Ventura County’s Lake Sherwood Contamination: Environmental Impact Assessment and Water Pollution Prevention Strategies
“Lake Sherwood’s recent sewage overflow affected a significant portion of Ventura County’s water ecosystem, impacting thousands of residents.”
In the wake of a significant environmental health crisis, we find ourselves grappling with the critical importance of sustainable sewage management and water pollution prevention in Ventura County. The recent sewage overflow into Lake Sherwood has sent ripples of concern throughout our community, highlighting the urgent need for advanced environmental monitoring techniques and robust strategies to protect our precious water resources.
As we delve into this pressing issue, we’ll explore the environmental impact assessment of the spill, detail the cleanup efforts, and discuss the public safety measures put in place. Our goal is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the challenges we face in maintaining water sanitation infrastructure and the innovative solutions available to prevent such incidents in the future.
The Incident: A Closer Look at the Lake Sherwood Sewage Spill
On December 29, 2023, at approximately 6:05 PM, a significant sewage spill occurred near the 2500 block of Calbourne Lane in Ventura County. The Ventura County Environmental Health Division reported this incident on December 30, 2023, shedding light on a situation that would soon become a pressing environmental concern for the entire community.
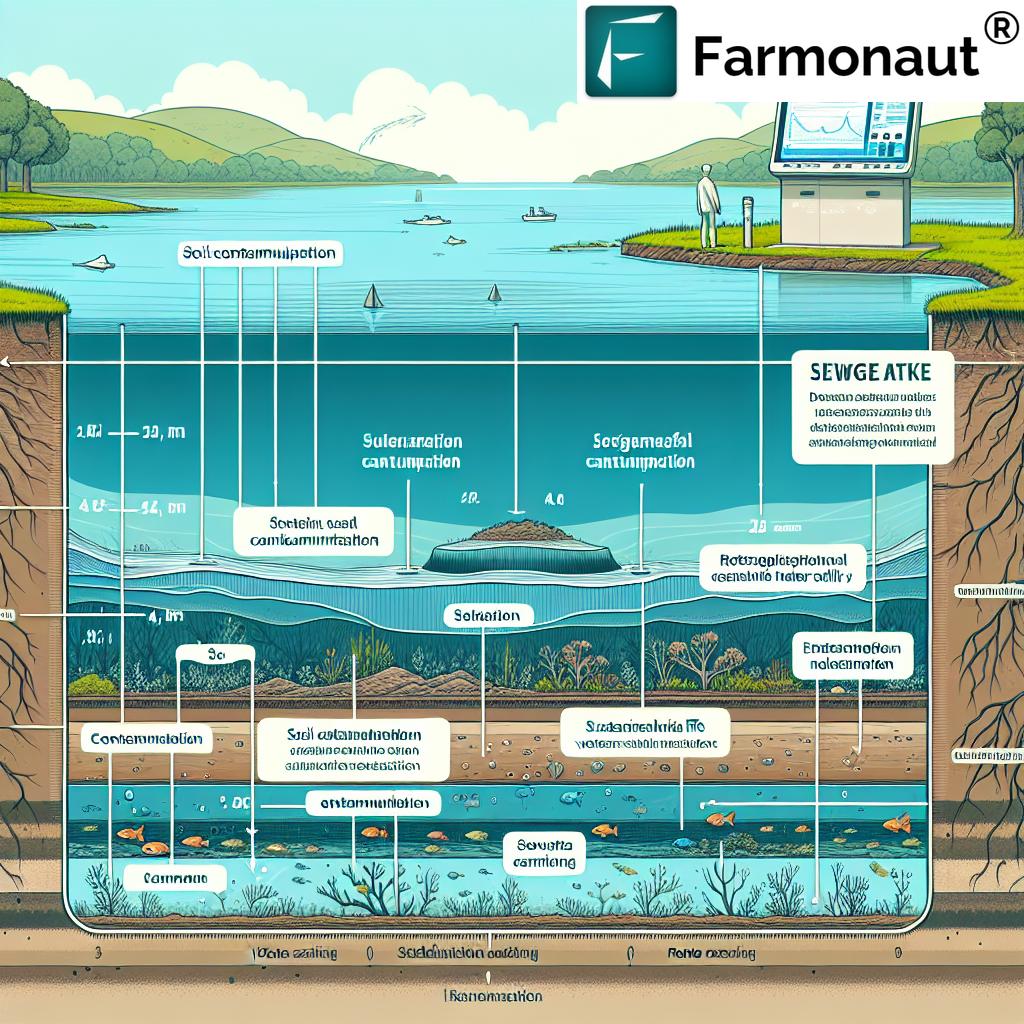
The root cause of this spill was as unexpected as it was problematic. A pile of gravel had been inadvertently placed on top of a manhole cover, leading to a series of unfortunate events. As the gravel shifted, it fell into the manhole, creating a blockage in the sewer main. This obstruction resulted in an overflow of sewage, with approximately 2,500 gallons spilling into the surrounding soil and, alarmingly, into Lake Sherwood itself.

The Triunfo Water and Sanitation District, responsible for managing the sewer system in the area, promptly alerted the Environmental Health Division about the overflow. By Monday, cleanup efforts were already underway, with crews utilizing vacuum trucks to mitigate the situation. However, the exact volume of sewage that contaminated Lake Sherwood remains undetermined, adding an element of uncertainty to the environmental impact assessment.
Immediate Response and Public Safety Measures
In response to this environmental emergency, the Ventura County Environmental Health Division took swift action to protect public health and safety. They implemented the following measures:
- Warning Signage: Signs were placed around Lake Sherwood, alerting residents and visitors to the potential hazards.
- Area Restrictions: The public was advised to avoid any contact with the impacted areas of the lake and surrounding soil.
- Extended Precautions: These warnings will remain in place until January 2, 2025, ensuring long-term safety as the environmental impact is assessed and addressed.
These immediate actions underscore the seriousness of the situation and the commitment of local authorities to safeguarding public health while dealing with this environmental challenge.
Environmental Impact Assessment: A Comprehensive Overview
To fully understand the ramifications of this sewage spill on Lake Sherwood and its surrounding ecosystem, we must conduct a thorough environmental impact assessment. This process involves evaluating various factors affected by the contamination and developing strategies for remediation and future prevention.
| Environmental Factor | Pre-Spill Condition (Estimated) | Post-Spill Impact (Estimated) | Recovery Measures | Monitoring Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Quality (pH) | 6.5 – 8.5 | 5.0 – 9.0 | Chemical treatment, Aeration | Regular water sampling, Remote sensing |
| Dissolved Oxygen | 7-9 mg/L | 3-5 mg/L | Aeration systems, Algae control | Continuous monitoring buoys, Satellite imagery |
| Bacterial Count | <200 CFU/100mL | >2000 CFU/100mL | UV disinfection, Chlorination | Lab analysis, Rapid test kits |
| Soil Contamination Levels | Low | Moderate to High | Bioremediation, Soil removal | Soil testing, Vegetation health analysis |
| Aquatic Ecosystem Health | Stable | Stressed | Habitat restoration, Fish restocking | Biodiversity surveys, Satellite monitoring |
| Vegetation Impact | Healthy | Mild to Moderate Stress | Nutrient management, Replanting | NDVI analysis, Ground surveys |
| Public Health Risk | Low | Elevated | Public advisories, Access restrictions | Health surveys, Water quality monitoring |
This comprehensive table provides a clear overview of the various environmental factors affected by the sewage spill. It highlights the estimated pre-spill conditions, the immediate impact of the contamination, the recovery measures being implemented, and the monitoring methods used to track progress.
As we can see, the spill has had significant effects on water quality, soil contamination, and the overall health of the aquatic ecosystem. The elevated bacterial count and decreased dissolved oxygen levels are particularly concerning, as they pose immediate risks to aquatic life and human health.
Cleanup Efforts and Remediation Strategies
In the aftermath of the Lake Sherwood sewage spill, a multi-faceted approach to cleanup and remediation has been implemented. These efforts are crucial for mitigating the environmental impact and restoring the lake’s ecosystem to its pre-spill condition.
- Water Treatment: Advanced filtration systems and chemical treatments are being used to remove contaminants and restore water quality.
- Soil Decontamination: Affected soil areas are undergoing bioremediation and, where necessary, removal and replacement.
- Ecosystem Restoration: Efforts are underway to support the recovery of aquatic life, including habitat restoration and potential restocking of affected species.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regular testing of water and soil samples to track progress and adjust strategies as needed.
These cleanup efforts are labor-intensive and require significant resources. However, they are essential for ensuring the long-term health of Lake Sherwood and the safety of the surrounding community.
The Role of Advanced Technology in Environmental Monitoring
“Environmental monitoring techniques can detect water pollutants at concentrations as low as parts per billion, crucial for Lake Sherwood’s recovery.”
In addressing environmental challenges like the Lake Sherwood contamination, advanced technology plays a pivotal role. Remote sensing and satellite-based monitoring systems, such as those offered by Farmonaut, provide invaluable tools for environmental assessment and ongoing monitoring.
Farmonaut’s precision agriculture and remote sensing solutions offer several advantages in environmental monitoring:
- Real-time Data: Satellite imagery provides up-to-date information on water bodies, vegetation health, and land use changes.
- Wide Coverage: Large areas can be monitored efficiently, allowing for comprehensive environmental assessments.
- Vegetation Health Analysis: NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) measurements help track the impact of contamination on surrounding plant life.
- Soil Moisture Monitoring: Crucial for assessing the spread of contaminants in the soil and planning remediation efforts.
By leveraging these technologies, environmental agencies and water management authorities can make more informed decisions and respond more effectively to incidents like the Lake Sherwood spill.
Sustainable Sewage Management: Preventing Future Incidents
The Lake Sherwood incident serves as a stark reminder of the importance of sustainable sewage management practices. To prevent similar occurrences in the future, we must focus on several key areas:
- Infrastructure Maintenance: Regular inspections and upgrades of sewer systems to prevent blockages and leaks.
- Smart Monitoring Systems: Implementation of IoT-based sensors to detect anomalies in sewage flow and pressure.
- Public Awareness: Education programs to inform residents about proper waste disposal and the impact of their actions on the sewer system.
- Emergency Response Plans: Development and regular testing of rapid response protocols for sewage spills.
By adopting these strategies, we can significantly reduce the risk of future sewage overflows and protect our valuable water resources.
Water Pollution Prevention: A Community Effort
Preventing water pollution requires a collective effort from all members of the community. Here are some key strategies that individuals and organizations can adopt:
- Proper Disposal of Household Chemicals: Never pour chemicals, pharmaceuticals, or other hazardous substances down drains or toilets.
- Reduce Plastic Usage: Minimize the use of single-use plastics to prevent them from entering waterways.
- Responsible Lawn Care: Use organic fertilizers and pesticides sparingly to reduce runoff into water bodies.
- Support Local Clean Water Initiatives: Participate in community clean-up events and support policies aimed at protecting water resources.
The Future of Environmental Health Monitoring
As we look to the future, the integration of technology with environmental stewardship will be crucial in safeguarding public health and natural resources. Innovative agritech solutions, like those provided by Farmonaut, are set to play an increasingly important role in environmental health monitoring and sustainable water conservation practices.
Some key developments we can expect include:
- AI-Powered Predictive Analytics: Using machine learning algorithms to forecast potential environmental risks before they occur.
- Drone Technology: Complementing satellite data with high-resolution, low-altitude imagery for more detailed environmental assessments.
- Blockchain for Data Integrity: Ensuring the transparency and traceability of environmental data collection and reporting.
- Citizen Science Initiatives: Engaging the public in environmental monitoring through user-friendly apps and devices.
These advancements will enhance our ability to detect, respond to, and prevent environmental incidents like the Lake Sherwood contamination.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned and Moving Forward
The Lake Sherwood sewage spill serves as a sobering reminder of the delicate balance between our infrastructure and the natural environment. It underscores the need for vigilance, advanced monitoring systems, and proactive management strategies in protecting our water resources.
As we move forward, it’s clear that a multi-faceted approach combining technology, community engagement, and sustainable practices is essential. By leveraging the power of remote sensing, precision agriculture, and data-driven insights, we can better prevent, detect, and respond to environmental challenges.
The road to recovery for Lake Sherwood may be long, but it also presents an opportunity for Ventura County to emerge as a leader in environmental stewardship. By embracing innovative solutions and fostering a culture of environmental responsibility, we can ensure the long-term health and sustainability of our precious water resources for generations to come.
FAQs
Q: How long will it take for Lake Sherwood to recover from the sewage spill?
A: The recovery time for Lake Sherwood will depend on various factors, including the effectiveness of cleanup efforts and natural ecosystem resilience. It’s estimated that significant improvements may be seen within 6-12 months, but full recovery could take several years.
Q: What are the health risks associated with the sewage spill?
A: The primary health risks include exposure to harmful bacteria and pathogens that can cause gastrointestinal illnesses, skin infections, and other health issues. It’s crucial to avoid contact with contaminated water and soil until authorities declare the area safe.
Q: How can residents help in the recovery process?
A: Residents can help by adhering to water usage guidelines, properly disposing of waste, participating in local cleanup efforts, and staying informed about the ongoing situation through official channels.
Q: What role does Farmonaut play in environmental monitoring?
A: Farmonaut provides advanced satellite-based monitoring solutions that can be used to assess vegetation health, soil moisture, and land use changes. These tools are valuable for tracking the environmental impact of incidents like the Lake Sherwood spill and monitoring recovery efforts.
Q: How can we prevent similar incidents in the future?
A: Preventing future incidents involves improving infrastructure maintenance, implementing smart monitoring systems, enhancing public awareness about proper waste disposal, and developing robust emergency response plans.
Farmonaut Subscriptions
For more information on how Farmonaut’s technology can assist in environmental monitoring and sustainable agriculture practices, visit our API page or check out our API Developer Docs.