Maximizing Crop Yields: Sustainable Soil Water Retention Techniques for Ontario Farmers
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on sustainable soil water retention techniques for Ontario farmers. As we navigate the challenges of changing climate conditions, understanding and implementing effective soil management practices has become more crucial than ever for maximizing crop yields. In this article, we’ll explore how soil acts as nature’s sponge, delve into the specific water requirements for key crops like corn and soybeans, and provide valuable insights into improving soil health for optimal moisture management.

“Corn requires approximately 20-30 inches of water per growing season for optimal yields in Ontario.”
As we embark on this journey to revolutionize soil and water management in agriculture, we’ll uncover the secrets to turning your soil into a moisture-retaining powerhouse. From the importance of root system development to the role of organic matter in enhancing water-holding capacity, we’ll provide you with a wealth of knowledge to boost your crop production, even in dry conditions.
The Soil Sponge: Understanding Water Retention
Soil is often referred to as nature’s sponge, and for good reason. Its ability to absorb, retain, and release water is crucial for plant growth and overall agricultural productivity. Let’s dive deeper into how soil performs this vital function:
- Soil Structure: The arrangement of soil particles (sand, silt, and clay) creates pores that can hold water. Well-structured soil has a mix of large and small pores, allowing for both water retention and drainage.
- Organic Matter: This component acts like a sponge within the soil, significantly increasing its water-holding capacity.
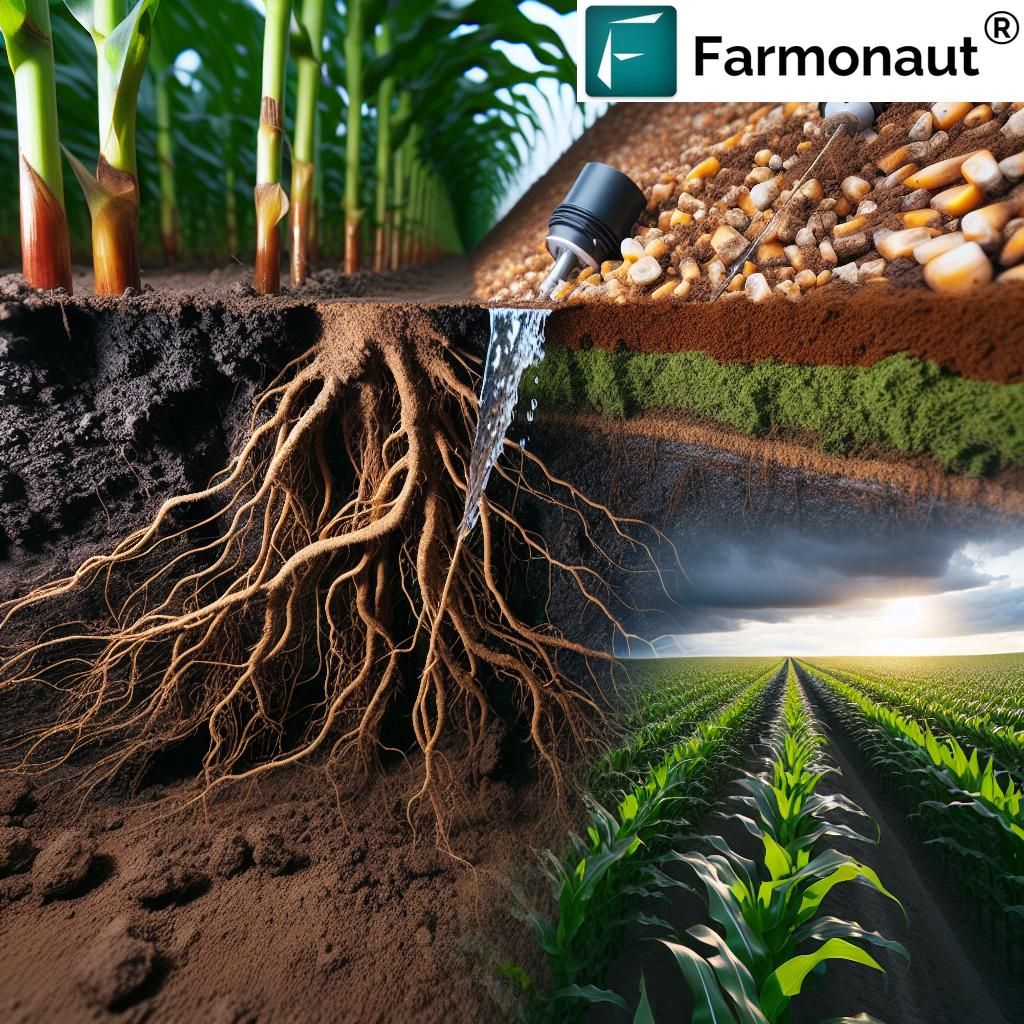
- Root Systems: Plant roots create channels in the soil, improving water infiltration and retention.
Understanding these mechanisms is the first step in implementing effective soil water retention techniques. By optimizing these natural processes, we can create an environment where crops thrive, even in challenging conditions.
Water Requirements for Corn and Soybeans in Ontario
In Ontario’s agricultural landscape, corn and soybeans are major players. Each of these crops has specific water needs that farmers must understand to ensure optimal yields:
Corn Water Requirements
- Corn typically requires 20-30 inches of water per growing season for optimal yields in Ontario.
- Critical periods for water demand include the silking and grain fill stages.
- Adequate moisture during these stages can significantly impact final yield.
Soybean Water Requirements
- Soybeans generally need 18-25 inches of water throughout their growing season.
- The flowering and pod-filling stages are particularly sensitive to water stress.
- Consistent moisture during these periods is crucial for maximizing soybean yields.
Understanding these water requirements is essential for implementing effective irrigation strategies and soil moisture management techniques. By aligning our farming practices with these crop-specific needs, we can significantly improve our yields and resource efficiency.
Improving Soil Health for Optimal Moisture Management
Healthy soil is the foundation of sustainable agriculture. When it comes to water retention, soil health plays a pivotal role. Here are some key strategies to improve soil health and enhance its moisture management capabilities:
- Increase Organic Matter: Adding organic matter through compost, cover crops, or crop residues improves soil structure and water-holding capacity.
- Minimize Soil Disturbance: Practices like no-till farming help maintain soil structure and prevent moisture loss.
- Promote Soil Biodiversity: Encouraging a diverse soil ecosystem enhances nutrient cycling and improves overall soil health.
- Implement Crop Rotation: Rotating crops helps break pest cycles, improves soil structure, and enhances water retention.
“Increasing soil organic matter by 1% can boost water retention capacity by up to 20,000 gallons per acre.”
By focusing on these aspects of soil health, we can create an environment that naturally retains more moisture, reducing the need for irrigation and improving crop resilience in dry conditions.
The Importance of Root System Development
A robust root system is crucial for efficient water uptake and soil moisture retention. Here’s why root development matters:
- Water Access: Deeper roots can access water from lower soil layers during dry periods.
- Soil Structure Improvement: Roots create channels that enhance water infiltration and retention.
- Organic Matter Contribution: As roots decay, they add organic matter to the soil, improving its water-holding capacity.
To promote healthy root development:
- Avoid soil compaction by minimizing heavy machinery use when soil is wet.
- Implement deep tillage practices where necessary to break up compacted layers.
- Choose crop varieties known for robust root systems.
By focusing on root system development, we can significantly improve our crops’ ability to access and utilize soil moisture effectively.
The Role of Organic Matter in Water Retention
Organic matter is a key component in improving soil water retention. Here’s why it’s so important:
- Increased Water-Holding Capacity: Organic matter can hold up to 20 times its weight in water.
- Improved Soil Structure: It helps create stable soil aggregates, enhancing water infiltration and retention.
- Enhanced Microbial Activity: A thriving soil ecosystem contributes to better nutrient cycling and overall soil health.
To increase organic matter in your soil:
- Implement cover cropping practices
- Incorporate crop residues into the soil
- Apply well-composted manure or other organic amendments
By prioritizing organic matter addition, we can significantly improve our soil’s ability to retain moisture and support healthy crop growth.
Effective Soil Moisture Management Techniques
Implementing effective soil moisture management techniques is crucial for maximizing crop yields while conserving water resources. Here are some key strategies:
- Precision Irrigation: Utilize technologies like soil moisture sensors and weather data to apply water only when and where it’s needed.
- Mulching: Apply organic mulches to reduce evaporation and maintain consistent soil moisture levels.
- Contour Farming: Planting along the contours of sloped land helps reduce runoff and improve water infiltration.
- Terracing: On steeper slopes, terracing can significantly reduce water runoff and soil erosion.
These techniques, when implemented correctly, can lead to significant improvements in water use efficiency and overall crop productivity.
The Benefits of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is a powerful tool in sustainable agriculture, offering numerous benefits for soil health and water retention:
- Improved Soil Structure: Different crop root systems help create varied soil pore sizes, enhancing water infiltration and retention.
- Increased Organic Matter: Rotating crops with different residue types contributes to a more diverse soil organic matter profile.
- Better Nutrient Management: Rotating crops with different nutrient needs helps maintain soil fertility and reduces nutrient leaching.
- Pest and Disease Control: Breaking pest cycles through rotation reduces the need for chemical interventions that can impact soil health.
When planning your crop rotation, consider:
- Alternating deep-rooted crops with shallow-rooted ones
- Including cover crops or green manures in your rotation
- Balancing high-residue crops with low-residue crops
By implementing a well-designed crop rotation plan, we can significantly improve our soil’s water retention capabilities while promoting overall soil health.
Climate-Resilient Agriculture Practices
As climate conditions become more unpredictable, adopting climate-resilient agriculture practices is essential. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Drought-Resistant Crop Varieties: Select crop varieties bred for drought tolerance and efficient water use.
- Conservation Tillage: Minimize soil disturbance to preserve soil moisture and structure.
- Agroforestry: Integrate trees into farming systems to improve water retention and provide additional benefits like windbreaks.
- Water Harvesting: Implement techniques to capture and store rainwater for use during dry periods.
These practices not only help in managing water more efficiently but also contribute to the overall resilience of the farming system in the face of climate variability.
Adapting to Water Stress: Long-Term Soil Management Strategies
Developing long-term strategies for soil management is crucial in adapting to increasing water stress. Here are some approaches to consider:
- Soil Health Monitoring: Regularly assess soil health indicators to track improvements and identify areas needing attention.
- Integrated Nutrient Management: Balance organic and inorganic nutrient sources to promote soil health and water retention.
- Erosion Control: Implement practices like contour plowing and cover cropping to prevent soil loss and improve water infiltration.
- Soil Microbiology Enhancement: Encourage beneficial soil microorganisms through practices like reduced tillage and organic matter addition.
By focusing on these long-term strategies, we can build resilient agricultural systems that are better equipped to handle water stress and maintain productivity.
Optimizing Soil Structure for Water Retention
The structure of your soil plays a critical role in its ability to retain water. Here are some techniques to optimize soil structure:
- Avoid Compaction: Limit heavy machinery use when soil is wet and use controlled traffic farming where possible.
- Promote Aggregation: Encourage the formation of soil aggregates through organic matter addition and minimal tillage.
- Enhance Porosity: Create a balance of macro and micropores through proper soil management practices.
- Maintain Soil Cover: Use cover crops or residue management to protect soil structure from the impact of rain and wind.
By focusing on these aspects of soil structure, we can significantly improve our soil’s ability to absorb and retain water, leading to more resilient and productive agricultural systems.
Leveraging Technology for Soil and Water Management
In today’s digital age, technology plays a crucial role in optimizing soil and water management. Here’s how farmers can leverage modern tools:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Utilize services like Farmonaut for real-time insights into crop health and soil moisture levels.
- Precision Agriculture Tools: Implement variable-rate irrigation and fertilization based on field-specific data.
- Weather Forecasting: Use advanced weather prediction models to plan irrigation and other farm activities.
- Soil Sensors: Deploy in-field sensors to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels in real-time.
By integrating these technological solutions, farmers can make more informed decisions, leading to improved water use efficiency and crop yields.
Comparison of Soil Water Retention Techniques
| Technique | Water Retention Improvement (%) | Crop Yield Increase (%) | Implementation Cost | Time to See Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cover Cropping | 15-25 | 10-20 | Low | Medium-term |
| No-Till Farming | 20-30 | 5-15 | Medium | Long-term |
| Organic Matter Addition | 25-35 | 15-25 | Medium | Medium-term |
| Crop Rotation | 10-20 | 10-30 | Low | Long-term |
| Drought-Resistant Varieties | 5-15 | 10-20 | Medium | Short-term |
This table provides a quick comparison of various soil water retention techniques, helping farmers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and resources.
Implementing Drought-Resistant Farming Methods
As climate variability increases, implementing drought-resistant farming methods becomes crucial. Here are some effective strategies:
- Drought-Tolerant Crop Selection: Choose crop varieties bred for water efficiency and drought resistance.
- Water-Efficient Irrigation Systems: Implement drip irrigation or other precision watering methods to minimize water waste.
- Mulching: Use organic or synthetic mulches to reduce soil evaporation and maintain consistent soil moisture.
- Windbreaks: Establish tree or shrub windbreaks to reduce wind speed and evaporation rates in fields.
By adopting these methods, farmers can significantly improve their crop’s resilience to dry conditions and maintain productivity even in challenging weather scenarios.
The Role of Data in Modern Agriculture
In today’s farming landscape, data-driven decision-making is becoming increasingly important. Here’s how data can enhance soil and water management:
- Soil Mapping: Create detailed soil maps to understand variability across fields and optimize management practices.
- Yield Data Analysis: Use historical yield data to identify areas needing improvement in water management.
- Weather Data Integration: Combine local weather data with soil moisture information for precise irrigation scheduling.
- Remote Sensing: Utilize satellite or drone imagery to monitor crop health and soil moisture status across large areas.
By leveraging these data sources, farmers can make more informed decisions about water management, leading to improved resource efficiency and crop yields.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Path Forward
As we’ve explored throughout this article, sustainable soil water retention techniques are crucial for maximizing crop yields in Ontario’s changing climate. By understanding the intricate relationship between soil health, water retention, and crop productivity, farmers can implement strategies that not only improve yields but also contribute to long-term environmental sustainability.
From optimizing soil structure and increasing organic matter content to leveraging cutting-edge technology and data-driven insights, there are numerous ways to enhance water retention and crop resilience. By adopting these practices, Ontario farmers can ensure their operations remain productive and sustainable in the face of increasing climate variability.
Remember, improving soil health and water retention is an ongoing process. It requires patience, consistent effort, and a willingness to adapt to new information and technologies. But the rewards – in terms of improved crop yields, reduced input costs, and enhanced environmental stewardship – are well worth the investment.
As we move forward, let’s continue to share knowledge, embrace innovation, and work together towards a more resilient and sustainable agricultural future for Ontario and beyond.
FAQs
- Q: How long does it take to see improvements in soil water retention?
A: The timeline for improvements can vary, but generally, you can start seeing results within 1-3 years of implementing sustainable practices. Significant improvements may take 5-10 years or more. - Q: Can I improve water retention in sandy soils?
A: Yes, sandy soils can be improved by adding organic matter, using cover crops, and implementing practices that increase soil aggregation. - Q: How does climate change impact soil water retention in Ontario?
A: Climate change can lead to more extreme weather events, including prolonged dry spells and intense rainfall. This makes effective soil water retention even more critical for maintaining crop yields. - Q: Are there government programs supporting soil health initiatives in Ontario?
A: Yes, Ontario offers various programs and incentives for farmers implementing soil health and water conservation practices. Check with the Ontario Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs for current offerings. - Q: How can I measure the effectiveness of my soil water retention efforts?
A: You can use soil moisture sensors, conduct regular soil tests, monitor crop health and yields, and utilize satellite-based monitoring services like Farmonaut to track improvements over time.
For more information on how technology can support your soil and water management efforts, explore Farmonaut’s services:
















