EU Deforestation Regulation: How GIS and Remote Sensing Revolutionize Sustainable Agricultural Supply Chains
“The EU Deforestation Regulation, effective 2025, targets 6 key crops including cocoa, coffee, and palm oil to ensure deforestation-free production.”
In the ever-evolving landscape of global agriculture and environmental conservation, the European Union (EU) has taken a groundbreaking step with the introduction of the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). As we at Farmonaut closely monitor these developments, we recognize the profound impact this regulation will have on sustainable agricultural supply chains worldwide. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into how Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies are at the forefront of this revolution, reshaping the way we approach forest conservation and agricultural sustainability.
Understanding the EU Deforestation Regulation
The EUDR, set to take effect in 2025, marks a pivotal shift in how we approach the production and trade of key agricultural commodities. Its primary aim is to ensure that products entering the EU market are not linked to deforestation or forest degradation. This regulation specifically targets six crucial commodities:
- Cocoa
- Coffee
- Palm oil
- Soy
- Beef
- Wood
By focusing on these products, the EU is addressing some of the most significant drivers of global deforestation. The regulation’s impact extends far beyond Europe’s borders, influencing agricultural practices, supply chain management, and environmental policies worldwide.
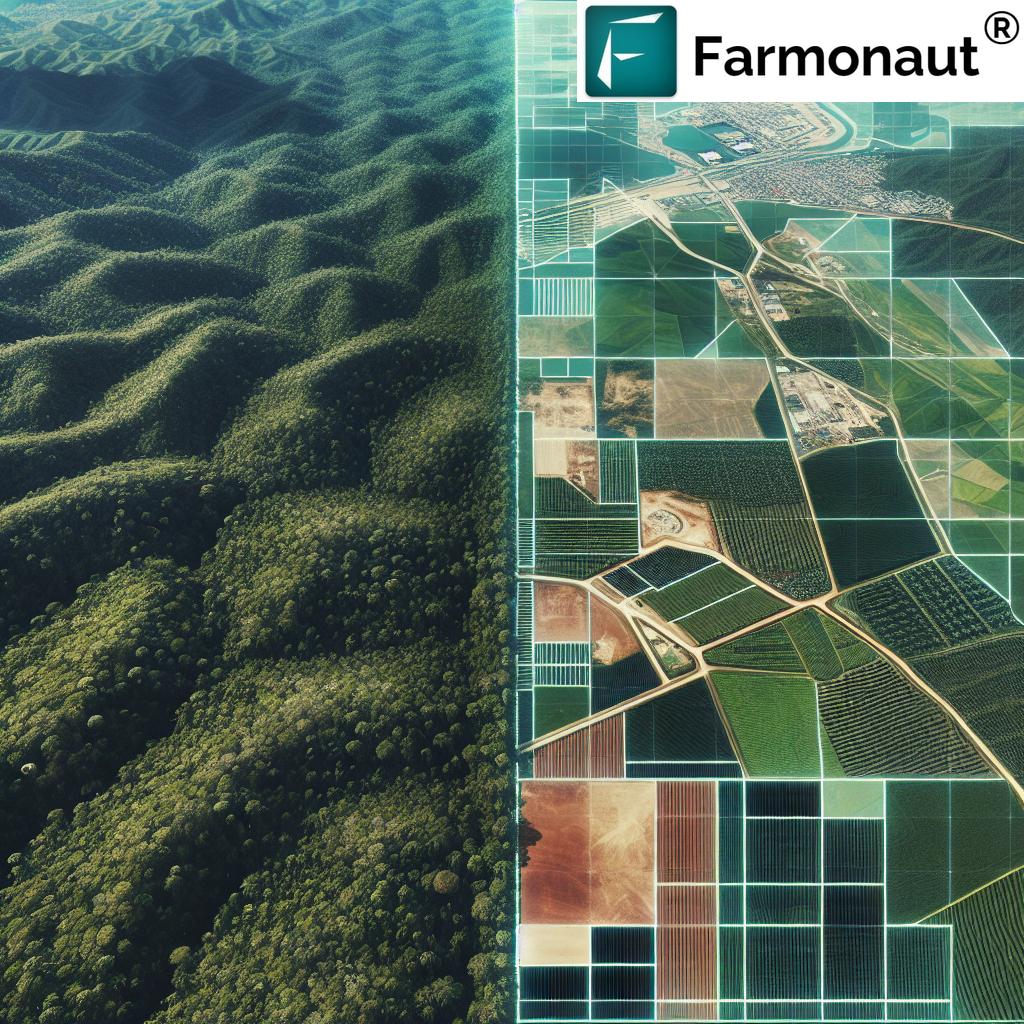
The Role of GIS and Remote Sensing in Forest Monitoring
At the heart of implementing and enforcing the EUDR are cutting-edge technologies like GIS and remote sensing. These tools are revolutionizing our ability to monitor forests and agricultural activities on a global scale. Here’s how:
- Precise Canopy Assessments: Remote sensing technologies allow for accurate and real-time monitoring of forest canopies. This is crucial for detecting early signs of deforestation or degradation.
- Large-Scale Monitoring: GIS enables the analysis of vast areas of land, making it possible to track changes in forest cover across entire regions or countries.
- Data Integration: These technologies can integrate various data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and ground-based observations, providing a comprehensive view of forest health and agricultural activities.
At Farmonaut, we leverage these technologies to provide farmers and agricultural businesses with valuable insights into their land use and crop health. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system uses multispectral imagery to assess vegetation health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This data is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices while minimizing environmental impact.
Tropical Farming and Its Impact on Forests
Tropical farming plays a significant role in the global agricultural landscape, but it also poses unique challenges to forest conservation. Many of the commodities targeted by the EUDR, such as cocoa, coffee, and palm oil, are primarily grown in tropical regions. The expansion of these crops has historically been a major driver of deforestation.
However, with the advent of GIS and remote sensing technologies, we now have the tools to balance agricultural productivity with forest conservation:
- Precision Agriculture: By using satellite data, farmers can optimize their land use, reducing the need for expansion into forested areas.
- Yield Prediction: Advanced algorithms can predict crop yields, helping farmers and policymakers make informed decisions about land use and resource allocation.
- Sustainable Intensification: These technologies support strategies for increasing agricultural output on existing farmland, reducing pressure on forests.
Our Jeevn AI Advisory System at Farmonaut is designed to support such sustainable farming practices. By providing real-time insights and personalized recommendations, we help farmers maximize their productivity while minimizing their environmental footprint.
Innovative Approaches to Pest Management and Irrigation
Sustainable agricultural supply chains require innovative approaches to common farming challenges. GIS and remote sensing are transforming pest management and irrigation practices:
- Early Pest Detection: Satellite imagery can detect changes in crop health that may indicate pest infestations, allowing for early and targeted interventions.
- Precision Irrigation: By analyzing soil moisture data from satellites, farmers can implement precise irrigation strategies, conserving water and reducing runoff.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: These technologies help farmers adapt to changing climate conditions, ensuring resilience in agricultural practices.
Through our platform, we provide farmers with access to this critical data, enabling them to make informed decisions about pest control and water management. This not only improves crop yields but also contributes to more sustainable farming practices.
“Forest 500 initiative ranks 500 companies based on their forest conservation efforts, influencing global agricultural and textile practices.”
The EUDR and Human Rights: Protecting Indigenous Communities
An often-overlooked aspect of the EUDR is its focus on human rights, particularly concerning Indigenous communities affected by deforestation. The regulation recognizes the intrinsic link between forest conservation and the rights of Indigenous peoples who have been stewards of these lands for generations.
GIS and remote sensing play a crucial role in this aspect as well:
- Land Rights Mapping: These technologies can help map and document Indigenous territories, supporting land rights claims.
- Monitoring Encroachment: Satellite imagery can detect illegal encroachment on Indigenous lands, aiding in protection efforts.
- Sustainable Resource Management: GIS tools can support Indigenous communities in managing their resources sustainably, balancing conservation with economic needs.
At Farmonaut, we believe in the importance of inclusive agricultural development. Our technologies are designed to be accessible and beneficial to all farmers, including Indigenous communities, supporting sustainable practices that respect both the environment and human rights.

The Forest 500: Ranking Companies on Forest Conservation Efforts
The Forest 500 initiative is a critical tool in the global effort to combat deforestation. This project ranks the most influential companies and financial institutions based on their policies and actions related to forest conservation. Here’s a table showcasing some top companies and their efforts:
| Company Name | Industry Sector | Forest 500 Ranking Score (out of 100) | Key Deforestation Mitigation Strategies | GIS/Remote Sensing Technologies Employed | Estimated Progress Towards EUDR Compliance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nestlé | Food | 85 | Sustainable sourcing, reforestation programs | Satellite monitoring, AI-driven risk assessment | 80% |
| Unilever | Consumer Goods | 82 | Zero deforestation commitment, supplier engagement | Blockchain traceability, satellite imagery | 75% |
| L’Oréal | Cosmetics | 80 | Sustainable palm oil sourcing, biodiversity protection | GIS mapping, remote sensing for supply chain monitoring | 70% |
| Mars | Food | 78 | Cocoa for Generations program, supplier verification | Satellite-based deforestation alerts, GIS analysis | 72% |
| IKEA | Retail | 75 | Responsible wood sourcing, forest positive agenda | Lidar technology, satellite monitoring | 68% |
| H&M Group | Textiles | 73 | Sustainable material sourcing, circular fashion initiatives | GIS for supply chain mapping, remote sensing for fiber production | 65% |
| Cargill | Agriculture | 70 | Soy Moratorium, sustainable palm oil commitment | Satellite-based land use monitoring, AI for risk assessment | 62% |
| Procter & Gamble | Consumer Goods | 68 | No deforestation policy, responsible palm oil sourcing | Satellite imagery analysis, GIS for supply chain tracking | 60% |
| Mondelez International | Food | 65 | Cocoa Life program, forest protection initiatives | Remote sensing for cocoa farm mapping, GIS for risk assessment | 58% |
| Adidas | Textiles | 63 | Sustainable material sourcing, supply chain transparency | GIS for supplier mapping, satellite monitoring of raw material sources | 55% |
This ranking system serves as a powerful tool for accountability and transparency in the fight against deforestation. It highlights the efforts of leading companies across various sectors and demonstrates the growing importance of sustainable practices in global supply chains.
Reshaping Global Agricultural Practices
The EUDR, coupled with advancements in GIS and remote sensing, is fundamentally reshaping global agricultural practices. This transformation extends from food production to textiles, affecting every stage of the supply chain:
- Traceability: GIS and blockchain technologies are enabling unprecedented levels of traceability in agricultural supply chains. At Farmonaut, our blockchain-based traceability solutions help ensure that every step of a product’s journey, from farm to consumer, is transparent and verifiable.
- Sustainable Intensification: Remote sensing data helps farmers optimize their existing farmland, reducing the need for expansion into forested areas.
- Precision Agriculture: GIS-based tools allow for precise application of fertilizers and pesticides, minimizing environmental impact while maximizing yields.
- Supply Chain Redesign: Companies are reevaluating their supply chains to ensure compliance with EUDR, often leading to more localized and sustainable sourcing practices.
The Role of Technology in Compliance and Verification
Compliance with the EUDR requires robust systems for monitoring and verification. This is where cutting-edge technologies come into play:
- Satellite Monitoring: High-resolution satellite imagery provides real-time data on land use changes, allowing for quick detection of deforestation activities.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict areas at risk of deforestation.
- Blockchain: Ensures the integrity of supply chain data, making it tamper-proof and transparent.
- Mobile Applications: Enable on-the-ground reporting and verification, complementing satellite data.
Our platform at Farmonaut integrates many of these technologies. For instance, our satellite-based crop health monitoring system provides farmers with real-time insights into their fields, helping them make sustainable decisions. Additionally, our blockchain-based traceability solutions offer a secure and transparent way to track agricultural products from farm to consumer.
Explore our solutions:
Challenges and Opportunities
While the EUDR presents significant opportunities for sustainable agriculture, it also poses challenges:
- Implementation Costs: Adopting new technologies and practices can be costly, especially for smaller farmers and businesses.
- Data Accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of GIS and remote sensing data is crucial for effective implementation.
- Capacity Building: There’s a need for widespread training and education on using these new technologies effectively.
- Global Cooperation: Successful implementation requires cooperation between governments, businesses, and NGOs across different regions.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to making our technologies accessible and user-friendly, helping to bridge the gap between advanced technology and practical application in agriculture.
The Future of Sustainable Agricultural Supply Chains
As we look to the future, it’s clear that the integration of GIS and remote sensing technologies in agriculture will continue to grow. We anticipate several key trends:
- Increased Automation: AI and machine learning will play a larger role in analyzing data and providing actionable insights.
- Enhanced Integration: Greater integration between different technologies and data sources will provide more comprehensive and accurate monitoring.
- Democratization of Technology: As technologies become more accessible, smaller farmers and businesses will be better equipped to implement sustainable practices.
- Policy Alignment: We expect to see more global policies aligning with the principles of the EUDR, creating a more unified approach to combating deforestation.
At Farmonaut, we’re constantly innovating to stay at the forefront of these trends. Our goal is to provide farmers and businesses with the tools they need to thrive in this new era of sustainable agriculture.
Conclusion
The EU Deforestation Regulation represents a significant step forward in the global fight against deforestation and unsustainable agricultural practices. By leveraging the power of GIS and remote sensing technologies, we have the opportunity to create truly sustainable agricultural supply chains.
As we’ve explored in this article, these technologies offer unprecedented capabilities in monitoring, traceability, and sustainable farm management. From precise canopy assessments to innovative pest management strategies, the applications are vast and impactful.
At Farmonaut, we’re proud to be part of this revolution in sustainable agriculture. Our suite of tools and services, from satellite-based crop monitoring to blockchain traceability solutions, are designed to help farmers and businesses navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by the EUDR and similar regulations.
As we move forward, the key to success will be collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to balancing agricultural productivity with environmental conservation. By embracing these technologies and principles, we can create a future where agriculture thrives without compromising our forests and ecosystems.
FAQs
- What is the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR)?
The EUDR is a regulation set to take effect in 2025, aiming to ensure that products entering the EU market are not linked to deforestation or forest degradation. It targets key commodities like cocoa, coffee, palm oil, soy, beef, and wood. - How do GIS and remote sensing help in implementing the EUDR?
GIS and remote sensing technologies enable precise monitoring of forest cover, detection of deforestation activities, and tracking of agricultural practices. They provide real-time data and insights crucial for compliance with the EUDR. - What is Farmonaut’s role in sustainable agriculture?
Farmonaut provides advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions that help farmers and businesses optimize their agricultural practices while minimizing environmental impact. Our tools include crop health monitoring, AI-based advisory systems, and blockchain-based traceability solutions. - How does the Forest 500 initiative relate to the EUDR?
The Forest 500 ranks influential companies and financial institutions based on their forest conservation efforts. This ranking system aligns with the goals of the EUDR by promoting transparency and accountability in deforestation-free supply chains. - Can small-scale farmers benefit from these technologies?
Yes, Farmonaut is committed to making precision agriculture technologies accessible to farmers of all scales. Our platform offers affordable solutions that can help small-scale farmers improve productivity and sustainability.
For more information on our API and developer resources, visit:
Farmonaut Subscriptions






