Unlocking Soil Secrets: How Micromorphology Revolutionizes Agricultural Analysis and Crop Management
“Soil micromorphology techniques can reveal details of soil structure as small as 1 micron, enhancing precision farming practices.”
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, understanding the intricate details of soil composition and structure has become increasingly crucial. At Farmonaut, we recognize the pivotal role that soil micromorphology techniques play in revolutionizing agricultural soil analysis. This advanced approach offers unprecedented insights into microscopic soil structure, paving the way for more informed and efficient crop management strategies.
In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the cutting-edge world of optical microscopy in agriculture and how digital soil imaging is transforming our understanding of soil formation processes. We’ll uncover the power of soil thin section analysis in revealing the intricate details of soil microstructure and mineralogy, and how these advanced techniques contribute to precision farming.
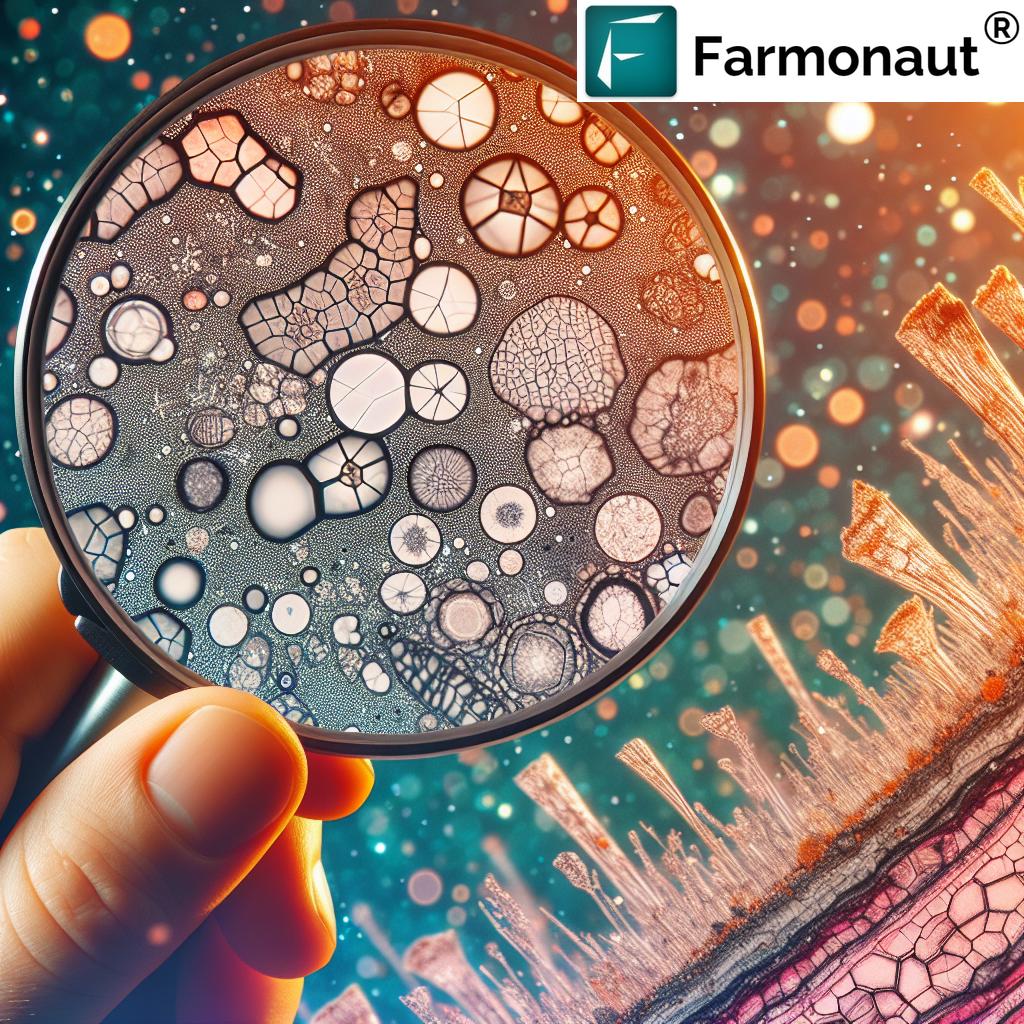
The Foundation of Soil Micromorphology
Soil micromorphology is a specialized branch of soil science that focuses on the microscopic examination of soil samples. This technique allows us to observe and analyze the arrangement of soil particles, organic matter, and pore spaces at a scale that was previously unimaginable. By employing advanced optical microscopy and digital imaging technologies, we can now peer into the hidden world beneath our feet with unprecedented clarity.
The primary tools in soil micromorphology include:
- High-powered optical microscopes
- Polarized light microscopes
- Digital imaging systems
- Soil thin section preparation equipment
These tools work in concert to provide a comprehensive view of soil structure, mineral composition, and organic matter distribution. The insights gained from these analyses are invaluable for improving agricultural practices and optimizing crop yield.
Optical Microscopy in Agriculture: A Game-Changer
Optical microscopy has long been a staple in geological and biological sciences, but its application in agriculture has opened new frontiers in soil analysis. In the context of agriculture, optical microscopy allows us to:
- Identify and characterize soil minerals
- Observe soil microstructure and pore spaces
- Analyze the distribution of organic matter
- Study soil-root interactions at a microscopic level
By employing various optical techniques, such as brightfield, darkfield, and polarized light microscopy, we can gather a wealth of information about soil properties that directly influence crop growth and health.
The Power of Soil Thin Section Analysis
One of the most powerful tools in soil micromorphology is thin section analysis. This technique involves creating ultra-thin slices of soil samples, typically 20-30 micrometers thick, which can be examined under a microscope. Soil thin section analysis provides unparalleled insights into:
- Soil fabric and structure
- Mineral composition and weathering patterns
- Organic matter decomposition
- Soil formation processes
- Microbial activity and its effects on soil properties
By studying these thin sections, we can unravel the complex relationships between soil components and their influence on soil fertility and crop growth. This level of detail is crucial for developing targeted soil management strategies that can significantly boost agricultural productivity.
At Farmonaut, we leverage these advanced soil science applications to provide farmers with actionable data on soil properties and mineral composition. Our innovative approach combines traditional soil science with modern technology, offering a comprehensive solution for precision farming.
Digital Soil Imaging: A New Frontier
The advent of digital imaging technologies has revolutionized soil micromorphology. Digital soil imaging allows us to capture, store, and analyze high-resolution images of soil samples with unprecedented ease and accuracy. This technology offers several advantages:
- Rapid acquisition of large datasets
- Enhanced image processing and analysis capabilities
- Improved quantification of soil features
- Easy sharing and collaboration among researchers
By harnessing the power of digital soil imaging, we can quickly process vast amounts of soil data, leading to more comprehensive and accurate analyses of soil properties across large agricultural areas.
“Advanced optical microscopy in agriculture can analyze up to 1000 soil thin sections per day, revolutionizing soil formation studies.”
Unraveling Soil Formation Processes
One of the most significant contributions of soil micromorphology to agriculture is its ability to illuminate soil formation processes. By examining soil samples at a microscopic level, we can observe and interpret:
- Pedogenesis (soil development over time)
- Weathering of primary minerals
- Formation of secondary minerals
- Accumulation and transformation of organic matter
- Development of soil structure and porosity
Understanding these processes is crucial for predicting how soils will respond to different management practices and environmental changes. This knowledge allows farmers to make informed decisions about crop selection, irrigation strategies, and soil amendment applications.
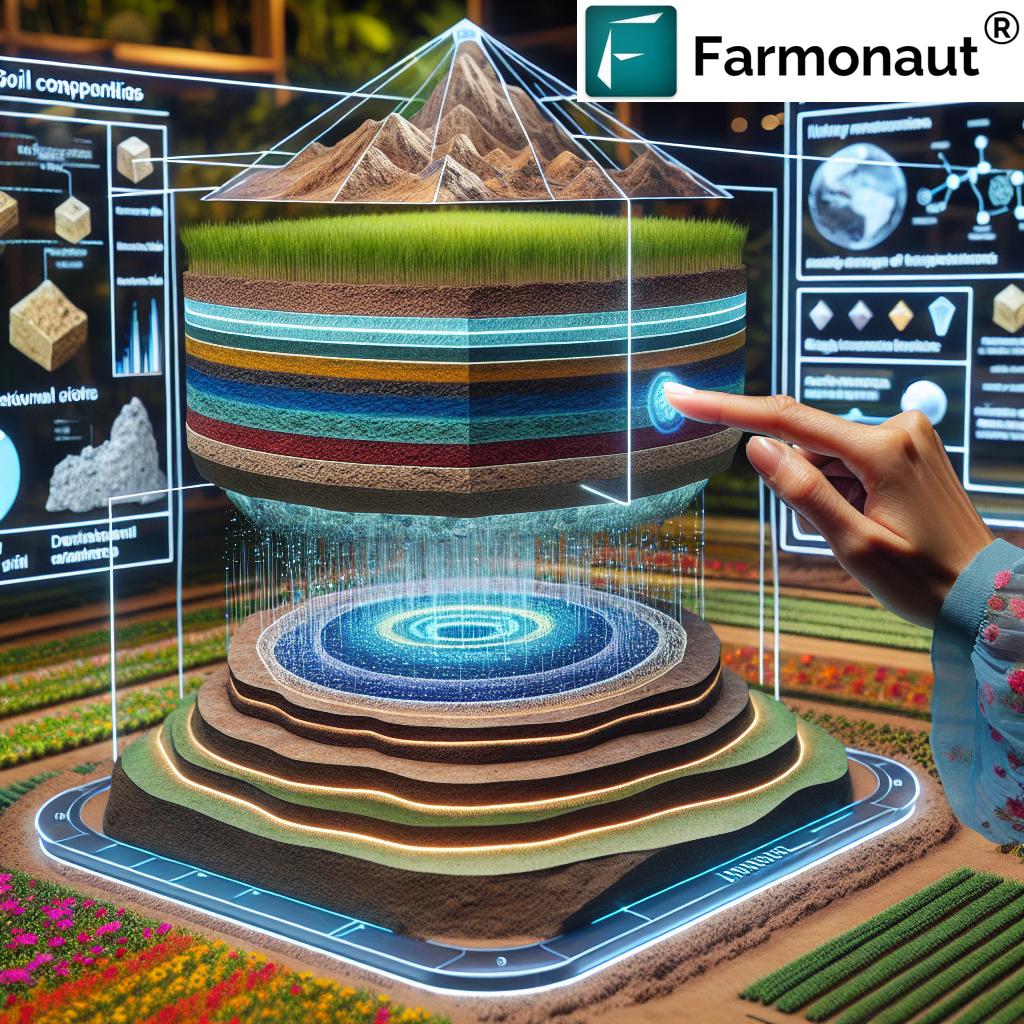
Soil Microstructure Analysis: The Key to Soil Health
Soil microstructure refers to the arrangement of soil particles, aggregates, and pore spaces at the microscopic level. This structure plays a critical role in:
- Water retention and movement
- Aeration and gas exchange
- Root penetration and growth
- Nutrient availability and cycling
- Microbial habitat and activity
Through soil micromorphology techniques, we can visualize and quantify these microstructural features, providing valuable insights into soil health and fertility. This information is essential for developing sustainable soil management practices that promote long-term agricultural productivity.
Agricultural Soil Mineralogy: Unveiling the Building Blocks
The mineral composition of soil is a crucial factor in determining its fertility and suitability for different crops. Soil micromorphology allows us to identify and characterize soil minerals with remarkable precision. This includes:
- Primary minerals (e.g., quartz, feldspars, micas)
- Secondary minerals (e.g., clay minerals, iron oxides)
- Amorphous materials (e.g., volcanic glass, organic compounds)
By understanding the mineralogical makeup of soils, we can better predict their behavior under different environmental conditions and management practices. This knowledge is invaluable for optimizing fertilizer applications, managing soil pH, and selecting crops that are best suited to specific soil types.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring system complements these soil analysis techniques, providing a comprehensive view of soil-crop interactions. Our AI-driven Jeevn advisory system integrates soil data with satellite imagery to deliver personalized recommendations for optimal crop management.
Interpreting Complex Soil Features
Soil micromorphology techniques allow us to observe and interpret a wide range of complex soil features that are invisible to the naked eye. These include:
- Cutans (clay coatings on soil particles)
- Pedofeatures (concretions, nodules, and other soil formations)
- Microstructures (aggregates, peds, and pore networks)
- Biological features (root channels, faunal excrement, microbial colonies)
Interpreting these features provides valuable information about soil-forming processes, past environmental conditions, and the impact of human activities on soil properties. This knowledge is crucial for developing sustainable land management practices and predicting how soils will respond to climate change and other environmental pressures.
Analyzing Water Retention Capabilities
Water is a critical factor in agriculture, and understanding how soils retain and transmit water is essential for effective crop management. Soil micromorphology techniques allow us to examine the pore structure of soils in detail, providing insights into:
- Water holding capacity
- Infiltration rates
- Drainage characteristics
- Potential for waterlogging or drought stress
By analyzing the size, distribution, and connectivity of soil pores, we can make informed decisions about irrigation strategies, crop selection, and soil amendment practices to optimize water use efficiency in agriculture.
Enhancing Precision Farming Through Micromorphology
The insights gained from soil micromorphology have profound implications for precision farming. By understanding the microscopic properties of soils across a field, farmers can:
- Develop site-specific management zones
- Optimize fertilizer and pesticide applications
- Tailor irrigation practices to soil water dynamics
- Select crop varieties best suited to specific soil conditions
- Implement targeted soil improvement strategies
This level of precision allows for more efficient use of resources, reduced environmental impact, and improved crop yields. At Farmonaut, we integrate these soil science applications with our satellite-based monitoring and AI advisory systems to provide farmers with comprehensive, data-driven solutions for optimizing their agricultural practices.
Our platform’s API access allows developers and businesses to integrate Farmonaut’s satellite and weather data into their own systems, further enhancing the potential for precision farming applications. Learn more about our API capabilities at https://sat.farmonaut.com/api.
The Future of Soil Micromorphology in Agriculture
As technology continues to advance, the field of soil micromorphology is poised for even greater breakthroughs. Some exciting developments on the horizon include:
- 3D imaging and reconstruction of soil samples
- Integration of artificial intelligence for automated feature recognition
- Development of portable microscopy tools for in-field analysis
- Combination of micromorphology with other analytical techniques (e.g., spectroscopy, X-ray tomography)
These advancements promise to make soil micromorphology more accessible, efficient, and informative, further revolutionizing agricultural soil analysis and crop management practices.
Comparative Analysis of Soil Micromorphology Techniques
| Technique Name | Primary Application | Depth of Analysis (μm) | Sample Preparation Time (hours) | Key Insights Provided | Impact on Crop Yield (estimated %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Microscopy | Mineral identification, soil structure analysis | 1-1000 | 2-4 | Mineral composition, pore structure, organic matter distribution | 5-10 |
| Soil Thin Section Analysis | Detailed microstructure examination | 20-30 | 24-48 | Soil fabric, pedofeatures, microbial activity | 10-15 |
| Digital Soil Imaging | Large-scale soil mapping, quantitative analysis | 0.1-1000 | 1-2 | Spatial distribution of soil properties, 3D visualization | 8-12 |
| X-ray Microtomography | Non-destructive 3D imaging of soil structure | 1-100 | 4-8 | Pore network analysis, root-soil interactions | 12-18 |
Conclusion: Embracing the Microscopic Revolution
The field of soil micromorphology has opened up a new world of possibilities for agricultural analysis and crop management. By peering into the microscopic realm of soils, we can unlock secrets that have profound implications for farming practices, sustainability, and food security.
At Farmonaut, we are committed to harnessing these advanced soil science applications and integrating them with our cutting-edge satellite monitoring and AI advisory systems. Our goal is to provide farmers with the most comprehensive and actionable data possible, empowering them to make informed decisions that optimize crop yield while promoting sustainable land management practices.
As we continue to push the boundaries of agricultural technology, the insights gained from soil micromorphology will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping the future of farming. By embracing these advanced techniques and combining them with innovative technologies, we can work towards a more productive, sustainable, and resilient agricultural sector.
To explore how Farmonaut’s advanced agricultural solutions can benefit your farming operations, visit our website or download our mobile app today. Together, we can unlock the full potential of your soil and take your agricultural practices to new heights.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is soil micromorphology?
Soil micromorphology is a specialized branch of soil science that focuses on the microscopic examination of soil samples to analyze their structure, composition, and properties. - How does soil micromorphology benefit agriculture?
It provides detailed insights into soil structure, mineral composition, and organic matter distribution, which helps in optimizing crop management practices and improving soil health. - What equipment is used in soil micromorphology?
Key equipment includes high-powered optical microscopes, polarized light microscopes, digital imaging systems, and soil thin section preparation tools. - How does Farmonaut incorporate soil micromorphology data?
Farmonaut integrates soil micromorphology insights with satellite-based monitoring and AI advisory systems to provide comprehensive, data-driven solutions for precision farming. - Can soil micromorphology help improve crop yields?
Yes, by providing detailed information about soil properties, micromorphology can help farmers make informed decisions about crop selection, irrigation, and fertilization, potentially leading to significant yield improvements.






