Global Agricultural Tariffs: How US-India Trade Barriers Impact Farmers and International Markets
“India imposes tariffs up to 150% on US agricultural products, significantly impacting American farmers’ market access.”
In the complex world of international trade, agricultural tariffs play a pivotal role in shaping global market dynamics and farmers’ livelihoods. As we delve into the intricate web of trade barriers between major economies like the United States and India, we uncover a landscape fraught with challenges and opportunities for farmers, policymakers, and consumers alike.
The impact of these trade barriers extends far beyond national borders, influencing everything from crop prices to diplomatic relations. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll examine how US-India trade barriers, along with those imposed by other nations, are reshaping the agricultural sector and international markets.
Understanding International Trade Tariffs in Agriculture
International trade tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, designed to protect domestic industries and generate revenue for governments. In the realm of agriculture, these tariffs can have far-reaching consequences, affecting farmers’ incomes, consumer prices, and global food security.
Agricultural import duties, a specific type of tariff, are particularly contentious in international trade negotiations. These duties can significantly increase the cost of imported agricultural products, making them less competitive in foreign markets. As a result, farmers often find themselves caught in the crossfire of trade disputes between nations.
The US-India Tariff Tussle: A Deep Dive
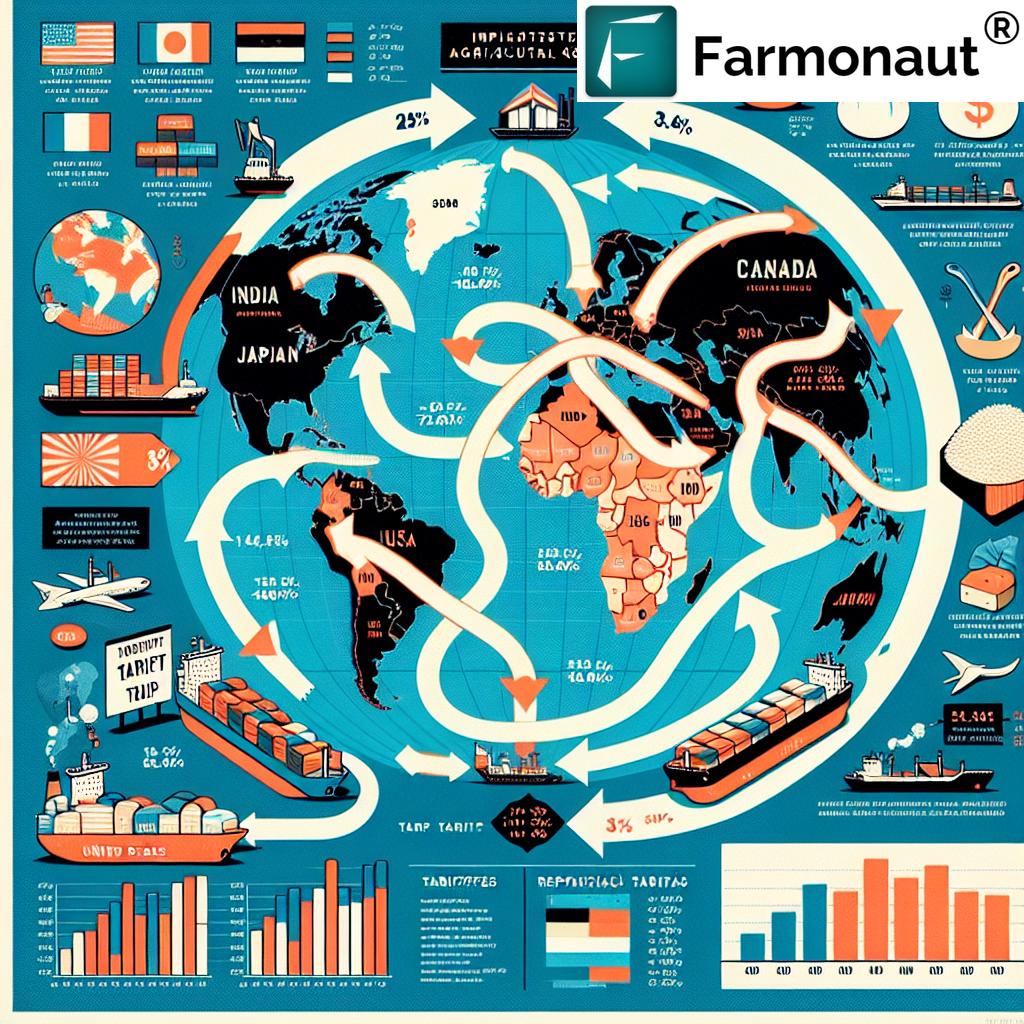
The trade relationship between the United States and India has been marked by ongoing tensions, particularly in the agricultural sector. India’s high tariffs on American agricultural products have been a point of contention, with the White House citing them as a major barrier to fair trade.
According to recent statements, India imposes a staggering 100% tariff on certain American agricultural products. This makes it “virtually impossible” for these goods to compete in the Indian market, effectively shutting out US farmers from one of the world’s largest consumer bases.
Key Products Affected by High Tariffs
- Dairy products
- Rice
- Fruits and nuts
- Processed foods
These high tariffs not only impact US exporters but also limit choices for Indian consumers and potentially drive up food prices in the country.
US Export Challenges: A Global Perspective
While India’s tariffs are particularly high, the United States faces similar challenges in other major markets. For instance:
- The European Union imposes a 50% tariff on American dairy products
- Japan maintains a 700% tariff on American rice
- Canada levies nearly 300% tariffs on American butter and cheese
These trade barriers create significant hurdles for US agricultural exports, impacting farmers’ incomes and the overall competitiveness of American agriculture in the global market.
The Concept of Reciprocal Tariffs
In response to these high tariffs, the United States has been considering the implementation of reciprocal tariffs. This approach aims to level the playing field by imposing similar tariffs on imported goods from countries that maintain high barriers to US products.
President Trump has announced plans to roll out a set of reciprocal tariffs on April 2, which he refers to as “Liberation Day” for the US. This move could potentially reshape global trade relations and have significant implications for farmers and consumers worldwide.
Impact on Farmers and International Markets
The ongoing tariff disputes have far-reaching consequences for farmers and international agricultural markets:
- Reduced Market Access: High tariffs make it difficult for farmers to access foreign markets, limiting their potential customer base and revenue streams.
- Price Fluctuations: Tariffs can lead to price volatility in agricultural commodities, affecting farmers’ income stability and consumers’ purchasing power.
- Shifts in Production Patterns: As certain markets become less accessible due to tariffs, farmers may need to shift their production to other crops or seek alternative markets.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Tariffs can disrupt established supply chains, forcing businesses to seek new suppliers or alter their operations.
In this challenging environment, farmers and agribusinesses are increasingly turning to technology to optimize their operations and navigate market uncertainties. Platforms like Farmonaut offer valuable tools for precision agriculture, helping farmers make data-driven decisions to improve yields and reduce costs.

Trade Policy Changes on the Horizon
As the global trade landscape continues to evolve, several key policy changes are on the horizon that could significantly impact agricultural trade:
- Reciprocal Tariffs: The proposed implementation of reciprocal tariffs by the US could lead to a reshuffling of global trade relationships.
- Trade Negotiations: Ongoing negotiations between major economies may result in new trade agreements that alter existing tariff structures.
- WTO Reforms: Efforts to reform the World Trade Organization could lead to new rules governing international trade disputes and tariff implementations.
- Sustainability Measures: Increasing focus on sustainable agriculture may lead to new trade policies that prioritize environmentally friendly farming practices.
These potential changes underscore the importance of staying informed and adaptable in the face of evolving trade policies. Farmers and agribusinesses can leverage tools like Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory services to make informed decisions based on real-time market data and environmental factors.
“Trade barriers affect over $100 billion worth of global agricultural trade annually, reshaping international market dynamics.”
The Role of Technology in Navigating Trade Challenges
As farmers and agribusinesses grapple with the complexities of international trade barriers, technology is emerging as a crucial tool for adaptation and resilience. Advanced agricultural technologies can help mitigate some of the challenges posed by trade restrictions:
- Precision Agriculture: By optimizing resource use and improving yields, precision farming techniques can help offset some of the financial impacts of reduced market access.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Access to real-time market data and crop health information allows farmers to make informed decisions about what to grow and when to sell.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain-based traceability solutions can enhance trust in agricultural products, potentially opening new market opportunities despite trade barriers.
Farmonaut’s suite of tools, including its carbon footprinting service, can help farmers and agribusinesses adapt to changing market conditions by providing valuable insights into their operations and environmental impact.
Comparative Tariff Rate Table
| Agricultural Product | US Export Value (est.) | India Tariff Rate | Japan Tariff Rate | Canada Tariff Rate | EU Tariff Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy Products | $5 billion | 100% | 150% | 300% | 50% |
| Rice | $2 billion | 70% | 700% | 0% | 65% |
| Soybeans | $20 billion | 30% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Wheat | $6 billion | 40% | 200% | 0% | 12% |
| Corn | $8 billion | 60% | 50% | 0% | 5% |
| Beef | $7 billion | 50% | 38% | 26% | 12% |
This table illustrates the stark differences in tariff rates across different countries and products, highlighting the challenges faced by US exporters in accessing these markets.
The Ripple Effects of Trade Barriers
The impact of high agricultural tariffs extends far beyond the immediate concerns of farmers and exporters. These trade barriers can have wide-reaching effects on various aspects of the global economy and society:
- Food Security: High tariffs can limit the diversification of food sources, potentially impacting food security in importing countries.
- Rural Economies: As farmers struggle with reduced export opportunities, rural communities that depend on agriculture may face economic challenges.
- Innovation: Trade barriers can sometimes stifle innovation by limiting competition and reducing incentives for efficiency improvements.
- Diplomatic Relations: Ongoing trade disputes can strain diplomatic ties between nations, potentially affecting cooperation in other areas.
To navigate these complex issues, stakeholders across the agricultural value chain are increasingly turning to data-driven solutions. Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management tools can help agribusinesses optimize their operations and adapt to changing market conditions.
The Path Forward: Balancing Protection and Free Trade
As nations grapple with the complexities of international trade, finding a balance between protecting domestic industries and promoting free trade remains a significant challenge. Several potential strategies are being explored to address the issues surrounding agricultural tariffs:
- Bilateral Negotiations: Direct negotiations between countries to reduce tariffs on specific products or sectors.
- Multilateral Agreements: Broader trade agreements involving multiple nations, aimed at reducing overall trade barriers.
- Targeted Support Programs: Domestic policies that support farmers without resorting to high tariffs, such as direct subsidies or investment in agricultural research and development.
- Trade Facilitation Measures: Efforts to streamline customs procedures and reduce non-tariff barriers to trade.
As these discussions continue, farmers and agribusinesses must remain agile and informed. Tools like Farmonaut’s fleet management system can help optimize logistics and reduce costs, providing a competitive edge in challenging market conditions.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Agricultural Trade
As we navigate the complex landscape of international agricultural trade, technology is emerging as a powerful force for change and adaptation. Advanced agricultural technologies are not only helping farmers improve productivity but also enabling them to respond more effectively to market challenges posed by trade barriers:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Technologies like those offered by Farmonaut allow farmers to monitor crop health and predict yields with greater accuracy, enabling better planning and risk management in the face of market uncertainties.
- AI-Driven Advisory Systems: Artificial intelligence can analyze vast amounts of data to provide farmers with personalized recommendations, helping them optimize their operations and adapt to changing market conditions.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Blockchain technology can enhance transparency in agricultural supply chains, potentially reducing non-tariff barriers related to food safety and quality standards.
- Digital Marketplaces: Online platforms can connect farmers directly with buyers across borders, potentially mitigating some of the impacts of trade barriers.
By leveraging these technologies, farmers and agribusinesses can enhance their resilience to trade-related challenges and explore new opportunities in the global market.
The Future of Agricultural Trade: Trends and Predictions
As we look to the future of agricultural trade, several key trends are likely to shape the landscape:
- Increasing Focus on Sustainability: Trade policies may increasingly incorporate environmental considerations, potentially favoring producers who can demonstrate sustainable practices.
- Rise of Regional Trade Blocs: We may see a shift towards stronger regional trade agreements as an alternative to global multilateral deals.
- Technology-Driven Trade: Digital technologies are likely to play an increasingly important role in facilitating trade, from online marketplaces to blockchain-based customs processes.
- Emphasis on Food Security: Countries may prioritize domestic food security, potentially leading to new approaches in agricultural trade policies.
In this evolving landscape, tools like Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance services can help farmers manage financial risks and access the capital needed to adapt to changing market conditions.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of Agricultural Trade
The challenges posed by international trade tariffs, particularly in the context of US-India relations, highlight the complex and often contentious nature of global agricultural trade. As farmers, policymakers, and consumers grapple with the impacts of these trade barriers, it’s clear that a multifaceted approach is needed to address the issues at hand.
While negotiations and policy changes will play a crucial role in shaping the future of agricultural trade, technology and innovation offer powerful tools for adaptation and resilience. By leveraging advanced agricultural technologies and data-driven insights, farmers and agribusinesses can navigate market uncertainties, optimize their operations, and explore new opportunities in the global marketplace.
As we move forward, it’s crucial to continue monitoring trade policy developments, embracing technological advancements, and fostering international cooperation to create a more equitable and sustainable global agricultural trade system. By doing so, we can work towards a future where farmers can thrive, consumers have access to diverse and affordable food options, and nations can balance their economic interests with the broader goals of global food security and environmental sustainability.
FAQ Section
- Q: What are agricultural tariffs?
A: Agricultural tariffs are taxes imposed on imported agricultural products, designed to protect domestic farmers and industries. - Q: How do high tariffs impact US farmers?
A: High tariffs make US agricultural products more expensive in foreign markets, reducing their competitiveness and limiting export opportunities for American farmers. - Q: What is a reciprocal tariff?
A: A reciprocal tariff is a retaliatory measure where a country imposes similar tariffs on imported goods from countries that maintain high barriers to its products. - Q: How can technology help farmers navigate trade challenges?
A: Technology can provide farmers with real-time market data, optimize crop management, and improve supply chain efficiency, helping them adapt to changing market conditions. - Q: What are some potential solutions to the current trade disputes?
A: Potential solutions include bilateral negotiations, multilateral trade agreements, domestic support programs for farmers, and trade facilitation measures.
Earn With Farmonaut: Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Watch our video to learn more about the Farmonaut affiliate program
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you navigate the challenges of international agricultural trade, visit our website:
Download our mobile apps:
For developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s satellite and weather data into their own applications, check out our API and API Developer Docs.