Revolutionizing Minnesota Farms: Sustainable Water Management Practices for Precision Agriculture
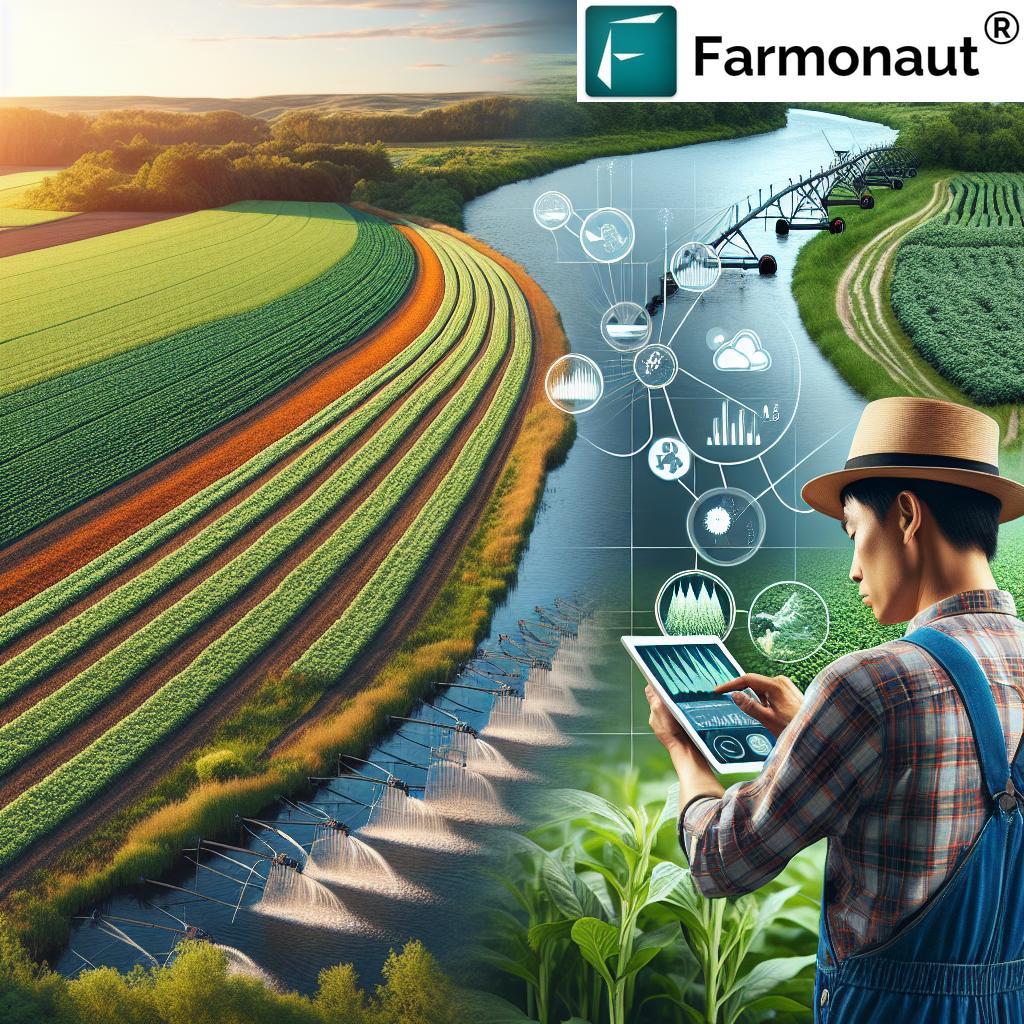

“Minnesota farmers implementing sustainable water management practices have reduced nitrogen runoff by up to 30% in some areas.”
In recent years, the agricultural landscape of Minnesota has undergone a remarkable transformation. As we delve into the world of sustainable agriculture practices and water quality management, we’re witnessing a revolution that’s reshaping the future of farming in the North Star State. From the banks of the Mississippi River to the fertile plains of the Minnesota River Valley, farmers are embracing innovative solutions that not only boost crop yields but also safeguard our precious water resources.
In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll uncover the latest trends in nutrient management for crops, examine cutting-edge conservation practices, and showcase how precision agriculture technologies are making waves across Minnesota’s farms. Join us as we navigate through the intricacies of soil erosion prevention techniques, agricultural water resource conservation, and the impact of urban landscapes on water quality.
The Pillars of Sustainable Water Management in Minnesota Agriculture
- Precision irrigation systems
- Nutrient management strategies
- Buffer zones and riparian management
- Cover cropping and soil health initiatives
- Wetland restoration and conservation
As we embark on this journey, it’s crucial to understand that sustainable water management is not just about conservation—it’s about creating a harmonious balance between agricultural productivity and environmental stewardship. Let’s explore how Minnesota’s farmers are leading the charge in this green revolution.
Nutrient Management: The Cornerstone of Sustainable Farming
At the heart of Minnesota’s agricultural transformation lies a renewed focus on nutrient management. The excessive use of nitrogen and phosphorus has long been a concern for water quality in our lakes, rivers, and groundwater. Today, we’re seeing a shift towards more precise and efficient nutrient application methods.
The 4R Nutrient Stewardship Approach
Minnesota farmers are increasingly adopting the 4R Nutrient Stewardship approach:
- Right Source: Matching fertilizer type to crop needs
- Right Rate: Matching amount of fertilizer to crop needs
- Right Time: Making nutrients available when crops need them
- Right Place: Keeping nutrients where crops can use them
This approach not only optimizes crop uptake of nutrients but also minimizes runoff, protecting our valuable water resources. Farmers using these principles have reported significant reductions in nutrient loss while maintaining or even improving crop yields.
Precision Agriculture Technologies in Nutrient Management
Advancements in precision agriculture have revolutionized how we approach nutrient management. Satellite-based technologies, such as those offered by Farmonaut, are enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions about fertilizer application.
These innovative tools provide:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- Soil moisture analysis
- Variable rate fertilizer recommendations
By leveraging these technologies, Minnesota farmers are able to apply nutrients with unprecedented precision, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
Conservation Practices: Protecting Minnesota’s Waters
Conservation practices play a crucial role in sustainable water management. Minnesota farmers are implementing a variety of techniques to protect our waterways and improve soil health.
Buffer Strips: Nature’s Water Filters
The implementation of buffer strips along waterways has been a game-changer for Minnesota’s water quality. These strips of vegetation act as natural filters, capturing sediment, nutrients, and pesticides before they can enter our rivers and lakes.
Key benefits of buffer strips include:
- Reduced soil erosion
- Improved water quality
- Enhanced wildlife habitat
- Increased biodiversity
The Minnesota Buffer Law, enacted in 2015, has been instrumental in promoting the adoption of these crucial conservation practices across the state.
Cover Crops: Building Soil Health and Water Retention
Cover crops are gaining popularity among Minnesota farmers as a powerful tool for improving soil health and water management. By planting crops like rye, oats, or clover during off-seasons, farmers are:
- Reducing soil erosion
- Increasing organic matter in soil
- Improving water infiltration
- Suppressing weeds naturally
These benefits not only contribute to better water quality but also enhance the overall resilience of farm ecosystems.
Explore Farmonaut’s Satellite API for advanced agricultural insights
Precision Agriculture: The Future of Farming in Minnesota
Precision agriculture is transforming the way Minnesota farmers manage their land and resources. By utilizing advanced technologies, farmers can make more informed decisions, leading to improved efficiency and sustainability.
Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Satellite technology, such as that provided by Farmonaut, offers farmers unprecedented insights into their fields. These tools allow for:
- Early detection of crop stress
- Precise irrigation management
- Targeted pest and disease control
By leveraging these technologies, Minnesota farmers can optimize their resource use, reducing water consumption and minimizing the need for chemical inputs.
Variable Rate Technology (VRT)
Variable Rate Technology allows farmers to apply inputs like water, fertilizer, and pesticides at varying rates across their fields, based on the specific needs of each area. This precision approach results in:
- Reduced input costs
- Improved crop yields
- Minimized environmental impact
VRT is particularly effective when combined with satellite imagery and soil mapping, enabling farmers to create highly targeted management zones within their fields.
Soil Erosion Prevention: Safeguarding Minnesota’s Farmland
Soil erosion is a significant concern for Minnesota’s agricultural community, impacting both farm productivity and water quality. Innovative techniques are being employed to combat this issue:
Contour Farming and Terracing
By plowing and planting crops across the slope of the land rather than up and down, farmers can significantly reduce soil erosion. This practice:
- Slows water runoff
- Increases water infiltration
- Reduces soil loss
In areas with steeper slopes, terracing is used to create level platforms for crops, further mitigating erosion risks.
Conservation Tillage
Many Minnesota farmers are adopting conservation tillage practices, which leave crop residue on the soil surface. This approach offers multiple benefits:
- Improved soil structure
- Increased water retention
- Reduced soil erosion
- Enhanced soil biodiversity
By minimizing soil disturbance, conservation tillage helps maintain the integrity of our farmlands while promoting sustainable water management.
Agricultural Water Resource Conservation: Every Drop Counts
In Minnesota, where water is abundant but not limitless, efficient water use in agriculture is paramount. Farmers are implementing various strategies to conserve this precious resource:
Drip Irrigation and Micro-Sprinklers
These advanced irrigation systems deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Benefits include:
- Water savings of up to 50% compared to traditional methods
- Improved crop yields due to consistent moisture levels
- Reduced energy costs for pumping water
Water Recycling and Rainwater Harvesting
Innovative farmers are finding ways to capture and reuse water on their farms:
- Collecting rainwater for irrigation
- Recycling water from washing and processing facilities
- Implementing tailwater recovery systems to capture and reuse runoff
These practices not only conserve water but also reduce the farm’s overall environmental footprint.
“The Green Star Initiative has helped over 1,000 Minnesota farms adopt precision agriculture technologies for improved water conservation.”
The Impact of Urban Landscapes on Water Quality
While our focus has been on agricultural practices, it’s important to recognize the role urban areas play in water quality management. The intersection of urban and rural landscapes presents both challenges and opportunities for sustainable water management in Minnesota.
Urban Runoff and Its Effects
Urban areas contribute significantly to water pollution through:
- Stormwater runoff carrying pollutants from roads and parking lots
- Excess fertilizer from lawns and gardens
- Improper disposal of household chemicals
These urban sources of pollution can have far-reaching effects on downstream agricultural areas and natural ecosystems.
Green Infrastructure Solutions
Cities across Minnesota are implementing green infrastructure to mitigate urban runoff:
- Rain gardens and bioswales to filter stormwater
- Permeable pavements to reduce runoff
- Green roofs to absorb rainwater and reduce urban heat island effects
These urban conservation practices complement agricultural efforts, creating a more holistic approach to water quality management across the state.
Legislative Updates and Funding Opportunities
The landscape of agricultural water management in Minnesota is constantly evolving, shaped by new legislation and funding initiatives. Here are some key developments:
The Minnesota Agricultural Water Quality Certification Program (MAWQCP)
This voluntary program incentivizes farmers to implement best practices for water quality management. Benefits include:
- Regulatory certainty for a period of 10 years
- Recognition as certified water quality stewards
- Priority for technical and financial assistance
Clean Water Fund Grants
Minnesota’s Clean Water Fund provides grants for various water quality improvement projects, including:
- Watershed restoration and protection
- Groundwater and drinking water protection
- Soil and water conservation district capacity building
These funding opportunities are crucial in supporting farmers’ transition to more sustainable practices.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
As we’ve seen throughout this exploration, technology plays a pivotal role in advancing sustainable agriculture practices. Platforms like Farmonaut are at the forefront of this technological revolution, offering farmers powerful tools for optimizing crop management and resource conservation.
Satellite-Based Farm Management
Farmonaut’s satellite-based technology provides farmers with:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- Precise irrigation management recommendations
- Early detection of pest and disease outbreaks
- Yield prediction and harvest optimization
By leveraging these insights, Minnesota farmers can make data-driven decisions that improve both productivity and sustainability.
AI-Powered Advisory Systems
Artificial Intelligence is transforming agricultural decision-making. Farmonaut’s AI advisory system offers:
- Personalized crop management strategies
- Weather-based recommendations for planting and harvesting
- Optimization of resource use based on historical and real-time data
These AI-driven insights enable farmers to fine-tune their practices for maximum efficiency and minimal environmental impact.
Explore Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs for integration options
Sustainable Water Management Practices in Minnesota Agriculture
| Practice | Water Conservation Impact | Crop Yield Impact | Implementation Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Irrigation | High | Medium | $$$ |
| Cover Cropping | Medium | Medium | $ |
| Buffer Strips | High | Low | $$ |
| Nutrient Management | High | High | $$ |
| Conservation Tillage | Medium | Medium | $ |
The Future of Sustainable Agriculture in Minnesota
As we look to the future, the path forward for Minnesota’s agriculture is clear: sustainability, efficiency, and innovation will be the driving forces. The integration of advanced technologies, conservation practices, and data-driven decision-making is reshaping the agricultural landscape, creating a more resilient and environmentally responsible farming sector.
Key trends to watch include:
- Increased adoption of precision agriculture technologies
- Further integration of AI and machine learning in farm management
- Expansion of regenerative agriculture practices
- Growing emphasis on water quality trading programs
- Development of climate-resilient crop varieties
As Minnesota farmers continue to embrace these innovations, they’re not just securing the future of their farms—they’re safeguarding our state’s water resources and natural ecosystems for generations to come.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future for Minnesota Agriculture
The journey towards sustainable water management in Minnesota’s agriculture is ongoing, but the progress made is truly remarkable. From the implementation of buffer strips along our waterways to the adoption of cutting-edge satellite technologies, Minnesota farmers are leading the charge in creating a more sustainable and productive agricultural sector.
As we’ve explored throughout this blog, the key to success lies in the integration of:
- Innovative conservation practices
- Precision agriculture technologies
- Sustainable nutrient management strategies
- Collaborative efforts between rural and urban communities
By continuing to embrace these principles and leveraging advanced tools like those offered by Farmonaut, Minnesota’s agricultural community is well-positioned to meet the challenges of the future while preserving our precious water resources.
The revolution in sustainable water management practices for precision agriculture is not just transforming Minnesota’s farms—it’s setting a standard for sustainable agriculture across the nation and around the world.
FAQ Section
Q: What are the main benefits of implementing sustainable water management practices in agriculture?
A: The main benefits include improved water quality, reduced soil erosion, increased crop yields, lower input costs, and enhanced long-term farm sustainability.
Q: How does precision agriculture contribute to water conservation?
A: Precision agriculture technologies enable farmers to apply water and other inputs more efficiently, reducing waste and minimizing runoff. This leads to significant water savings and improved crop water use efficiency.
Q: What role do buffer strips play in water quality management?
A: Buffer strips act as natural filters, capturing sediment, nutrients, and pesticides before they can enter waterways. They also provide habitat for wildlife and help prevent soil erosion.
Q: How can urban residents contribute to agricultural water quality efforts?
A: Urban residents can help by properly managing lawn fertilizers, reducing impervious surfaces, installing rain gardens, and supporting local initiatives that promote green infrastructure and stormwater management.
Q: What funding opportunities are available for Minnesota farmers looking to implement sustainable water management practices?
A: Farmers can access funding through programs like the Minnesota Agricultural Water Quality Certification Program, Clean Water Fund grants, and various USDA conservation programs.