Spotted Bollworm vs Pink Bollworm: Understanding and Managing These Cotton Pests
At Farmonaut, we understand the challenges that farmers face when it comes to pest management, especially in cotton cultivation. Two of the most notorious pests that plague cotton crops are the spotted bollworm and the pink bollworm. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore these pests in detail, helping you identify, differentiate, and effectively manage them using modern agricultural technologies.
Introduction to Bollworms
Bollworms are a group of lepidopteran pests that cause significant damage to cotton and other crops. The term “bollworm” refers to the larval stage of several moth species that feed on the fruiting bodies (bolls) of cotton plants. Two of the most problematic bollworm species are the spotted bollworm and the pink bollworm.
Understanding the Spotted Bollworm
The spotted bollworm (Earias vittella) is a serious pest that affects not only cotton but also other crops in the Malvaceae family. Let’s delve into the details of this destructive pest.
Spotted Bollworm Order and Family
The spotted bollworm order is Lepidoptera, which includes moths and butterflies. It belongs to the spotted bollworm family Nolidae, a group of moths known for their distinctive wing patterns and agricultural pest status.
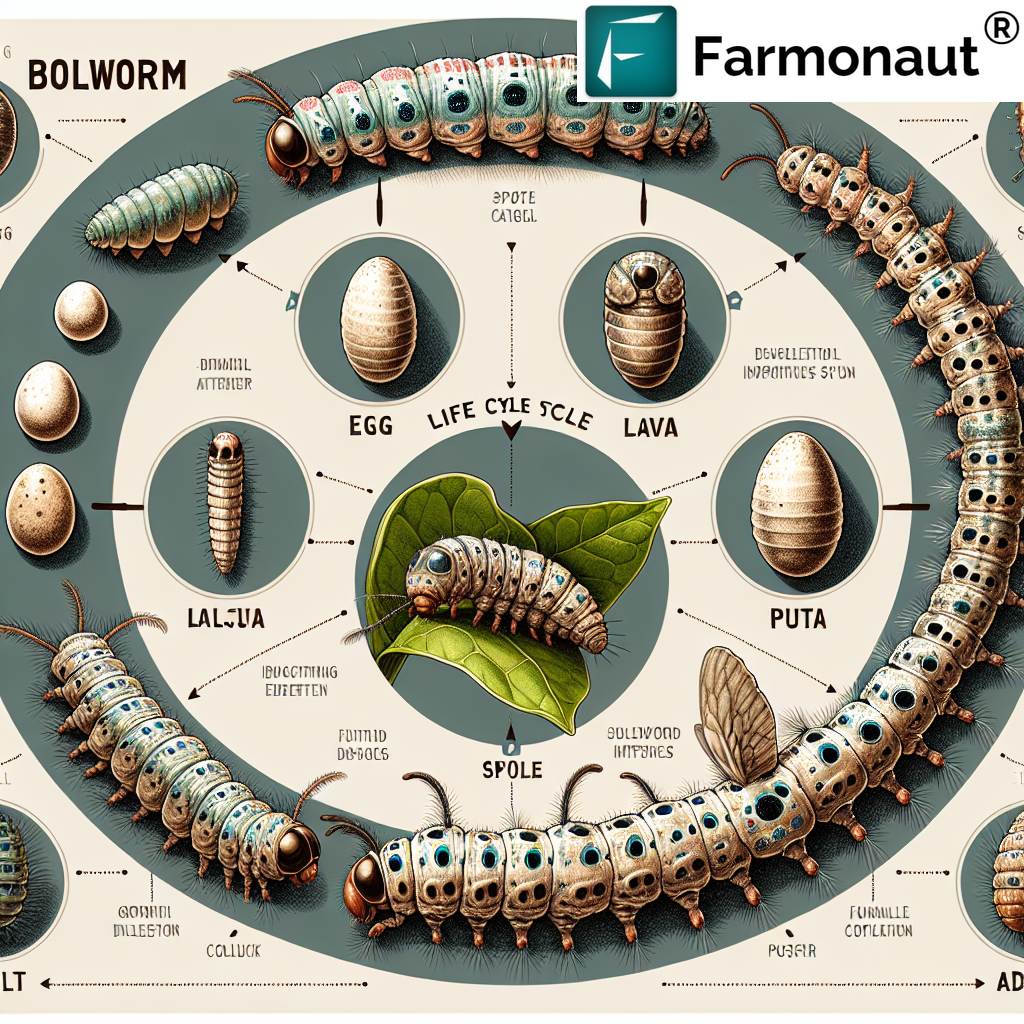
Lifecycle and Characteristics
Understanding the lifecycle of the spotted bollworm is crucial for effective pest management. Here’s a breakdown of its life stages:
- Egg Stage: Female moths lay small, round eggs on young leaves, flower buds, or tender shoots.
- Larval Stage: The larvae, which are the damaging stage, hatch and begin feeding on plant tissues.
- Pupal Stage: After several molts, the larvae pupate in cocoons, often within plant debris.
- Adult Stage: The spotted bollworm adult emerges as a small moth with distinctive wing patterns.
Spotted Bollworm Symptoms
Recognizing spotted bollworm symptoms is essential for early detection and management. Some key indicators include:
- Circular holes in squares and bolls
- Shedding of damaged squares and young bolls
- Presence of frass (insect excrement) near entry holes
- Distorted growth of shoots and flower buds
- Wilting and drooping of affected plant parts
Spotted Bollworm Diagram
A spotted bollworm diagram can be an invaluable tool for farmers and agronomists to identify the pest at various life stages. While we don’t have a specific diagram to show here, such illustrations typically depict the egg, larval, pupal, and adult stages, highlighting key identifying features.
Crops Affected: Spotted Bollworm is a Pest of
The spotted bollworm is a pest of several important crops, including:
- Cotton
- Okra (Bhindi)
- Hibiscus
- Other plants in the Malvaceae family
Spotted Bollworm in Bhendi
While cotton is a primary host, the spotted bollworm in bhendi (okra) is also a significant concern. In okra cultivation, the pest can cause severe damage to fruits, leading to substantial yield losses if not managed properly.
Pink Bollworm: Another Cotton Menace
The pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) is another major pest of cotton that requires careful management. Understanding its characteristics is crucial for differentiating it from the spotted bollworm.
Characteristics of Pink Bollworm
- Adult moths are small with brownish-gray wings
- Larvae are pink in color, giving the pest its common name
- Primarily attacks cotton bolls, feeding on seeds and lint
- Can overwinter in cotton seeds, making it difficult to eradicate
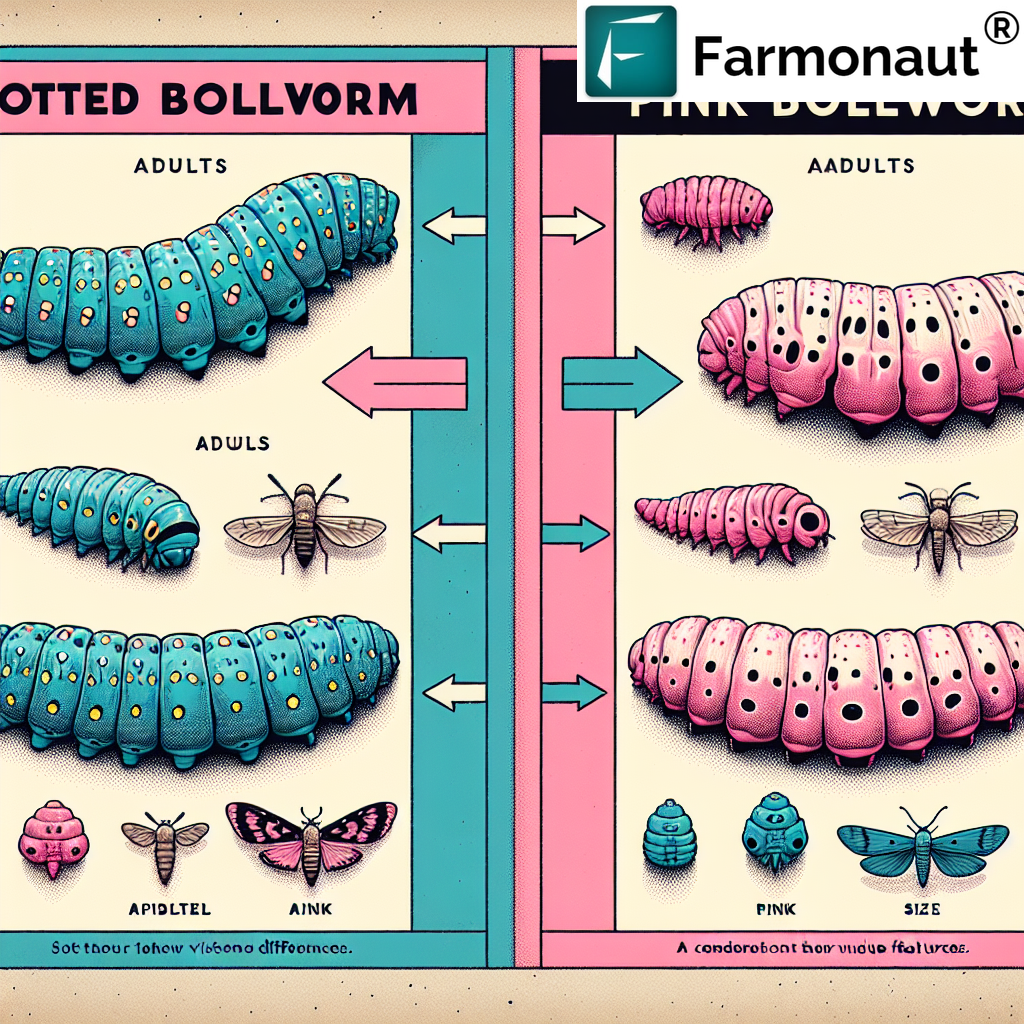
Difference Between Spotted Bollworm and Pink Bollworm
Understanding the difference between spotted bollworm and pink bollworm is crucial for implementing targeted pest management strategies. Here’s a comparison of these two cotton pests:
| Characteristic | Spotted Bollworm | Pink Bollworm |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Earias vittella | Pectinophora gossypiella |
| Larval Color | Varies, often with spots | Pink |
| Primary Host | Cotton, okra, and other Malvaceae | Primarily cotton |
| Feeding Habit | Attacks shoots, flower buds, and bolls | Primarily feeds on cotton seeds and lint |
| Overwintering | Usually in plant debris | Can overwinter in cotton seeds |
Integrated Pest Management for Bollworms
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an integrated approach to pest management that combines traditional methods with cutting-edge technology. Here’s how we can help farmers combat bollworms effectively:
1. Early Detection with Satellite Imagery
Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system can detect early signs of pest infestation by analyzing vegetation health indices. This allows farmers to take prompt action before the pest population reaches damaging levels.
2. AI-Powered Advisory
Our Jeevn AI advisory system provides personalized recommendations for pest management based on real-time data and historical patterns. This helps farmers make informed decisions about when and how to apply control measures.
3. Weather-Based Forecasting
Bollworm populations are often influenced by weather conditions. Our advanced weather forecasting capabilities help predict potential pest outbreaks, allowing for preemptive action.
4. Precision Application of Control Measures
By identifying specific areas of infestation through our satellite imagery, farmers can apply pesticides or biological control agents precisely where they’re needed, reducing costs and environmental impact.
5. Crop Rotation Guidance
Our platform can provide recommendations for crop rotation strategies that help break the pest lifecycle and reduce bollworm populations over time.
Why Choose Farmonaut for Bollworm Management?
Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers several advantages over traditional drone and IoT-based farm monitoring methods when it comes to managing pests like bollworms:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale, entire farms at once | Limited by flight time and regulations | Depends on sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data | Regular updates without manual intervention | Requires manual flights | Continuous but localized data |
| Cost-effectiveness | High, especially for large areas | Moderate to high initial investment | High initial cost for sensor network |
| Data Analysis | Advanced AI and machine learning algorithms | Requires specialized software and expertise | Often limited to basic metrics |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly interface, accessible anywhere | Requires trained operators | Requires technical setup and maintenance |
Implementing Farmonaut’s Solutions
To get started with our advanced pest management solutions, farmers and agribusinesses can:
- Download our mobile app: Android | iOS
- Access our web platform: Farmonaut Web App
- Integrate our API for custom solutions: Farmonaut API
- Explore our developer documentation: API Documentation
Subscription Options
To access our full range of bollworm management and other agricultural solutions, consider subscribing to Farmonaut:
Conclusion
Managing bollworms, whether spotted or pink, requires a comprehensive approach that combines traditional agricultural knowledge with modern technology. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing farmers with the tools and insights they need to protect their crops effectively and sustainably. By leveraging our satellite-based monitoring, AI-powered advisory systems, and integrated pest management strategies, farmers can stay ahead of bollworm infestations and optimize their cotton yields.
FAQs
-
Q: How can I distinguish between spotted bollworm and pink bollworm in the field?
A: The main difference is in the larval color and feeding habits. Spotted bollworm larvae vary in color and often have spots, while pink bollworm larvae are distinctly pink. Spotted bollworms tend to attack various plant parts, while pink bollworms primarily feed on cotton seeds and lint. -
Q: Can Farmonaut’s satellite imagery detect bollworm infestations?
A: While our satellite imagery can’t directly detect individual pests, it can identify changes in crop health that may indicate pest infestations, allowing for early intervention. -
Q: How often should I monitor my cotton fields for bollworm activity?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial, especially during vulnerable growth stages. With Farmonaut’s system, you can receive frequent updates on crop health without manual field visits. -
Q: Are there any natural predators that can help control bollworm populations?
A: Yes, several natural enemies like parasitic wasps, predatory bugs, and birds can help control bollworm populations. Our AI advisory system can provide guidance on promoting beneficial insects in your fields. -
Q: How can crop rotation help in managing bollworm infestations?
A: Crop rotation disrupts the pest lifecycle by removing their preferred host plants. Our platform can suggest optimal rotation strategies based on your specific farm conditions and pest pressure.
By understanding the nuances of spotted and pink bollworms and leveraging advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, farmers can significantly improve their pest management strategies. Remember, effective bollworm control is not just about reacting to infestations but proactively managing your crops with precision and insight.