Mississippi River New Orleans: 7 Powerful Ways It Shapes the City
Summary: New Orleans and the Mighty Mississippi
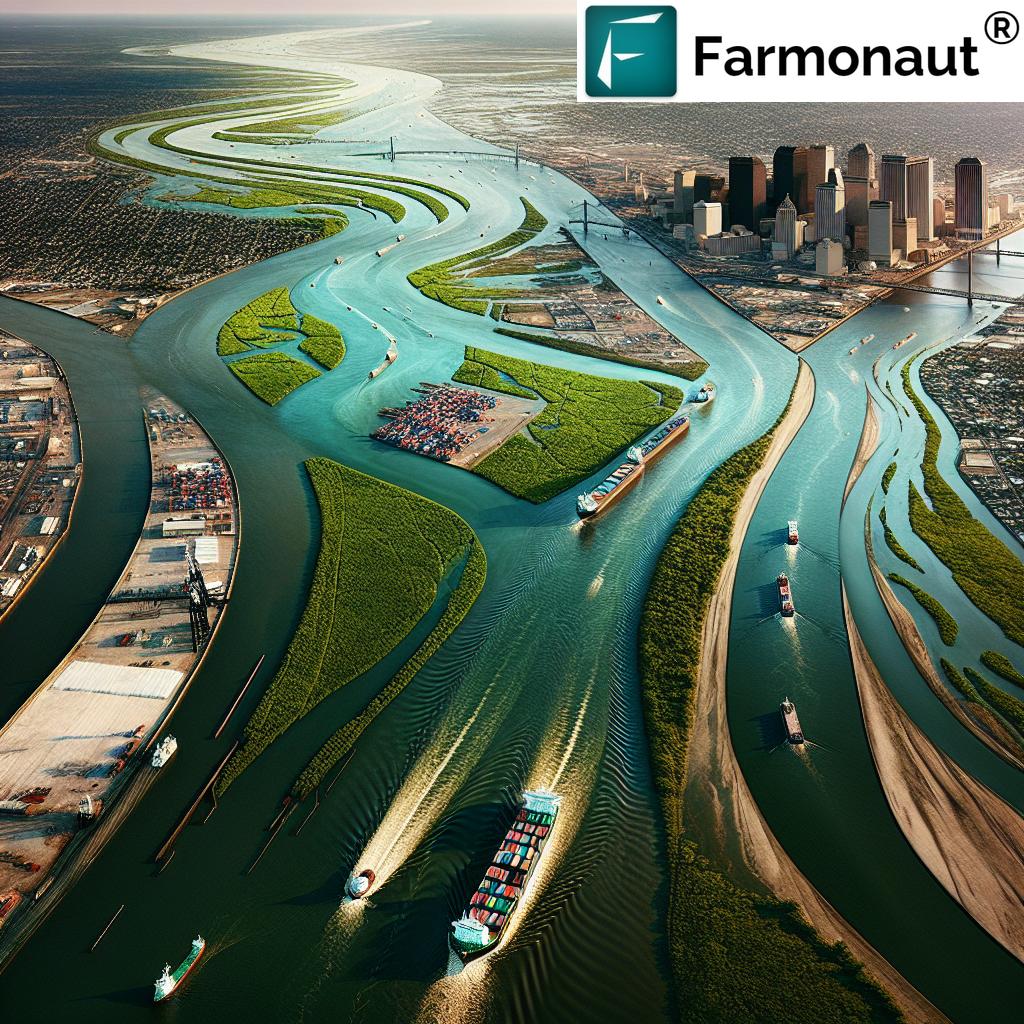
New Orleans is a city built, battled for, and reborn at the edge of the Mississippi River. This mighty waterway is far more than a geographical feature; it’s the city’s lifeblood, natural artery, and perpetual challenge. Connected to global trade, vulnerable to floods, and defined by its delta, New Orleans is truly a city forged by the Mississippi River.
The Mississippi River New Orleans relationship shapes our region’s economy, cultural identity, flood control infrastructure, and even the fate of our future in the face of climate change. By exploring these seven powerful ways the river influences the city, we gain a deeper understanding of our city’s origins, our resilience, and the sustainability required to protect our home.
Historical Context: How the Mississippi River Forged New Orleans
Our story begins with a strategic location at the mouth of North America’s greatest river. From the city’s founding as a French colony in 1718, New Orleans leveraged its position along the Mississippi River to dominate trade routes that spanned the continent and connected the interior with the Gulf of Mexico and the world’s oceans.
The river’s flow provided transportation for agricultural goods (grain, cotton, and more), fostered a melting pot of culture, and dictated cycles of boom and bust across centuries. But the river’s natural tendency to flood meant the city faced existential threats—battling for survival with every high-water spring and hurricane season.
As engineering, navigation, and levee construction advanced, New Orleans’ growth accelerated. Yet the delicate dance between harnessing the river and surviving its power—a core theme—remains central to our present-day realities, especially as we face modern threats from coastal erosion and climate change Mississippi River intensifies.
7 Powerful Ways the Mississippi River Shapes New Orleans
1. Economic Engine & Trade Powerhouse
The Mississippi River New Orleans partnership is, first and foremost, an economic juggernaut. Our city’s incredible economic importance was established because the river acts as a vital transportation and communication artery, providing the main conduit for agricultural goods transportation from the heartland to the rest of the world.
Key facts about this economic relationship:
- The Port of New Orleans handles over 50 million tons of cargo annually, including grain, petroleum, chemicals, machinery, and manufactured goods.
- Over $100 billion in annual trade value flows through the New Orleans region, making the port system a top ten in the United States.
- As a key link in continental exports, the port ties America’s heartland to global maritime routes—impacting farming, manufacturing, and energy sectors.
- Thousands of jobs in shipping, logistics, and agriculture are supported by this ongoing commerce and trade.
Our city’s economic prosperity is inseparable from the river’s role as both a global gateway and a local sustainer. However, the same commercial forces that drive growth also amplify the urgency of environmental management challenges like erosion, pollution, and sustainable port development.
Discover Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting
to track and reduce farming’s environmental impact—critical for both river health and sustainable agriculture in Louisiana.
2. Levees & New Orleans Flood Control: Our Lifeline Against the River
No discussion of New Orleans flood control is complete without the Mississippi River. For centuries, citizens and engineers have built and reinforced levees—earthen embankments and now sophisticated floodwalls—along the riverbanks to protect the city from inundation.
- The city is uniquely vulnerable: much of it lies below sea level, hemmed in between the river and Lake Pontchartrain.
- Without levee systems, the city would regularly flood from both river overflow and hurricane-induced storm surges. The catastrophic events of Hurricane Katrina tragically exposed the region’s vulnerabilities in 2005.
- New Orleans’ floodwalls and spillway structures, like the Bonnet Carré Spillway, are designed to divert excess water and relieve the pressure on levees during extreme floods.
The natural levees Mississippi River created by centuries of sediment deposition once protected the region, but urban expansion and engineered channeling have shifted the balance. Today, we rely on a multi-layered system of control, maintenance, and vigilance—a constant battle as climate change increases both riverine and coastal threats.
Mitigate disaster risks in farming with Farmonaut’s Satellite Verification for Crop Loans & Insurance, ensuring resilience for rural communities in flood-prone Louisiana areas.
3. Coastal Erosion in Louisiana: Ongoing Challenge
The devastating rate of coastal erosion Louisiana faces is directly tied to the Mississippi River’s course and its engineered state. Naturally, the river’s flow would meander seasonally, distributing sediment and building wetland habitats. But decades of levee construction have disconnected the river from its deltaic wetlands.
Key facts:
- Louisiana loses over 16 square miles of land per year, a rate like a football field every 100 minutes!
- This erosion threatens critical habitats, urban areas, and the integrity of our levee systems.
- Primary causes: river leveeing (limiting new sediment), sea level rise, storm surges, and human activity.
With climate change and more intense hurricanes, reversing and slowing land loss is a central challenge for delta restoration and the city’s future sustainability.
Learn about Farmonaut’s Blockchain-Based Product Traceability—bringing transparency and sustainability to agricultural supply chains across Mississippi-linked markets.
4. Port of New Orleans & Maritime Commerce: Gateway to the World
Our city’s port is not merely a regional facility—it is a continental trade and transportation linchpin. The port of New Orleans links inland river routes (stretching north as far as Minnesota) directly to the Gulf of Mexico and global markets.
- Handles goods spanning agricultural grain, coal, petroleum products, aluminum, steel, and more.
- Supports vital sectors: manufacturing, oil refining, and international container shipping.
- Thousands of jobs depend on ongoing port operations, logistics, and maritime security.
- Exports of soybeans, corn, wheat, and rice shape not only New Orleans’ fate, but agricultural regions throughout the Mississippi Basin.
The river’s role as a waterway enables barge transport of bulk cargo, which is both cost-effective and environmentally preferable compared to other modes. Balancing shipping expansion with wetland preservation and community needs remains a pressing environmental management challenge.
Optimize agribusiness logistics with Farmonaut’s Fleet Management Tools—empowering agricultural product movement from Louisiana farms to the port, maximizing resource use while reducing environmental impact.
5. Mississippi River Delta Restoration Efforts
One of the biggest long-term sustainability battles we face is Mississippi River Delta restoration. Maintaining and restoring these dynamic wetlands isn’t just environmental—it’s about defending the city itself.
Key Delta Restoration facts:
- The Delta originally spanned over 3 million acres; less than half remains intact today.
- Diversion projects are underway to re-route the river’s sediment flow into erosion-prone wetlands, helping to rebuild land and create a buffer for future storm surges.
- The Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority (CPRA) oversees these ambitious projects—combining engineering, ecological science, and public engagement.
Land loss isn’t just a problem for New Orleans: it affects regional agriculture, fisheries, and the culture of the entire Gulf Coast. Delta restoration is our shared responsibility.
For governments and NGOs: Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management platform provides landscape-level monitoring to support sustainable delta management and restoration.
6. Climate Change, Storms & City Resilience
As we enter an era of accelerating climate change, the interplay of river and sea threats grows more dangerous for New Orleans. Our vulnerability is defined by:
- Rising sea levels threatening to inundate low-lying areas.
- Harsher storms and increased river flow creating a need for more frequent floodgate and spillway operations.
- Increased frequency of major floods (e.g., the Bonnet Carré Spillway now opens more often than ever before).
- Disrupted rainfall and evaporation patterns altering river flow and impacting both urban infrastructure and agriculture.
Adapting to these new realities requires innovation—from ecosystem restoration and upgraded levees to smarter water and resource management. It also means measuring and reducing agriculture’s environmental impact, a challenge Farmonaut addresses via real-time carbon tracking.
7. Urban Development, Culture & Identity—A City Shaped by Water
Finally, the Mississippi River New Orleans story is deeply cultural—defining everything from our culinary traditions to our unique music, architecture, and festivals.
Highlights include:
- New Orleans’ famous cuisine (think gumbo, jambalaya, crawfish) is inseparable from the bounty of the river and the Gulf.
- Jazz and blues music grew from the docks, levees, and multicultural communities clustered near the riverbanks.
- The city’s multicultural identity owes as much to migration via the Mississippi as to its European and Caribbean roots.
- Even the city’s layout, traditions, and annual Mardi Gras celebrations are influenced by the rhythms of the river’s flow.
In this way, the river is not just a constraint or a resource—it is the wellspring of the city’s soul.
Comparative Impact Table: Ways the River Shapes New Orleans
| Impact Area | Description | Estimated Quantitative Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Economy & Trade | River and port system fueling city, state, & national commerce; essential for agricultural & manufactured goods exports. | $100+ billion in annual trade; 50M+ tons shipped/yr |
| Levee Protection & Flood Control | Artifical and natural levees, floodwalls, and spillways shield city from river and storm floods. | 1.3+ million people regionally protected; 350+ mi levees |
| Coastal Erosion & Habitat Loss | Altered river flow causes sediment loss and rapid Louisiana land disappearance. | 16+ sq miles land lost/yr; 1 football field/100 min |
| Port Trade & Maritime Industry | Port of New Orleans is a continental logistics hub, moving US goods globally via river-gulf routes. | 2,000+ vessels/year; 10th largest US port |
| Delta Restoration Efforts | Projects diverting sediment to restore marsh, buffer storms, and rebuild disappearing coastline. | 10,000+ acres delta habitat restored (2020s) |
| Climate Change Influence | Amplifies flood risks, sea level rise, storm damage, and strains city infrastructure. | 3x+ increase in major floods since 1980 |
| Urban Development, Culture & Identity | River influences cuisine, music, architecture, diversity, and annual events—defines “the soul” of New Orleans. | Millions engaged in cultural tourism every year |
Cutting-Edge Technologies Shaping Mississippi River-Connected Agriculture
To address the intertwined economic and environmental challenges of the Mississippi River New Orleans region, technology is playing a transformative role. Smart, data-driven agriculture helps reduce runoff, optimize land use, sustain wetland habitats, and ensure agricultural productivity even as the climate shifts.
Farmonaut is a leader in these farm technology solutions, supporting everyone from individual Louisiana farmers to regional administrators with:
- Satellite-based Crop Health Monitoring: Using high-resolution satellite imagery, we help farmers monitor vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, pest hotspots, and nutrient deficiencies. This real-time intelligence helps optimize input use, reducing harmful nutrient runoff gulf of Mexico and promoting sustainability.
- AI-Driven Advisory: Personalized crop management advice delivered via our Jeevn AI system enables farmers to react to dynamic weather, river levels, and field conditions—vital for flood-prone environments near the Mississippi River.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: We bring farm-to-fork transparency via blockchain-powered product traceability, ensuring ethically and sustainably produced agricultural goods on both local and export markets.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Our tools empower agribusinesses to efficiently move goods from farm-fields to the port using satellite monitoring, higher crop yields, and reduced carbon footprint.
Our technologies are accessible on Android, iOS, and online app, plus full-featured Farmonaut API for developers and institutions. Interested in integrating satellite and weather data? See API developer docs.
Sustainability, Innovation & the Future: The Path Forward
To secure the future of New Orleans and preserve the delta, we must balance economic vitality with smart environmental management. Here’s how our region can move forward:
- Support sediment diversion projects to restore wetlands and reverse coastal erosion in Louisiana.
- Reduce nutrient runoff by adopting precision agriculture—minimizing fertilizer waste and protecting Gulf marine life from algae blooms and dead zones.
- Invest in modern levee systems, guided by data and adaptive engineering to withstand both river floods and hurricane surges amplified by climate change Mississippi River effects.
- Foster sustainable trade via green logistics and transparent supply chains, benefiting both our economy and our ecosystem.
- Monitor carbon footprint and adopt best practices for resource management in agriculture, leveraging technology for climate resilience.
It’s a future built on resilience, innovation, and a shared commitment to keep New Orleans thriving at the intersection of river, delta, and sea for generations to come.
Try Farmonaut’s satellite-powered advisory today to enhance your sustainability strategy—whether you’re a producer, agribusiness, or policy maker.
Farmonaut Subscriptions: Affordable, Scalable Tech for All
FAQ: Mississippi River – New Orleans Relationship
Why was New Orleans built at its current location on the Mississippi River?
The city’s location was chosen for its access to trade between the interior of North America and global routes via the Gulf of Mexico. This strategic position made New Orleans a key port and hub for agricultural and commercial goods flowing through the continent.
How does the Mississippi River influence New Orleans’ culture?
The river has been a mixing ground for cultures from Europe, Africa, and the Caribbean. It shapes the city’s music, food, festivals, and even its neighborhoods. Jazz, blues, and the world-famous cuisine all owe their origins in part to river commerce and the diverse people attracted to its banks.
What is the ‘Dead Zone’ in the Gulf of Mexico and how is it connected to the Mississippi River?
The “Dead Zone” refers to a vast area of low oxygen caused by nutrient runoff from the Mississippi basin. Excess fertilizer and pollutants flow into the river, then into the Gulf, fueling algae blooms that deplete oxygen, harm fisheries, and disrupt ecosystems.
What are some major climate change impacts on New Orleans and the river?
Rising sea levels, more intense storms, higher river floods, and rapid erosion all threaten New Orleans’ safety and economy. Adaptation efforts focus on levee upgrades, marsh restoration, smart water management, and precision agriculture (visit Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting to learn more).
How do levees and spillways work to protect New Orleans?
Levees are embankments built along the river’s banks to stop water from overflowing. Spillways like the Bonnet Carré are designed to purposely divert excess river flow into Lake Pontchartrain or other safe areas to reduce pressure during floods.
What initiatives are underway for Mississippi River Delta restoration?
Projects led by the CPRA and partners divert fresh water and sediment to replenish coastal marshes, rebuild land, and buffer against storms. These include marsh creation, sediment diversions, and coastal restoration—recognized globally as vital for New Orleans’ long-term survival.
How does advanced farm management technology like Farmonaut help protect the river environment?
By applying precision agriculture and resource tracking (using satellites and AI), Farmonaut helps reduce fertilizer runoff and soil erosion into the river. This, in turn, combats the dead zone, supports sustainable farming, and promotes resilience against flooding.
Sources & References
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
- Louisiana CPRA (coastal.la.gov)
- NOAA National Coastal Data
- National Weather Service and NOAA National Hurricane Center
- Farmonaut (farmonaut.com)
- Pew Center – “Mississippi River and the City”
- Farmonaut Satellite Weather API
Want to put data-driven, sustainable agriculture to work—protecting the river, the city, and your farmland? Get started with Farmonaut today.