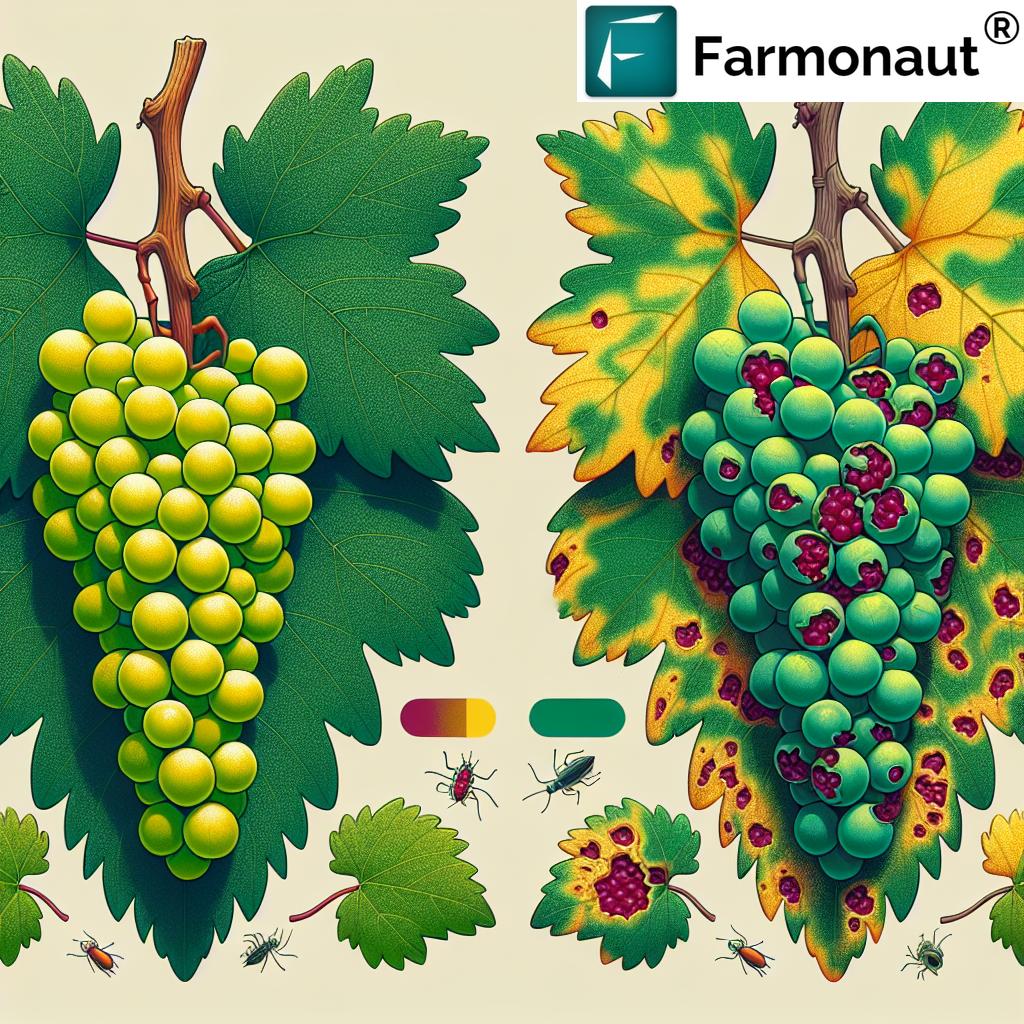
Organic Grape Protection: Controlling Leafhoppers from Bud Break to Harvest

In the world of viticulture, protecting grapevines from pests and diseases is crucial for ensuring a bountiful harvest and producing high-quality wines. At Farmonaut, we understand the challenges that vineyard owners face, especially when it comes to managing persistent pests like leafhoppers. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore organic methods for controlling leafhoppers in vineyards, from bud break to harvest, and how our satellite-based monitoring system can revolutionize pest management in your vineyard.
Understanding Leafhoppers: The Grape’s Tiny Nemesis
Leafhoppers are small, wedge-shaped insects belonging to the families Cicadellidae and Cicadidae. These agile pests are known for their ability to pierce and suck sap from plant tissues, causing significant damage to grape leaves and potentially spreading diseases.
Lifecycle of Leafhoppers in Vineyards
- Winter Survival: Adult leafhoppers overwinter in vineyard debris or nearby vegetation.
- Springtime Emergence: As temperatures rise, they become active and begin feeding on early weeds and emerging grape foliage.
- Bud Break to Early Foliage: Leafhoppers lay eggs in leaf veins, which hatch into nymphs.
- Nymphal Stages: The nymphs go through several molts before becoming adults.
- Multiple Generations: Depending on the climate, leafhoppers can produce multiple generations per growing season.
The Impact of Leafhoppers on Grape Production
Leafhoppers can cause significant damage to grapevines, affecting both yield and quality. Understanding their impact is crucial for developing effective control strategies.
Direct Damage
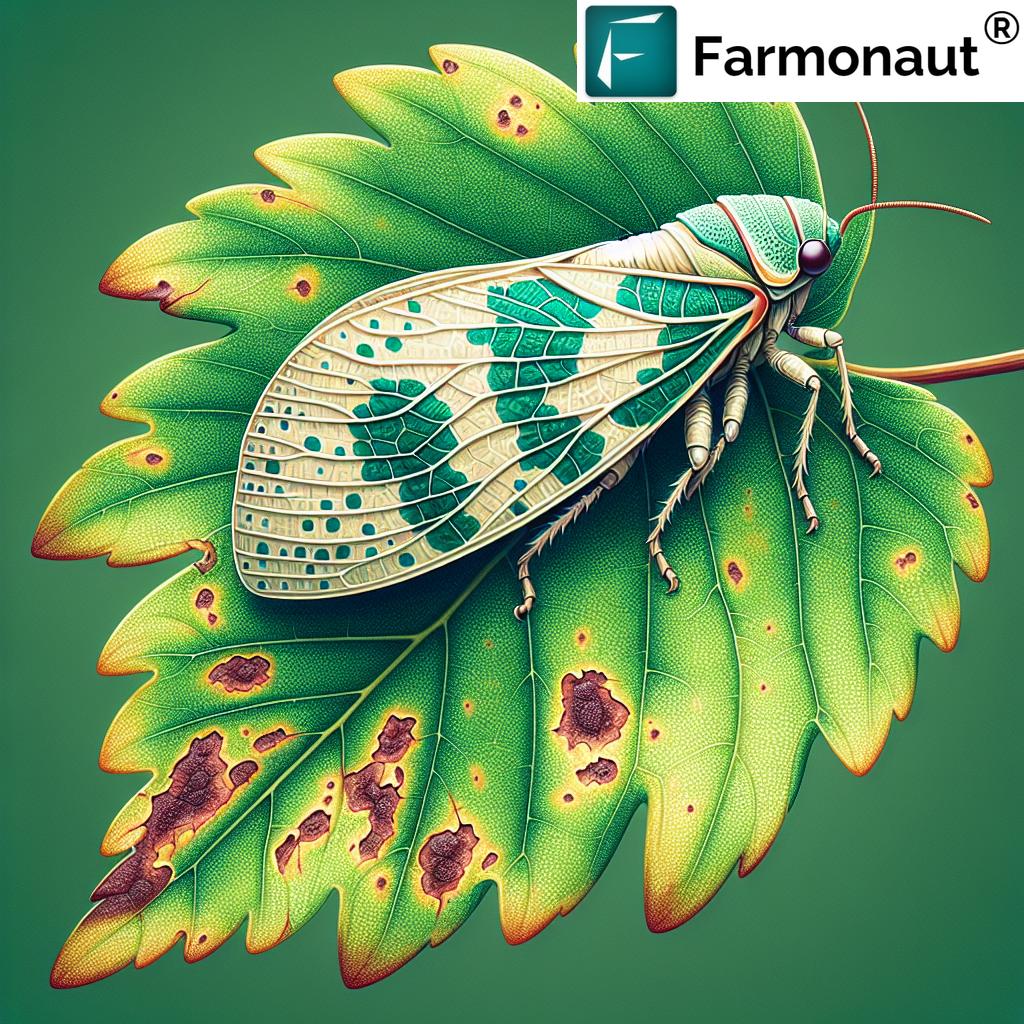
- Leaf Stippling: Feeding activity results in small, pale spots on leaves.
- Reduced Photosynthesis: Damaged leaves are less efficient at producing energy for the plant.
- Leaf Drop: Severe infestations can cause premature defoliation.
Indirect Damage
- Disease Transmission: Some leafhopper species can transmit grapevine diseases.
- Reduced Fruit Quality: Weakened vines produce lower quality grapes.
- Increased Susceptibility: Stressed vines are more vulnerable to other pests and diseases.
Organic Approaches to Leafhopper Control
At Farmonaut, we advocate for sustainable farming practices. Here are some organic methods for managing leafhoppers in your vineyard:
1. Cultural Control Methods
- Vineyard Sanitation: Remove debris and weeds that provide overwintering sites.
- Cover Crops: Plant cover crops that don’t host leafhoppers to reduce their population.
- Pruning and Canopy Management: Proper pruning improves air circulation and reduces humidity, making the environment less favorable for leafhoppers.
2. Biological Control
- Beneficial Insects: Encourage natural predators like lacewings, ladybugs, and parasitic wasps.
- Neem Oil: This natural product can disrupt leafhopper feeding and reproduction.
- Diatomaceous Earth: Sprinkle this natural substance on leaves to deter leafhoppers.
3. Organic Sprays
- Kaolin Clay: Creates a protective barrier on leaves, deterring leafhopper feeding.
- Pyrethrin: A natural insecticide derived from chrysanthemum flowers.
- Insecticidal Soaps: Effective against nymphs when applied directly.
Implementing an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategy
An effective IPM strategy combines various control methods to manage leafhopper populations while minimizing environmental impact. Here’s how to implement IPM in your vineyard:
1. Monitoring and Scouting
Regular monitoring is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. Traditional methods include:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly examine leaves for signs of damage or presence of leafhoppers.
- Yellow Sticky Traps: Place these traps throughout the vineyard to monitor leafhopper populations.
- Leaf Sampling: Count nymphs on a set number of leaves to estimate population density.
However, these methods can be time-consuming and may not provide a comprehensive view of large vineyards. This is where Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system comes into play.
2. Farmonaut’s Satellite Monitoring for Leafhopper Detection
Our advanced satellite technology offers a revolutionary approach to pest monitoring in vineyards. Here’s how it works:
- Wide Coverage: Satellite imagery covers entire vineyards, providing a comprehensive view of plant health.
- Early Detection: Our AI algorithms can detect subtle changes in plant vigor indicative of leafhopper infestation before visible symptoms appear.
- Regular Updates: Frequent satellite passes ensure up-to-date information on vineyard health.
- Data Integration: Combine satellite data with ground-level observations for a complete picture of pest pressure.
To learn more about our satellite monitoring capabilities, visit Farmonaut’s App.
Comparison: Traditional Monitoring vs. Farmonaut Satellite Monitoring
| Feature | Traditional Monitoring | Farmonaut Satellite Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Slow (manual inspection required) | Fast (automated analysis of satellite data) |
| Accuracy | Variable (depends on inspector’s expertise) | High (AI-powered analysis) |
| Coverage Area | Limited (time-consuming for large areas) | Comprehensive (entire vineyard at once) |
| Cost-effectiveness | Low (labor-intensive) | High (automated, requires less manpower) |
3. Setting Action Thresholds
Establish population thresholds that trigger control measures. These thresholds may vary based on:
- Grape Variety: Some varieties are more susceptible to leafhopper damage.
- Growth Stage: Vines are most vulnerable during certain growth stages.
- Environmental Conditions: Drought stress can exacerbate leafhopper impact.
4. Implementing Control Measures
When thresholds are reached, implement appropriate control measures:
- Start with least disruptive methods (e.g., encouraging natural predators).
- Progress to targeted organic sprays if necessary.
- Time applications based on leafhopper life cycle and vine phenology.
5. Evaluating and Adjusting
Continuously assess the effectiveness of your control strategies:
- Use Farmonaut’s satellite data to track changes in vine health over time.
- Adjust your approach based on results and changing conditions.
- Keep detailed records to inform future management decisions.
Seasonal Approach to Leafhopper Control
Managing leafhoppers effectively requires a year-round approach. Here’s a seasonal guide to leafhopper control in vineyards:
Winter (Dormant Season)
- Remove fallen leaves and debris to reduce overwintering sites.
- Prune vines to improve air circulation and reduce humidity.
- Plan your IPM strategy for the upcoming season.
Spring (Bud Break to Early Shoot Growth)
- Monitor for early leafhopper activity using Farmonaut’s satellite imagery.
- Implement cover crops that don’t attract leafhoppers.
- Apply kaolin clay as a preventive measure.
Late Spring to Early Summer (Flowering and Fruit Set)
- Intensify monitoring as leafhopper populations begin to build.
- Release beneficial insects if population thresholds are reached.
- Apply organic sprays if necessary, avoiding flowering periods to protect pollinators.
Summer (Fruit Development)
- Continue regular monitoring with satellite imagery and ground-level checks.
- Implement targeted sprays based on population thresholds.
- Maintain vine health through proper irrigation and nutrition to increase resilience.
Late Summer to Fall (Harvest and Post-Harvest)
- Monitor for late-season population spikes.
- Implement post-harvest treatments if necessary to reduce overwintering populations.
- Begin planning for next season based on this year’s data and experiences.
Advanced Technologies in Leafhopper Management
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of integrating advanced technologies into vineyard management. Here are some cutting-edge tools we offer:
1. AI-Powered Pest Prediction
Our Jeevn AI Advisory System analyzes historical data, weather patterns, and current vineyard conditions to predict leafhopper outbreaks before they occur. This allows for proactive rather than reactive pest management.
2. Drone-Based Precision Spraying
While our primary focus is on satellite monitoring, we also integrate data from drone surveys for ultra-precise pest control. This technology allows for targeted application of organic treatments, reducing overall pesticide use.
3. IoT Sensors for Microclimate Monitoring
Our platform integrates data from in-field sensors to provide real-time information on temperature, humidity, and other factors that influence leafhopper populations. This data is correlated with satellite imagery for comprehensive pest risk assessment.
4. Blockchain for Treatment Traceability
For vineyards focused on organic certification, our blockchain technology ensures complete traceability of all pest management activities. This provides transparency and verifiability for certification bodies and consumers alike.
To explore these advanced features, check out our API documentation.
Economic Considerations in Organic Leafhopper Control
Implementing organic leafhopper control methods can have significant economic implications for vineyard operations. Here’s a breakdown of the costs and benefits:
Costs Associated with Organic Control
- Initial Investment: Setting up monitoring systems and purchasing organic products.
- Labor: Increased time for monitoring and applying organic treatments.
- Reduced Yield: Potential short-term yield reduction during transition to organic methods.
Long-Term Economic Benefits
- Premium Pricing: Organic grapes often command higher market prices.
- Reduced Input Costs: Lower expenses on synthetic pesticides over time.
- Improved Vine Health: Healthier vines lead to more consistent yields and higher quality grapes.
- Ecosystem Services: Enhanced biodiversity can provide natural pest control, reducing management costs.
Cost-Benefit Analysis with Farmonaut
Our platform provides tools for conducting detailed cost-benefit analyses of your pest management strategies:
- ROI Calculator: Input your vineyard data to estimate the return on investment for implementing organic control methods.
- Yield Prediction: Use our AI models to predict potential yield improvements from better pest management.
- Resource Optimization: Analyze data to optimize the use of organic products and labor resources.
Regulatory Considerations for Organic Grape Production
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for vineyards transitioning to or maintaining organic status. Here’s what you need to know:
Organic Certification Requirements
- Transition Period: Typically 3 years of organic management before certification.
- Approved Substances: Only USDA-approved organic substances can be used for pest control.
- Record Keeping: Detailed logs of all pest management activities must be maintained.
Farmonaut’s Compliance Tools
Our platform offers features to help you stay compliant with organic regulations:
- Digital Record Keeping: Automatically log all pest management activities.
- Certification Checklist: Track your progress towards organic certification.
- Regulatory Updates: Receive alerts on changes to organic standards that may affect your operation.
Case Studies: Successful Organic Leafhopper Management
While we don’t provide specific case studies, we can share general insights from successful organic leafhopper management strategies:
Diverse Ecosystem Approach
A California vineyard reduced leafhopper populations by 60% over three years by:
- Planting diverse cover crops to attract beneficial insects
- Installing owl boxes and raptor perches for natural rodent control
- Using Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring to target problem areas quickly
Precision Organic Spraying
An Oregon vineyard optimized their use of organic sprays by:
- Using Farmonaut’s AI predictions to time applications precisely
- Implementing drone-based spraying for targeted application
- Reducing overall spray use by 30% while maintaining effective control
Future Trends in Organic Pest Management
As technology continues to evolve, so do the possibilities for organic pest management in vineyards. Here are some trends we’re watching closely at Farmonaut:
1. Gene Editing for Pest Resistance
Emerging CRISPR technology could lead to the development of grape varieties with enhanced natural resistance to leafhoppers, reducing the need for interventions.
2. Pheromone Disruption
Advanced pheromone technologies could disrupt leafhopper mating cycles on a large scale, providing an eco-friendly control method.
3. Microbiome Management
Understanding and manipulating the vineyard microbiome could lead to natural suppression of pest populations.
4. AI-Driven Ecosystem Management
Future iterations of our AI systems may provide holistic vineyard management recommendations, balancing pest control with overall ecosystem health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I tell if my vineyard has a leafhopper problem?
A: Look for stippling on leaves, small pale spots caused by leafhopper feeding. You may also see the insects themselves on the undersides of leaves. Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring can detect early signs of stress before visible damage occurs.
Q: Are organic methods as effective as conventional pesticides for leafhopper control?
A: When implemented correctly as part of an integrated pest management strategy, organic methods can be just as effective as conventional pesticides. They often provide more sustainable long-term control by preserving beneficial insects and soil health.
Q: How often should I monitor for leafhoppers?
A: Regular monitoring is key. With traditional methods, weekly inspections during the growing season are recommended. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can receive updates as frequently as every 3-5 days, depending on satellite pass frequency.
Q: Can leafhoppers develop resistance to organic treatments?
A: While resistance is less common with organic treatments, it can occur. Rotating different control methods and maintaining a diverse ecosystem helps prevent resistance development.
Q: How does climate change affect leafhopper populations in vineyards?
A: Climate change can lead to milder winters and longer growing seasons, potentially increasing leafhopper populations and generations per year. Farmonaut’s predictive models take climate trends into account for more accurate pest forecasting.
Conclusion
Organic leafhopper control in vineyards is a complex but rewarding endeavor. By combining traditional wisdom with cutting-edge technology like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring and AI-driven insights, vineyard owners can effectively manage these persistent pests while maintaining the health of their vines and the surrounding ecosystem. Remember, successful pest management is an ongoing process that requires patience, adaptability, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
Ready to revolutionize your vineyard’s pest management strategy? Explore Farmonaut’s solutions:
Join the future of sustainable viticulture with Farmonaut!