Understanding Land Classification in Agriculture: From Village Importance to Global Perspectives
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, understanding the intricacies of land classification is crucial for sustainable farming practices and optimal resource management. At Farmonaut, we recognize the significance of this knowledge and its impact on agricultural productivity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the various aspects of land classification, exploring its importance from the village level to national scales, with a particular focus on the UK’s approach.
The Importance of Land Classification in Agriculture
Land classification in agriculture is a fundamental process that categorizes land based on its characteristics, capabilities, and potential uses. This classification serves as a cornerstone for effective land management, agricultural planning, and sustainable development. Let’s explore why the classification of land in agriculture is so crucial:
- Optimized Land Use: By understanding the capabilities of different land types, farmers and policymakers can make informed decisions about crop selection and farming practices.
- Resource Conservation: Proper classification helps in preserving soil quality and managing water resources more efficiently.
- Sustainable Development: It aids in balancing agricultural needs with environmental conservation efforts.
- Economic Planning: Land classification guides investment decisions in agriculture and rural development.
- Policy Formulation: Governments use land classification data to develop agricultural policies and land use regulations.
Classification of Land Resources: A Comprehensive Approach
The classification of land resources involves a systematic categorization of land based on various factors. This process is essential for understanding the potential and limitations of different land areas for agricultural use. Here’s an overview of the key aspects considered in land resource classification:
- Soil Characteristics:
- Texture and structure
- Depth and fertility
- pH levels and mineral content
- Topography:
- Slope and elevation
- Landform types (plains, hills, valleys)
- Climate:
- Rainfall patterns
- Temperature ranges
- Humidity levels
- Water Resources:
- Availability of surface water
- Groundwater levels
- Irrigation potential
- Vegetation Cover:
- Natural vegetation types
- Forest cover
At Farmonaut, we integrate these factors into our satellite-based monitoring systems, providing farmers with comprehensive insights into their land resources. Our advanced technology allows for real-time assessment of soil health, vegetation indices, and water availability, enabling more informed decision-making in agricultural practices.
Land Capability Classification: A Tool for Sustainable Agriculture
Land capability classification is a systematic framework used to evaluate and categorize land based on its potential for sustainable agricultural use. This classification system takes into account both the physical characteristics of the land and the potential risks associated with its use. The primary objective is to guide land use decisions that maximize productivity while minimizing environmental degradation.
Key Principles of Land Capability Classification
- Soil Quality Assessment: Evaluating soil depth, texture, structure, and fertility.
- Erosion Risk: Considering factors that contribute to soil erosion and land degradation.
- Drainage Characteristics: Assessing natural drainage and potential for waterlogging.
- Climate Suitability: Matching land capabilities with local climate conditions.
- Topography: Analyzing slope and landform for agricultural suitability.
At Farmonaut, we incorporate these principles into our satellite-based monitoring systems. Our advanced algorithms analyze multispectral imagery to provide detailed insights into land capability, helping farmers make informed decisions about crop selection and land management practices.
The USDA Land Capability Classification System
One of the most widely recognized systems is the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Land Capability Classification. This system categorizes land into eight classes based on their capability to support agricultural production:
- Class I: Soils have few limitations that restrict their use
- Class II: Soils have moderate limitations that reduce the choice of plants or require moderate conservation practices
- Class III: Soils have severe limitations that reduce the choice of plants or require special conservation practices, or both
- Class IV: Soils have very severe limitations that restrict the choice of plants or require very careful management, or both
- Class V: Soils are subject to little or no erosion but have other limitations that are impractical to remove, limiting their use largely to pasture, rangeland, forestland, or wildlife habitat
- Class VI: Soils have severe limitations that make them generally unsuitable for cultivation
- Class VII: Soils have very severe limitations that make them unsuitable for cultivation and restrict their use largely to grazing, forestland, or wildlife habitat
- Class VIII: Soils and miscellaneous areas have limitations that preclude commercial plant production and that restrict their use to recreational purposes, wildlife habitat, watershed, or aesthetic purposes
This classification system helps in determining the most appropriate use for each land parcel, ensuring sustainable agricultural practices and environmental conservation.
Land Classification Maps: Visual Tools for Agricultural Planning
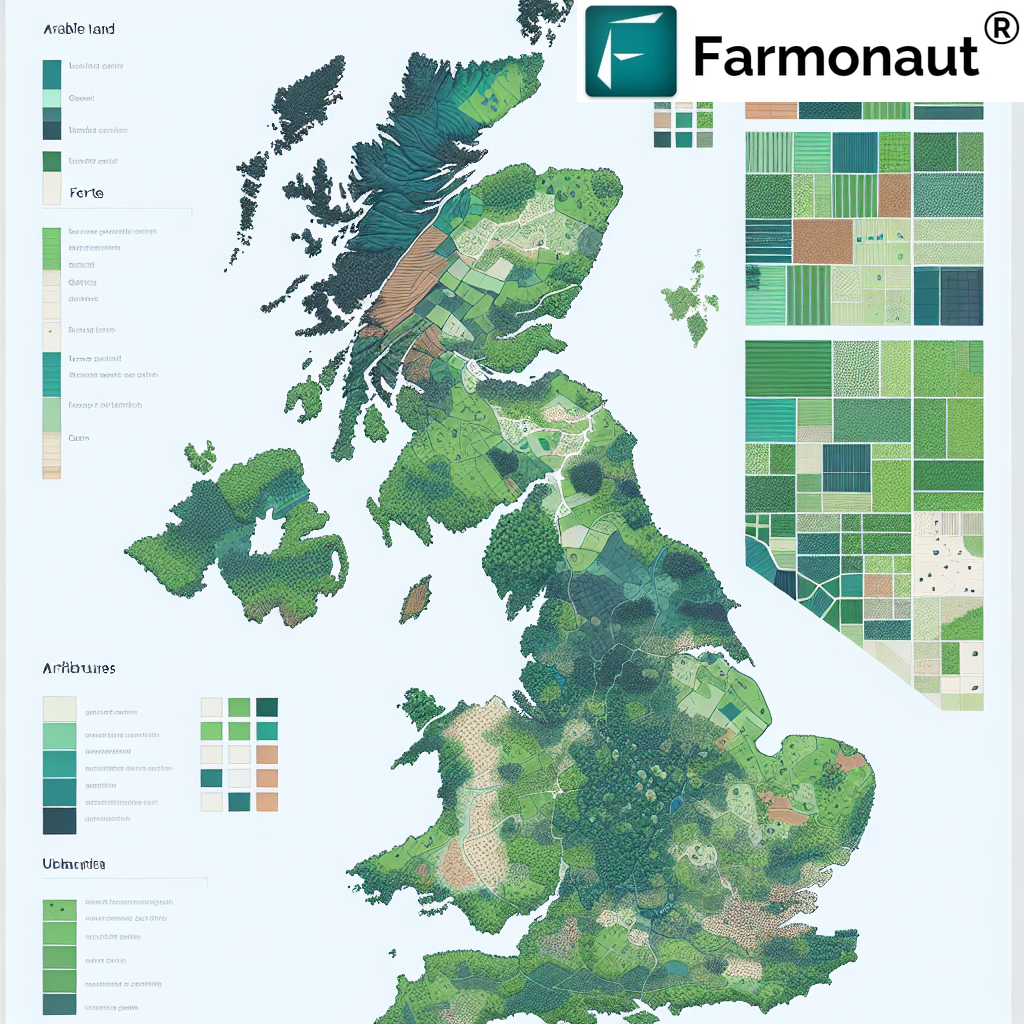
A land classification map is a powerful visual representation of land capabilities and characteristics. These maps serve as essential tools for farmers, policymakers, and land managers in making informed decisions about land use and agricultural planning. At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of these visual aids and incorporate them into our satellite-based monitoring systems.
Components of a Land Classification Map
- Soil Types: Different soil textures and compositions are color-coded or symbolized.
- Topography: Contour lines or shading indicate elevation and slope.
- Land Use Categories: Areas are designated for specific agricultural, forestry, or conservation purposes.
- Water Resources: Rivers, lakes, and irrigation potential are marked.
- Vegetation Cover: Natural vegetation and crop types are indicated.
Benefits of Land Classification Maps
- Spatial Understanding: Provides a clear visual representation of land characteristics across a region.
- Decision Support: Aids in crop selection, irrigation planning, and conservation efforts.
- Resource Allocation: Helps in efficient distribution of agricultural resources.
- Risk Assessment: Identifies areas prone to erosion, flooding, or other environmental risks.
- Policy Implementation: Supports the development and implementation of land use policies.
At Farmonaut, we integrate advanced mapping technologies with our satellite imagery to create dynamic, up-to-date land classification maps. These maps are accessible through our mobile and web applications, providing farmers with real-time insights into their land’s capabilities and potential.
Land Classification in the UK: A Model for Sustainable Agriculture
The United Kingdom has developed a comprehensive approach to land classification that serves as a model for many countries. The UK’s system, known as the Agricultural Land Classification (ALC), provides a framework for assessing the quality of agricultural land and its potential for crop production.
The UK Agricultural Land Classification System
The ALC system classifies land into five grades, with Grade 1 being the best quality and Grade 5 the poorest:
- Grade 1: Excellent quality agricultural land
- Grade 2: Very good quality agricultural land
- Grade 3: Good to moderate quality agricultural land (subdivided into 3a and 3b)
- Grade 4: Poor quality agricultural land
- Grade 5: Very poor quality agricultural land
This classification is based on factors such as climate, site characteristics, and soil properties. It provides a standardized method for assessing land quality across the UK, guiding agricultural practices and land use planning.
Application of Land Classification in UK Agriculture
- Policy Development: The ALC system informs national and local policies on agricultural land use and protection.
- Planning Decisions: It guides decisions on land development, helping to preserve high-quality agricultural land.
- Farm Management: Farmers use this classification to optimize crop selection and farming practices.
- Environmental Conservation: It aids in identifying areas suitable for environmental schemes and habitat restoration.
- Research and Development: The classification system supports agricultural research and innovation efforts.
At Farmonaut, we appreciate the UK’s structured approach to land classification and incorporate similar principles in our global satellite monitoring systems. Our technology allows for the adaptation of these classification methods to diverse agricultural landscapes worldwide.
Why is Classification of Land in a Village Important?
The question “why is classification of land in a village important” is crucial for understanding the role of land management in rural development. Village-level land classification forms the foundation for sustainable agricultural practices and community development. Here’s why it’s so vital:
- Resource Optimization: Proper classification ensures that each parcel of land is used for its most suitable purpose, maximizing agricultural productivity.
- Sustainable Farming: It helps in implementing farming practices that are in harmony with the land’s capabilities, reducing environmental degradation.
- Economic Planning: Village-level classification aids in economic decision-making, guiding investments in agriculture and rural infrastructure.
- Community Development: It supports equitable land distribution and use, fostering balanced community growth.
- Environmental Conservation: Identifies areas that need protection or special management for ecological balance.
- Disaster Preparedness: Helps in identifying areas prone to natural disasters like flooding or landslides, aiding in risk management.
At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of village-level land classification. Our satellite monitoring systems can be scaled down to provide detailed insights for small rural communities, empowering village-level decision-making with advanced technological support.
Farmonaut’s Role in Modern Land Classification and Management
As a pioneering agricultural technology company, Farmonaut integrates advanced satellite-based solutions with traditional land classification methods to provide comprehensive farm management tools. Our approach combines the best of both worlds – the time-tested principles of land classification with cutting-edge technology.
How Farmonaut Enhances Land Classification and Management
- Real-Time Monitoring: Our satellite imagery provides up-to-date information on land conditions, allowing for dynamic classification updates.
- AI-Powered Analysis: Advanced algorithms analyze multispectral data to assess soil health, crop conditions, and land capabilities.
- Customized Mapping: We generate detailed, customized land classification maps accessible through our web and mobile applications.
- Precision Agriculture Support: Our tools help farmers implement precision farming techniques based on land classification insights.
- Sustainability Tracking: We offer features like carbon footprint monitoring, promoting sustainable land use practices.
To experience the benefits of our advanced land classification and management tools, visit Farmonaut’s Application.
Farmonaut Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (Global) | Limited (Local) | Very Limited (Field-specific) |
| Data Frequency | Regular updates (Daily to weekly) | As per flight schedule | Continuous |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High | Medium to High |
| Operational Complexity | Low (User-friendly interface) | High (Requires skilled operator) | Medium (Requires maintenance) |
| Data Integration | Seamless with AI and blockchain | Limited | Good but localized |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited scalability | Moderate scalability |
Integrating Farmonaut’s Technology with Land Classification
Our innovative approach to integrating satellite technology with traditional land classification methods offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Satellite imagery provides precise, up-to-date data for more accurate land classification.
- Dynamic Monitoring: Our system allows for continuous monitoring of land conditions, enabling rapid response to changes.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: By leveraging satellite technology, we offer affordable precision agriculture solutions to farmers of all scales.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Our AI-powered insights help farmers make informed decisions based on real-time land classification data.
- Sustainable Practices: By providing detailed land capability information, we promote sustainable farming practices that align with land potential.
For developers interested in integrating our satellite and weather data into their systems, check out our API documentation.
The Future of Land Classification in Agriculture
As we look to the future, land classification in agriculture is set to become even more sophisticated and integral to sustainable farming practices. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of this evolution, continuously innovating to meet the changing needs of the agricultural sector.
Emerging Trends in Land Classification
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms will provide more nuanced and accurate land classification.
- Big Data Integration: Combining multiple data sources for comprehensive land analysis.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Land classification systems will evolve to account for changing climate patterns.
- Precision Agriculture: Increased integration with precision farming techniques for optimal resource use.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Ensuring transparency and traceability in land use and agricultural production.
Stay ahead of these trends with Farmonaut’s cutting-edge solutions. Download our app for Android or iOS to start optimizing your agricultural practices today.
Conclusion
Land classification in agriculture remains a cornerstone of effective farm management and sustainable agricultural practices. From understanding its importance at the village level to exploring national systems like the UK’s ALC, it’s clear that proper land classification is crucial for optimizing agricultural productivity and preserving our natural resources.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to bridging the gap between traditional land classification methods and modern technology. Our satellite-based solutions offer farmers, policymakers, and agricultural professionals the tools they need to make informed decisions about land use and management.
As we move forward, the integration of advanced technologies like AI, blockchain, and big data analytics with established land classification principles will pave the way for more sustainable, efficient, and productive agricultural practices worldwide.
Join us in revolutionizing agriculture. Explore our solutions and start your journey towards precision farming today.
FAQs
Q: What is the primary purpose of land classification in agriculture?
A: The primary purpose is to categorize land based on its characteristics and capabilities, guiding optimal land use for sustainable agricultural practices and resource management.
Q: How does the UK’s Agricultural Land Classification system work?
A: The UK’s ALC system classifies land into five grades based on quality, with Grade 1 being excellent and Grade 5 being very poor quality agricultural land.
Q: Why is village-level land classification important?
A: Village-level classification is crucial for optimizing local resources, implementing sustainable farming practices, guiding economic planning, and supporting community development.
Q: How does Farmonaut integrate with traditional land classification methods?
A: Farmonaut enhances traditional methods by providing real-time satellite imagery and AI-powered analysis, offering more accurate and up-to-date land classification data.
Q: Can Farmonaut’s technology be used for small-scale farming?
A: Yes, Farmonaut’s solutions are scalable and can be applied to farms of all sizes, from small village plots to large agricultural operations.
Q: How often is land classification data updated using satellite technology?
A: With Farmonaut’s technology, land classification data can be updated frequently, typically ranging from daily to weekly, depending on satellite pass frequency and cloud cover.
Q: Is Farmonaut’s technology available worldwide?
A: Yes, Farmonaut’s satellite-based solutions are designed for global use, adaptable to various agricultural landscapes and climate zones worldwide.
For more information on how Farmonaut can revolutionize your agricultural practices through advanced land classification and management, visit our developer documentation or contact our support team.