Sustainable Water Solutions: New Mexico’s Strategic Plan for Addressing Severe Shortages in a Changing Climate
“New Mexico’s water plan considers treating naturally occurring salty aquifers, potentially securing millions of gallons of freshwater annually.”
In the face of escalating water scarcity exacerbated by climate change, New Mexico has embarked on an ambitious journey to secure its water future. Our state’s strategic water supply plan aims to address severe water shortages through innovative and sustainable solutions. As we delve into this comprehensive strategy, we’ll explore how New Mexico is pioneering new approaches to water management that could serve as a model for other regions facing similar challenges.
The Evolution of New Mexico’s Water Strategy
New Mexico Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham made headlines in 2023 when she announced a bold plan to ensure a secure water source for our state. Initially, the proposal focused on two unorthodox, untapped water resources:
- Brackish water – naturally occurring, salty water found in underground aquifers
- Produced water – a byproduct of hydraulic fracturing in the oil and gas industry
The inclusion of produced water, also known as fracking wastewater, immediately sparked controversy and debate among lawmakers, environmental groups, and the public. This contentious aspect of the plan highlighted the complex challenges we face in balancing industrial needs with environmental concerns and public health.
Refining the Approach: From Controversy to Consensus
As discussions progressed, it became clear that a more focused and sustainable approach was necessary. The strategic water supply plan has since evolved to concentrate primarily on sustainable groundwater utilization, with a particular emphasis on brackish water treatment. This shift reflects ongoing debates about water scarcity, climate impacts, and the need for innovative approaches to ensure water security.
Rebecca Roose, who leads the strategic water supply plan for the Governor’s Office, explained the key changes in the revised proposal:
- Removal of fracking wastewater projects from the measure
- Expansion of the scope to include a “broader universe” of brackish water resources
- Allowance for shallower wells to be tapped, with safeguards for existing water rights
These modifications aim to address concerns raised by lawmakers and stakeholders while maintaining the core objective of securing a sustainable water supply for New Mexico.
The Urgent Need for Water Solutions in New Mexico
“Climate change has exacerbated New Mexico’s water shortages, with some regions experiencing up to 20% reduction in annual precipitation.”
New Mexico, like many states in the American Southwest, is grappling with severe water shortages. Climate change is amplifying these challenges, leading to more frequent and intense droughts, reduced snowpack, and increased evaporation rates. The urgency of the situation cannot be overstated, as it affects not only our environment but also our economy, agriculture, and way of life.
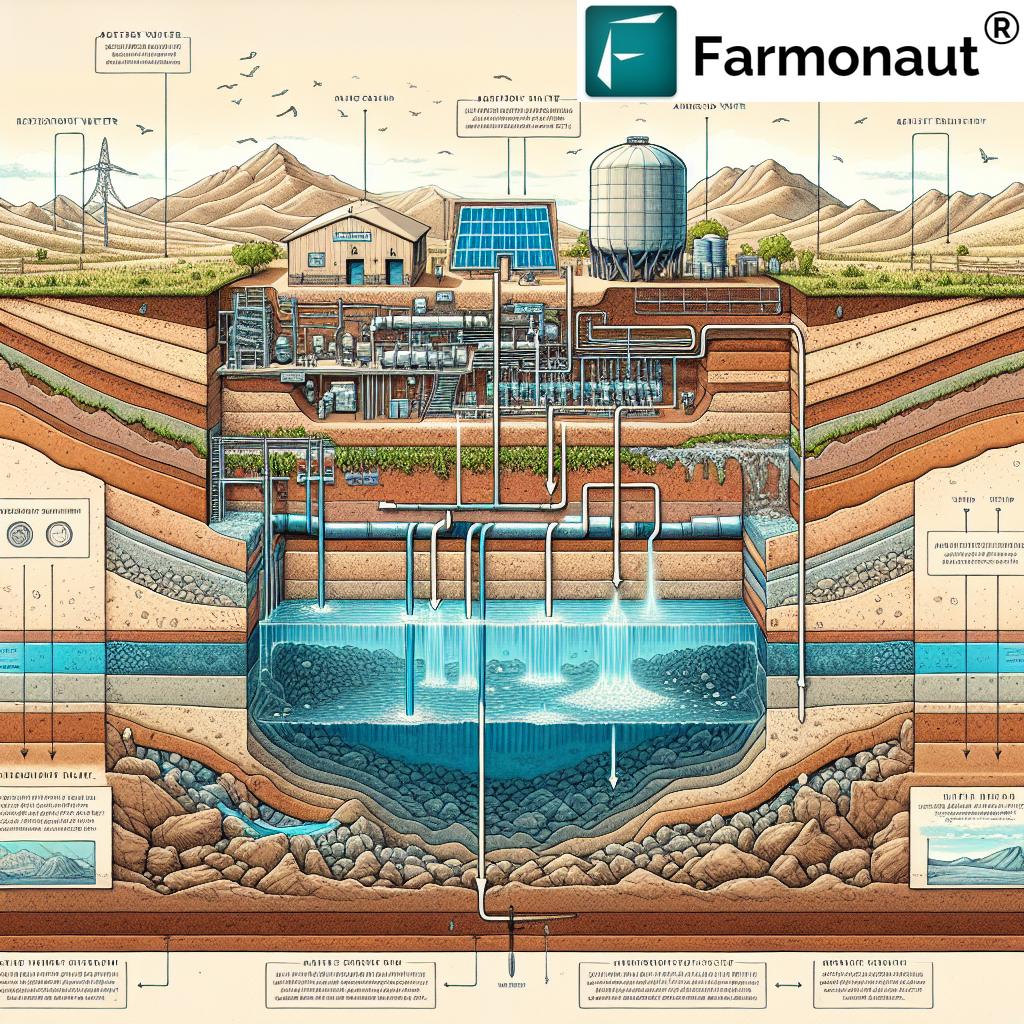
Exploring Brackish Water as a Sustainable Resource
At the heart of New Mexico’s strategic water supply plan is the focus on brackish water resources. Brackish water is naturally occurring salty water found in underground aquifers. While not suitable for direct consumption or agricultural use, it presents a promising opportunity when treated properly.
Key aspects of the brackish water strategy include:
- Identifying and mapping brackish aquifers across the state
- Developing and implementing cost-effective desalination technologies
- Ensuring sustainable extraction rates to prevent aquifer depletion
- Addressing environmental concerns related to brine disposal
By tapping into these vast reserves of brackish water, New Mexico aims to secure a reliable water source that can supplement existing freshwater supplies and reduce pressure on overtaxed rivers and aquifers.
Innovative Water Management Solutions
In addition to brackish water treatment, New Mexico’s strategic plan encompasses a range of innovative water management solutions. These include:
- Advanced Water Recycling Technologies: Implementing state-of-the-art water recycling systems to maximize the reuse of treated wastewater for non-potable purposes.
- Aquifer Recharge and Storage: Developing projects to replenish groundwater aquifers during wet periods for use during droughts.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: Promoting the adoption of precision agriculture techniques and smart irrigation technologies to reduce water waste in the agricultural sector.
- Water-Efficient Urban Design: Encouraging water-conscious urban planning and landscaping to minimize water consumption in cities and towns.
These solutions aim to create a more resilient and sustainable water management system for New Mexico, capable of withstanding the challenges posed by climate change and population growth.
The Role of Technology in Water Conservation
As we strive to implement these innovative water management solutions, technology plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and effectiveness. Advanced monitoring systems, data analytics, and artificial intelligence are being leveraged to optimize water use across various sectors.
For instance, Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company, offers satellite-based farm management solutions that can significantly contribute to water conservation efforts in agriculture. Their platform provides real-time crop health monitoring and AI-based advisory systems, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions about irrigation and resource management.
Balancing Industrial Needs with Environmental Concerns
One of the most challenging aspects of New Mexico’s water strategy is striking a balance between industrial water needs and environmental protection. The state’s economy relies heavily on water-intensive industries such as agriculture, mining, and energy production. However, these activities can put significant strain on water resources and ecosystems.
The strategic water supply plan aims to address this balance through several measures:
- Incentivizing water-efficient practices in industry
- Promoting the use of recycled water for industrial processes
- Implementing stricter regulations on water use and discharge in industrial operations
- Encouraging the adoption of clean technologies that reduce water consumption
By fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders and environmental advocates, New Mexico hopes to create a sustainable water management framework that supports economic growth while protecting our precious natural resources.
Legislative Challenges and Public Engagement
The path to implementing New Mexico’s strategic water supply plan has not been without obstacles. Legislative debates and public concerns have shaped the evolution of the proposal. Key challenges include:
- Securing adequate funding for water infrastructure projects
- Addressing concerns about potential environmental impacts
- Navigating complex water rights issues
- Building public trust and support for new water management strategies
To overcome these challenges, the state government has emphasized transparency and public engagement throughout the planning process. Town halls, public hearings, and educational campaigns have been organized to inform citizens and gather feedback on proposed water management solutions.
Comparative Analysis of Water Management Strategies
To better understand the various approaches being considered in New Mexico’s water management plan, let’s examine a comparative analysis of key strategies:
| Strategy Name | Estimated Water Yield (acre-feet/year) | Implementation Cost ($ millions) | Environmental Impact | Timeline for Implementation (years) | Sustainability Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brackish Aquifer Treatment | 50,000 – 100,000 | 200 – 500 | Medium | 5 – 10 | 8 |
| Water Recycling Technologies | 30,000 – 60,000 | 100 – 300 | Low | 3 – 7 | 9 |
| Aquifer Conservation Measures | 20,000 – 40,000 | 50 – 150 | Low | 2 – 5 | 10 |
| Industrial Water Use Optimization | 15,000 – 30,000 | 75 – 200 | Medium | 3 – 6 | 7 |
This comparison highlights the diverse approaches being considered, each with its own set of benefits and challenges. The sustainability score takes into account long-term viability, environmental impact, and resource efficiency.
The Role of Climate Change in Water Policy
Climate change is a critical factor driving New Mexico’s water policy decisions. As temperatures rise and precipitation patterns become more erratic, traditional water management approaches are proving inadequate. The strategic water supply plan acknowledges this reality and incorporates climate resilience as a core principle.
Key climate-related considerations in the plan include:
- Projecting future water availability based on climate models
- Developing adaptive management strategies to respond to changing conditions
- Investing in climate-resilient water infrastructure
- Promoting water conservation as a means of reducing vulnerability to climate impacts
By prioritizing climate resilience, New Mexico aims to create a water management system that can withstand the uncertainties of a changing climate and ensure long-term water security for its residents.
Leveraging Technology for Efficient Water Management
As we strive to implement these innovative water management solutions, technology plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and effectiveness. Advanced monitoring systems, data analytics, and artificial intelligence are being leveraged to optimize water use across various sectors.
For instance, agricultural technology companies like Farmonaut offer satellite-based farm management solutions that can significantly contribute to water conservation efforts in agriculture. Their platform provides real-time crop health monitoring and AI-based advisory systems, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions about irrigation and resource management.
To explore Farmonaut’s innovative solutions, you can access their services through various platforms:
For developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s technology into their own systems, the company offers a robust API with comprehensive documentation.
Public Engagement and Education
The success of New Mexico’s water management strategy depends heavily on public understanding and support. To this end, the state has launched several initiatives aimed at educating citizens about water conservation and the importance of sustainable water management:
- School programs to teach students about water conservation
- Community workshops on water-saving techniques for homes and gardens
- Public awareness campaigns highlighting the state’s water challenges
- Citizen science projects to engage the public in water quality monitoring
These efforts aim to create a culture of water consciousness and empower individuals to contribute to the state’s water conservation goals.
Economic Implications of Water Management
The implementation of New Mexico’s strategic water supply plan has significant economic implications. While the upfront costs of infrastructure development and technology adoption are substantial, the long-term benefits are expected to outweigh these investments:
- Job creation in water treatment, technology, and conservation sectors
- Increased agricultural productivity through more efficient water use
- Enhanced economic stability by reducing vulnerability to water shortages
- Potential for exporting water management expertise and technology
Moreover, by securing a stable water supply, New Mexico can attract new businesses and industries, further diversifying its economy and creating additional opportunities for growth.
Collaboration with Neighboring States
Water management in the American Southwest requires cooperation across state lines. New Mexico’s strategic plan recognizes the importance of collaboration with neighboring states to address shared water challenges. Key areas of interstate cooperation include:
- Coordinated management of shared river basins
- Joint research initiatives on water conservation technologies
- Information sharing on best practices in water management
- Collaborative efforts to secure federal funding for regional water projects
By working together, states in the region can develop more comprehensive and effective solutions to their common water scarcity issues.
Looking to the Future: Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
New Mexico’s strategic water supply plan is not a static document but a living strategy that will evolve as new challenges arise and technologies emerge. The state is committed to continuous improvement and adaptation of its water management approaches. This includes:
- Regular review and update of water policies and regulations
- Ongoing investment in research and development of water technologies
- Flexible management strategies that can adapt to changing climatic conditions
- Continuous monitoring and assessment of water resources and usage patterns
By maintaining this adaptive approach, New Mexico aims to stay at the forefront of sustainable water management and ensure long-term water security for its residents.
Conclusion: A Model for Sustainable Water Management
New Mexico’s strategic water supply plan represents a bold and innovative approach to addressing severe water shortages in a changing climate. By focusing on sustainable groundwater utilization, advanced water treatment technologies, and comprehensive resource management, the state is paving the way for a more water-secure future.
While challenges remain, the evolving strategy demonstrates New Mexico’s commitment to balancing economic needs with environmental stewardship. As the plan continues to develop and be implemented, it has the potential to serve as a model for other regions facing similar water scarcity issues.
The success of this initiative will depend on ongoing collaboration between policymakers, scientists, industry leaders, and the public. By working together and leveraging innovative technologies like those offered by companies such as Farmonaut, New Mexico can transform its water challenges into opportunities for sustainable growth and resilience.
FAQ Section
- What is brackish water, and why is it important for New Mexico’s water strategy?
Brackish water is naturally occurring salty water found in underground aquifers. It’s important because it represents a vast, untapped water resource that, when properly treated, can supplement existing freshwater supplies and reduce pressure on overtaxed rivers and aquifers. - How does climate change impact New Mexico’s water supply?
Climate change leads to more frequent and intense droughts, reduced snowpack, and increased evaporation rates. This exacerbates water scarcity and makes traditional water management approaches less effective. - What role does technology play in New Mexico’s water management plan?
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and effectiveness of water management. This includes advanced monitoring systems, data analytics, AI-driven decision-making tools, and innovative water treatment technologies. - How is New Mexico balancing industrial water needs with environmental concerns?
The state is implementing measures such as incentivizing water-efficient practices in industry, promoting the use of recycled water for industrial processes, and implementing stricter regulations on water use and discharge in industrial operations. - What are some of the economic implications of New Mexico’s water management strategy?
The strategy is expected to create jobs in water treatment and conservation sectors, increase agricultural productivity, enhance economic stability, and potentially create opportunities for exporting water management expertise and technology.
Earn With Farmonaut
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Farmonaut Subscriptions







