Revolutionizing Suffolk Farms: Precision Agriculture and Sustainable Cultivation Techniques for the Modern Grower
“Precision agriculture techniques can reduce fuel costs by up to 30% through efficient machinery use and optimized field operations.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on revolutionizing Suffolk farms through precision agriculture and sustainable cultivation techniques. As we embark on this journey of agricultural innovation, we’ll explore cutting-edge technologies and practices that are transforming the landscape of modern farming. From advanced machinery to data-driven decision-making, we’ll uncover how these advancements are reshaping the way we approach crop establishment, soil health management, and overall farm productivity.
The Evolution of Farming in Suffolk
Suffolk, with its rich agricultural heritage, has long been at the forefront of farming innovation. As we delve into the world of precision agriculture, it’s essential to understand how these new technologies are building upon centuries of farming wisdom. Today, we’re witnessing a harmonious blend of traditional knowledge and cutting-edge science, creating a new paradigm for sustainable and efficient farming practices.

Embracing Precision Agriculture Technology
Precision agriculture is revolutionizing the way Suffolk farmers approach their craft. By leveraging advanced technologies, growers can now make data-driven decisions that optimize every aspect of their operations. Let’s explore some of the key technologies that are making this possible:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Using multispectral imagery to assess crop health and soil moisture levels.
- GPS-Guided Machinery: Enhancing accuracy in planting, spraying, and harvesting operations.
- Soil Sensors: Providing real-time data on soil conditions to inform irrigation and fertilization decisions.
- Drones: Offering aerial insights for crop scouting and mapping.
These technologies work in concert to provide farmers with unprecedented levels of insight into their fields. By harnessing this data, growers can make more informed decisions, leading to improved yields, reduced input costs, and enhanced sustainability.
Sustainable Farming Practices for Suffolk’s Future
As stewards of the land, Suffolk farmers are increasingly adopting sustainable farming practices that not only benefit their bottom line but also protect the environment for future generations. Some key sustainable practices include:
- Conservation Tillage: Minimizing soil disturbance to improve soil health and reduce erosion.
- Cover Cropping: Planting non-cash crops to protect and enrich the soil between growing seasons.
- Integrated Pest Management: Using a combination of biological, cultural, and chemical methods to control pests while minimizing environmental impact.
- Precision Irrigation: Utilizing advanced systems to deliver water exactly where and when it’s needed, reducing waste.
These practices not only contribute to the long-term health of Suffolk’s agricultural lands but also align with growing consumer demand for sustainably produced food.
Direct Drilling: A Game-Changer for Crop Establishment
One of the most significant advancements in modern cultivation techniques is direct drilling. This method involves planting seeds directly into undisturbed soil, offering numerous benefits for Suffolk farmers:
- Reduced soil erosion and improved soil structure
- Lower fuel and labor costs
- Improved moisture retention
- Enhanced soil biodiversity
Direct drilling is particularly well-suited to Suffolk’s diverse soil types, from the heavy clays to the lighter sandy loams. By minimizing soil disturbance, this technique helps preserve the natural soil ecosystem, leading to healthier crops and more resilient farmland.
Soil Health Management: The Foundation of Sustainable Agriculture
At the heart of Suffolk’s agricultural revolution is a renewed focus on soil health management. Healthy soils are the foundation of productive farms, and precision agriculture tools are helping farmers understand and improve their soil like never before. Key aspects of modern soil health management include:
- Soil Testing and Mapping: Using GPS-linked soil sampling to create detailed nutrient maps.
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT): Applying fertilizers and amendments at varying rates across fields based on soil needs.
- Biochar and Compost Applications: Enhancing soil organic matter and microbial activity.
- Precision pH Management: Tailoring lime applications to specific areas within fields.
By focusing on soil health, Suffolk farmers are not only improving their yields but also increasing the resilience of their farms to weather extremes and pest pressures.
Agricultural Machinery Innovations
The machinery used on Suffolk farms is undergoing a technological revolution. Modern equipment is smarter, more efficient, and more precise than ever before. Some of the most exciting innovations include:
- Combination Drills: Machines that can perform multiple operations in a single pass, reducing soil compaction and fuel use.
- Autonomous Tractors: Self-driving machines that can work around the clock with minimal human intervention.
- Smart Sprayers: Equipment that can detect and target individual weeds, dramatically reducing herbicide use.
- Robotic Harvesters: Machines capable of selectively harvesting crops based on ripeness and quality.
These advanced machines are not just improving efficiency; they’re also helping to address labor shortages and reduce the physical demands on farmers.
“Modern seed drills can increase crop establishment rates by 15-20% compared to traditional broadcasting methods.”
Data-Driven Agriculture: The Power of Information
In the age of big data, information is power, and Suffolk farmers are harnessing this power to make better decisions than ever before. Data-driven agriculture involves:
- Farm Management Software: Integrating data from various sources to provide a holistic view of farm operations.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical and real-time data to forecast crop yields, pest outbreaks, and optimal harvest times.
- IoT Sensors: Connecting farm equipment and environmental sensors to provide real-time insights.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Analyzing complex data sets to identify patterns and make recommendations.
By leveraging these tools, Suffolk farmers can make more informed decisions, reduce risks, and optimize their operations for maximum efficiency and profitability.
Conservation Tillage: Balancing Productivity and Sustainability
Conservation tillage methods are gaining traction among Suffolk farmers as a way to balance productivity with environmental stewardship. These techniques include:
- No-Till Farming: Planting crops without disturbing the soil through tillage.
- Strip-Till: Tilling only narrow strips where seeds will be planted.
- Ridge-Till: Planting on ridges of soil, reducing erosion and improving drainage.
By adopting these methods, Suffolk farmers are seeing benefits such as improved soil structure, increased organic matter, and reduced fuel costs. Conservation tillage also plays a crucial role in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Crop Establishment Strategies for Suffolk’s Diverse Landscape
Suffolk’s varied soil types and microclimates require tailored crop establishment strategies. Modern growers are using a combination of techniques to ensure optimal crop growth:
- Precision Seeding: Using GPS-guided planters to achieve perfect seed spacing and depth.
- Variable Rate Seeding: Adjusting seed rates based on soil type and field conditions.
- Controlled Traffic Farming: Limiting machinery traffic to specific lanes to reduce soil compaction.
- Starter Fertilizer Applications: Providing young plants with readily available nutrients for a strong start.
These strategies help ensure that every seed has the best possible chance of developing into a productive plant, maximizing yield potential across Suffolk’s diverse agricultural landscape.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Livestock Farming
While much of our focus has been on arable farming, precision agriculture is also transforming Suffolk’s livestock sector. Innovative technologies are helping farmers improve animal welfare, increase productivity, and reduce environmental impact:
- Automated Milking Systems: Allowing cows to be milked on their own schedule, improving comfort and yield.
- Precision Feeding Systems: Tailoring feed rations to individual animal needs, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Wearable Sensors: Monitoring animal health and behavior in real-time, enabling early intervention when issues arise.
- Methane Capture Technology: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions from livestock operations.
These technologies are helping Suffolk’s dairy, beef, and sheep farmers remain competitive while meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Adapting to Climate Change: Resilience Through Technology
Climate change presents significant challenges for Suffolk farmers, but precision agriculture tools are helping growers adapt and build resilience:
- Weather Stations and Forecasting: Providing hyperlocal weather data to inform planting and harvesting decisions.
- Drought-Resistant Crop Varieties: Utilizing genetic advances to develop crops better suited to changing conditions.
- Water Management Systems: Implementing smart irrigation and drainage solutions to cope with extreme weather events.
- Crop Modeling Software: Simulating different climate scenarios to help farmers plan for the future.
By leveraging these tools, Suffolk farmers are not only protecting their livelihoods but also ensuring food security for the region in the face of climate uncertainty.
The Economic Impact of Precision Agriculture in Suffolk
The adoption of precision agriculture technologies is having a significant economic impact on Suffolk’s farming sector:
- Reduced input costs through more efficient use of seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides
- Increased yields and crop quality, leading to higher revenues
- Improved labor efficiency, helping to address workforce challenges
- New revenue streams from data-driven services and sustainability initiatives
While the initial investment in precision agriculture technologies can be substantial, many Suffolk farmers are finding that the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs.
The Future of Farming in Suffolk: Trends and Predictions
As we look to the future of farming in Suffolk, several trends are emerging that will shape the industry in the coming years:
- Vertical Farming: Utilizing indoor, stacked growing systems to produce crops year-round.
- Blockchain Technology: Enhancing traceability and transparency in the food supply chain.
- Artificial Intelligence: Developing more sophisticated predictive models and autonomous systems.
- Gene Editing: Creating more resilient and nutritious crop varieties.
These emerging technologies have the potential to further revolutionize Suffolk’s agricultural sector, creating new opportunities for innovation and growth.
Comparison: Traditional vs. Precision Agriculture Techniques
| Farming Aspect | Traditional Method | Precision Agriculture Method | Benefits of Precision Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Management | Uniform tillage across fields | Variable-depth tillage based on soil maps | 20% reduction in fuel use, improved soil health |
| Crop Establishment | Fixed seeding rates | Variable rate seeding | 15% increase in germination rates |
| Irrigation | Scheduled, uniform irrigation | Sensor-based, variable rate irrigation | 30% reduction in water usage |
| Fertilizer Application | Blanket application | Precision application based on soil needs | 25% reduction in fertilizer use |
| Pest Control | Whole-field spraying | Targeted spraying using AI and sensors | 50% reduction in pesticide use |
| Yield Monitoring | Manual sampling | Real-time yield mapping | 10% increase in overall yield |
Embracing Digital Tools for Farm Management
To fully leverage the power of precision agriculture, Suffolk farmers are increasingly turning to digital tools for farm management. These platforms integrate data from various sources to provide a comprehensive view of farm operations:
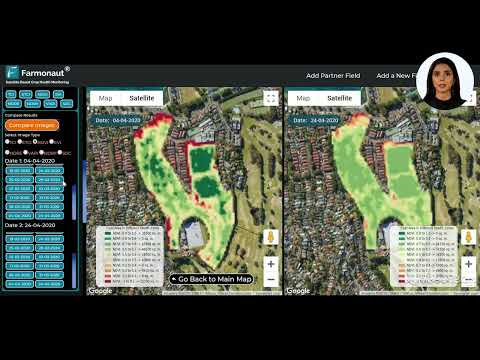
- Satellite-based crop monitoring for real-time insights into crop health and development
- Weather forecasting and historical data analysis to inform planting and harvesting decisions
- Field mapping and zone management for precision input application
- Equipment tracking and maintenance scheduling to optimize machinery use
One such tool that’s gaining popularity among Suffolk farmers is Farmonaut. This advanced platform offers satellite-based farm management solutions, providing valuable services such as real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisory systems, and resource management tools.
Explore Farmonaut’s solutions:
For developers and businesses looking to integrate advanced agricultural data into their own systems, Farmonaut also offers API access. Learn more about their API services and check out the API Developer Docs.
Challenges and Opportunities in Adopting Precision Agriculture
While the benefits of precision agriculture are clear, Suffolk farmers face several challenges in adopting these technologies:
- Initial Investment Costs: The upfront expense of precision equipment can be significant.
- Technical Skills Gap: Farmers need to develop new skills to effectively use and interpret data from precision tools.
- Data Management: Handling and securing large amounts of farm data presents new challenges.
- Connectivity Issues: Reliable internet access in rural areas is crucial for many precision agriculture tools.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration within Suffolk’s agricultural community. Government initiatives, farmer cooperatives, and partnerships with technology providers are helping to overcome these hurdles and accelerate the adoption of precision agriculture techniques.
The Role of Education and Training in Modern Agriculture
As farming becomes increasingly high-tech, education and training play a crucial role in preparing the next generation of Suffolk farmers. Local agricultural colleges and universities are adapting their curricula to include:
- Courses on precision agriculture technologies and data analysis
- Hands-on training with the latest farm machinery and software
- Workshops on sustainable farming practices and environmental stewardship
- Business management skills for the digital age
Additionally, ongoing professional development opportunities are essential for established farmers looking to stay current with rapidly evolving technologies and practices.
Biodiversity and Conservation in Modern Farming
While precision agriculture focuses on optimizing crop production, it’s equally important to consider the role of biodiversity and conservation in sustainable farming. Suffolk farmers are implementing various strategies to promote ecological balance:
- Habitat Creation: Establishing wildflower margins and beetle banks to support beneficial insects and wildlife.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs into crop and livestock systems to enhance biodiversity and improve soil health.
- Precision Conservation: Using technology to identify and protect sensitive areas within fields.
- Crop Rotation and Diversification: Implementing diverse crop rotations to break pest cycles and improve soil health.
These practices not only benefit local ecosystems but also contribute to the long-term sustainability and resilience of Suffolk’s agricultural landscape.
The Future of Suffolk Agriculture: A Vision for Sustainability and Innovation
As we look to the future, Suffolk’s agricultural sector is poised for continued growth and innovation. By embracing precision agriculture and sustainable cultivation techniques, farmers are not only improving their productivity and profitability but also positioning themselves as leaders in environmental stewardship.
The integration of advanced technologies, data-driven decision-making, and sustainable practices is creating a new paradigm for farming in Suffolk. This approach not only benefits individual farmers but also contributes to broader goals of food security, environmental conservation, and rural economic development.
As we continue to face challenges such as climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity, the innovations being implemented on Suffolk farms today will play a crucial role in shaping a resilient and sustainable agricultural future for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is precision agriculture?
A: Precision agriculture is an approach to farm management that uses information technology and specialized equipment to optimize crop yields and reduce waste. It involves collecting and analyzing data about variability in fields to make more precise decisions about planting, fertilizing, and harvesting crops.
Q: How does direct drilling benefit soil health?
A: Direct drilling, also known as no-till farming, benefits soil health by minimizing soil disturbance. This preserves soil structure, reduces erosion, improves water retention, and promotes the growth of beneficial soil organisms. Over time, it can lead to increased organic matter in the soil and improved overall soil health.
Q: What are some examples of conservation tillage methods?
A: Conservation tillage methods include no-till farming, strip-till, and ridge-till. These techniques aim to minimize soil disturbance while maintaining crop residues on the soil surface, which helps to reduce erosion, improve soil structure, and conserve moisture.
Q: How can precision agriculture help farmers adapt to climate change?
A: Precision agriculture helps farmers adapt to climate change by providing tools for more efficient resource use, such as water and fertilizers. It also offers data-driven insights that can help farmers make better decisions about crop selection, planting times, and pest management in the face of changing weather patterns.
Q: What role does satellite technology play in modern farming?
A: Satellite technology plays a crucial role in modern farming by providing high-resolution imagery for crop monitoring, soil mapping, and yield forecasting. It allows farmers to track crop health, identify problem areas, and make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control across large areas.
In conclusion, the revolution in Suffolk farms through precision agriculture and sustainable cultivation techniques represents a exciting new chapter in the region’s rich agricultural history. By embracing these innovative approaches, Suffolk farmers are not only enhancing their productivity and profitability but also contributing to a more sustainable and resilient food system for the future.