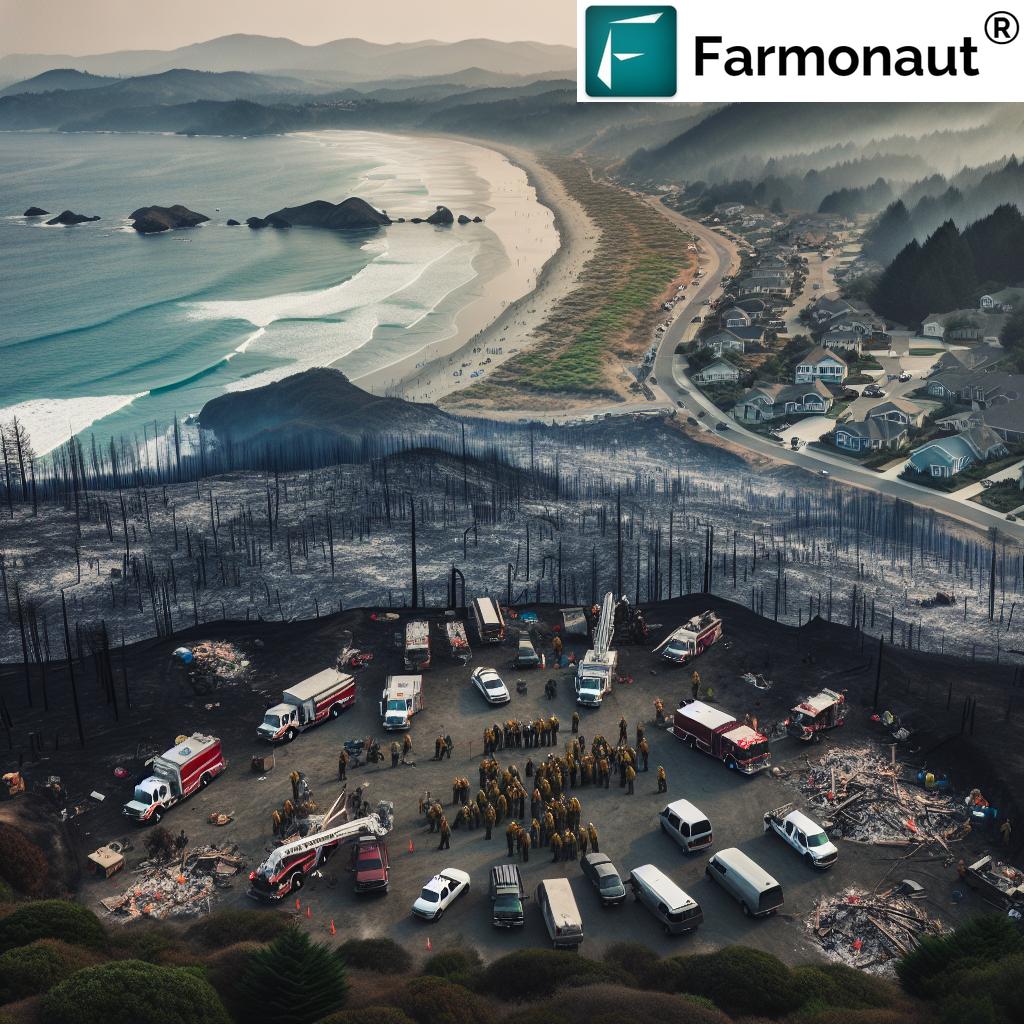
California Wildfire Recovery: Federal Disaster Aid Conditions and Coastal Development Regulations
“California’s Coastal Commission oversees development along 1,100 miles of coastline, impacting wildfire recovery efforts.”
In recent weeks, the complex interplay between California wildfire assistance and federal disaster aid has taken center stage in discussions between state and federal officials. As we delve into this critical issue, we’ll explore the multifaceted aspects of disaster recovery, environmental protection, and the political landscape shaping these decisions.
The Current Landscape: Wildfires and Federal Aid
California’s wildfire season has once again left devastating scars across the state, particularly in Los Angeles County. The Eaton and Palisades fires have thrust the issue of disaster relief conditions into the spotlight, with the Trump administration signaling a new approach to providing federal assistance.
At the heart of these discussions is the delicate balance between providing much-needed aid and ensuring long-term environmental protection and disaster preparedness. The administration’s stance, as articulated by Ric Grenell, Trump’s presidential envoy for special missions, suggests that future aid will come with strings attached.

Key Areas of Focus in Federal Aid Negotiations
As we navigate through this complex situation, several key areas have emerged as focal points in the negotiations between state and federal authorities:
- Forestry Management: Improving practices to reduce wildfire risks
- Wildfire Debris Removal: Expediting the cleanup process
- Disaster Resiliency Funding: Allocating resources for long-term preparedness
- Water Management: Addressing California’s ongoing water challenges
- Hazardous Material Clearing: Ensuring safe and efficient removal of dangerous substances
- Overgrowth Protection: Implementing strategies to manage vegetation
These areas highlight the comprehensive approach needed to address California’s wildfire challenges and underscore the complexity of the recovery process.
The California Coastal Commission: A Central Point of Contention
One of the most contentious aspects of the current negotiations is the role and future of the California Coastal Commission. This agency, responsible for regulating development along the state’s coastal zones, has become a focal point in discussions about coastal development regulations.
Grenell’s comments at the Conservative Political Action Conference in Washington shed light on the administration’s perspective:
“Everyone who’s involved knows that the California Coastal Commission is a disaster, and it needs to absolutely be defunded. And from just a way to think about government, we already have local government making these decisions.”
This stance reflects a broader debate about the balance between environmental protection and development, particularly in the context of disaster recovery.
The Historical Context of the Coastal Commission
To understand the current controversy, it’s essential to look back at the origins of the California Coastal Commission. Established in 1976 through the Coastal Act, the commission was a response to unregulated shoreline development. Its creation was a landmark moment in California’s environmental protection efforts.
However, since its inception, the commission has faced pushback from various interest groups and property owners who view its regulations as overly restrictive. The current debate over its role in wildfire recovery is just the latest chapter in this ongoing discussion.
Federal Response and Local Challenges
The federal response to California’s wildfire crisis has been multifaceted. Current efforts are focused on:
- Expediting regular debris removal
- Accelerating the Environmental Protection Agency’s hazardous debris removal process
- Speeding up Angelenos’ access to their homes
However, the administration has noted that some allocated funds, particularly those designated for resiliency measures like clearing overgrowth, had not been fully utilized by local authorities prior to the recent fires. This observation has fueled discussions about the efficiency of resource allocation and the need for proactive measures in wildfire prevention.
Political Dynamics and Public Reaction
The proposed conditions on federal aid have sparked a range of reactions from politicians and the public. Rep. Laura Friedman (D-Glendale) characterized the administration’s position as “extortion,” highlighting the political tensions surrounding this issue.
On the other hand, supporters of the administration’s approach argue that attaching conditions to aid could lead to more effective long-term solutions for California’s wildfire challenges. This debate underscores the complex interplay between environmental concerns, disaster response, and political decision-making in California’s wildfire-prone regions.
“Federal disaster aid negotiations for California wildfires involve discussions on managing 33 million acres of forest land.”
The Role of Technology in Wildfire Management and Recovery
As we discuss the challenges of wildfire recovery and prevention, it’s worth noting the growing role of technology in these efforts. Advanced satellite imaging and data analysis tools are becoming increasingly important in monitoring forest health, predicting fire risks, and managing resources effectively.
For instance, platforms like Farmonaut are pioneering the use of satellite-based technologies in agriculture and environmental monitoring. While primarily focused on agricultural applications, such technologies demonstrate the potential for satellite data to inform decision-making in areas like forestry management and disaster preparedness.

Comparative Analysis: California Wildfire Recovery Measures
| Recovery Measure | Federal Conditions | State/Local Actions | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disaster Aid Funding | Proposed strings attached to funding; emphasis on long-term solutions | Negotiating terms; seeking flexibility in fund allocation | Potential for improved long-term environmental management |
| Coastal Development Regulations | Scrutiny of California Coastal Commission’s role | Executive order to lift some commission requirements for rebuilding | Concerns over potential relaxation of environmental protections |
| Forestry Management | Push for more aggressive management practices | Implementing new strategies for forest health and fire prevention | Possible reduction in wildfire risks; ecosystem impact to be monitored |
| Debris Removal | Expediting EPA’s hazardous debris removal process | Coordinating with federal agencies for efficient cleanup | Immediate environmental benefits; potential for improved recycling practices |
| Water Management | Emphasis on improving water resource allocation | Exploring new water conservation and distribution methods | Long-term implications for ecosystem health and drought resilience |
The Path Forward: Balancing Immediate Needs and Long-Term Sustainability
As California grapples with the aftermath of recent wildfires and prepares for future challenges, the path forward requires a delicate balance between addressing immediate recovery needs and implementing long-term, sustainable solutions. This balance must consider:
- Immediate disaster relief for affected communities
- Long-term strategies for wildfire prevention and management
- Environmental protection and coastal development regulations
- Efficient allocation and use of federal and state resources
- Integration of advanced technologies in disaster preparedness and response
The outcome of current negotiations between state and federal officials will significantly shape California’s approach to wildfire management and environmental protection for years to come.
The Role of Local Communities and Governments
While much of the focus has been on federal and state-level discussions, the role of local communities and governments in wildfire recovery and prevention cannot be overstated. Local authorities are often the first line of defense and response in wildfire situations, and their input and cooperation are crucial for effective implementation of any new policies or strategies.
Key areas where local involvement is critical include:
- Zoning and land-use planning to reduce wildfire risks
- Community education and preparedness programs
- Local firefighting and emergency response capabilities
- Coordination of evacuation plans and procedures
Empowering local communities with the resources and authority to implement tailored solutions could be a crucial component of a comprehensive wildfire management strategy.
Environmental Protection and Economic Considerations
The debate over coastal development regulations and wildfire recovery measures brings to the forefront the ongoing challenge of balancing environmental protection with economic development. Critics of the California Coastal Commission argue that its regulations can impede economic growth and recovery efforts, while supporters maintain that these protections are crucial for preserving California’s unique coastal ecosystems and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Finding a middle ground that supports both environmental sustainability and economic recovery will be crucial in the coming years. This may involve:
- Developing more flexible regulatory frameworks that can adapt to changing environmental and economic conditions
- Investing in green technologies and sustainable development practices
- Creating incentives for businesses and property owners to adopt fire-resistant and environmentally friendly building practices
- Exploring innovative financing models for disaster recovery that align with long-term environmental goals
The resolution of these issues will have far-reaching implications for California’s coastal communities and their resilience to future wildfire threats.
Leveraging Technology for Disaster Preparedness
As we look to the future of wildfire management and disaster preparedness in California, the role of technology cannot be overstated. Advanced tools and platforms are becoming increasingly crucial in predicting, monitoring, and responding to wildfire threats.
For example, satellite-based technologies like those used by Farmonaut in agricultural applications demonstrate the potential for wider use in environmental monitoring and disaster management. While Farmonaut focuses on agricultural solutions, similar technologies could be adapted for:
- Real-time monitoring of forest health and fire risks
- Predictive modeling of wildfire spread based on environmental conditions
- Efficient resource allocation during firefighting efforts
- Post-fire assessment and recovery planning
Integrating these technological advancements into California’s wildfire management strategies could significantly enhance the state’s ability to prevent, respond to, and recover from wildfires.
The Importance of Collaborative Approaches
As we navigate the complex landscape of wildfire recovery and environmental protection in California, it’s becoming increasingly clear that collaborative approaches are essential. The challenges posed by wildfires and climate change are too vast and interconnected for any single entity to address alone.
Effective collaboration should involve:
- Coordination between federal, state, and local government agencies
- Partnerships with academic institutions for research and innovation
- Engagement with private sector companies developing relevant technologies
- Community involvement in planning and implementation of recovery strategies
By fostering a collaborative ecosystem, California can leverage diverse expertise and resources to develop more comprehensive and effective solutions to its wildfire challenges.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Wildfire Management in California
As we conclude our exploration of California’s wildfire recovery efforts and the ongoing negotiations surrounding federal disaster aid, it’s clear that the state faces significant challenges and opportunities in the years ahead. The decisions made today will shape California’s approach to wildfire management, environmental protection, and coastal development for generations to come.
Key considerations for the future include:
- Developing adaptive strategies that can respond to changing climate conditions
- Investing in cutting-edge technologies for fire prediction and management
- Balancing economic development with environmental conservation
- Strengthening community resilience through education and preparedness programs
- Fostering collaboration between diverse stakeholders to create holistic solutions
By addressing these areas comprehensively, California can work towards a future where wildfires are managed more effectively, communities are more resilient, and the state’s natural beauty is preserved for future generations.
FAQ Section
- Q: What are the main conditions being proposed for federal disaster aid to California?
A: The Trump administration is considering attaching conditions related to environmental protection, coastal development regulations, and forestry management practices to federal disaster aid for California’s wildfire recovery efforts. - Q: How does the California Coastal Commission factor into the wildfire recovery discussions?
A: The California Coastal Commission’s role in regulating coastal development has come under scrutiny, with proposals to potentially defund or restructure the agency as part of broader discussions on disaster recovery and environmental management. - Q: What are the key areas of focus in wildfire recovery efforts?
A: Key areas include forestry management, wildfire debris removal, disaster resiliency funding, water management, hazardous material clearing, and overgrowth protection. - Q: How are local communities involved in wildfire recovery and prevention?
A: Local communities play a crucial role in zoning and land-use planning, community education, local firefighting capabilities, and coordinating evacuation procedures. - Q: What role does technology play in wildfire management and recovery?
A: Advanced technologies, including satellite imaging and data analysis tools, are increasingly important for monitoring forest health, predicting fire risks, and managing resources effectively during wildfire situations.
Conclusion
The ongoing discussions surrounding California wildfire assistance and federal disaster aid highlight the complex challenges facing the state in its efforts to recover from recent wildfires and prepare for future threats. As negotiations continue between state and federal officials, the outcome will have significant implications for California’s approach to disaster preparedness, environmental protection, and coastal development.
By balancing immediate recovery needs with long-term sustainability goals, leveraging advanced technologies, and fostering collaboration among diverse stakeholders, California has the opportunity to develop more resilient and effective strategies for managing wildfires and protecting its unique natural resources.
As we move forward, it’s clear that addressing these challenges will require innovative thinking, adaptive policies, and a commitment to balancing environmental protection with economic development. The decisions made in the coming months and years will shape California’s landscape and communities for generations to come.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!