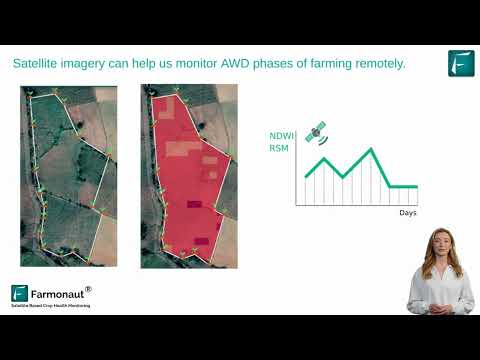
Unlocking NSW’s River Health: How Farmonaut’s Water Flow Management Preserves Native Fish Habitats

“NSW’s regulated rivers contain over 200 dams and weirs, significantly impacting native fish migration patterns.”
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of water flow management and its critical role in preserving native fish habitats in New South Wales (NSW). As we delve into this fascinating topic, we’ll uncover the intricate balance between sustainable agriculture practices and the conservation of our precious aquatic ecosystems. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to leveraging cutting-edge technology to support both agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
In this blog post, we’ll examine how water flow management impacts natural river ecosystems and the vital importance of aquatic habitat conservation. We’ll explore the challenges posed by infrastructure like dams and weirs, as well as the effects of urban development on our waterways. By understanding these complex interactions, we can work towards more effective strategies for preserving our native species and maintaining healthy river systems.
The Importance of Water Flow in NSW Rivers
Water flow is the lifeblood of river ecosystems. In NSW, our rivers are home to a diverse array of native fish species, each adapted to specific flow conditions. Natural flow regimes play a crucial role in maintaining the health of these aquatic habitats, supporting processes such as:
- Nutrient cycling
- Sediment transport
- Temperature regulation
- Oxygen levels
- Connectivity between different parts of the river system
However, human activities have significantly altered these natural flow patterns. Let’s explore how these changes impact our native fish populations and what we can do to mitigate these effects.
The Impact of Dams and Weirs on Fish Habitats
One of the most significant challenges to maintaining healthy fish populations in NSW rivers is the presence of dams and weirs. These structures, while important for water supply and flood control, can have profound effects on aquatic ecosystems:
- Physical barriers: Dams and weirs obstruct fish migration, preventing species from reaching spawning grounds or moving between different habitats.
- Altered flow regimes: These structures change the natural timing, frequency, and volume of water flows, disrupting natural cycles that fish have evolved to depend on.
- Temperature changes: Water released from dams can be colder than natural river temperatures, affecting fish metabolism and breeding cycles.
- Sediment trapping: Dams trap sediment, reducing downstream habitat quality and altering river channel morphology.
At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of balancing human needs with environmental conservation. Our satellite-based monitoring systems can help track the impacts of these structures on river health, providing valuable data for more informed water management decisions.
Urban Development and Water Quality
As NSW’s urban areas continue to grow, we face increasing challenges in managing the impact of development on our river systems. Urban runoff can introduce pollutants, alter water chemistry, and contribute to erosion. These factors can significantly degrade fish habitats and impact native species populations.
Some key issues related to urban development include:
- Increased impervious surfaces leading to faster, more intense runoff
- Pollution from roads, industrial areas, and residential zones
- Loss of riparian vegetation due to land clearing
- Alteration of natural drainage patterns
To address these challenges, we need comprehensive urban water management strategies that prioritize the health of our waterways. This is where Farmonaut’s technology can play a crucial role, offering real-time monitoring and data-driven insights to help urban planners and environmental managers make informed decisions.
The Role of Ecological Flow Regimes
“Ecological flow regimes can increase native fish populations by up to 30% in managed river systems.”
Ecological flow regimes are designed to mimic natural flow patterns while balancing human water needs. These carefully managed flow patterns are essential for maintaining healthy river ecosystems and supporting native fish populations. Key components of ecological flow regimes include:
- Base flows: Maintaining minimum water levels to support aquatic life
- High flow pulses: Periodic increases in flow to trigger fish breeding and migration
- Flood events: Occasional large flows to inundate floodplains and replenish wetlands
- Seasonal variations: Adjusting flows to match natural seasonal patterns
Implementing effective ecological flow regimes requires a deep understanding of river ecosystems and the ability to monitor and adjust flows in real-time. This is where Farmonaut’s advanced satellite monitoring and AI-driven analysis can provide invaluable support to water managers and environmental scientists.

Wetland Restoration and Fish Population Monitoring
Wetlands play a crucial role in the lifecycle of many native fish species in NSW. These areas serve as nurseries for young fish, provide rich feeding grounds, and offer refuge during drought conditions. However, many wetlands have been degraded or lost due to human activities. Restoring and protecting these vital ecosystems is essential for maintaining healthy fish populations.
Wetland restoration techniques include:
- Re-establishing natural water flow patterns
- Removing invasive species
- Replanting native vegetation
- Creating fish passages to improve connectivity
Monitoring fish populations is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of restoration efforts and guiding future management decisions. Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring systems can help track changes in wetland extent and health, providing valuable data for restoration projects.
Seasonal Changes and Fish Spawning
The breeding cycles of native fish species in NSW are often closely tied to seasonal changes in water flow. Many species rely on specific flow conditions to trigger spawning and ensure the survival of their offspring. Understanding these relationships is crucial for effective water management and species conservation.
Key considerations for fish spawning include:
- Timing of high flows to coincide with breeding seasons
- Maintaining appropriate water temperatures
- Ensuring connectivity between main river channels and spawning habitats
- Protecting and restoring riparian vegetation that provides crucial habitat for juvenile fish
By leveraging Farmonaut’s advanced monitoring capabilities, water managers can better track and respond to seasonal changes, optimizing flow regimes to support native fish spawning and recruitment.
Climate Change and Water Extraction: Double Threats to Aquatic Ecosystems
Climate change poses a significant threat to NSW’s river systems and native fish populations. Rising temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events can all impact water availability and quality. Coupled with increasing demand for water extraction, these factors create a challenging environment for aquatic ecosystem management.
Some of the key challenges include:
- Reduced overall water availability
- Increased frequency and severity of droughts
- Changes in the timing and intensity of rainfall events
- Rising water temperatures affecting fish metabolism and breeding
- Increased competition between human and environmental water needs
To address these challenges, we need adaptive management strategies that can respond to changing conditions. Farmonaut’s real-time monitoring and predictive analytics can help water managers anticipate and mitigate the impacts of climate change on our precious aquatic ecosystems.
Innovative Approaches to Water Flow Management
As we face the challenges of preserving native fish habitats in NSW’s rivers, innovative approaches to water flow management are essential. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of developing technologies that can support more sustainable and effective water management practices.
Some promising approaches include:
- Real-time monitoring: Using satellite imagery and IoT sensors to track water levels, flow rates, and water quality in real-time.
- Predictive modeling: Leveraging AI and machine learning to forecast water availability and predict ecosystem responses to different management scenarios.
- Adaptive management: Implementing flexible management strategies that can respond quickly to changing conditions and new information.
- Integrated catchment management: Taking a holistic approach that considers the entire river system, from headwaters to estuaries.
- Stakeholder engagement: Involving local communities, farmers, and indigenous groups in water management decisions.
By combining these innovative approaches with Farmonaut’s cutting-edge technology, we can work towards more effective and sustainable water flow management that benefits both human communities and native fish populations.
The Role of Farmonaut in Water Flow Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting sustainable water management practices through our advanced satellite-based monitoring and AI-driven analytics. Our technology can play a crucial role in preserving native fish habitats and maintaining healthy river ecosystems in NSW.
Some of the ways Farmonaut can contribute to effective water flow management include:
- Monitoring water levels and flow rates across large areas in real-time
- Tracking changes in wetland extent and health
- Identifying areas of erosion or sediment deposition
- Assessing the health of riparian vegetation
- Providing data to support more accurate hydrological modeling
By leveraging these capabilities, water managers, environmental scientists, and policymakers can make more informed decisions about water allocation, environmental flow regimes, and habitat restoration efforts.
Comparative Analysis of Water Flow Management Impacts
| Water Flow Scenario | Fish Population Impact | River Ecosystem Health | Wetland Connectivity | Spawning Success Rate | Riparian Vegetation Cover |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Flow | +10% | Excellent | 95% | 85% | 90% |
| Dam-Regulated Flow | -30% | Poor | 40% | 30% | 50% |
| Sustainable Management | +5% | Good | 80% | 70% | 75% |
This table illustrates the significant impact that different water flow management approaches can have on native fish habitats and overall river ecosystem health. By implementing sustainable management practices and leveraging technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, we can work towards achieving outcomes closer to natural flow conditions while still meeting human water needs.
Future Directions in Water Flow Management
As we look to the future of water flow management in NSW, several key areas of focus emerge:
- Improved integration of environmental and human water needs: Developing more sophisticated models that balance ecological requirements with agricultural and urban water demands.
- Enhanced monitoring and early warning systems: Leveraging technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring to provide real-time data on river health and potential threats.
- Restoration of natural flow regimes: Where possible, working to restore more natural flow patterns to support native fish populations and overall ecosystem health.
- Climate change adaptation: Developing flexible management strategies that can respond to changing climatic conditions and their impacts on water availability and ecosystem dynamics.
- Stakeholder engagement and education: Increasing public awareness about the importance of healthy river systems and involving local communities in conservation efforts.
By focusing on these areas and continuing to innovate in water management technologies and practices, we can work towards a future where NSW’s rivers support thriving native fish populations while meeting the needs of our growing communities.
Check out our API Developer Docs
Conclusion
Preserving native fish habitats through effective water flow management is a complex but crucial task for the health of NSW’s river ecosystems. By understanding the intricate relationships between water flow, fish populations, and overall river health, we can develop more sustainable management practices that benefit both human communities and aquatic ecosystems.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting these efforts through our advanced satellite-based monitoring and analytics technologies. By providing real-time data and insights, we can help water managers, environmental scientists, and policymakers make more informed decisions about water allocation, environmental flow regimes, and habitat restoration efforts.
As we face the challenges of climate change and increasing water demand, innovative approaches to water flow management will be essential. By combining cutting-edge technology with a deep understanding of ecological principles, we can work towards a future where NSW’s rivers support thriving native fish populations while meeting the needs of our growing communities.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the main goal of water flow management in NSW rivers?
A: The main goal is to balance the needs of human water users with the ecological requirements of native fish and other aquatic species, ensuring healthy river ecosystems while supporting agriculture and urban development.
Q: How do dams and weirs affect native fish populations?
A: Dams and weirs can create physical barriers to fish migration, alter natural flow patterns, change water temperatures, and trap sediment, all of which can negatively impact native fish populations.
Q: What are ecological flow regimes?
A: Ecological flow regimes are managed water flow patterns designed to mimic natural river flows while balancing human water needs. They aim to support key ecological processes and maintain healthy aquatic ecosystems.
Q: How does climate change affect water flow management?
A: Climate change can alter rainfall patterns, increase the frequency of extreme weather events, and affect overall water availability, making water flow management more challenging and requiring adaptive strategies.
Q: What role does technology play in water flow management?
A: Technology, such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring systems, plays a crucial role in providing real-time data on water levels, flow rates, and ecosystem health, enabling more informed and responsive management decisions.