Organic Thrips Control: Protecting Crops from Scirtothrips dorsalis Without Chemical Insecticides
In the world of agriculture, pests pose a significant threat to crop health and yield. Among these pests, thrips, particularly the species Scirtothrips dorsalis, have become a major concern for farmers worldwide. As we at Farmonaut continue to innovate in agricultural technology, we recognize the importance of addressing pest problems with sustainable and effective solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore organic methods to control thrips and protect various crops without relying on conventional chemical insecticides.
Understanding Thrips and Their Impact on Crops
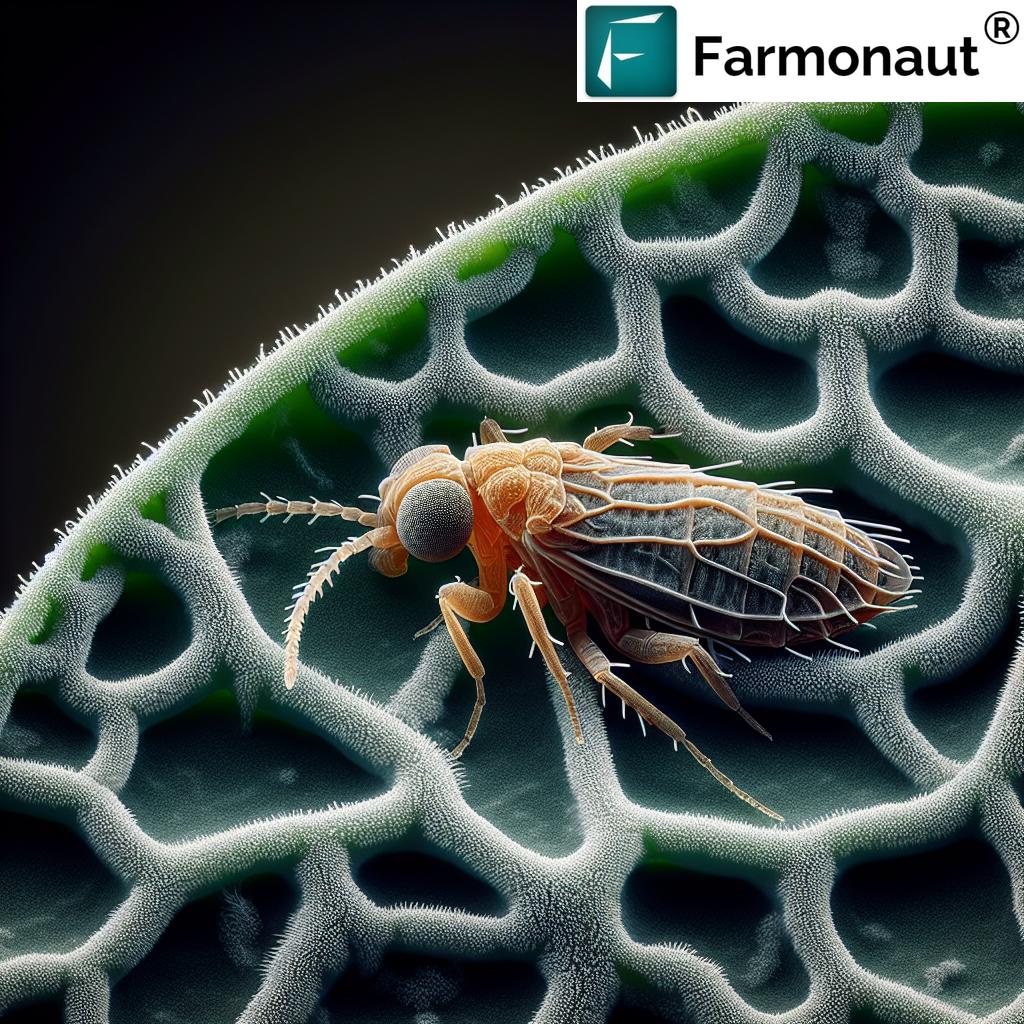
Thrips are tiny insects that can cause substantial damage to a wide range of plants and crops. Scirtothrips dorsalis, also known as the chili thrips or yellow tea thrips, is a particularly problematic species due to its broad host range and potential for rapid population growth.
Characteristics of Scirtothrips dorsalis
- Size: Extremely small, typically less than 2 mm in length
- Color: Pale yellow to brown
- Wings: Present in adults, allowing for easy dispersal
- Life cycle: Egg, two larval stages, prepupa, pupa, and adult
Host Plants and Crops Affected
Scirtothrips dorsalis is known to infest a wide variety of plants, including both crops and ornamentals. Some of the most commonly affected crops include:
- Chili peppers and other peppers
- Citrus fruits
- Blueberries
- Grapevines
- Peanuts
- Cotton
- Soybeans
- Tea
Damage Caused by Thrips
Thrips can cause significant damage to plants through their feeding activities:
- Scarring and distortion of leaves, flowers, and fruits
- Stunted growth
- Reduced yield
- Transmission of plant viruses
The Importance of Organic Pest Control
As the agricultural industry shifts towards more sustainable practices, organic pest control methods have gained increasing attention. At Farmonaut, we believe in promoting environmentally friendly farming techniques that maintain ecological balance while ensuring crop protection.
Benefits of Organic Thrips Control
- Reduced environmental impact
- Preservation of beneficial insects and natural predators
- Improved soil health
- Enhanced food safety
- Compliance with organic certification standards
Organic Treatment Methods for Thrips Control
We’ve compiled a comprehensive list of organic methods to control thrips infestations, focusing on Scirtothrips dorsalis and other common thrips species.
1. Cultural Control Methods
Cultural control methods focus on creating an environment that is less favorable for thrips proliferation:
- Crop rotation: Rotating crops can disrupt the life cycle of thrips and reduce their populations.
- Intercropping: Planting companion crops that repel thrips or attract their natural predators can help manage infestations.
- Proper irrigation: Maintaining adequate soil moisture can help plants withstand thrips damage and recover more quickly.
- Weed management: Removing weeds that may serve as alternative hosts for thrips can reduce their populations.
- Proper spacing: Ensuring adequate spacing between plants can improve air circulation and make the environment less favorable for thrips.
2. Physical Control Methods
Physical control methods involve creating barriers or using traps to prevent or reduce thrips infestations:
- Reflective mulches: Using reflective materials like silver-colored plastic mulch can disorient thrips and reduce their ability to locate host plants.
- Sticky traps: Blue or yellow sticky traps can be used to monitor and capture adult thrips.
- Fine mesh screens: Installing fine mesh screens on greenhouse vents and openings can prevent thrips from entering protected growing environments.
- Pruning and destruction of infested plant parts: Removing heavily infested plant parts can help reduce thrips populations and prevent further spread.
3. Biological Control Methods
Biological control involves using natural predators, parasitoids, or pathogens to manage thrips populations:
- Predatory mites: Species like Amblyseius swirskii and Neoseiulus cucumeris are effective predators of thrips.
- Predatory bugs: Orius insidiosus (minute pirate bug) is known to feed on thrips.
- Entomopathogenic fungi: Fungi like Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae can infect and kill thrips.
- Nematodes: Certain species of nematodes, such as Steinernema feltiae, can be effective against thrips pupae in the soil.
4. Botanical Insecticides
While not synthetic chemicals, botanical insecticides derived from plants can be effective against thrips:
- Neem oil: Derived from the neem tree, this natural insecticide can disrupt the feeding and reproduction of thrips.
- Pyrethrin: Extracted from chrysanthemum flowers, pyrethrin is effective against many insect pests, including thrips.
- Spinosad: A natural substance produced by soil bacteria, spinosad is highly effective against thrips while having minimal impact on beneficial insects.
- Garlic and chili pepper sprays: Homemade sprays using garlic and chili peppers can repel thrips and other pests.
Implementing an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approach
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach, which combines various control methods to achieve effective pest management while minimizing environmental impact. Here’s how to implement an IPM strategy for thrips control:
1. Monitoring and Scouting
Regular monitoring is crucial for early detection of thrips infestations. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system can help detect potential thrips problems at an early stage, allowing for timely intervention.
2. Establishing Thresholds
Determine the level of thrips infestation that warrants action. This threshold may vary depending on the crop, growth stage, and economic considerations.
3. Prevention
Implement preventive measures such as cultural controls and physical barriers to reduce the likelihood of thrips infestations.
4. Control
When thresholds are exceeded, apply appropriate control measures, starting with the least disruptive methods (e.g., biological controls) before moving to more intensive treatments if necessary.
5. Evaluation
Continuously assess the effectiveness of control measures and adjust strategies as needed.
Case Studies: Successful Organic Thrips Control in Various Crops
Let’s examine how organic thrips control methods have been successfully implemented in different crops:
Chili Peppers
In a study conducted on chili pepper farms in South Asia, researchers found that a combination of reflective mulch, predatory mites (Amblyseius swirskii), and neem oil applications reduced Scirtothrips dorsalis populations by 75% compared to untreated controls. The integrated approach not only controlled thrips but also improved overall plant health and yield.
Citrus
A citrus orchard in Florida implemented an IPM program focusing on conservation biological control. By reducing broad-spectrum insecticide use and creating habitats for natural predators, they observed a significant decrease in thrips populations over three growing seasons. The approach also led to an increase in beneficial insects and improved fruit quality.
Blueberries
Organic blueberry growers in the Pacific Northwest have successfully managed thrips using a combination of cultural practices and biological controls. Pruning to improve air circulation, coupled with releases of predatory mites and minute pirate bugs, has helped maintain thrips populations below economic thresholds without the use of chemical insecticides.
Grapevines
In a vineyard in California, researchers tested the efficacy of entomopathogenic fungi against thrips. Applications of Beauveria bassiana reduced thrips populations by up to 60% when combined with proper canopy management practices. The treatment also showed minimal impact on beneficial insects present in the vineyard ecosystem.
The Role of Technology in Organic Thrips Management
At Farmonaut, we believe that technology plays a crucial role in modern agriculture, including organic pest management. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system can aid in the early detection and management of thrips infestations:
Early Detection
Our advanced satellite imagery analysis can detect subtle changes in crop health that may indicate the presence of thrips or other pests before they become visible to the naked eye.
Precision Application
By identifying specific areas of infestation, our technology allows for targeted application of organic control methods, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Our AI-powered advisory system, Jeevn AI, analyzes satellite data along with other environmental factors to provide personalized recommendations for thrips management, helping farmers make informed decisions about when and how to intervene.
Monitoring Effectiveness
Continuous monitoring through our satellite system allows farmers to track the effectiveness of their thrips control measures over time, enabling them to adjust strategies as needed.
Comparison: Traditional vs. Farmonaut Satellite System for Thrips Detection
| Method | Detection Speed | Accuracy | Coverage Area | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Slow | Moderate | Limited | Low |
| Sticky Traps | Moderate | Moderate | Limited | Moderate |
| Farmonaut Satellite System | Fast | High | Extensive | High |
As demonstrated in the table above, the Farmonaut Satellite System offers significant advantages in terms of detection speed, accuracy, coverage area, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods of thrips detection.
Best Practices for Implementing Organic Thrips Control
To maximize the effectiveness of organic thrips control methods, consider the following best practices:
- Start early: Implement preventive measures before thrips populations become established.
- Diversify control methods: Use a combination of cultural, physical, and biological controls for best results.
- Maintain plant health: Healthy plants are more resistant to thrips damage. Ensure proper nutrition and irrigation.
- Encourage biodiversity: Create habitats for natural predators by planting diverse flowering plants around crop areas.
- Time applications carefully: Apply botanical insecticides during periods of low bee activity to protect pollinators.
- Monitor regularly: Use our satellite-based monitoring system to track crop health and pest populations continuously.
- Keep records: Document all control measures and their effectiveness to refine strategies over time.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest research and recommendations for organic thrips control.
Challenges and Future Directions in Organic Thrips Control
While organic methods for thrips control have shown promising results, there are still challenges to overcome and areas for future research:
Challenges
- Variability in effectiveness of biological control agents across different environments
- Limited availability of some organic control products in certain regions
- Potential for thrips to develop resistance to botanical insecticides
- Higher labor costs associated with some organic control methods
Future Directions
- Development of new, more effective biological control agents
- Improvement of application techniques for botanical insecticides
- Integration of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning for more precise pest detection and management
- Research into plant breeding for thrips resistance
- Exploration of novel organic compounds with insecticidal properties
Conclusion
Organic thrips control, particularly for managing Scirtothrips dorsalis and other thrips species, is a complex but achievable goal. By integrating cultural, physical, and biological control methods, along with judicious use of botanical insecticides, farmers can effectively protect their crops from thrips damage while maintaining ecological balance and meeting organic production standards.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in their journey towards sustainable and effective pest management. Our advanced satellite-based crop monitoring system, combined with AI-powered advisory services, provides valuable tools for early detection and precision management of thrips infestations.
As we continue to innovate and develop new technologies, we envision a future where organic pest control becomes increasingly efficient and accessible to farmers worldwide. By working together and embracing sustainable practices, we can protect our crops, preserve our environment, and ensure food security for generations to come.
FAQs
Q1: How can I tell if my plants are infested with thrips?
A1: Look for signs such as silvery or bronze patches on leaves, distorted growth, and tiny black fecal spots. You may also see the thrips themselves, which are very small, slender insects.
Q2: Are organic methods as effective as chemical insecticides for thrips control?
A2: When implemented correctly as part of an integrated pest management strategy, organic methods can be highly effective. While they may work more slowly than chemical insecticides, they offer long-term, sustainable control with fewer negative environmental impacts.
Q3: How often should I apply botanical insecticides for thrips control?
A3: The frequency of application depends on the specific product and the severity of the infestation. Generally, applications every 7-14 days are recommended, but always follow the product label instructions.
Q4: Can Farmonaut’s satellite system detect thrips infestations in all types of crops?
A4: Our satellite system can detect changes in plant health that may indicate thrips infestations across a wide range of crops. However, the accuracy may vary depending on the crop type and the severity of the infestation.
Q5: How do I get started with Farmonaut’s crop monitoring system?
A5: You can sign up for our services through our website or mobile app. We offer various subscription plans tailored to different farm sizes and needs.
For more information about our services and to explore how Farmonaut can help you manage thrips and other agricultural challenges, visit our website or download our app:
For developers interested in integrating our satellite and weather data into their own systems, check out our API documentation: