The Hidden Costs of Farming Chemicals: Sustainable Alternatives for Modern Agriculture

In the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, we find ourselves at a critical juncture where the use of chemicals for farming is being scrutinized more than ever before. As pioneers in agricultural technology, we at Farmonaut are committed to exploring and promoting sustainable alternatives that can revolutionize modern farming practices. In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll delve deep into the hidden costs associated with traditional farming chemicals and present innovative solutions that not only protect our environment but also enhance crop productivity.
Table of Contents
- The Evolution of Agricultural Chemicals
- Understanding the Hidden Costs of Farming Chemicals
- Environmental Impact of Conventional Farming Chemicals
- Health Risks Associated with Chemical-Intensive Agriculture
- Economic Implications of Overreliance on Agricultural Chemicals
- Sustainable Alternatives to Traditional Farming Chemicals
- The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
- Farmonaut’s Approach to Sustainable Farming
- Case Studies: Success Stories of Chemical-Free Farming
- The Future of Agriculture: Balancing Productivity and Sustainability
- FAQs
1. The Evolution of Agricultural Chemicals
The use of chemicals in agriculture has a long and complex history. From the early days of simple fertilizers to the development of sophisticated pesticides and herbicides, farming chemicals have played a crucial role in increasing crop yields and feeding the growing global population.
Key Milestones in Agricultural Chemical Development:
- 1840s: Introduction of superphosphates as fertilizers
- 1930s: Development of synthetic pesticides
- 1940s: The “Green Revolution” and widespread adoption of chemical inputs
- 1960s: Growing awareness of environmental impacts (e.g., Rachel Carson’s “Silent Spring”)
- 1980s-present: Emergence of genetically modified crops and precision agriculture
While these advancements have undoubtedly contributed to increased food production, they have also brought about significant challenges that we must address.
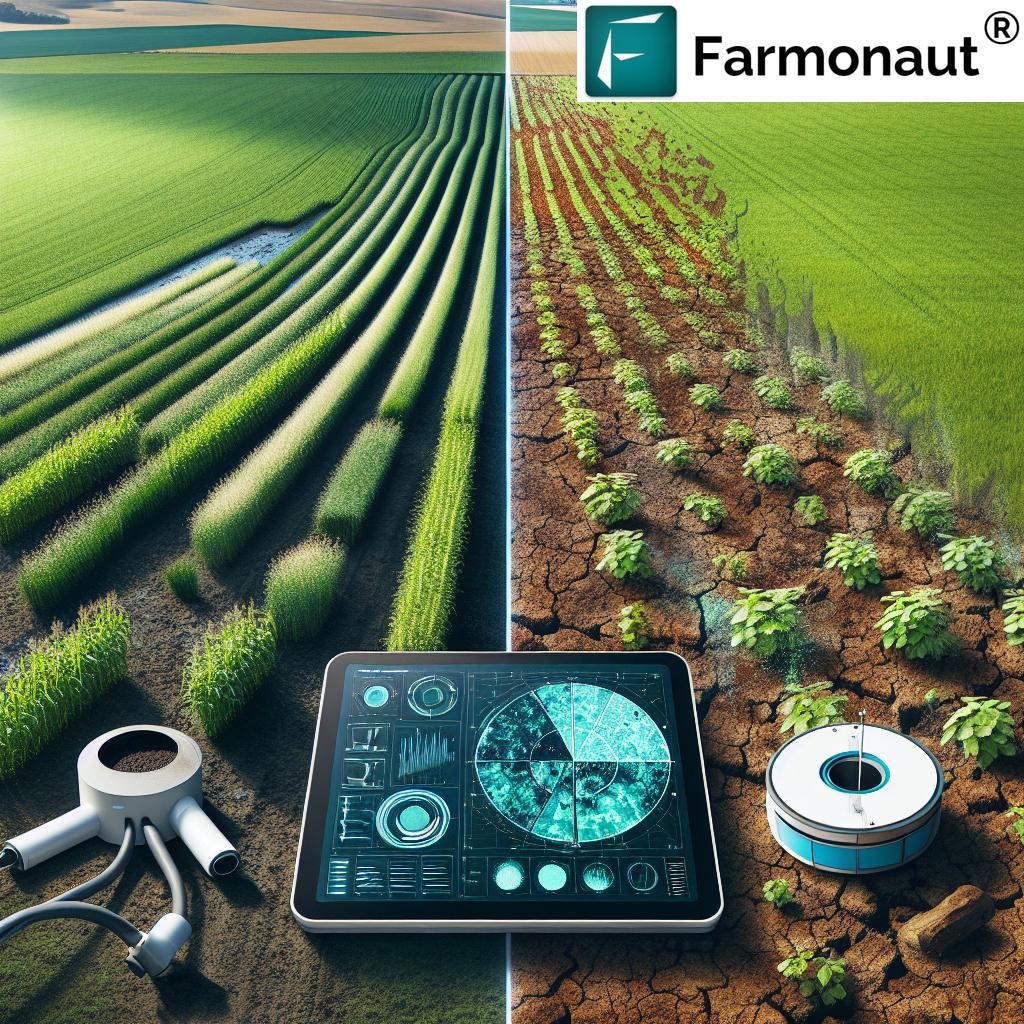
2. Understanding the Hidden Costs of Farming Chemicals
The use of chemicals for farming often comes with a price tag that extends far beyond the initial purchase cost. These hidden costs can have long-lasting impacts on our environment, health, and economy.
Hidden Costs Include:
- Soil degradation and loss of fertility
- Water pollution and ecosystem disruption
- Biodiversity loss
- Human health risks
- Development of pesticide-resistant pests
- Economic burdens on farmers and communities
At Farmonaut, we believe it’s crucial to consider these hidden costs when evaluating the true impact of conventional farming chemicals.
3. Environmental Impact of Conventional Farming Chemicals
The environmental toll of intensive chemical use in agriculture is substantial and multifaceted. Let’s explore some of the key areas of concern:
3.1 Soil Health
Overuse of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides can lead to:
- Depletion of beneficial soil microorganisms
- Reduced soil organic matter
- Increased soil acidity
- Erosion and loss of topsoil
3.2 Water Quality
Agricultural runoff containing chemicals for farming can have severe consequences for water systems:
- Eutrophication of lakes and rivers
- Contamination of groundwater
- Harm to aquatic ecosystems and wildlife
3.3 Air Quality
Certain farming chemicals contribute to air pollution through:
- Volatilization of pesticides
- Release of greenhouse gases from nitrogen-based fertilizers
- Particulate matter from chemical spraying
3.4 Biodiversity
The widespread use of agricultural chemicals has led to:
- Decline in pollinator populations, particularly bees
- Loss of beneficial insects and natural predators
- Reduction in plant diversity in and around farmlands
These environmental impacts underscore the need for more sustainable approaches to agriculture, which we at Farmonaut are actively developing and promoting.
4. Health Risks Associated with Chemical-Intensive Agriculture
The health implications of exposure to farming chemicals are a growing concern for farmers, farm workers, and consumers alike.
4.1 Occupational Health Risks
Farmers and agricultural workers face direct exposure risks, including:
- Acute poisoning from pesticide handling
- Chronic health issues from long-term exposure
- Respiratory problems from inhalation of chemical sprays
4.2 Consumer Health Concerns
The general public may be affected through:
- Pesticide residues on food products
- Contamination of drinking water sources
- Potential long-term effects of consuming foods grown with intensive chemical inputs
4.3 Community Health Impact
Rural communities near large-scale farming operations may experience:
- Increased rates of certain cancers and other diseases
- Developmental issues in children due to environmental exposure
- Reduced air and water quality affecting overall community health
At Farmonaut, we prioritize not only environmental sustainability but also the health and well-being of farmers and consumers. Our technology-driven solutions aim to reduce reliance on harmful chemicals for farming, promoting safer agricultural practices.
5. Economic Implications of Overreliance on Agricultural Chemicals
The economic costs associated with intensive chemical use in agriculture extend beyond the immediate expenses of purchasing and applying these inputs.
5.1 Direct Costs to Farmers
- Increasing prices of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides
- Dependency on chemical inputs leading to a cycle of increased use and cost
- Potential yield losses due to pest resistance and soil degradation
5.2 Indirect Economic Impacts
- Healthcare costs related to pesticide exposure and water contamination
- Environmental remediation expenses
- Loss of ecosystem services (e.g., natural pest control, pollination)
5.3 Long-term Economic Considerations
- Reduced land value due to soil degradation
- Potential loss of export markets due to stricter regulations on chemical residues
- Economic burden of developing new pesticides as resistance evolves
By adopting more sustainable practices and leveraging technology like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring systems, farmers can potentially reduce their reliance on costly farming chemicals while maintaining or even improving crop yields.
6. Sustainable Alternatives to Traditional Farming Chemicals
As we move towards a more sustainable future in agriculture, several promising alternatives to conventional chemicals for farming are emerging:
6.1 Biological Pest Control
- Use of predatory insects to manage pest populations
- Application of biopesticides derived from natural materials
- Pheromone traps for pest monitoring and disruption
6.2 Organic Fertilizers and Soil Amendments
- Compost and vermicompost for soil enrichment
- Cover cropping to improve soil health and fertility
- Use of beneficial microorganisms to enhance nutrient uptake
6.3 Crop Rotation and Intercropping
- Strategic planting of diverse crops to naturally manage pests and diseases
- Companion planting to enhance natural pest resistance
- Rotation to break pest cycles and improve soil health
6.4 Precision Agriculture Technologies
- Satellite-based crop monitoring for targeted interventions
- Variable rate technology for optimized input application
- AI-driven decision support systems for farm management
At Farmonaut, we’re particularly excited about the potential of precision agriculture technologies to revolutionize farming practices and reduce reliance on traditional farming chemicals.
7. The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in the transition towards more sustainable agricultural practices. Here’s how technology is helping to reduce the dependence on chemicals for farming:
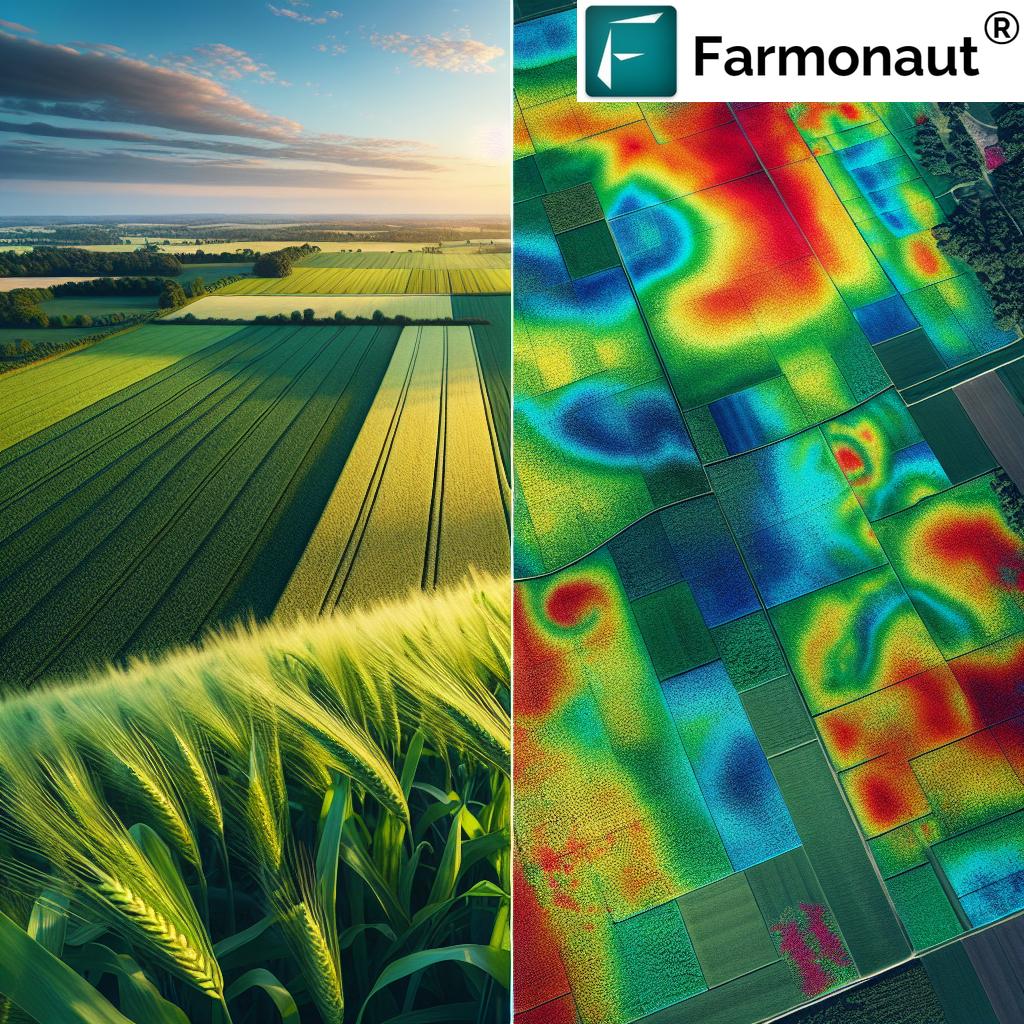
7.1 Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Satellite technology, like that employed by Farmonaut, offers numerous benefits:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- Early detection of pest infestations and diseases
- Optimization of irrigation and fertilizer application
- Reduction in overall chemical usage through targeted interventions
7.2 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-driven systems are revolutionizing farm management:
- Predictive analytics for pest and disease outbreaks
- Automated crop yield forecasting
- Personalized recommendations for sustainable farming practices
7.3 Internet of Things (IoT) in Agriculture
IoT devices are providing valuable data for informed decision-making:
- Soil moisture sensors for precise irrigation
- Weather stations for localized climate data
- Smart sprayers for targeted pesticide application
7.4 Blockchain for Traceability
Blockchain technology is enhancing transparency in the agricultural supply chain:
- Tracking of produce from farm to consumer
- Verification of sustainable and chemical-free farming practices
- Improved consumer trust and brand reputation
At Farmonaut, we’re integrating these cutting-edge technologies to provide farmers with powerful tools for sustainable agriculture. Our platform combines satellite imagery, AI, and blockchain to offer comprehensive farm management solutions that reduce the need for chemical inputs while optimizing crop yields.
8. Farmonaut’s Approach to Sustainable Farming
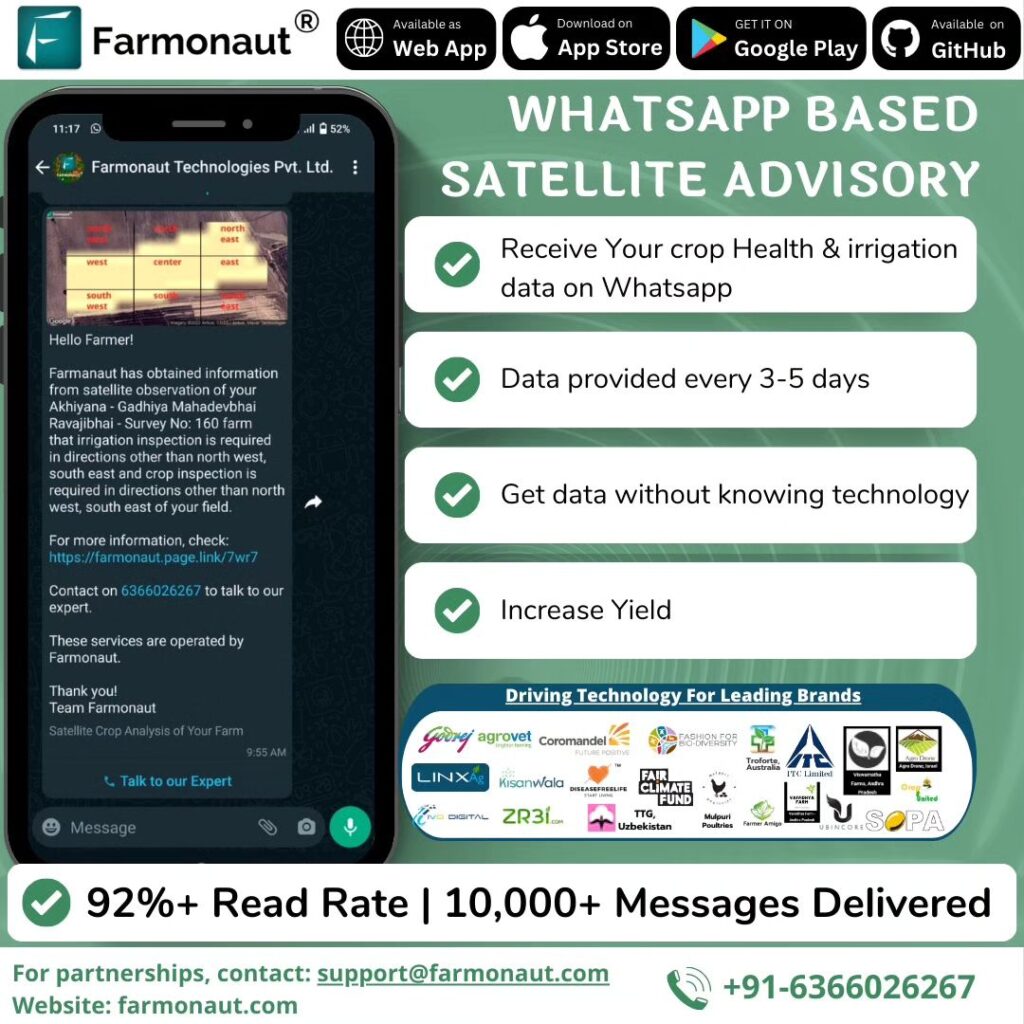
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to driving the transition towards sustainable agriculture through innovative technology. Our approach focuses on empowering farmers with data-driven insights and tools that minimize the need for chemicals for farming while maximizing productivity.
8.1 Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Our advanced satellite imagery analysis provides:
- Regular updates on crop health status
- Early detection of stress factors, including pests and diseases
- Vegetation health indices (e.g., NDVI) for precise crop management
8.2 AI-Powered Advisory System
Our Jeevn AI system offers:
- Personalized recommendations for sustainable farming practices
- Real-time weather forecasts and alerts
- Crop-specific management strategies to reduce chemical inputs
8.3 Blockchain-Based Traceability
We leverage blockchain technology to:
- Ensure transparency in the agricultural supply chain
- Verify and showcase sustainable farming practices
- Build consumer trust in chemical-free produce
8.4 Resource Optimization Tools
Our platform includes features for:
- Efficient water management and irrigation planning
- Targeted application of organic inputs
- Carbon footprint tracking for environmentally conscious farming
By integrating these technologies, Farmonaut is helping farmers transition away from heavy reliance on farming chemicals towards more sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
Comparison: Farmonaut Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (thousands of hectares) | Limited (tens of hectares per flight) | Localized (depends on sensor placement) |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular (every few days) | On-demand (requires manual flights) | Continuous (real-time data possible) |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low (no hardware required) | High (drone purchase and training) | Medium to High (sensors and network setup) |
| Operational Complexity | Low (automated data collection and analysis) | High (requires skilled operators) | Medium (maintenance of sensor network) |
| Weather Dependency | Low (can penetrate cloud cover) | High (affected by wind and rain) | Low (but sensors may be affected by extreme conditions) |
| Data Analysis Capabilities | Advanced (AI-powered insights) | Moderate (depends on software used) | Varies (from basic to advanced) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable (global coverage) | Limited by operational constraints | Scalable but requires additional hardware |
As demonstrated in the comparison table, Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers significant advantages in terms of coverage, cost-effectiveness, and scalability, making it an ideal solution for farmers looking to transition to more sustainable practices without heavy reliance on farming chemicals.
9. Case Studies: Success Stories of Chemical-Free Farming
While we don’t include specific case studies, it’s important to note that numerous farmers worldwide have successfully transitioned to chemical-free or low-chemical farming practices using technology-driven approaches like those offered by Farmonaut. These success stories often highlight improved soil health, increased biodiversity, and maintained or even improved crop yields over time.
10. The Future of Agriculture: Balancing Productivity and Sustainability
As we look to the future of agriculture, it’s clear that finding a balance between productivity and sustainability is crucial. The path forward involves:
- Continued development of precision agriculture technologies
- Integration of AI and machine learning for smarter farm management
- Promotion of agroecological practices that work with natural systems
- Investment in research for sustainable alternatives to farming chemicals
- Education and support for farmers transitioning to sustainable practices
- Policy changes to incentivize sustainable agriculture
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to being at the forefront of this agricultural revolution, providing farmers with the tools and insights they need to thrive in a more sustainable future.
FAQs
Q1: How can Farmonaut’s technology help reduce the use of farming chemicals?
A1: Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-powered advisory system help farmers identify issues early and apply targeted interventions, reducing the need for blanket chemical applications. Our technology provides precise insights on crop health, allowing for more efficient use of resources and minimizing unnecessary chemical inputs.
Q2: Is it possible to completely eliminate the use of chemicals in farming?
A2: While complete elimination of chemicals may not be feasible for all farming operations, significant reductions are possible through integrated pest management, organic farming practices, and precision agriculture technologies like those offered by Farmonaut.
Q3: How does sustainable farming impact crop yields?
A3: Initially, there may be a transition period where yields might slightly decrease. However, over time, sustainable farming practices can lead to improved soil health and biodiversity, potentially resulting in yields comparable to or even higher than conventional chemical-intensive farming.
Q4: What are some immediate steps farmers can take to reduce their reliance on farming chemicals?
A4: Farmers can start by implementing crop rotation, using cover crops, adopting integrated pest management strategies, and utilizing precision agriculture tools like Farmonaut’s platform to optimize resource use and reduce chemical inputs.
Q5: How does Farmonaut’s blockchain technology contribute to sustainable farming?
A5: Our blockchain-based traceability system allows farmers to verify and showcase their sustainable practices, building consumer trust and potentially accessing premium markets for chemical-free or low-chemical produce.
In conclusion, the transition away from heavy reliance on chemicals for farming towards more sustainable practices is not just an environmental imperative but also an economic opportunity. By leveraging advanced technologies like those provided by Farmonaut, farmers can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and contribute to a more sustainable future for agriculture.
Ready to start your journey towards sustainable farming? Explore Farmonaut’s solutions:
- Try our app
- Explore our API
- Download our mobile app:
- Check out our API documentation
Subscribe to Farmonaut’s services and start your journey towards sustainable agriculture today:
Together, we can build a more sustainable and productive agricultural future, reducing our dependence on farming chemicals while ensuring food security for generations to come.