they are essential. Let’s explore the multifaceted nature of their work:
- Wildfire Prevention and Management
- Prescribed Burns for Fire Control
- Water Quality Maintenance
- Forest Management and Conservation
- Public Education and Outreach
Each of these areas contributes significantly to the safety and well-being of Oklahoma’s communities, as well as the preservation of our natural heritage. The recent devastating wildfires have brought the importance of these services into sharp focus, highlighting the need for robust forestry management techniques and adequate firefighting resources in Oklahoma.
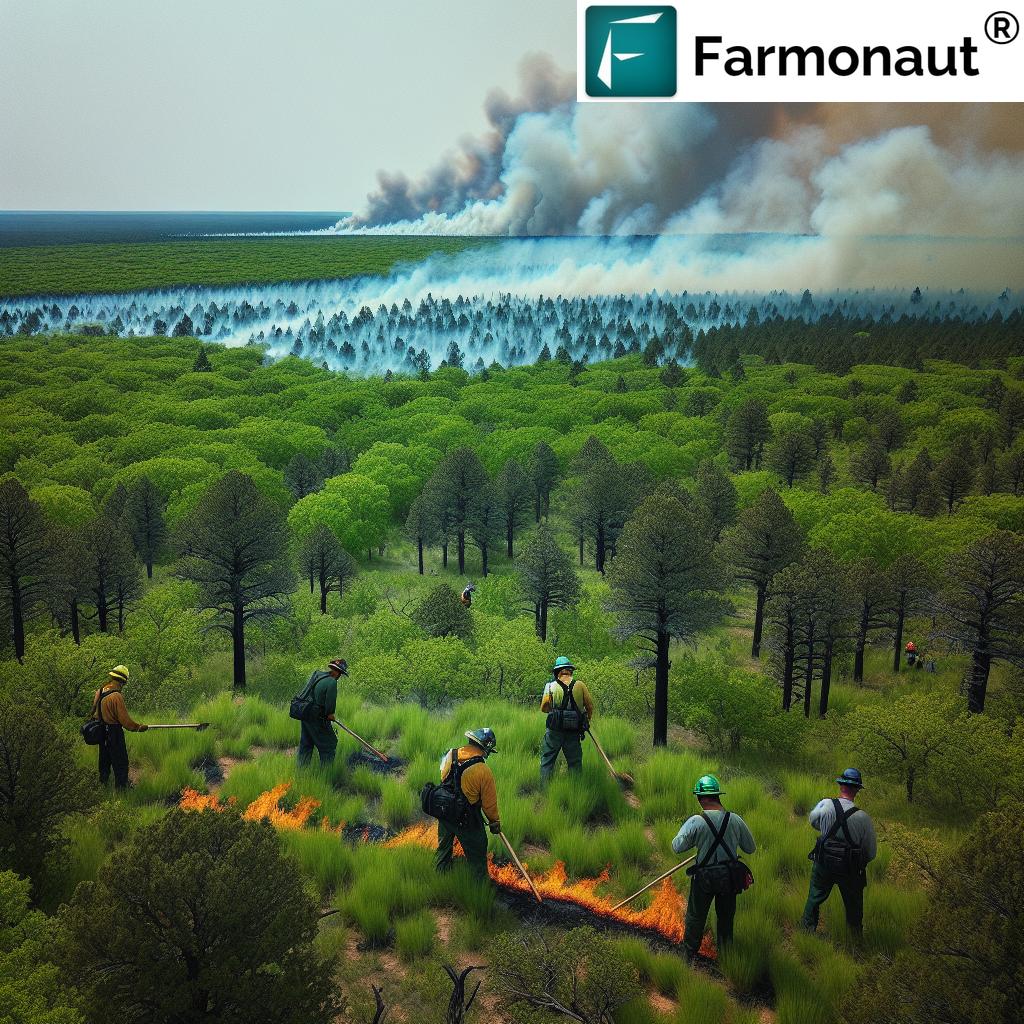

The March 14th Wildfires: A Turning Point
The wildfires that swept through Oklahoma on March 14th were a stark reminder of the destructive power of nature and the critical importance of our forestry services. As hurricane-force winds fanned the flames, our firefighters and forestry personnel found themselves facing an unprecedented challenge. The impact of these wildfires on communities was devastating, leaving many to question the adequacy of our current wildfire prevention strategies and the resources allocated to combating such disasters.
In the aftermath, we’ve seen a flurry of activity and discussion at the highest levels of state government. Governor Kevin Stitt’s decision to fire the state forester, Mark Goeller, and his subsequent suggestion to cut the entire forestry department have sent shockwaves through the community of public servants and citizens alike.
The Governor’s Stance: A Call for Accountability or a Misguided Approach?
Governor Stitt’s comments have sparked intense debate about the future of Oklahoma’s forestry services. His assertion that resources weren’t used properly during the March 14th fires has been met with pushback from department officials who maintain that all available resources were deployed effectively.
Craig Marquardt, Assistant Director and Forest Management Chief, defended the department’s actions, stating, “There were so many fires that day. We had all our resources obligated. I don’t know what we would’ve done differently.” This sentiment echoes throughout the ranks of forestry professionals who found themselves battling an unprecedented confluence of factors during the wildfires.
The Human Cost: State Employee Job Security in the Balance
As discussions about potential cuts to the forestry department continue, we must not lose sight of the human element in this equation. The dedicated men and women who serve in Oklahoma’s forestry services are more than just employees; they are the front-line defenders of our natural resources and public safety.
Gene Blankenship, deputy director of the Oklahoma Public Employees Association, voiced concerns about the impact of these discussions on state employees: “The ongoing threat of dismantling state agencies demonstrates a clear lack of prioritization for state employees and their families. Reducing state jobs diminishes the quality of state services which only hurts Oklahoma communities.”
This sentiment underscores a critical aspect of the debate: the intertwined nature of public service, job security, and community well-being. As we consider the future of Oklahoma’s forestry services, we must also consider the ripple effects that major changes could have on our workforce and the communities they serve.
Balancing Fiscal Responsibility and Public Safety
The crux of this issue lies in finding a balance between fiscal responsibility and maintaining essential services. While it’s important to ensure that public resources are used efficiently, we must also recognize the invaluable role that forestry services play in protecting our state from natural disasters.
Let’s consider a comparative analysis of the potential impacts of proposed changes to Oklahoma Forestry Services:
| Service Area | Current Resources/Staff | Proposed Cuts | Estimated Impact on Public Safety | Potential Job Losses | Community Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wildfire Prevention | 100 full-time staff | 50% reduction | Significant decrease in prevention activities | 50 jobs | High |
| Prescribed Burns | 50 specialized personnel | 30% reduction | Fewer controlled burns, increased wildfire risk | 15 jobs | Medium |
| Water Quality Management | 30 technicians | 20% reduction | Reduced monitoring and maintenance | 6 jobs | Medium |
| Forest Management | 80 foresters and support staff | 40% reduction | Decreased forest health and resilience | 32 jobs | High |
| Emergency Response | 60 firefighters and coordinators | 25% reduction | Slower response times to wildfires | 15 jobs | High |
This table illustrates the potential consequences of budget cuts across various aspects of forestry services. It’s clear that reductions in staff and resources could significantly impact public safety and increase community risk levels.
Innovative Solutions for Forest Management
As we grapple with these challenges, it’s worth exploring innovative solutions that could enhance our forest management techniques and wildfire prevention strategies. One such solution comes from the realm of agricultural technology, where companies like Farmonaut are revolutionizing land management practices.
While Farmonaut’s primary focus is on agricultural applications, their satellite-based monitoring systems and AI-driven analytics could potentially be adapted for forestry management. For instance, their carbon footprinting tools could be valuable in assessing the environmental impact of forestry practices and wildfires.
Similarly, Farmonaut’s fleet management solutions could be adapted to optimize the deployment of firefighting resources during emergencies. By leveraging advanced technology, we might be able to enhance the efficiency of our forestry services without compromising on public safety or job security.
The Path Forward: A Call for Collaborative Solutions
“Recent wildfires in Oklahoma, exacerbated by hurricane-force winds, have affected hundreds of square miles and thousands of residents.”
As we navigate this complex issue, it’s clear that a collaborative approach is necessary. We must bring together stakeholders from all sides – forestry professionals, state employees, policymakers, and community representatives – to craft solutions that address fiscal concerns without compromising public safety or job security.
Here are some key considerations for moving forward:
- Comprehensive review of current forestry management techniques
- Assessment of firefighting resources and their distribution across the state
- Exploration of technology-driven solutions to enhance efficiency
- Development of sustainable funding models for essential services
- Creation of retraining and job transition programs for affected employees
By addressing these areas, we can work towards a solution that balances the need for fiscal responsibility with the imperative of maintaining robust forestry services and protecting state employee job security.
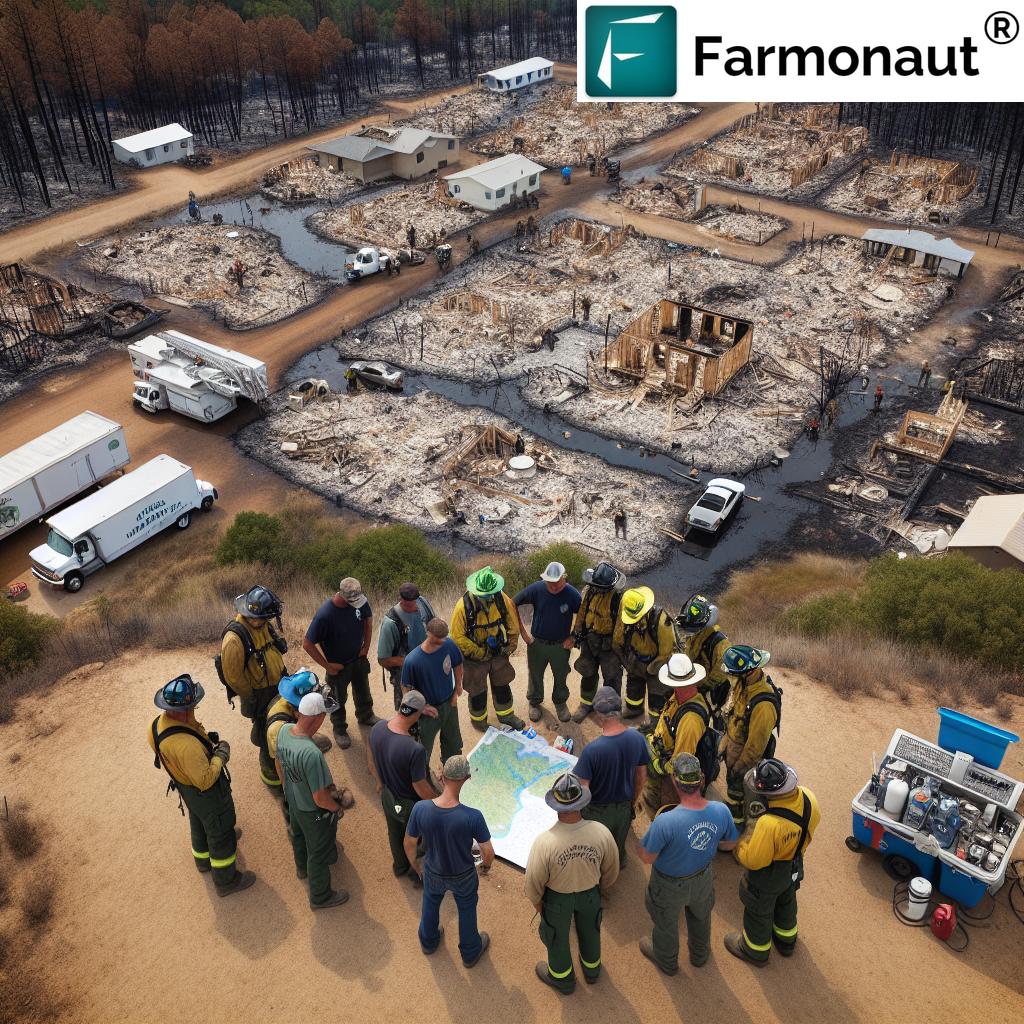

The Role of Technology in Modern Forestry
As we look to the future of forestry services in Oklahoma, it’s crucial to consider how technology can play a role in enhancing our capabilities while potentially reducing costs. Advanced monitoring systems, predictive analytics, and AI-driven decision-making tools could revolutionize how we approach forest management and wildfire prevention.
For instance, satellite-based monitoring systems could provide real-time data on forest health, detecting early signs of disease or potential fire hazards. This proactive approach could significantly improve our ability to prevent and respond to wildfires, potentially reducing the need for large-scale emergency responses.
Moreover, AI-powered predictive models could help forecast high-risk periods for wildfires, allowing for more targeted allocation of resources and personnel. By leveraging these technologies, we might be able to maintain or even improve our level of forest protection while optimizing our use of human and financial resources.
Community Engagement and Public Education
An often overlooked aspect of forestry services is their role in public education and community engagement. These programs are crucial for fostering a sense of shared responsibility for our natural resources and promoting safe practices that can prevent wildfires.
As we consider the future of Oklahoma’s forestry services, we must recognize the value of these educational initiatives. They not only help prevent human-caused wildfires but also build public support for forestry programs and create a more informed citizenry.
Potential areas for enhanced community engagement include:
- School outreach programs on forest conservation and fire safety
- Community workshops on creating defensible spaces around properties
- Volunteer programs for forest maintenance and monitoring
- Public awareness campaigns on the role of prescribed burns in wildfire prevention
By investing in these areas, we can create a more resilient and knowledgeable community, potentially reducing the strain on our forestry services in the long run.
The Economic Impact of Forestry Services
While discussions about cutting the forestry department often focus on potential cost savings, it’s crucial to consider the broader economic impact of these services. Healthy forests contribute significantly to Oklahoma’s economy through various channels:
- Tourism and recreation
- Timber industry
- Ecosystem services (e.g., water filtration, carbon sequestration)
- Property value protection in forested areas
Moreover, the cost of fighting wildfires and recovering from their damage can far exceed the budget allocations for preventive forestry services. A comprehensive economic analysis should consider these factors when evaluating the true value of our forestry department.
The Human Element: Valuing Our Forestry Professionals
At the heart of this debate are the dedicated professionals who make up Oklahoma’s forestry services. These individuals bring years of experience, specialized knowledge, and a deep commitment to protecting our natural resources. As we consider potential changes to the department, we must recognize the invaluable human capital that these employees represent.
Blankenship’s statement resonates deeply: “State employees should not have to live under the umbrella of job insecurity based on the shifts in political climate.” This sentiment underscores the need for a stable and supported workforce in our essential services.
Consider the following impacts of job insecurity on our forestry professionals:
- Decreased morale and productivity
- Loss of institutional knowledge if experienced staff leave
- Difficulty in attracting and retaining top talent
- Potential safety risks if understaffing leads to overwork
By valuing and supporting our forestry professionals, we not only ensure better service delivery but also maintain a workforce ready to face the challenges of wildfire prevention and forest management in Oklahoma.
Looking to the Future: A Balanced Approach
As we navigate the complex issues surrounding Oklahoma’s forestry services, it’s clear that a balanced approach is necessary. We must find ways to optimize our resources without compromising on public safety or the well-being of our state employees.
Here are some potential strategies for moving forward:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of current forestry practices and resource allocation
- Invest in technology and training to enhance efficiency and effectiveness
- Explore public-private partnerships to supplement state resources
- Develop a long-term strategic plan for sustainable forest management and wildfire prevention
- Engage in ongoing dialogue with forestry professionals, policymakers, and community stakeholders
By adopting a thoughtful, collaborative approach, we can work towards a solution that ensures the continued protection of Oklahoma’s forests while addressing fiscal concerns and supporting our valuable workforce.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The challenges facing Oklahoma’s forestry services are complex, but not insurmountable. As we’ve explored throughout this discussion, the importance of maintaining robust forestry management and wildfire prevention capabilities cannot be overstated. At the same time, we must be mindful of fiscal realities and the need for efficient use of public resources.
We call upon all stakeholders – from policymakers and forestry professionals to community members and technology innovators – to come together in crafting solutions that protect our forests, our communities, and our dedicated public servants. By working collaboratively and leveraging the best of human expertise and technological advancements, we can forge a path forward that ensures the safety and prosperity of Oklahoma for generations to come.
The future of Oklahoma’s forests, and the livelihoods of those who protect them, depends on the actions we take today. Let us approach this challenge with the wisdom, compassion, and foresight it deserves.
FAQ Section
Q: What are the main responsibilities of Oklahoma Forestry Services?
A: Oklahoma Forestry Services is responsible for wildfire prevention and management, prescribed burns for fire control, water quality maintenance, forest management and conservation, and public education and outreach.
Q: How do wildfires impact Oklahoma communities?
A: Wildfires can have devastating effects on Oklahoma communities, including property damage, loss of life, environmental destruction, and economic impacts on industries like tourism and agriculture.
Q: What role does technology play in modern forestry management?
A: Technology plays a crucial role in modern forestry management, including satellite-based monitoring systems, AI-driven predictive analytics, and advanced resource management tools that enhance efficiency and effectiveness in forest protection and wildfire prevention.
Q: How might cuts to the forestry department affect public safety?
A: Cuts to the forestry department could potentially lead to reduced wildfire prevention activities, slower response times to fires, decreased forest health monitoring, and overall increased risk to public safety and natural resources.
Q: What are some alternative solutions to budget cuts for forestry services?
A: Alternative solutions could include investing in technology to improve efficiency, exploring public-private partnerships, implementing sustainable funding models, and enhancing community engagement and volunteer programs to supplement state resources.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!