Idaho Sustainable Agriculture: 5 Powerful Grant Criteria Changes
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Transforming Idaho Sustainable Agriculture Grants
- Context: PCSC, USDA, IAMP & the New AMP Initiative
- Idaho Grant Criteria: Overview of 5 Powerful Changes in 2024
- Comparative Criteria Table: Old vs. New Grant Requirements
- USDA Initiatives and the Rise of Traceability Technology in Agriculture
- Supporting Producers & Cost Saving in Idaho Agriculture
- Farmonaut’s Eco-Technology: Bringing Precision and Traceability to Idaho’s Fields
- Grant Application Updates: How Idaho Producers Can Stay Eligible
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Farmonaut Subscription Options
- Summary & Conclusion: The Future of Idaho Sustainable Agriculture
Introduction: Transforming Idaho Sustainable Agriculture Grants
As we stand on the brink of a transformative moment for Idaho’s farmers, the very landscape of sustainable agriculture funding is evolving. Strong, data-driven shifts in grant criteria for farmers are re-shaping opportunities for those committed to sustainability. Recent actions from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) have brought sweeping changes to programs like Partnerships for Climate-Smart Commodities (PCSC)—now relaunched as the Advancing Markets for Producers (AMP) Initiative.
Notably, nearly $59 million in sustainable agriculture grants were initially allocated to the University of Idaho’s Innovative Agriculture and Marketing Partnership (IAMP) project. These funds were designed to nurture sustainable practices in Idaho, including critical focus areas like soil health, irrigation, fertilizers, precision agriculture, and traceability technology in agriculture. However, with new grant criteria for farmers requiring at least 65% of incentives to go directly to Idaho producers—not just supporting services—the future of sustainable farming in our state is in sharp focus.
In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll detail all 5 powerful grant criteria changes and what they mean for producers, funding proposals, and the adoption of cost-saving technologies such as precision analytics, blockchain traceability, GIS, and AI-powered resource management. We’ll also discuss the vital role Farmonaut’s solutions play as Idaho agriculture advances into a greener, more resilient era.
Context: PCSC, USDA, IAMP & the New AMP Initiative in Idaho
In early 2024, sustainable agriculture funding entered the limelight with Idaho’s IAMP project—championed by the University of Idaho and set to serve 201 producers across 34 Idaho counties. At its heart, IAMP was structured to incentivize the adoption of climate-smart practices: conserving soil quality, optimizing irrigation, calibrating fertilizer use, and integrating traceability technology into agriculture.
However, a seismic shift was triggered when the USDA revised its policies under the PCSC program, introducing the AMP Initiative. Funding mechanisms, allowable costs, and application criteria experienced significant modifications—pivotal for Idaho farmers looking to secure their place in these sustainable agriculture funding streams.
- Original Vision: Provide direct incentive payments to farmers (over half of grant funds), with the remainder reserved for technical support, data analysis, soil analysis, and marketing services.
- USDA’s Revision: Now, a minimum of 65% of grant funds must go directly to producers as incentive payments. Administrative, analytic, and marketing support funds are further tightened.
- Applications Affected: The change placed proposals—particularly IAMP’s with 201 enrolled producers in Idaho—under review, requiring quick adaptation to new rules.
As we examine these developments, it’s crucial to understand both the rationale and the repercussions for grant-seeking farmers in Idaho, especially those already advancing soil and irrigation management, integrating technology-based agricultural risk reduction strategies, and contributing to a more resilient food system.
To encourage readers to explore precision agriculture tools, check out Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solution, a resource designed to help Idaho producers achieve environmental compliance and sustainable productivity benchmarks.
Idaho Grant Criteria: Overview of 5 Powerful Changes in 2024
The following five criteria represent the most pronounced changes impacting the Idaho sustainable agriculture grant landscape this year. Each has substantial implications—from how funds are allocated, to the rise of traceability requirements, to the core focus on measurable environmental benefits.
-
Direct-to-Producer Payment Shift
The new requirement stipulates that at least 65% of grant funds must be disbursed directly to enrolled Idaho producers as incentive payments. This sharper focus on direct payment (versus indirect support or administrative costs) prioritizes farmers’ bottom lines and intends to maximize on-farm adoption of sustainable methods. -
Increased Emphasis on Actionable Data and Verification
Farmers must now collect and analyze data on their sustainable activities with greater scrutiny. There are expanded requirements for verified measurement, data sharing, and use of technology-enabled tracking (e.g., blockchain product traceability). This is vital for Idaho’s engagement in international agricultural commodities marketing. -
Expanded Environmental Impact and Traceability Technology
Grants place explicit emphasis on quantifiable ecosystem benefits: carbon sequestration, soil health, water irrigation efficiency, and reduced chemical fertilizer and pesticide use. Use of traceability technology in agriculture is rapidly becoming a funding precondition. -
Cost Savings and Producer Autonomy
Support for technical, soil analysis, or marketing services has been limited—now, more is expected to be procured independently by the producer. Grants reward those who demonstrate agricultural risk reduction strategies and cost-saving measures, including resource management (inputs such as water, fertilizer), and integration of “DIY” solutions. -
Modernized Record-Keeping and Compliance
The new framework demands detailed, digital record-keeping—from precision GPS-logged field activities to blockchain tracking of commodities. Grants now require transparent documentation, continuous compliance, and strong alignment with the US sustainable farming initiatives for futureproof support.
These criteria aren’t simply bureaucratic hurdles—they represent a broader transformation in the way Idaho agriculture secures funding, modernizes operations, and drives sustainability.
Comparative Criteria Table: Old vs. New Grant Requirements
To help Idaho farmers and grant applicants grasp the practical impacts of the recent policy update, we present a clear, concise table. This comparative breakdown makes it easy to scan and internalize how each specific criterion has evolved, what the potential cost saving in agriculture is, and how modern sustainability and traceability expectations have risen.
| Affected Grant Criterion | Old Grant Criteria | New Grant Criteria (2024) | Estimated Cost Impact (%) | Sustainability Focus | Traceability Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Health Management | Basic soil sampling and improvement practices encouraged | Data-driven soil analysis and quantifiable improvements are required | -10% (cost-saving on inputs due to optimized use) | Explicit reduction in fertilizer/pesticide use | Digital soil records, verification needed |
| Water Usage / Irrigation | Voluntary water-saving activities | Mandatory precision irrigation and reporting via tech | -15% (reduced water, energy costs) | Water conservation benchmarks required | Real-time usage logs; traceability preferred |
| Size of Farm (Eligibility) | Wide range; emphasis on larger-scale adoption | Still inclusive, but incentives favor small/medium with measurable sustainability actions | Varies (increased for proactive producers) | Net regional environmental impact | Documented per field via GIS |
| Technology Adoption | Optional/encouraged; minimal requirement | Required: satellite imagery, traceability, digital records (blockchain preferred) | -10% to -20% (via increased efficiency, but requires initial investment) | Core to grant eligibility | End-to-end field-to-market traceability |
| Record-Keeping & Reporting | Annual reports; paper/electronic acceptable | Continuous, digital record-keeping, blockchain and satellite validation | -5% to -12% (labor time, fraud risk down) | Transparency, measurable outcomes | Mandatory; accessible to auditors |
By adapting to these newly clarified grant criteria for farmers, Idaho’s agricultural community can continue to thrive while reducing risks and improving long-term sustainability—especially as climate challenges and global market demands intensify.
USDA Initiatives and the Rise of Traceability Technology in Agriculture
The revised policies under USDA’s AMP Initiative put Idaho at the national forefront—not only for funding but for traceability technology in agriculture. This trend is best understood as a platform for cost saving in agriculture, agricultural commodities marketing, and compliance with evolving global standards.
- Blockchain-based Traceability: Ensures Idaho products are transparently tracked from the field to end markets, decreasing fraud and increasing value. Learn more about Farmonaut’s Traceability Solution designed for modern agricultural supply chains.
- GIS and Satellite Data: Idaho grants now encourage, and often require, mapping via GIS, with crop activities and soil management validated through satellite analytics.
- Real-Time Data Collection and Sharing: The integration of AI and digital platforms enables both compliance and smarter farm management through automated reporting, remote monitoring, and instant optimization.
The practical outcome? Producers not only meet grant eligibility but also strengthen their resilience to climate risk and market shocks—a central priority of the USDA’s US sustainable farming initiatives.
Learn how unlocking soil organic carbon, tracked by satellite-based services, is now a requirement and an opportunity for sustainable agriculture funding in Idaho.
Supporting Producers & Cost Saving in Idaho Agriculture
The new AMP Initiative’s focus is clear: move the majority of grant dollars directly to Idaho producers’ hands. While this increases the need for farmers to procure their own technical, GIS, soil analysis, and marketing services, it also reduces reliance on costly intermediaries. Here’s how it helps:
- Incentive Payments: At least 65% of all grant funds must be allocated as incentive payments, maximizing farmers’ usable funding and minimizing unnecessary administrative leakage.
- Cost Saving in Agriculture: By controlling how inputs (fertilizers, water, energy) are managed, costs for Idaho’s sustainable agricultural operations are decreasing by up to 20%, according to estimated impacts in our table above.
- Autonomy and Technical Innovation: Producers using self-managed digital services (like Farmonaut’s Large-Scale Farm Management App) achieve greater precision and cost-efficiency—enabling participation in risk reduction strategies, compliance, and competitive grant applications.
Satellite technology, now central to grant-supported sustainability, empowers smarter land use—from monitoring irrigation to precision soil management—and plays a direct role in maximizing Idaho’s agricultural grant program benefits.
For those needing direct access to satellite and weather data APIs for farm input support programs or custom integrations, explore Farmonaut API and the API Developer Docs. These resources help both farmers and Idaho agtech innovators connect directly with required technical services.
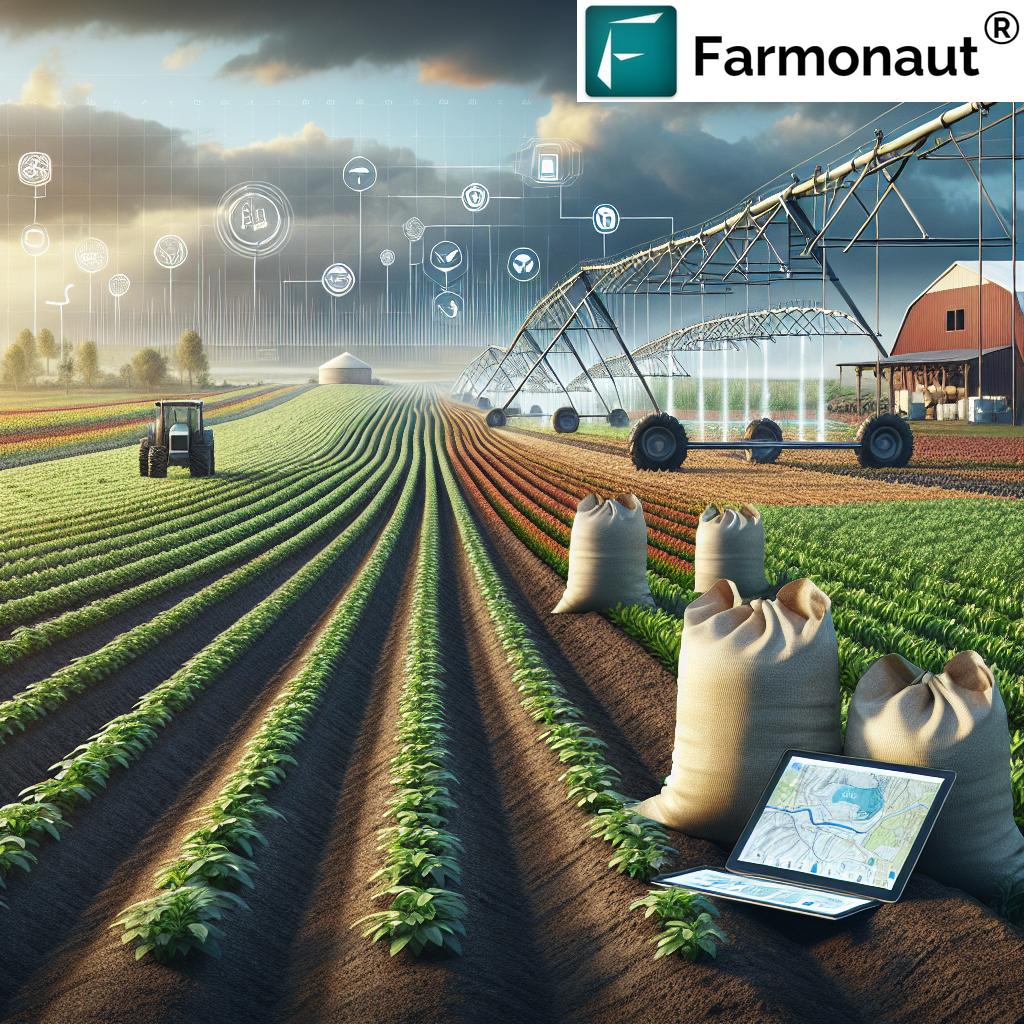
Farmonaut’s Eco-Technology: Bringing Precision and Traceability to Idaho’s Fields
As the sustainable agriculture landscape in Idaho adapts to stringent grant criteria and compliance demands, advanced technologies are no longer optional—they’re essential. Farmonaut is redefining farm input support with a platform designed for the diverse needs of Idaho producers:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Multispectral imaging covering soil moisture, NDVI, and crop health—reducing risks and enabling smarter fertilizer and irrigation usage.
- AI Farm Advisory (Jeevn AI): Personalized, real-time, weather-integrated farm insights, boosting productivity and lowering costs.
- Blockchain Traceability: Field-to-market tracking with end-to-end security—now a staple for sustainable agriculture funding and global commodities marketing.
- Carbon Footprinting: On-demand emissions tracking, streamlining compliance with environmental grant requirements.
- Fleet & Resource Management: For large and small farms alike, Farmonaut’s tools cut operational waste and labor costs.
- API Integrations: Seamless connection for Idaho’s agricultural developers and research groups, enabling them to build custom soil, irrigation, or risk management analytics.
We recommend Idaho ag businesses explore Farmonaut Fleet Management—designed to boost operational efficiency and resource usage tracking, aligning perfectly with the new grant focus on precision and documented sustainability action.
Through accessible web, iOS, and Android platforms, Farmonaut ensures Idaho’s smallest and largest farms can meet the evolving compliance landscape, maximize grant and funding outcomes, and contribute to a sustainable agricultural future.
Grant Application Updates: How Idaho Producers Can Stay Eligible
With the grant resubmission window open until June 20, Idaho producers, universities, and partners must ensure new proposals directly align with the updated AMP Initiative requirements. We suggest the following for successful Idaho agricultural grant applications:
- Allocate at least 65% of grant funds as direct incentive payments to enrolled Idaho producers.
- Plan for robust data collection and digital reporting, including satellite-validated environmental metrics (soil, irrigation, input savings).
- Include traceability platforms—preferably blockchain-based— to connect on-farm activities to end-user commodities marketing.
- Demonstrate cost saving in agriculture by adopting precision input management and quantifiable agricultural risk reduction strategies.
- Invest in continuous digital record-keeping, using solutions like Farmonaut’s AI and resource management tools for easy compliance.
Those who adapt quickly will maximize both sustainable agriculture funding potential and resilience to regulatory or market changes.
Grant programs increasingly reward producers who employ advanced, verifiable measurement of agricultural inputs—and who use those data points to reduce risks and costs in the field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Idaho Sustainable Agriculture Grant Criteria
What are the most important changes to Idaho sustainable agriculture grant criteria in 2024?
Five criteria stand out: increased minimum for direct-to-producer payments (65%+), required digital data collection/verification, mandatory adoption of traceability technology in agriculture, explicit cost-saving/resource management strategies, and tighter continuous record-keeping demands.
How can Idaho producers best position themselves for successful grant applications?
Producers should plan to utilize digital tools (satellite, AI, blockchain), focus on measurable soil and irrigation improvements, allocate incentives efficiently, and maintain transparent, up-to-date records of all sustainability activities and resource inputs.
Why is traceability so important for Idaho agricultural grants?
Traceability ensures that every dollar and activity can be transparently linked to positive environmental or economic results. It reduces fraud, builds global trust in Idaho commodities, and is now a funding precondition under new grant criteria.
Can Idaho producers use their own choice of technical providers for services like soil analysis and GIS mapping?
Yes, and in fact, producers are now expected to independently contract or self-manage these services, using incentive funds. Platforms like Farmonaut help fill this role with affordable, high-tech monitoring, mapping, and advisory tools.
How does cost saving in agriculture relate to new grant criteria?
Producers who demonstrate efficient use of grant funding—for example, reducing fertilizer or water usage through precision technology—are more likely to be awarded and retain funding under the revised USDA initiative.
What kind of record-keeping is now required for Idaho sustainable agriculture grants?
Continuous, digital record-keeping is required. This includes annotated field activity, satellite/A.I.-logged intervention points, precision input measurement, and potentially blockchain-based records to support verification and transparency.
Where can I access real-time farm data and monitoring to meet these grant requirements?
You can use Farmonaut’s web and mobile apps for satellite imagery, soil monitoring, AI advisories, and complete field data management.
Is there developer access or integration support for Idaho agtech companies?
Yes, the Farmonaut API and API docs are available for custom development and integrations, allowing local agtech to build compliant solutions.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Farmonaut offers flexible subscription plans tailored for Idaho producers, agribusinesses, and research institutions seeking to navigate the new grant criteria for farmers. Our satellite-based analytics, AI-powered dashboards, and blockchain-enabled traceability help users minimize risk, maximize compliance, and unlock new funding opportunities in sustainable agriculture.
Find the subscription that’s right for your farm or enterprise below:
Summary & Conclusion: The Future of Idaho Sustainable Agriculture
2024 marks a pivotal year for Idaho’s sustainable agriculture community—as new, powerful grant criteria emphasize not only direct support for producers but measurable progress on soil health, water and input savings, and traceability from field to market. The redirection of funding, the demand for advanced technical services, and the requirement of end-to-end data transparency empower Idaho’s farms to become more resilient, economically viable, and environmentally sound.
As we move forward, leveraging precision tools like Farmonaut’s crop monitoring, traceability, and carbon footprinting will be crucial. By embracing these new standards, Idaho agriculture is set to retain its leadership in climate-smart, sustainable production—and to unlock better cost savings and risk reduction than ever before.
Idaho’s agricultural future belongs to those who innovate, adapt, and steward our environment—one data-driven, sustainable field at a time.