Elkhorn Slough Environmental Crisis: Battery Fire Releases Toxic Heavy Metals into Fragile Ecosystem
“Scientists detected significant concentrations of nickel, manganese, and cobalt in marsh soils following a battery fire near Elkhorn Slough.”
In recent weeks, the serene beauty of Elkhorn Slough, a treasured estuary in Monterey County, California, has been overshadowed by an environmental crisis of alarming proportions. A devastating fire at a nearby battery storage facility has unleashed a torrent of toxic heavy metals into this fragile ecosystem, raising serious concerns about the long-term impacts on local wildlife, plant life, and human health. As we delve into this urgent matter, we’ll explore the intricate web of consequences stemming from this incident and discuss the critical importance of balancing our energy needs with environmental preservation.
The Incident: A Battery Fire with Far-Reaching Consequences
On January 16, a significant fire erupted at the Vistra Plant, a battery storage facility in Moss Landing. This incident, which might have seemed isolated at first, has since unfolded into a complex environmental crisis. The fire, fueled by lithium-ion batteries, released a plume of toxic smoke containing nanoparticles of heavy metals – primarily nickel, manganese, and cobalt – into the surrounding area.
These elements, crucial components in the cathode materials of lithium-ion batteries, have now found their way into the delicate ecosystem of Elkhorn Slough. The impact of this contamination extends far beyond the immediate vicinity of the fire, with significant concentrations detected within a two-mile radius of the facility.
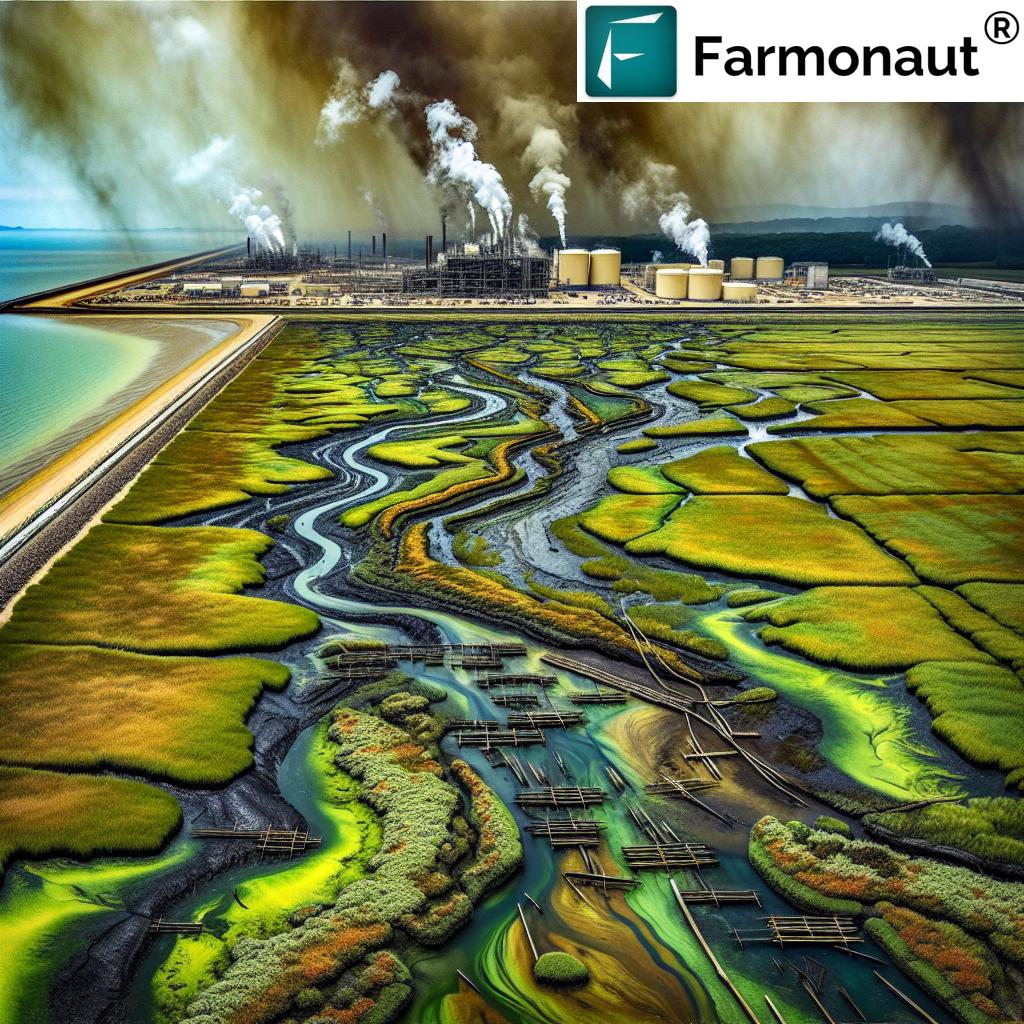

Scientific Findings: Alarming Levels of Heavy Metal Contamination
The gravity of the situation came to light through the diligent work of scientists at San José State University’s Moss Landing Marine Laboratories. As part of an ongoing monitoring program focused on the Elkhorn Slough estuary, research teams conducted thorough analyses of soil composition in the aftermath of the fire. The findings were nothing short of shocking.
Professor Ivano Aiello, a marine geology expert overseeing the research, reported that the levels of nickel, manganese, and cobalt in marsh soils were hundreds to thousands of times higher than typical background levels. This dramatic increase in heavy metal concentrations poses a significant threat to the delicate balance of the estuarine ecosystem.
| Heavy Metal | Detected Concentration (estimated) | Safe Threshold | Potential Ecological Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel | 500-1000 ppm | 50 ppm | Plant toxicity, disruption of aquatic food chains |
| Manganese | 1000-2000 ppm | 500 ppm | Impaired plant growth, neurological effects on wildlife |
| Cobalt | 200-400 ppm | 20 ppm | Reduced soil fertility, potential bioaccumulation in food web |
Environmental Impact: A Threat to Biodiversity
The introduction of these heavy metals into the Elkhorn Slough ecosystem presents a multi-faceted threat to local biodiversity. As these contaminants interact with the environment, they have the potential to transform chemically, exacerbating their impact on both aquatic and terrestrial life forms.
- Aquatic Life: Fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants may absorb these metals, leading to bioaccumulation up the food chain.
- Terrestrial Animals: Birds and mammals that rely on the slough for food and habitat are at risk of secondary contamination.
- Soil Health: The high concentrations of heavy metals can alter soil chemistry, affecting plant growth and microbial communities essential for nutrient cycling.
The long-term effects of this contamination on the fragile ecosystem of Elkhorn Slough are still unfolding. Researchers are particularly concerned about the potential for these nanoparticles to disrupt critical ecological processes and food webs.
Public Health Concerns: A Community on Alert
The environmental crisis at Elkhorn Slough is not just an ecological issue; it’s a matter of public health. Local authorities and health professionals have expressed deep concern about the potential impacts on human well-being. Monterey County Supervisor Glenn Church has urged residents to remain vigilant about their health, advising anyone experiencing unusual symptoms to consult their healthcare provider immediately.
The presence of heavy metals in the environment can lead to various health issues, including:
- Respiratory problems from inhaling contaminated dust particles
- Skin irritations from direct contact with contaminated soil or water
- Potential long-term health effects from consuming contaminated fish or produce
As the situation unfolds, public health officials are working to establish comprehensive monitoring programs to track potential exposure pathways and mitigate risks to the community.
“The battery fire incident highlights risks of energy storage facilities, impacting both aquatic and terrestrial food webs in fragile ecosystems.”
Regulatory Response and Future Implications
The Elkhorn Slough environmental crisis has prompted a swift response from regulatory bodies and local government officials. State Assemblywoman Dawn Addis has called for independent investigations by the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) to ensure a thorough examination of all environmental impacts.
This incident raises critical questions about the safety and management of battery storage facilities, particularly in environmentally sensitive areas. As we transition towards renewable energy solutions to combat climate change, the need for robust safety protocols and careful planning of energy infrastructure becomes increasingly apparent.
Key areas of focus for future regulations and safety measures include:
- Stricter guidelines for the location of battery storage facilities
- Enhanced fire safety and containment measures
- Regular environmental impact assessments and monitoring
- Improved emergency response protocols for hazardous material incidents
The Role of Technology in Environmental Monitoring
In the wake of this crisis, the importance of advanced environmental monitoring technologies has come to the forefront. Companies like Farmonaut are at the cutting edge of this field, offering sophisticated tools for environmental assessment and management.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring systems provide valuable insights into soil health, vegetation patterns, and environmental changes. While not directly involved in the Elkhorn Slough situation, the technologies offered by Farmonaut demonstrate the potential for remote sensing and data analytics in environmental crisis management.
Key applications of such technologies in environmental monitoring include:
- Real-time tracking of soil composition changes
- Detection of vegetation stress indicators
- Mapping of contamination spread in ecosystems
- Support for precision agriculture practices to minimize environmental impact
For those interested in exploring these technologies, Farmonaut offers various access points:
For developers looking to integrate environmental monitoring capabilities into their own applications, Farmonaut also provides an API with comprehensive documentation.
Community Engagement and Citizen Science
The Elkhorn Slough environmental crisis has highlighted the importance of community engagement in environmental monitoring and protection. Local residents, environmental groups, and citizen scientists play a crucial role in early detection and ongoing assessment of environmental issues.
Initiatives that empower communities to participate in environmental monitoring can include:
- Citizen science programs for water and soil quality testing
- Community-led biodiversity surveys
- Educational workshops on local ecology and environmental health
- Collaborative platforms for sharing observations and data
By fostering a sense of environmental stewardship within the community, we can create a more robust and responsive system for protecting fragile ecosystems like Elkhorn Slough.
The Balancing Act: Energy Needs and Environmental Protection
The Elkhorn Slough incident brings into sharp focus the delicate balance between meeting our growing energy needs and protecting sensitive environments. As we transition towards renewable energy sources and advanced energy storage solutions, it’s crucial to consider the potential environmental impacts of these technologies.
Key considerations for sustainable energy infrastructure development include:
- Comprehensive environmental impact assessments before facility siting
- Integration of ecological considerations into energy policy and planning
- Investment in research for safer and more environmentally friendly battery technologies
- Development of recycling and safe disposal methods for battery components
By adopting a holistic approach that considers both energy security and environmental protection, we can work towards a more sustainable future.
Looking Ahead: Long-term Monitoring and Ecosystem Recovery
As the immediate crisis response transitions into long-term management, the focus shifts to ongoing monitoring and ecosystem recovery efforts. The scientific community, led by institutions like the Moss Landing Marine Laboratories, will play a crucial role in tracking the long-term effects of heavy metal contamination and guiding restoration efforts.
Key aspects of long-term monitoring and recovery include:
- Regular soil and water quality testing
- Biodiversity assessments to track impacts on flora and fauna
- Studies on bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the food web
- Development and implementation of remediation strategies
Technologies like those offered by Farmonaut can provide valuable support in these efforts, offering satellite-based monitoring capabilities that can track changes in vegetation health and soil composition over time.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The environmental crisis at Elkhorn Slough serves as a stark reminder of the fragility of our ecosystems and the far-reaching consequences of industrial accidents. As we navigate the complex challenges of the 21st century, balancing our energy needs with environmental protection becomes increasingly crucial.
This incident calls for:
- Increased vigilance in the management and regulation of energy storage facilities
- Greater investment in research and development of safer battery technologies
- Enhanced environmental monitoring and rapid response capabilities
- Stronger community engagement in environmental protection efforts
By learning from this crisis and taking proactive steps to prevent future incidents, we can work towards a more sustainable and environmentally responsible energy future. The health of ecosystems like Elkhorn Slough depends on our collective commitment to balancing progress with preservation.
FAQ Section
Q: What are the main heavy metals released in the Elkhorn Slough incident?
A: The primary heavy metals detected in significant concentrations are nickel, manganese, and cobalt.
Q: How do these heavy metals affect the ecosystem?
A: These metals can disrupt food webs, impair plant growth, and potentially cause long-term damage to both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Q: What are the potential health risks for local residents?
A: Potential risks include respiratory issues from contaminated dust, skin irritations from contact with polluted soil or water, and long-term health effects from consuming contaminated fish or produce.
Q: How long will it take for the ecosystem to recover?
A: The recovery timeline is uncertain and depends on various factors. Long-term monitoring and remediation efforts will be crucial in assessing and supporting ecosystem recovery.
Q: What steps are being taken to prevent similar incidents in the future?
A: Regulatory bodies are calling for stricter guidelines on battery storage facility locations, enhanced safety measures, and more comprehensive environmental impact assessments.
Earn With Farmonaut
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Farmonaut Subscriptions







