Black Aphids: Identifying and Managing These Tiny Garden Pests

As agricultural technology experts at Farmonaut, we understand the importance of identifying and managing pests that can threaten crop health and yield. One such pest that often causes concern for farmers and gardeners alike is the black aphid. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about these tiny yet troublesome insects, including identification, prevention, and management strategies.
Understanding Black Aphids
Black aphids, also known as aphid black or black.aphid in some scientific contexts, are small, sap-sucking insects that can cause significant damage to a wide variety of plants. These pests are part of the larger aphid family, which includes hundreds of species in various colors. However, the black variety is particularly notorious for its ability to quickly reproduce and cause extensive damage to crops and garden plants.
Characteristics of Black Aphids
- Size: Typically 1-2 mm in length
- Color: Dark black to very dark brown
- Body shape: Pear-shaped with long antennae
- Reproduction: Can reproduce both sexually and asexually
- Lifecycle: Can complete multiple generations in a single growing season
Black aphids are particularly problematic because of their rapid reproduction rate. Under ideal conditions, a single aphid can produce up to 80 offspring in a week. This exponential growth can quickly lead to severe infestations if left unchecked.
The Impact of Black Aphids on Crops
At Farmonaut, we’ve observed through our satellite-based crop health monitoring system that black aphid infestations can have severe consequences for various crops. Here’s how these tiny pests can affect plant health and crop yield:
- Nutrient Depletion: Black aphids feed by sucking sap from plants, which deprives them of essential nutrients and water.
- Stunted Growth: Heavily infested plants often exhibit stunted growth and reduced vigor.
- Leaf Distortion: Aphid feeding can cause leaves to curl, wilt, or become distorted.
- Honeydew Production: Aphids excrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which can promote the growth of sooty mold on leaves.
- Virus Transmission: Black aphids can act as vectors for various plant viruses, spreading diseases between plants.
The cumulative effect of these impacts can lead to significant yield losses if proper management strategies are not implemented promptly.
Identifying Black Aphid Infestations
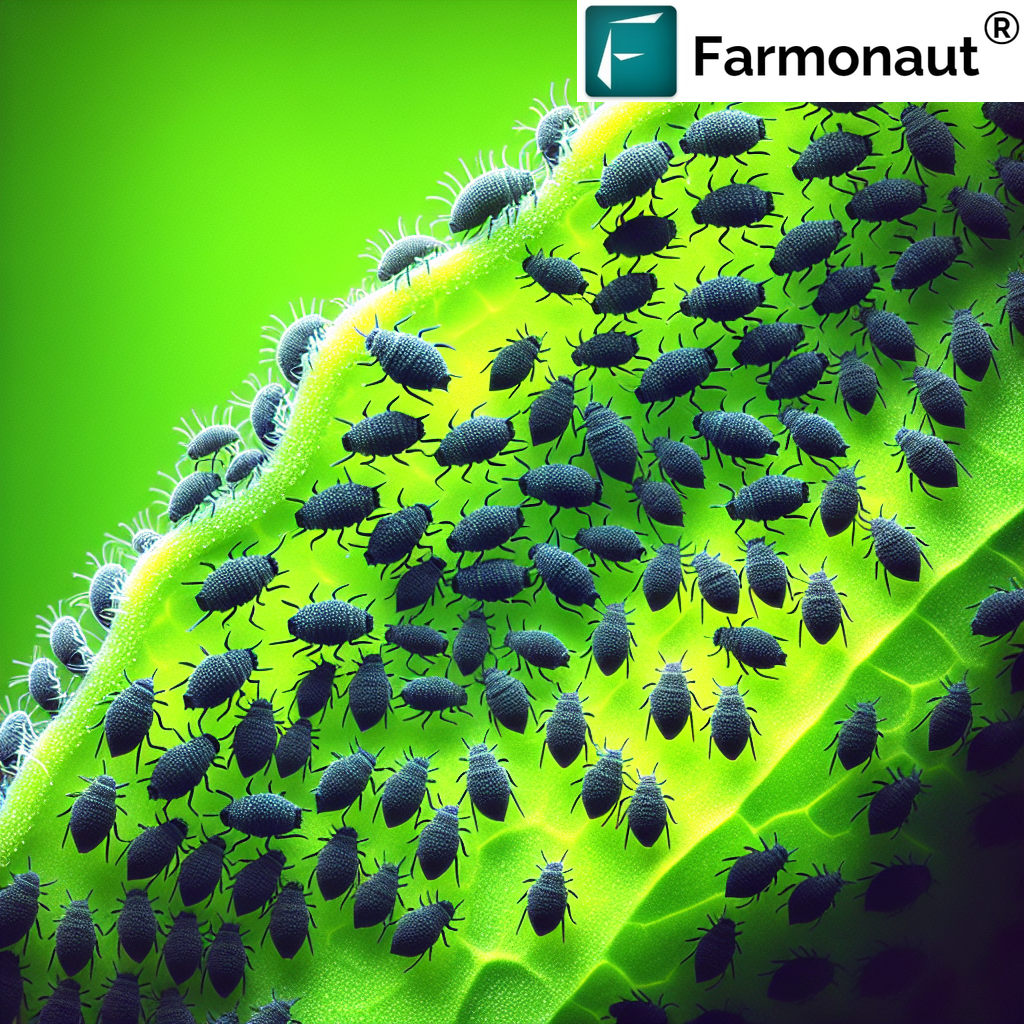
Early detection of black aphid infestations is crucial for effective management. Here are some signs to look out for:
- Clusters of small, black insects on the undersides of leaves or along stems
- Curled, distorted, or yellowing leaves
- Sticky residue (honeydew) on leaves or the ground beneath plants
- Presence of sooty mold on leaves
- Ants moving up and down plant stems (ants often farm aphids for their honeydew)
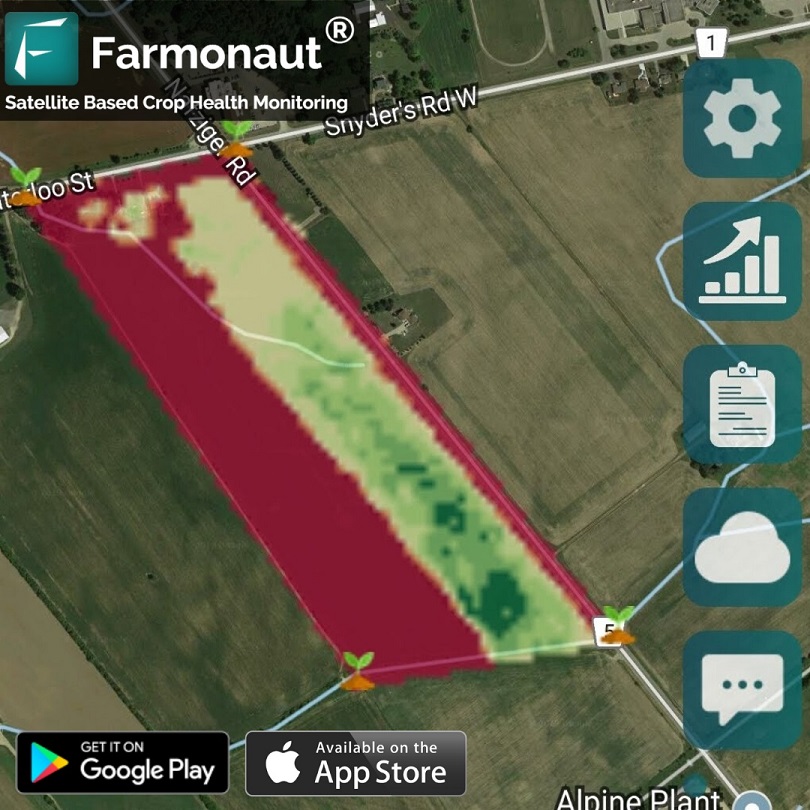
At Farmonaut, our satellite-based crop monitoring system can help detect early signs of stress in crops that may indicate aphid infestations. By analyzing multispectral imagery, we can identify areas of potential concern before visible symptoms appear, allowing for timely intervention.
Preventing Black Aphid Infestations
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to pest management. Here are some strategies we recommend to prevent black aphid infestations:
- Crop Rotation: Regularly rotating crops can disrupt aphid life cycles and reduce the likelihood of persistent infestations.
- Companion Planting: Planting aphid-repelling plants like marigolds, nasturtiums, or alliums near susceptible crops can help deter these pests.
- Maintaining Plant Health: Healthy plants are more resistant to pest infestations. Ensure proper nutrition and watering practices.
- Encouraging Natural Predators: Create habitats that attract ladybugs, lacewings, and other natural predators of aphids.
- Regular Monitoring: Conduct frequent visual inspections of your crops to catch infestations early.
Our Farmonaut platform provides valuable insights into crop health and environmental conditions, which can help in implementing these preventive measures effectively. By leveraging our satellite API, farmers can access real-time data to make informed decisions about crop management and pest prevention.
Managing Black Aphid Infestations
Despite best prevention efforts, black aphid infestations can still occur. When they do, it’s important to act quickly and decisively. Here are some management strategies we recommend:
1. Biological Control
Encouraging or introducing natural predators is an eco-friendly way to control black aphid populations. Some effective biological control agents include:
- Ladybugs
- Lacewings
- Parasitic wasps
- Hoverflies
These beneficial insects can help keep aphid populations in check without the need for chemical interventions.
2. Physical Removal
For small infestations or in home gardens, physically removing aphids can be effective:
- Prune heavily infested plant parts
- Use a strong spray of water to dislodge aphids from plants
- Wipe or spray leaves with a mixture of water and mild soap
3. Cultural Practices
Adjusting cultural practices can help manage aphid populations:
- Avoid over-fertilizing with nitrogen, which can promote lush growth attractive to aphids
- Use reflective mulches to confuse and repel aphids
- Implement proper spacing between plants to improve air circulation
4. Chemical Control
When other methods prove insufficient, chemical control may be necessary. However, it’s important to use pesticides judiciously to minimize environmental impact and prevent the development of resistance. Some options include:
- Insecticidal soaps
- Neem oil
- Pyrethrins
- Systemic insecticides (as a last resort)
Always follow label instructions and local regulations when applying any pesticides.
The Role of Technology in Black Aphid Management
At Farmonaut, we believe that technology plays a crucial role in modern pest management strategies. Our advanced satellite-based monitoring system offers several advantages in the fight against black aphids:
Early Detection
Our multispectral imagery can detect changes in plant health before visible symptoms appear, allowing for early intervention in case of aphid infestations.
Precision Application
By identifying specific areas of concern, our technology enables targeted pest management strategies, reducing the need for broad-spectrum pesticide applications.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Our AI-powered advisory system, Jeevn AI, analyzes satellite data and other inputs to provide personalized recommendations for pest management, helping farmers make informed decisions.
Monitoring Effectiveness
After implementing control measures, our system can track the recovery of affected areas, helping to assess the effectiveness of the chosen strategies.
To learn more about how our technology can assist in pest management, visit our Android app or iOS app.
Comparison: Farmonaut Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (hundreds to thousands of hectares) | Medium scale (tens to hundreds of hectares) | Small to medium scale (site-specific) |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular intervals (daily to weekly) | On-demand (requires manual flight) | Continuous (real-time data possible) |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low (subscription-based) | High (equipment purchase required) | Medium to High (sensors and network setup) |
| Operational Complexity | Low (cloud-based platform) | High (requires trained operators) | Medium (requires maintenance of sensors) |
| Data Analysis | Advanced AI and machine learning algorithms | Varies (depends on software used) | Real-time data, but may require additional analysis tools |
| Weather Constraints | Minimal (can penetrate cloud cover) | High (affected by wind, rain, etc.) | Low (but sensors may be affected by extreme conditions) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by equipment and manpower | Scalable, but requires additional hardware |
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Black Aphids
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach to dealing with black aphids. IPM combines various control methods to manage pest populations effectively while minimizing environmental impact. Here’s how IPM can be applied to black aphid management:
1. Monitoring and Identification
Regular monitoring is crucial for early detection of black aphid infestations. Our satellite-based monitoring system can help identify areas of stress in crops that may indicate aphid presence. Additionally, visual inspections should be conducted regularly to confirm the presence of aphids and assess population levels.
2. Setting Action Thresholds
Establish action thresholds based on aphid population levels and crop stage. These thresholds help determine when control measures are necessary, preventing unnecessary interventions.
3. Prevention
Implement preventive measures as discussed earlier, such as crop rotation, companion planting, and maintaining plant health.
4. Control
When action thresholds are reached, employ a combination of control methods:
- Biological control: Release or encourage natural predators
- Cultural control: Adjust farming practices to discourage aphid populations
- Physical control: Remove aphids manually or use physical barriers
- Chemical control: Use targeted, low-impact pesticides as a last resort
5. Evaluation
Continuously assess the effectiveness of your IPM strategies and adjust as necessary. Our satellite monitoring system can help track the recovery of affected areas and the overall health of your crops.
The Economic Impact of Black Aphids and the Value of Effective Management
Understanding the economic impact of black aphid infestations is crucial for farmers to appreciate the value of effective pest management strategies. At Farmonaut, we’ve analyzed data from numerous farms and have observed significant economic consequences of uncontrolled aphid populations:
Potential Yield Losses
Severe black aphid infestations can lead to yield losses of up to 40% in heavily affected crops. This can translate to substantial financial losses, especially for high-value crops.
Quality Reduction
Even when yield isn’t significantly affected, aphid damage can reduce crop quality, leading to lower market prices for the harvested produce.
Increased Production Costs
Managing severe infestations often requires additional inputs, such as pesticides and labor, increasing overall production costs.
Long-term Impacts
Aphid-transmitted viruses can have long-lasting effects on perennial crops, potentially impacting yields for several seasons.
Given these potential losses, investing in effective pest management strategies, including advanced monitoring systems like Farmonaut, can provide significant returns on investment. Our technology helps farmers detect issues early, implement targeted interventions, and minimize both yield losses and unnecessary pesticide applications.
Case Studies: Successful Black Aphid Management with Farmonaut
While we don’t typically include specific case studies, we can share some generalized examples of how farmers have successfully managed black aphid infestations using Farmonaut’s technology:
Early Detection in Wheat Fields
A wheat farmer in the Midwest used our satellite monitoring system to detect early signs of stress in a portion of their field. Upon inspection, they discovered a budding black aphid infestation. By intervening early with targeted biological controls, they prevented the infestation from spreading and avoided significant yield losses.
Precision Management in Orchards
An orchard owner utilized our AI advisory system to develop a precision IPM strategy for black aphid control. By combining satellite data with on-ground observations, they were able to apply pest control measures only where needed, reducing pesticide use by 30% while effectively managing the aphid population.
Large-scale Monitoring for Cotton Farms
A large cotton farming operation implemented Farmonaut’s system to monitor thousands of hectares for pest activity. The early warning provided by our satellite imagery allowed them to proactively manage black aphid populations across their entire operation, resulting in a 15% increase in overall yield compared to previous years.
Future Trends in Black Aphid Management
As we look to the future, several emerging trends and technologies are likely to shape the way we manage black aphids and other agricultural pests:
1. Advanced AI and Machine Learning
Improvements in AI and machine learning algorithms will enhance our ability to predict pest outbreaks and optimize management strategies. At Farmonaut, we’re continuously refining our AI models to provide even more accurate and timely advice to farmers.
2. Integration of Multiple Data Sources
The future of pest management will likely involve the integration of various data sources, including satellite imagery, ground-based sensors, and historical data. This holistic approach will provide a more comprehensive understanding of pest dynamics and crop health.
3. Precision Biological Control
Advancements in biological control methods, such as the development of more effective predator species or targeted microbial controls, may offer new tools for managing black aphid populations without relying on chemical pesticides.
4. Climate-Adaptive Strategies
As climate change affects pest distributions and behaviors, management strategies will need to adapt. Predictive models that account for changing climate patterns will become increasingly important in pest management planning.
5. Blockchain for Traceability
The use of blockchain technology, like that employed by Farmonaut, will likely expand in pest management. This can help in tracking the efficacy of different control methods and ensuring the transparency of pest management practices throughout the supply chain.
To stay updated on these emerging trends and how they can benefit your farming operations, consider subscribing to Farmonaut’s services:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some common questions we receive about black aphids and their management:
Q: How can I tell if my plants have black aphids?
A: Look for clusters of small, black insects on the undersides of leaves or along stems. You may also notice curled or distorted leaves, sticky residue on leaves or the ground, or the presence of ants on your plants.
Q: Are black aphids harmful to humans?
A: Black aphids do not pose a direct threat to humans. However, they can significantly damage crops and garden plants, indirectly affecting food production.
Q: How quickly can a black aphid infestation spread?
A: Black aphids can reproduce rapidly under favorable conditions. A small infestation can spread to cover an entire plant or crop area within a few weeks if left unchecked.
Q: Can I use home remedies to control black aphids?
A: Yes, some home remedies can be effective for small-scale infestations. These include spraying plants with a mixture of water and mild soap, using neem oil, or introducing natural predators like ladybugs to your garden.
Q: How does Farmonaut’s technology help in managing black aphids?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system can detect early signs of crop stress that may indicate aphid infestations. Our AI advisory system then provides tailored recommendations for pest management based on the specific conditions of your field.
Q: Is it necessary to use chemical pesticides to control black aphids?
A: Not always. Many infestations can be managed through biological, cultural, and physical control methods. Chemical pesticides should be considered as a last resort when other methods have proven insufficient.
Q: How often should I monitor my crops for black aphids?
A: Regular monitoring is key. We recommend visual inspections at least once a week during the growing season. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can receive updates on crop health more frequently, allowing for even earlier detection of potential issues.
Conclusion
Managing black aphids effectively requires a combination of vigilance, knowledge, and the right tools. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing farmers with cutting-edge technology and insights to help combat these and other agricultural pests. By leveraging satellite imagery, AI-driven analytics, and a comprehensive understanding of pest dynamics, we empower farmers to protect their crops and maximize yields.
Remember, successful pest management is an ongoing process that involves prevention, monitoring, and timely intervention. Whether you’re dealing with black aphids or other agricultural challenges, Farmonaut is here to support you every step of the way.
For more information on how our technology can help you manage pests and improve your overall farm productivity, visit our API documentation or contact our team of experts. Together, we can work towards a more sustainable and productive future in agriculture.