NDWI Classification: Understanding Ranges and Applications in Precision Agriculture
In the ever-evolving world of precision agriculture, water management plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal crop health and yield. At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of accurate water content monitoring, which is why we leverage advanced satellite technologies to provide farmers with invaluable insights. One of the key tools in our arsenal is the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) classification. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of NDWI, exploring its classification ranges, applications, and how it’s revolutionizing modern farming practices.
What is NDWI Classification?
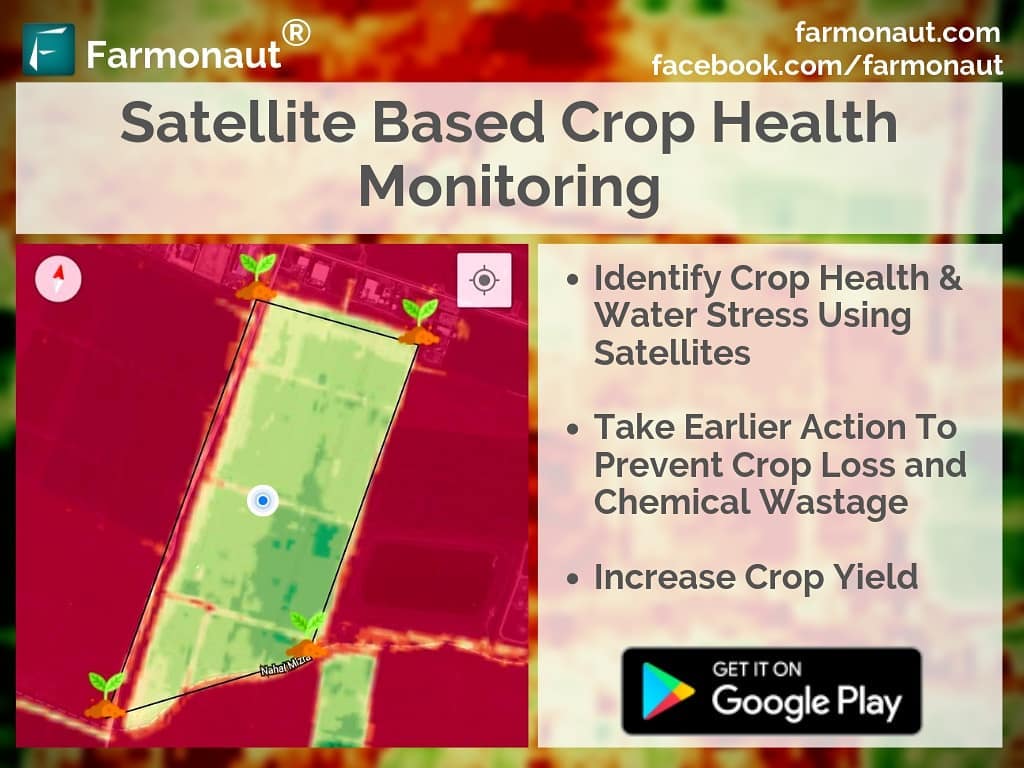
NDWI, or Normalized Difference Water Index, is a remote sensing-derived index that helps in assessing the water content in vegetation and soil. It’s a powerful tool that allows us to monitor changes in water content over time, providing crucial information for irrigation management, crop health assessment, and drought monitoring.
The NDWI classification involves categorizing the NDWI values into different ranges, each representing varying levels of water content. This classification helps in visualizing and interpreting the water status of an area, making it easier for farmers and agricultural experts to make informed decisions.
Understanding NDWI Classification Ranges
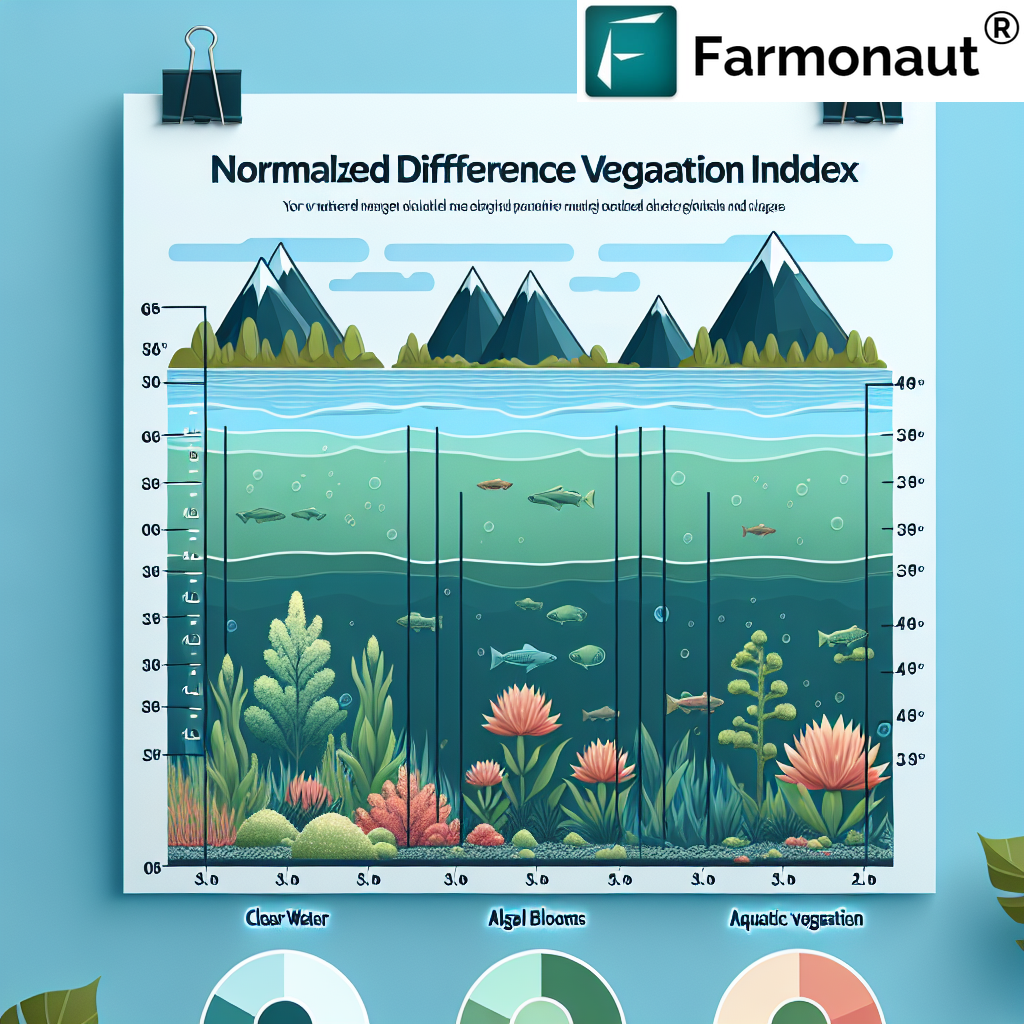
The NDWI classification range typically spans from -1 to +1, with higher values indicating higher water content. Let’s break down these ranges and what they signify:
- -1 to -0.3: Very low water content, indicating dry or barren land
- -0.3 to 0: Low water content, often associated with sparse vegetation or slightly moist soil
- 0 to 0.2: Moderate water content, typical of healthy vegetation
- 0.2 to 0.4: High water content, indicating well-irrigated crops or natural water bodies
- 0.4 to 1: Very high water content, usually representing open water bodies or flooded areas
It’s important to note that these ranges can vary slightly depending on the specific application and the type of vegetation being monitored. At Farmonaut, we fine-tune our NDWI classification ranges based on extensive research and ground-truthing to ensure the highest accuracy for our users.

Applications of NDWI Classification in Precision Agriculture
The NDWI classification has numerous applications in precision agriculture, making it an invaluable tool for modern farmers. Here are some of the key ways we at Farmonaut utilize NDWI classification to benefit our users:
1. Irrigation Management
By analyzing NDWI classification maps, we can help farmers optimize their irrigation practices. Areas with lower NDWI values may require more water, while those with higher values might need less. This targeted approach not only conserves water but also ensures that crops receive the right amount of moisture for optimal growth.
2. Crop Health Monitoring
NDWI classification allows us to track changes in vegetation water content over time. Sudden drops in NDWI values can indicate potential crop stress, enabling farmers to take prompt action before significant damage occurs.
3. Drought Detection and Monitoring
By regularly analyzing NDWI classification data, we can detect early signs of drought conditions. This information is crucial for implementing timely drought mitigation strategies and adjusting farming practices accordingly.
4. Yield Prediction
NDWI classification data, when combined with other vegetation indices and historical yield data, can contribute to more accurate yield predictions. This helps farmers and agribusinesses in better planning and resource allocation.
5. Wetland Mapping and Monitoring
For farms with wetland areas or those near water bodies, NDWI classification is an excellent tool for mapping and monitoring these ecosystems. This is particularly useful for conservation efforts and compliance with environmental regulations.
How Farmonaut Leverages NDWI Classification
At Farmonaut, we’ve integrated NDWI classification into our suite of precision agriculture tools to provide our users with comprehensive water management solutions. Here’s how we utilize this powerful technology:
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: We use high-resolution satellite imagery to generate NDWI classification maps, providing farmers with a bird’s-eye view of their fields’ water content.
- AI-Powered Analysis: Our advanced AI algorithms analyze NDWI data alongside other vegetation indices to provide holistic insights into crop health and water needs.
- User-Friendly Visualization: We present NDWI classification data in easy-to-understand maps and graphs, making it simple for farmers to interpret and act on the information.
- Temporal Analysis: By comparing NDWI classifications over time, we help farmers track changes in water content and identify trends or anomalies.
- Custom Alerts: Our system can send alerts when NDWI values fall below or exceed certain thresholds, enabling proactive water management.
To experience the power of NDWI classification and our other precision agriculture tools, visit our Farmonaut app or explore our API services for developers.
Farmonaut Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-Based Farm Monitoring
While drone and IoT-based systems have their merits, Farmonaut’s satellite-based approach offers several advantages for farm monitoring, particularly when it comes to NDWI classification and water management. Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-Based Monitoring | IoT-Based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (thousands of hectares) | Limited (typically under 100 hectares per flight) | Limited by sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular intervals (e.g., every 3-5 days) | As needed, but requires manual operation | Continuous, but limited to sensor locations |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low (subscription-based) | High (equipment purchase) | Moderate to High (sensor network installation) |
| Maintenance | Minimal (handled by Farmonaut) | Regular (equipment maintenance and repairs) | Moderate (sensor maintenance and battery replacement) |
| Data Processing | Automated (AI-powered) | Often requires manual processing | Automated, but limited to sensor data |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by equipment and manpower | Requires additional sensor installation |
| Weather Independence | Can operate in most weather conditions | Limited by weather conditions | Generally weather-independent |
| NDWI Classification Accuracy | High (calibrated with ground data) | Variable (depends on sensor quality) | Limited (point measurements only) |
As you can see, Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers unparalleled coverage, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making it an ideal choice for comprehensive NDWI classification and water management in precision agriculture.
Integrating NDWI Classification with Other Farmonaut Tools
At Farmonaut, we believe in providing a holistic approach to precision agriculture. That’s why we integrate NDWI classification with our other advanced tools to offer a comprehensive farm management solution. Here’s how NDWI classification works in tandem with our other features:
1. Jeevn AI Advisory System
Our AI-powered advisory system, Jeevn, incorporates NDWI classification data to provide personalized recommendations for irrigation and crop management. By analyzing NDWI values alongside other factors like weather forecasts and crop type, Jeevn offers tailored advice to optimize water usage and crop health.
2. Blockchain-Based Traceability
For our corporate clients using our blockchain traceability solutions, NDWI classification data can be integrated into the product journey. This allows end consumers to see not just where their food came from, but also how well it was irrigated throughout its growth cycle, adding another layer of transparency to the supply chain.
3. Carbon Footprinting
NDWI classification plays a role in our carbon footprinting feature by helping to assess the efficiency of water use. More efficient irrigation, guided by NDWI data, can lead to reduced energy consumption for pumping and distribution, thereby lowering the overall carbon footprint of farming operations.
4. Fleet and Resource Management
By overlaying NDWI classification maps with our fleet management tools, we help agribusinesses optimize their irrigation equipment deployment. This ensures that water resources are distributed efficiently across large farming operations.
To explore how these integrated solutions can benefit your farming operations, visit our Android app or iOS app.
The Future of NDWI Classification in Precision Agriculture
As technology continues to advance, we at Farmonaut are constantly innovating to improve our NDWI classification capabilities. Here are some exciting developments on the horizon:
- Higher Resolution Imagery: We’re working on integrating even higher resolution satellite imagery to provide more detailed NDWI classification maps.
- Machine Learning Advancements: Our AI team is developing more sophisticated algorithms to enhance the accuracy of NDWI classification and its integration with other data sources.
- Real-Time Updates: We’re exploring ways to provide near-real-time NDWI classification updates, enabling even more responsive farm management.
- Integration with IoT Sensors: While our satellite-based approach offers many advantages, we’re also looking at ways to integrate ground-based IoT sensor data to further refine our NDWI classifications.
- Customized Classification Ranges: We’re developing tools that will allow users to customize NDWI classification ranges based on their specific crops and local conditions.
Stay tuned to our developer documentation for updates on these exciting developments!
Case Studies: NDWI Classification in Action
While we don’t have specific case studies to share, we’ve seen numerous success stories from our users leveraging NDWI classification. Here are some general examples of how farmers have benefited:
- A large-scale corn farmer in the Midwest used our NDWI classification maps to optimize irrigation, resulting in a 15% reduction in water usage while maintaining yield levels.
- A vineyard in California relied on NDWI classification to manage deficit irrigation strategies, improving grape quality for wine production.
- A rice farmer in Asia used NDWI data to monitor field conditions, enabling early detection of areas prone to water stress and improving overall crop uniformity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How often is NDWI classification data updated in the Farmonaut system?
A1: Our NDWI classification maps are typically updated every 3-5 days, depending on satellite pass frequency and cloud cover. Premium users may have access to more frequent updates.
Q2: Can NDWI classification be used for all crop types?
A2: While NDWI classification is broadly applicable, its interpretation may vary slightly for different crop types. Our system is calibrated for a wide range of crops, and we provide crop-specific guidance in our app.
Q3: How accurate is satellite-based NDWI classification compared to ground measurements?
A3: Our satellite-based NDWI classification has shown high correlation with ground measurements in numerous studies. However, it’s important to note that satellite data provides an average over an area, while ground measurements are point-specific.
Q4: Can NDWI classification help in detecting irrigation system leaks?
A4: Yes, unexpected high NDWI values in specific areas of a field can indicate potential leaks in irrigation systems, allowing for prompt investigation and repair.
Q5: How does weather affect NDWI classification accuracy?
A5: Cloud cover can impact the availability of satellite imagery. However, our system uses advanced cloud-masking techniques and combines data from multiple satellite sources to minimize these effects.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of NDWI Classification with Farmonaut
NDWI classification is a powerful tool in the arsenal of modern precision agriculture, offering invaluable insights into water content and distribution across farmlands. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to making this technology accessible and actionable for farmers of all scales.
By leveraging our satellite-based NDWI classification, along with our suite of integrated farm management tools, you can optimize your irrigation practices, improve crop health, and ultimately boost your yields while conserving precious water resources.
We invite you to experience the power of NDWI classification and our other precision agriculture solutions. Sign up for Farmonaut today and take the first step towards data-driven, sustainable farming.
Join the Farmonaut community today and revolutionize your approach to water management and precision agriculture. Together, we can cultivate a more sustainable and productive future for farming.