Mastering High-Quality Hay Production: Expert Guide to Optimal Cutting, Baling, and Moisture Management Techniques
“Optimal hay moisture content for baling is typically between 15-20%, ensuring proper fermentation and storage.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on mastering high-quality hay production! As experts in agricultural technology and precision farming, we at Farmonaut are excited to share our knowledge on optimal hay cutting techniques, moisture management, and baling practices. Whether you’re a seasoned farmer or just starting out, this guide will provide valuable insights to elevate your hay farming game.

In this blog post, we’ll explore the secrets of producing nutritious hay through multiple cuttings per season, discuss the best practices for alfalfa and grass mix farming, and delve into effective soil management and fertilization strategies. We’ll also cover essential hay drying methods, including the use of windrowers and windrows to enhance air circulation. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to maximize your forage nutrient content and improve your farm’s efficiency.
The Importance of High-Quality Hay Production
High-quality hay production is crucial for livestock farmers, as it directly impacts the health and productivity of cattle, horses, and dairy cows. Nutritious hay provides essential proteins, vitamins, and minerals that animals need to thrive. By mastering the art of hay production, we can ensure a steady supply of top-notch feed for our livestock throughout the year.
At Farmonaut, we understand the challenges farmers face in producing high-quality hay. That’s why we’ve developed cutting-edge technology to help optimize every step of the hay production process, from field preparation to storage. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system provides real-time insights into vegetation health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics, enabling farmers to make informed decisions about their hay fields.
Optimal Hay Cutting Techniques
Mastering the art of hay cutting is essential for producing high-quality forage. Here are some key techniques to consider:
- Timing is everything: Cut hay at the optimal stage of maturity to maximize nutrient content. For alfalfa, this is typically at the early bloom stage, while grass should be cut before heading.
- Cutting height: Maintain a cutting height of 3-4 inches to promote rapid regrowth and protect the plant’s energy reserves.
- Sharp blades: Use well-maintained, sharp cutting equipment to ensure clean cuts and reduce damage to the plants.
- Proper equipment: Invest in quality mowers or windrowers suited to your field size and terrain.
By implementing these techniques, we can significantly improve the quality and quantity of our hay yield. Remember, the goal is to preserve as many leaves as possible, as they contain the highest concentration of nutrients.
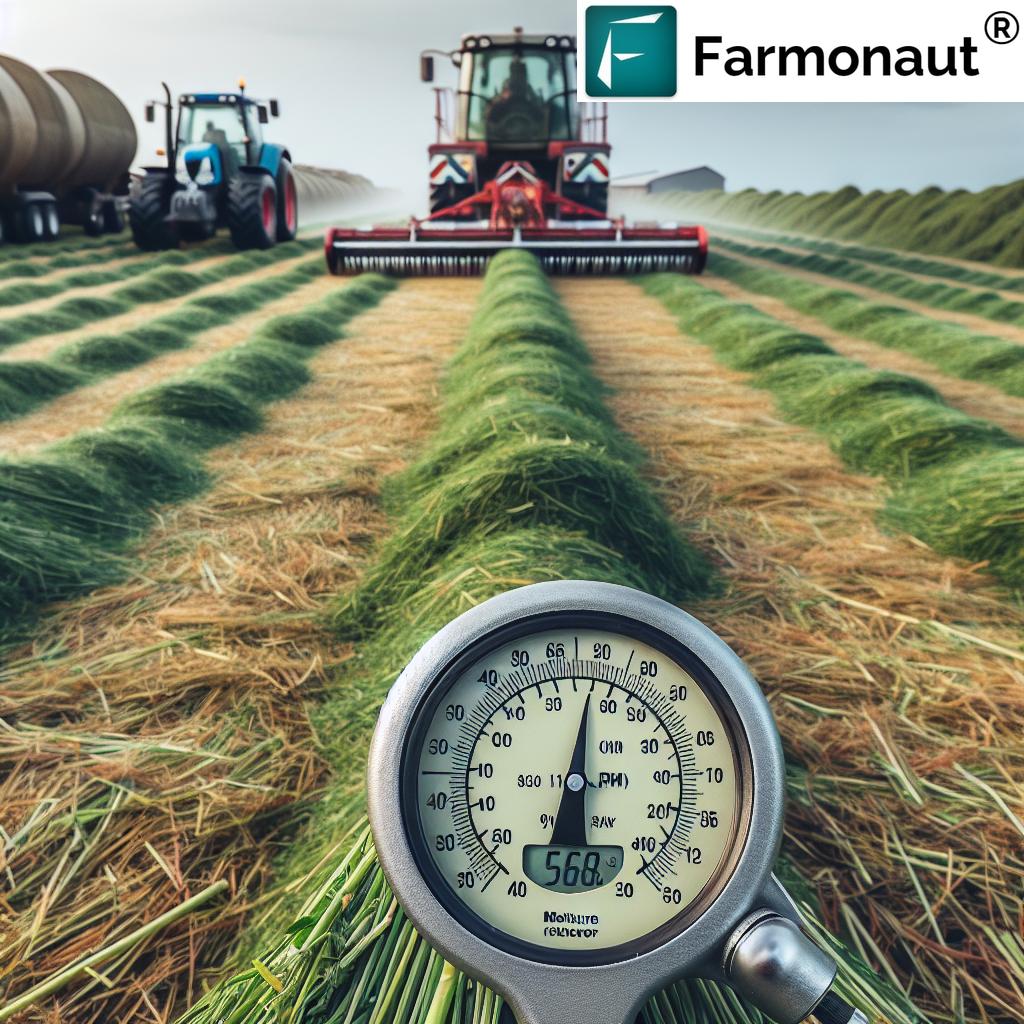
Hay Moisture Content Management
Managing hay moisture content is crucial for producing high-quality bales that store well and maintain their nutritional value. Here’s what you need to know:
- Ideal moisture levels: Aim for a moisture content between 15-20% for small square bales, and 14-18% for large round or square bales.
- Monitoring techniques: Use moisture meters or the “twist test” to assess hay moisture in the field.
- Drying methods: Utilize tedders and rakes to spread and fluff the hay, promoting faster and more even drying.
- Weather considerations: Keep an eye on weather forecasts and plan your cutting and baling accordingly to minimize moisture-related issues.
At Farmonaut, our advanced weather forecasting system can help you plan your hay cutting and baling activities with greater precision. By integrating this data with our satellite-based crop monitoring, we provide a comprehensive solution for optimal hay moisture management.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced weather and crop data integration
Baling Equipment and Techniques
Choosing the right baling equipment and employing proper techniques are essential for producing high-quality hay bales. Let’s explore some key aspects:
- Baler types: Choose between square balers for easier stacking and transportation, or round balers for larger operations and potentially better weather resistance.
- Bale density: Adjust your baler for the optimal density based on your hay type and storage conditions. Denser bales generally store better but may require more drying time.
- Bale size: Consider your handling equipment and storage facilities when selecting bale size. Smaller bales are easier to handle manually, while larger bales are more efficient for mechanized operations.
- Wrapping: For high-moisture hay or silage, consider using plastic wrap to create anaerobic conditions for proper fermentation.
Remember, the baling process is critical in preserving the quality of your hay. Proper baling techniques help maintain leaf attachment, reduce shattering, and ensure even distribution of moisture throughout the bale.

Alfalfa and Grass Mix Farming
Alfalfa and grass mix farming can provide a balanced and nutritious hay crop. Here are some tips for successful mixed hay production:
- Choosing compatible species: Select grass varieties that complement alfalfa’s growth habits and nutritional profile.
- Seeding rates: Adjust seeding rates to achieve the desired ratio of alfalfa to grass in your mix.
- Fertilization: Tailor your fertilization program to support both alfalfa and grass components of your mix.
- Harvesting timing: Find a balance between optimal cutting times for both alfalfa and grass to maximize overall quality.
Mixed hay can offer advantages such as reduced bloat risk for livestock, improved soil health, and potentially higher yields. However, it requires careful management to maintain the desired balance between species.
“Multiple cuttings per season can increase hay yield by up to 30-40% compared to a single harvest.”
Soil Management for Hay Fields
Proper soil management is the foundation of successful hay production. Here’s how we can optimize our hay fields through effective soil management:
- Soil testing: Conduct regular soil tests to assess nutrient levels and pH.
- pH adjustment: Maintain soil pH between 6.0 and 7.0 for optimal nutrient availability and plant growth.
- Nutrient management: Develop a fertilization plan based on soil test results and crop removal rates.
- Organic matter: Incorporate cover crops or manure to improve soil structure and fertility.
- Compaction prevention: Minimize field traffic and use flotation tires to reduce soil compaction.
At Farmonaut, our satellite-based soil moisture monitoring can help you make informed decisions about irrigation and field operations, ensuring optimal growing conditions for your hay crop.
Check out our API Developer Docs for integrating soil data into your farm management systems
Hay Fertilization Strategies
Implementing effective fertilization strategies is crucial for maximizing hay yield and quality. Consider the following approaches:
- Split applications: Apply fertilizer in multiple smaller doses throughout the growing season to improve nutrient uptake efficiency.
- Balanced nutrition: Ensure a proper balance of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium based on soil test results and crop requirements.
- Micronutrients: Don’t overlook the importance of micronutrients like boron, sulfur, and zinc in hay production.
- Timing: Apply fertilizers at key growth stages, such as early spring green-up and after each cutting.
Remember, over-fertilization can lead to environmental issues and reduced hay quality, so it’s essential to follow recommended application rates and best management practices.
Multiple Hay Cuttings Per Season
Implementing a multiple cutting system can significantly increase your hay yield and provide a steady supply of high-quality forage throughout the season. Here’s what you need to know:
- Cutting frequency: Depending on your climate and hay type, you may be able to achieve 3-5 cuttings per season.
- Regrowth periods: Allow sufficient time between cuttings for the plants to recover and rebuild energy reserves.
- Nutrient management: Adjust your fertilization program to support multiple cuttings, as each harvest removes nutrients from the soil.
- Weed control: Implement an effective weed management strategy to maintain hay quality across multiple cuttings.
By leveraging Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring, you can track your hay field’s recovery and growth between cuttings, optimizing your harvest schedule for maximum yield and quality.
Hay Drying Methods
Proper hay drying is crucial for preserving nutritional value and preventing spoilage. Let’s explore some effective drying methods:
- Natural air drying: Utilize sunny weather and wind to dry hay naturally in the field.
- Mechanical conditioning: Use hay conditioners or crimpers to crush or break stems, speeding up the drying process.
- Tedding: Spread and fluff the hay with a tedder to increase air circulation and promote even drying.
- Windrow management: Create properly sized windrows to balance drying speed with the risk of weather damage.
- Barn drying: For regions with unpredictable weather, consider investing in barn drying systems to finish the drying process.
Remember, the goal is to reduce moisture content as quickly as possible while minimizing leaf loss and maintaining nutritional quality.
Using Windrowers and Windrows
Windrowers and properly managed windrows play a crucial role in hay drying and quality preservation. Here’s how to make the most of these techniques:
- Windrow width: Adjust windrow width based on your hay’s moisture content, weather conditions, and available equipment.
- Windrow shape: Aim for a uniform, fluffy windrow that allows air to circulate through the hay.
- Windrow orientation: Consider aligning windrows to take advantage of prevailing winds for faster drying.
- Windrow turning: Use rake equipment to gently turn windrows if necessary to promote even drying.
Proper windrow management can significantly impact hay drying time and quality. By using Farmonaut’s weather forecasting tools, you can make informed decisions about when to cut and how to manage your windrows for optimal drying conditions.
Hay Cutting and Moisture Management Guide
To help you quickly reference optimal hay cutting practices and moisture management, we’ve compiled this handy table:
| Hay Type | Optimal Cutting Stage | Ideal Moisture Content for Baling (%) | Recommended Drying Time (hours) | Nutrient Content at Optimal Stage (estimated protein %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfalfa | Early bloom (10% flower) | 15-20 | 48-72 | 18-22 |
| Grass Mix | Boot to early heading | 15-18 | 24-48 | 12-16 |
| Timothy | Early heading | 14-16 | 36-60 | 10-14 |
| Oat Hay | Milk to soft dough stage | 12-15 | 48-72 | 8-12 |
This table serves as a quick reference guide, but remember that specific conditions may vary based on your local climate and management practices.
Optimizing Hay Production with Farmonaut’s Technology
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers optimize their hay production through cutting-edge technology. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system provides valuable insights that can enhance every aspect of hay farming:
- Vegetation health monitoring: Track your hay field’s NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) to assess crop health and determine optimal cutting times.
- Soil moisture analysis: Make informed decisions about irrigation and field operations based on real-time soil moisture data.
- Weather forecasting: Plan your cutting, drying, and baling activities with greater precision using our advanced weather prediction tools.
- Field variability mapping: Identify areas of your hay fields that may require additional attention or management.
By integrating Farmonaut’s technology into your hay production process, you can maximize yield, improve quality, and increase overall farm efficiency.
Conclusion
Mastering high-quality hay production requires attention to detail, proper timing, and the right techniques. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide and leveraging advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, you can significantly improve your hay yield, quality, and overall farm efficiency.
Remember, producing top-notch hay is not just about the end product; it’s about implementing sustainable practices that benefit your land, your livestock, and your bottom line. With careful management of cutting techniques, moisture content, and baling processes, you can ensure a steady supply of nutritious hay for your animals year-round.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights to help you elevate your hay farming game. By staying informed about the latest agricultural practices and embracing precision farming technologies, you’ll be well-equipped to face the challenges of modern hay production and thrive in this essential aspect of agriculture.
FAQs
- What is the ideal moisture content for baling hay?
The ideal moisture content for baling hay typically ranges from 15-20% for small square bales and 14-18% for large round or square bales. - How many cuttings of hay can I expect in a season?
Depending on your climate and hay type, you may be able to achieve 3-5 cuttings per season. Factors such as weather, fertilization, and management practices also influence cutting frequency. - What’s the best way to determine when to cut my hay?
The optimal time to cut hay depends on the type of hay and its intended use. Generally, cut alfalfa at early bloom stage and grasses before heading. Using tools like Farmonaut’s vegetation health monitoring can help determine the best cutting times. - How can I improve the drying time of my hay?
To improve drying time, use mechanical conditioners to crush stems, create proper windrows, and consider using tedders to spread and fluff the hay. Additionally, monitor weather forecasts to plan for optimal drying conditions. - What role does soil management play in hay production?
Proper soil management is crucial for hay production. Regular soil testing, maintaining optimal pH levels, and implementing effective fertilization strategies all contribute to healthy, high-yielding hay fields.