Revolutionizing Australian Wine Exports: Innovative Tech for Sustainable Vineyard Management and Production
“Australian wine exports to China reached a peak value of AUD $1.2 billion in 2019 before facing challenges.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the latest innovations revolutionizing the Australian wine export industry. In this article, we’ll explore cutting-edge strategies and technologies that are transforming vineyard management, sustainable winemaking, and production techniques. From enhancing red wine stability to optimizing grape tannin extraction, we’ll uncover the secrets behind Australia’s success in the global wine market.
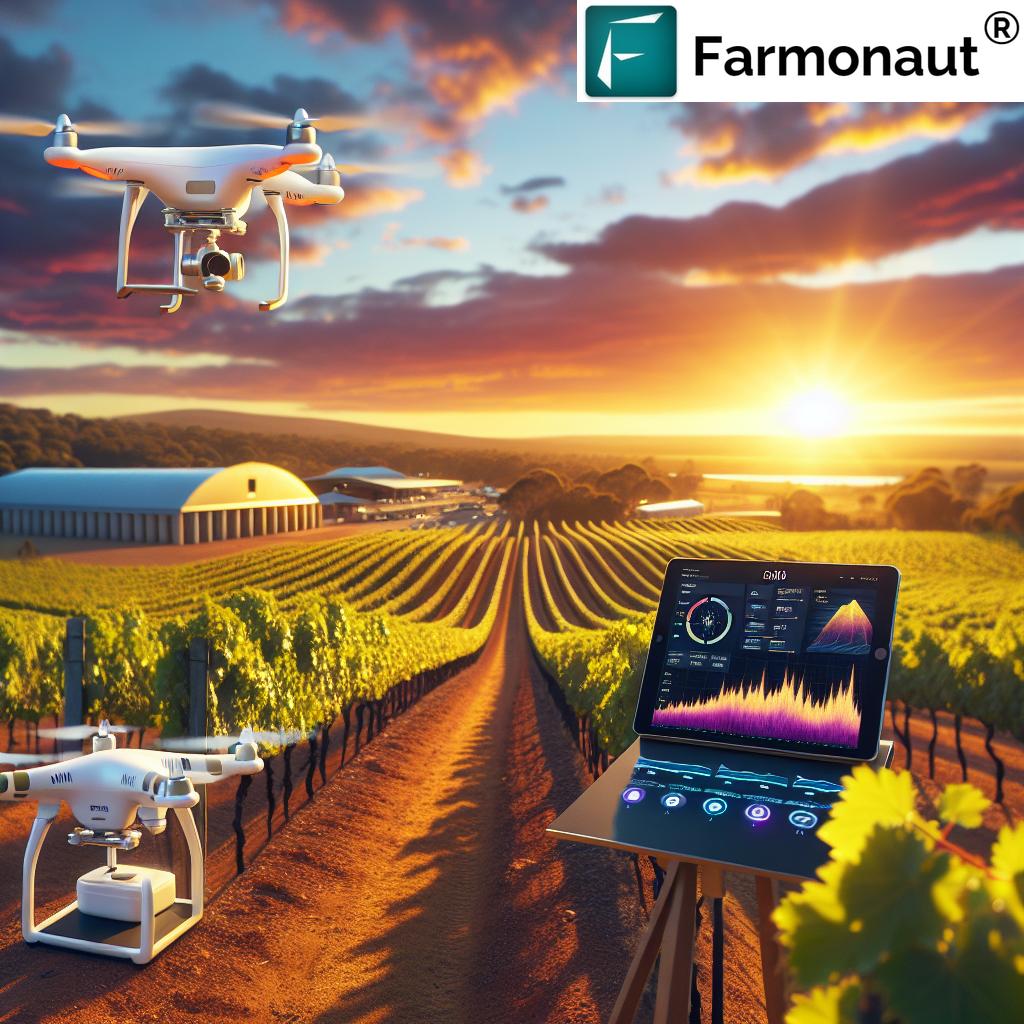

The Australian Wine Industry: A Global Powerhouse
Australia has long been recognized as a powerhouse in the global wine industry, known for its diverse wine regions and high-quality products. As we delve into the world of Australian wine, it’s crucial to understand the factors that have contributed to its success and the challenges it faces in an ever-evolving market.
Key Australian Wine Regions
- Barossa Valley, South Australia
- Margaret River, Western Australia
- Yarra Valley, Victoria
- Hunter Valley, New South Wales
- Tasmania
Each of these regions offers unique terroir and climate conditions, contributing to the rich diversity of Australian wines. From the bold Shiraz of the Barossa to the crisp Rieslings of Clare Valley, Australian winemakers have mastered the art of crafting wines that reflect their distinct origins.
Innovative Vineyard Management Techniques
At the heart of producing exceptional wines lies effective vineyard management. Australian winegrowers are at the forefront of adopting innovative technologies to optimize their vineyards’ health and productivity.
Satellite-Based Monitoring with Farmonaut
One of the most groundbreaking advancements in vineyard management is the use of satellite technology. Farmonaut, a leading agricultural technology company, offers sophisticated satellite-based solutions that are transforming how vineyards are managed.
Farmonaut’s satellite imagery provides real-time data on:
- Crop health (NDVI)
- Soil moisture levels
- Weather patterns
This information allows vineyard managers to make data-driven decisions about irrigation, fertilizer application, and pest management, ultimately leading to healthier vines and higher quality grapes.
Precision Viticulture
Precision viticulture is another area where technology is making a significant impact. By using drones, GPS mapping, and soil sensors, vineyard managers can:
- Identify areas of stress or disease in the vineyard
- Apply targeted treatments to specific areas
- Optimize irrigation and fertilization practices
- Improve overall vine health and grape quality
These precision techniques not only enhance wine quality but also contribute to more sustainable and efficient vineyard operations.
Sustainable Winemaking Practices
Sustainable winemaking is no longer just a trend; it’s a necessity in the face of climate change and increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. Australian winemakers are adopting various sustainable practices to reduce their environmental impact and improve wine quality.
Water Conservation
In a country known for its arid climate, water conservation is crucial. Innovative irrigation systems, such as:
- Drip irrigation
- Subsurface irrigation
- Precision irrigation based on real-time soil moisture data
These systems help wineries reduce water usage while ensuring optimal vine health. Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring plays a crucial role in optimizing water usage, potentially reducing consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional methods.
Organic and Biodynamic Viticulture
Many Australian wineries are embracing organic and biodynamic practices, which involve:
- Eliminating synthetic pesticides and fertilizers
- Promoting biodiversity in the vineyard
- Using natural predators for pest control
- Implementing cover crops to improve soil health
These practices not only benefit the environment but also contribute to the production of wines with a true sense of place.
Innovative Wine Production Techniques
“Cold maceration in winemaking can extend for up to 10 days, enhancing color extraction and flavor complexity.”
Australian winemakers are constantly pushing the boundaries of traditional winemaking techniques to produce wines of exceptional quality and character. Let’s explore some of the innovative wine production techniques that are shaping the future of Australian wines.
Cold Maceration Process
The cold maceration process is a technique that has gained popularity among Australian winemakers, particularly for red wines. This method involves:
- Cooling harvested grapes to near-freezing temperatures
- Allowing the grapes to soak for several days before fermentation
- Enhancing color extraction and developing complex flavor profiles
By extending the maceration period at low temperatures, winemakers can achieve greater phenolic extraction without the risk of harsh tannins, resulting in wines with deeper color, softer tannins, and more pronounced fruit flavors.
Advanced Fermentation Methods
Innovation in fermentation techniques is another area where Australian winemakers excel. Some cutting-edge methods include:
- Wild yeast fermentation for unique flavor profiles
- Controlled oxygen exposure during fermentation
- Use of concrete eggs or amphorae for fermentation and aging
These techniques allow winemakers to create wines with distinct characteristics and textures, setting Australian wines apart in the global market.
Enhancing Red Wine Stability and Quality
Ensuring the stability and quality of red wines is crucial for success in the export market. Australian winemakers are employing various techniques to achieve this:
Tannin Management
Grape tannin extraction is a critical aspect of red wine production. Australian winemakers are using innovative methods to optimize tannin extraction, including:
- Micro-oxygenation during fermentation
- Extended post-fermentation maceration
- Use of enzymes to enhance tannin extraction
These techniques result in wines with balanced tannins, improved mouthfeel, and enhanced aging potential.
Color Stabilization
Maintaining vibrant color in red wines is essential for consumer appeal. Australian winemakers use various methods to enhance color retention, such as:
- Co-pigmentation techniques
- Use of oak alternatives during fermentation
- Controlled oxygen exposure during aging
These methods help create wines with deep, stable color that can withstand the test of time and international shipping.
Wine Labelling and Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the complex world of wine labelling regulations is crucial for successful wine exports. Australian winemakers must adhere to both domestic and international standards to ensure their products meet all legal requirements.
Geographical Indications
Geographical indications (GIs) play a significant role in the Australian wine industry. These protected designations of origin help consumers identify wines from specific regions and ensure the authenticity of products. Some key aspects of GIs include:
- Strict regulations on grape sourcing
- Specific winemaking practices for each GI
- Clear labelling requirements
By adhering to GI regulations, Australian winemakers can protect the reputation of their regions and add value to their products in international markets.
Quality Control Measures
Maintaining the integrity of Australian wines is paramount for export success. The industry has implemented rigorous quality control measures, including:
- Regular laboratory testing for chemical composition
- Sensory evaluation panels
- Strict bottling and packaging standards
These measures ensure that Australian wines consistently meet the high standards expected by international consumers.

Exporting Australian Wines to Global Markets
The success of Australian wine exports relies on a deep understanding of international markets and consumer preferences. Let’s explore some key aspects of exporting Australian wines:
Emerging Asian Markets
While China has been a significant market for Australian wines, recent challenges have led to a focus on diversifying export destinations. Emerging Asian markets such as:
- Japan
- South Korea
- Singapore
- Vietnam
These countries present exciting opportunities for Australian wine exporters. Understanding local tastes, import regulations, and cultural nuances is crucial for success in these markets.
European and American Markets
Traditional wine-consuming regions like Europe and the Americas continue to be important export destinations for Australian wines. Key strategies for success in these markets include:
- Highlighting the unique characteristics of Australian wine regions
- Emphasizing sustainability and organic practices
- Tailoring marketing efforts to specific consumer segments
By focusing on these aspects, Australian winemakers can differentiate their products in highly competitive markets.
Wine Tourism: A Growing Industry
Wine tourism is becoming an increasingly important aspect of the Australian wine industry. It not only provides additional revenue streams for wineries but also helps build brand loyalty and awareness. Some key aspects of wine tourism in Australia include:
- Cellar door experiences
- Wine and food pairing events
- Vineyard tours and tastings
- Wine festivals and regional events
By leveraging technology and innovative marketing strategies, Australian wineries are creating unique and memorable experiences for visitors, further enhancing the global reputation of Australian wines.
Adapting to Climate Change
Climate change poses significant challenges to the wine industry worldwide, and Australia is no exception. Australian winegrowers are taking proactive steps to adapt to changing conditions and reduce their environmental impact:
Varietal Selection and Planting Strategies
Winegrowers are experimenting with new grape varieties and adapting planting strategies to cope with changing climate conditions. This includes:
- Planting heat-tolerant varieties
- Shifting vineyard locations to cooler areas
- Adjusting row orientation to manage sun exposure
Emissions Reduction
Reducing carbon emissions is a key focus for many Australian wineries. Initiatives include:
- Implementing renewable energy sources
- Improving energy efficiency in winemaking processes
- Adopting sustainable packaging solutions
These efforts not only help mitigate climate change but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers in global markets.
The Role of Technology in Wine Production
Technology plays a crucial role in modern wine production, from vineyard management to winemaking processes. Let’s explore how innovative tech solutions are shaping the future of Australian wines:
Farmonaut’s Satellite-Based Solutions
Farmonaut offers cutting-edge satellite-based farm management solutions that are revolutionizing vineyard management. Their technology provides:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- AI-based advisory systems
- Resource management tools
These tools enable vineyard managers to make data-driven decisions, optimizing vine health and grape quality.
Explore Farmonaut’s solutions:
AI and Machine Learning in Winemaking
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are being applied to various aspects of winemaking, including:
- Predicting optimal harvest times
- Analyzing fermentation processes in real-time
- Optimizing blending decisions
These technologies help winemakers consistently produce high-quality wines while reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Low Alcohol Wine Production
The trend towards healthier lifestyles has led to increased demand for low alcohol wine options. Australian winemakers are responding to this trend with innovative production techniques:
- Early harvest of grapes to reduce sugar content
- Reverse osmosis to remove alcohol
- Spinning cone technology for gentle alcohol removal
These methods allow for the production of lower alcohol wines without compromising on flavor and quality.
Wine Additives and Regulations
The use of wine additives is a complex and regulated aspect of winemaking. Australian winemakers must navigate strict regulations while striving to produce high-quality, stable wines. Common additives and their purposes include:
- Sulfur dioxide for preservation
- Enzymes for clarity and stability
- Fining agents for clarification
Australian winemakers are increasingly focusing on minimal intervention techniques, reducing the use of additives where possible to produce more natural wines.
Comparative Analysis of Vineyard Management Technologies
| Management Aspect | Traditional Methods | Other Technologies | Farmonaut Satellite System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation Management | Manual inspection, experience-based | Ground sensors, weather stations | Satellite-based soil moisture analysis, 30% water reduction |
| Pest Detection | Visual inspections | Drone imagery | Early warning system, 2-3 days faster response |
| Yield Prediction | Historical data, manual counting | AI-based image analysis | 90% accuracy vs. 70% for traditional methods |
| Nutrient Management | Periodic soil testing | IoT sensors | Real-time vegetation health index (NDVI) |
| Climate Adaptation | Long-term observations | Local weather stations | Micro-climate analysis and predictions |
The Future of Australian Wine Exports
As we look to the future, the Australian wine industry is well-positioned to maintain its status as a global leader. Key factors that will drive success include:
- Continued innovation in vineyard management and winemaking techniques
- Adaptation to changing climate conditions
- Embracing sustainability and organic practices
- Leveraging technology to improve efficiency and quality
- Expanding into new markets while strengthening existing relationships
By focusing on these areas, Australian winemakers can ensure their products remain competitive and sought-after in the global wine market.
Conclusion
The Australian wine industry continues to evolve and innovate, embracing new technologies and sustainable practices to produce world-class wines. From satellite-based vineyard management to cutting-edge winemaking techniques, Australian winemakers are at the forefront of the global wine industry.
As we’ve explored in this article, the combination of traditional winemaking expertise with modern technology and sustainable practices is key to the ongoing success of Australian wine exports. By adapting to changing market demands, environmental challenges, and consumer preferences, Australian wines are well-positioned to continue their reign as some of the world’s most beloved and respected wines.
FAQ Section
Q: What makes Australian wines unique in the global market?
A: Australian wines are known for their diversity, bold flavors, and innovative winemaking techniques. The country’s varied climate and soil types allow for a wide range of grape varieties to thrive, resulting in unique and distinctive wines.
Q: How are Australian winemakers adapting to climate change?
A: Australian winemakers are adapting to climate change through various methods, including planting heat-tolerant grape varieties, shifting vineyard locations to cooler areas, implementing water-saving irrigation techniques, and adopting sustainable farming practices.
Q: What role does technology play in modern Australian winemaking?
A: Technology plays a crucial role in modern Australian winemaking, from satellite-based vineyard management systems like Farmonaut to AI-driven fermentation monitoring. These technologies help winemakers optimize grape quality, improve efficiency, and consistently produce high-quality wines.
Q: How important are geographical indications for Australian wines?
A: Geographical indications (GIs) are very important for Australian wines as they help protect the reputation of specific wine regions and add value to the products in international markets. GIs ensure that wines labeled with a particular region meet strict quality and production standards.
Q: What are some emerging markets for Australian wine exports?
A: While traditional markets like the UK and US remain important, Australian winemakers are increasingly focusing on emerging Asian markets such as Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and Vietnam. These markets offer significant growth potential for Australian wine exports.