Controlling Grape Gall Mites: Protecting Your Vines from Eriophyes vitis Infestation
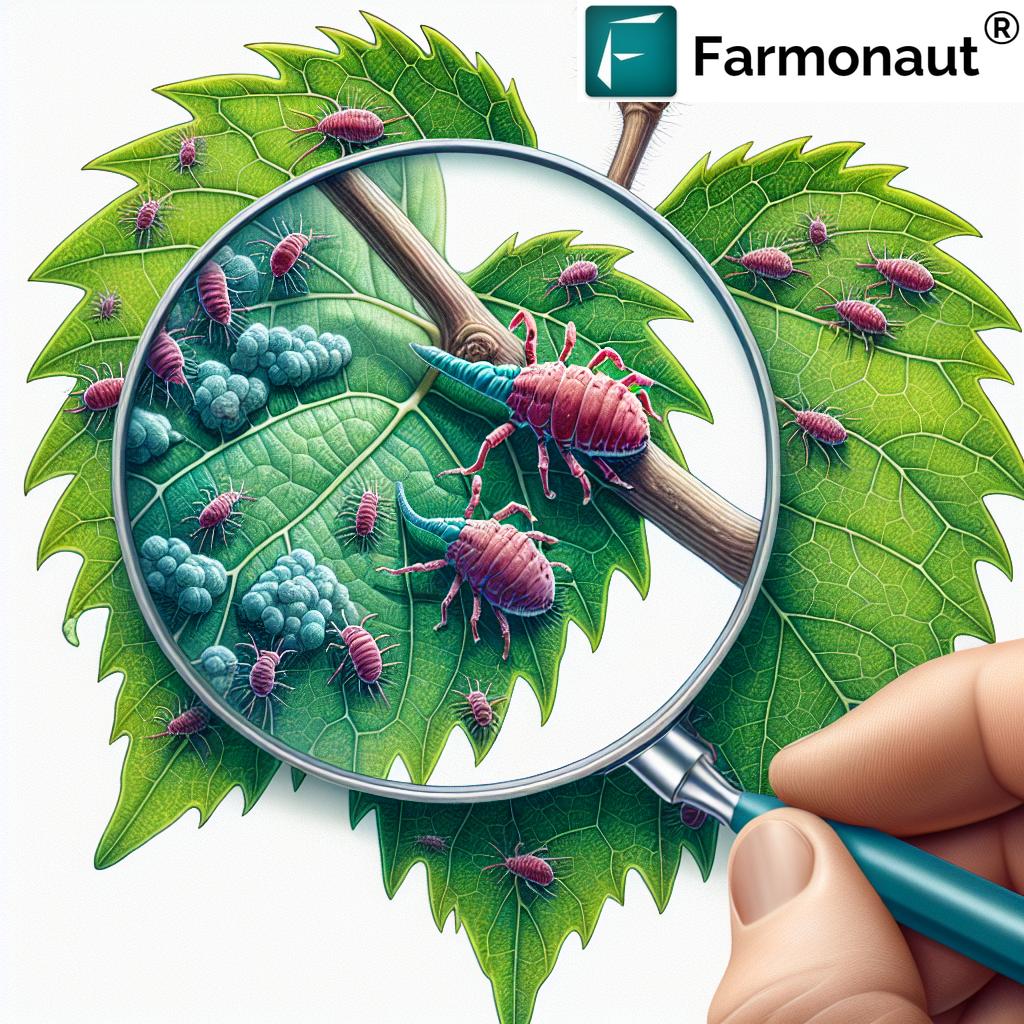

As vineyard owners and managers, we understand the importance of maintaining healthy grapevines for optimal yield and quality. One of the most persistent threats to our precious grapes is the grape gall mite, scientifically known as Eriophyes vitis. These microscopic pests can cause significant damage to our vines if left unchecked. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of grape gall mites, their impact on vineyards, and the most effective control measures to protect our crops.
Understanding Grape Gall Mites (Eriophyes vitis)
Eriophyes vitis, commonly known as grape erineum mite or grape leaf blister mite, is a species of eriophyid mite that specifically targets grapevines. These mites are incredibly small, measuring only about 0.2 mm in length, making them invisible to the naked eye. Despite their tiny size, they can cause significant damage to grape plants, affecting both the appearance and health of the vines.
Life Cycle and Behavior
To effectively control grape gall mites, it’s crucial to understand their life cycle and behavior:
- Winter Survival: During winter, adult female mites seek shelter in the bark crevices and under bud scales of grapevines.
- Spring Emergence: As temperatures rise in spring, mites emerge from their overwintering sites and begin to feed on new growth.
- Reproduction: Females lay eggs within the galls they create on leaves, stems, and buds.
- Development: Eggs hatch into larvae, which then develop into nymphs and finally adults.
- Multiple Generations: Grape gall mites can produce several generations per year, with populations peaking in mid-summer.
Identifying Grape Gall Mite Infestation
Recognizing the signs of a grape gall mite infestation is crucial for early intervention. Here are the key symptoms to look out for:
- Galls on Leaves: The most distinctive sign is the formation of galls on the undersides of grape leaves. These galls appear as raised, blister-like growths filled with mites.
- Leaf Discoloration: Affected leaves may show yellow or reddish-brown patches on the upper surface, corresponding to the galls beneath.
- Stunted Growth: Severe infestations can lead to stunted vegetative growth and reduced fruit production.
- Bud Damage: Mites can also attack buds, causing them to swell or fail to develop properly.
- Stem Distortion: In some cases, mites may cause stems to become twisted or deformed.
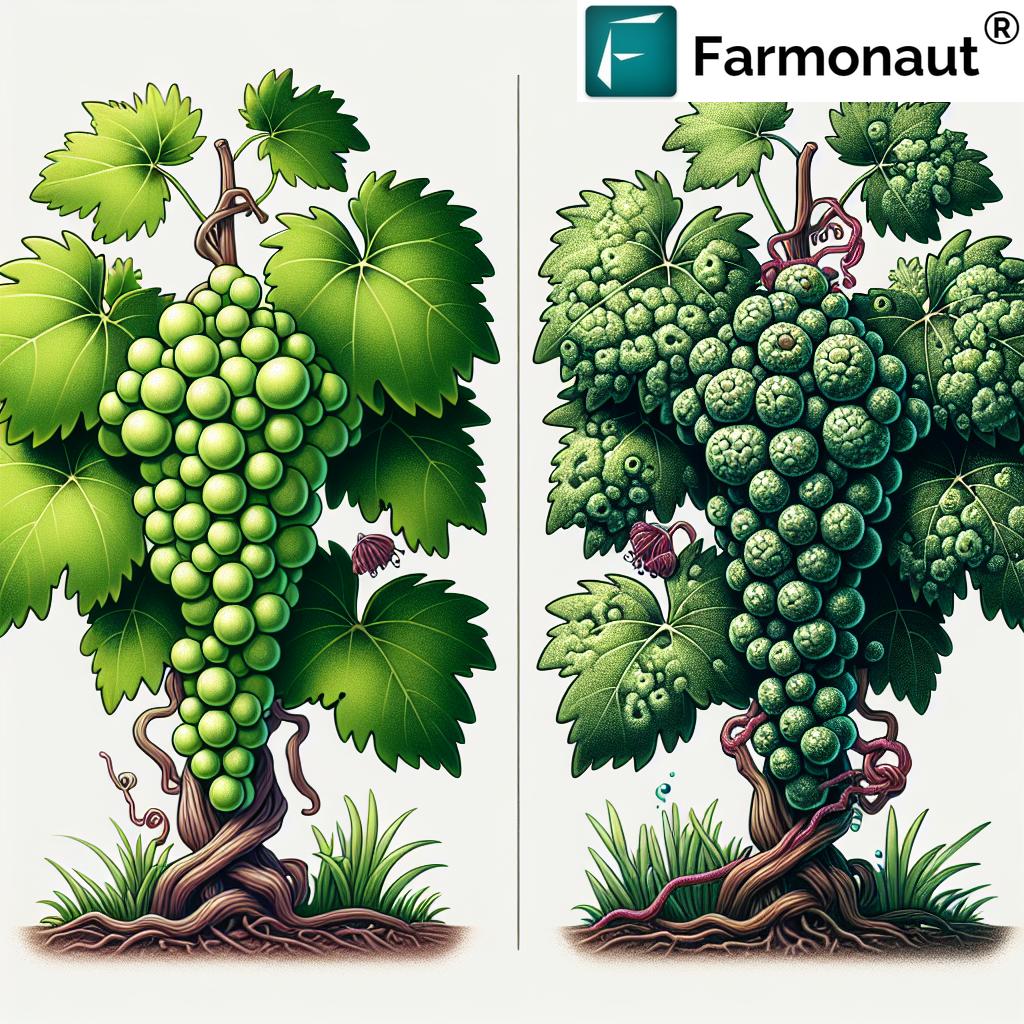
The Impact of Grape Gall Mites on Vineyards
While a minor infestation of grape gall mites may not significantly impact overall vine health, severe infestations can have serious consequences for vineyard productivity and grape quality:
- Reduced Photosynthesis: Damaged leaves are less efficient at photosynthesis, potentially affecting overall plant health and fruit development.
- Yield Reduction: Severe infestations can lead to reduced grape yields as the plant’s resources are diverted to combat the pest.
- Quality Issues: Mite damage can affect fruit quality, potentially impacting flavor profiles and wine production.
- Increased Susceptibility: Damaged vines may become more susceptible to other pests and diseases.
- Economic Losses: The combination of reduced yield and quality can result in significant economic losses for vineyard owners.
Effective Control Strategies for Grape Gall Mites
Controlling grape gall mites requires a multi-faceted approach that combines cultural practices, biological control, and chemical interventions when necessary. Here are some effective strategies we recommend:
1. Cultural Control Methods
- Pruning and Sanitation: Regular pruning and removal of infested plant material can help reduce mite populations.
- Proper Vine Management: Maintaining overall vine health through proper irrigation, fertilization, and canopy management can make plants more resistant to mite infestations.
- Weed Control: Keep the vineyard free of weeds that may serve as alternative hosts for mites.
2. Biological Control
Encouraging natural predators of grape gall mites can help keep populations in check:
- Predatory Mites: Species like Typhlodromus pyri and Amblyseius andersoni feed on eriophyid mites.
- Lacewings and Ladybugs: These beneficial insects can help control mite populations.
- Cover Crops: Planting cover crops between vine rows can provide habitat for beneficial insects.
3. Chemical Control
When cultural and biological methods are insufficient, chemical control may be necessary:
- Sulfur Applications: Sulfur-based products are effective against grape gall mites and are often used in organic vineyards.
- Horticultural Oils: Dormant oil sprays applied during the winter can smother overwintering mites.
- Miticides: In severe cases, specific miticides may be required. Always consult with a professional and follow label instructions.
4. Timing of Control Measures
The timing of control measures is crucial for effective management:
- Early Spring: Apply treatments as buds begin to swell to target emerging mites.
- Post-Harvest: Late-season treatments can help reduce overwintering populations.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuous monitoring throughout the growing season allows for timely interventions.
Leveraging Technology for Grape Gall Mite Management
At Farmonaut, we understand the challenges vineyard managers face in detecting and controlling grape gall mites across large areas. Our satellite-based monitoring system offers a revolutionary approach to vineyard management, including early detection of potential mite infestations.
Comparison of Gall Mite Detection Methods
| Method | Accuracy | Coverage Area | Frequency of Monitoring | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Visual Inspection | Moderate (subject to human error) | Limited (time-consuming for large areas) | Variable (labor-dependent) | Low (high labor costs for large vineyards) |
| Farmonaut’s Satellite-Based Monitoring | High (uses advanced spectral analysis) | Extensive (entire vineyard at once) | Regular (as frequent as daily) | High (scalable and efficient for large areas) |
Our satellite-based system offers several advantages for vineyard managers:
- Early Detection: Identify potential mite infestations before visible symptoms appear.
- Large-Scale Monitoring: Efficiently monitor vast vineyard areas without the need for extensive manual inspections.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Use real-time data to make informed decisions about treatment timing and areas of focus.
- Integration with Management Systems: Our API allows for seamless integration with existing vineyard management software.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can revolutionize your vineyard management, visit our application page or explore our API documentation.
Best Practices for Long-Term Grape Gall Mite Management
To ensure the long-term health of your vineyard and minimize the impact of grape gall mites, consider implementing these best practices:
- Regular Monitoring: Establish a routine for inspecting vines, focusing on new growth and undersides of leaves.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of mite populations, treatments applied, and their effectiveness.
- Resistance Management: Rotate control methods and products to prevent mites from developing resistance.
- Staff Training: Educate vineyard workers on identifying mite symptoms and proper reporting procedures.
- Quarantine Measures: Implement strict quarantine procedures for new plant material entering the vineyard.
- Collaborative Approach: Work with neighboring vineyards to implement area-wide management strategies.
The Role of Technology in Modern Vineyard Management
As we continue to face challenges like grape gall mites, technology plays an increasingly important role in vineyard management. Farmonaut’s suite of tools offers comprehensive solutions for modern viticulture:
- Satellite Imagery Analysis: Our advanced algorithms analyze multispectral satellite data to detect early signs of stress in grapevines, which may indicate mite infestations.
- AI-Powered Advisories: Receive personalized recommendations for mite control based on your vineyard’s specific conditions.
- Mobile App Integration: Access vital vineyard data on-the-go with our mobile apps available for Android and iOS.
- Weather Forecasting: Plan your mite control activities with precision using our integrated weather forecasting system.
- Data-Driven Decision Support: Leverage historical and real-time data to make informed decisions about pest management strategies.
For developers interested in integrating our powerful tools into their own systems, check out our comprehensive API documentation.
Sustainable Vineyard Management: Beyond Mite Control
While controlling grape gall mites is crucial, it’s just one aspect of sustainable vineyard management. Farmonaut’s holistic approach helps vineyard managers address multiple challenges:
- Resource Optimization: Use our satellite data to optimize irrigation and fertilizer application, reducing waste and improving vine health.
- Climate Adaptation: Stay ahead of changing climate patterns and their potential impact on pest pressures.
- Biodiversity Promotion: Implement strategies to enhance vineyard biodiversity, supporting natural pest control mechanisms.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Monitor and reduce your vineyard’s carbon footprint with our integrated tracking tools.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do grape gall mites spread between vines?
A: Grape gall mites can spread through various means, including:
- Wind dispersal
- Movement of infected plant material
- On clothing or equipment of vineyard workers
- Through grafting of infected plant material
Q: Can grape gall mites be completely eradicated from a vineyard?
A: Complete eradication is challenging due to the mites’ small size and reproductive capacity. However, with consistent management practices, populations can be kept at levels that do not significantly impact vine health or grape production.
Q: Are there any grape varieties resistant to gall mites?
A: While no grape varieties are completely immune to gall mites, some cultivars show higher tolerance. Research is ongoing to develop more resistant varieties. Consult with local agricultural extension services for recommendations suitable for your region.
Q: How often should I monitor my vineyard for grape gall mites?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial, especially during the growing season. We recommend weekly inspections during critical periods (spring growth and mid-summer) and less frequent checks during other times. Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring can provide daily updates on overall vine health, which may indicate potential mite issues.
Q: Can organic vineyards effectively control grape gall mites?
A: Yes, organic vineyards can implement effective control measures. These include:
- Use of sulfur-based products
- Encouraging natural predators
- Implementing strict cultural control practices
- Using approved organic miticides when necessary
Q: How does climate change affect grape gall mite populations?
A: Climate change can potentially lead to:
- Extended growing seasons, allowing for more mite generations per year
- Milder winters, increasing overwintering survival rates
- Changes in precipitation patterns, which may stress vines and make them more susceptible to infestations
Farmonaut’s climate monitoring tools can help vineyard managers adapt their strategies to these changing conditions.
Conclusion: Embracing Technology for Superior Vineyard Health
Managing grape gall mites and other vineyard challenges requires a combination of traditional knowledge and cutting-edge technology. By integrating Farmonaut’s advanced satellite monitoring and AI-driven insights into your vineyard management practices, you can stay ahead of potential issues, optimize resource use, and ensure the long-term health and productivity of your vines.
Ready to take your vineyard management to the next level? Explore our subscription options below and join the revolution in precision viticulture.
Together, we can build more resilient, productive, and sustainable vineyards for the future. Join us in revolutionizing grape cultivation with Farmonaut’s innovative solutions.