California Water Policy: Debunking Myths and Analyzing Central Valley Water Management Challenges
“California’s Central Valley produces 25% of the nation’s food supply while using only 1% of the country’s farmland.”
In the complex landscape of California water policy, recent events have brought long-standing issues into sharp focus. As we delve into the intricacies of water management in the Golden State, particularly concerning the Central Valley and Los Angeles, it’s crucial to separate fact from fiction. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll explore the realities of water distribution, environmental concerns, and the challenges facing both urban and agricultural regions.
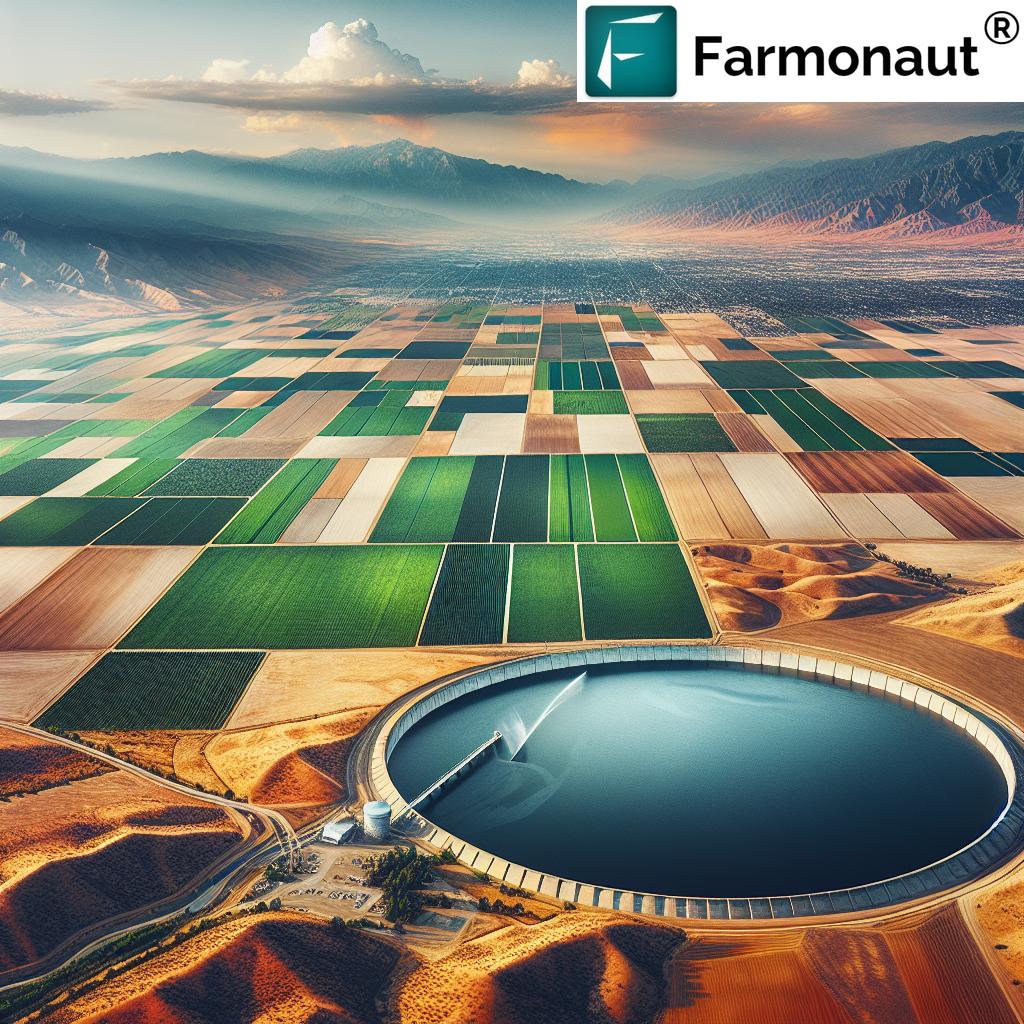

Unraveling the Truth: Recent Water Releases from Central Valley Dams
The recent controversy surrounding water releases from Central Valley dams has shed light on the complexities of California’s water management system. Contrary to claims made by some officials, including former President Donald Trump, the water released from these dams did not reach Los Angeles or aid in wildfire prevention efforts. Let’s break down the facts:
- Over 2 billion gallons of water were released from two dams in California’s Central Valley in late January and early February 2025.
- The water was directed to the Tulare Basin, more than 100 miles north of Los Angeles.
- The released water had no connection to the State Water Project that serves Southern California.
- Experts have described the water release as potentially wasteful and harmful to farmers.
Jeffrey Mount, a senior fellow at the Public Policy Institute of California’s Water Policy Center, stated unequivocally, “Not one drop of the water released into the Tulare Basin by the Army Corps of Engineers at the direction of the White House made it to Southern California.”
Understanding the State Water Project and Federal Water Systems
To comprehend why the released water couldn’t reach Los Angeles, it’s essential to understand the distinct water systems operating in California:
- The State Water Project (SWP): This California-run system serves Southern California, including Los Angeles.
- The Central Valley Project (CVP): This federally run system primarily serves the agricultural regions of the Central Valley and ends around Bakersfield.
The dams from which water was released are part of the CVP, which has no direct connection to the SWP. This geographical and infrastructural reality makes it impossible for water released from these dams to automatically flow to Los Angeles.
Environmental and Agricultural Implications of Water Releases
The decision to release water from Central Valley dams has far-reaching consequences for both the environment and agriculture:
- Impact on Farmers: The sudden release of water can disrupt agricultural planning and potentially waste resources that farmers rely on for irrigation.
- Ecological Concerns: Unplanned water releases can affect local ecosystems, potentially harming fish populations and altering natural habitats.
- Flood Risks: Experts warned that releasing the initially proposed 5 billion-plus gallons could have led to dangerous flooding in the region.
These issues highlight the delicate balance that must be maintained in California’s water management practices. The state’s water policy must consider the needs of various stakeholders, from urban centers to agricultural communities, while also protecting the environment.
California Drought Management and Wildfire Prevention
The misconception that the water releases were related to wildfire prevention in Los Angeles underscores the need for a clearer understanding of California’s drought management and fire prevention strategies:
- Los Angeles had sufficient water resources to combat the January 2025 wildfires.
- Localized water shortages during firefighting efforts were due to extreme demand in specific neighborhoods, not overall water scarcity.
- California’s wildfire prevention efforts involve various strategies beyond water management, including controlled burns and forest management practices.
It’s crucial to recognize that effective wildfire prevention in California requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply increasing water availability.
The Role of Environmental Regulations in Water Management
Environmental regulations play a significant role in shaping California’s water policy. Claims that these regulations prioritize obscure fish species over human needs oversimplify a complex issue:
- Environmental regulations aim to maintain ecological balance, which is crucial for long-term water sustainability.
- Protecting fish populations is not just about conservation; it’s about maintaining healthy ecosystems that support water quality and availability.
- Balancing environmental needs with human water use is an ongoing challenge that requires nuanced policy-making.
As we navigate these challenges, it’s important to recognize the interconnectedness of environmental health and water resource management. Sustainable water policy must consider both immediate human needs and long-term ecological stability.
“The State Water Project, California’s main water system, includes 34 storage facilities and 701 miles of aqueducts and pipelines.”
Central Valley Water Management: Key Factors and Impacts
| Factor | Current Status | Impact on Agriculture | Environmental Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Release from Dams | 2 billion+ gallons released in early 2025 | High – Potential waste of irrigation resources | Moderate – Disruption to local ecosystems |
| State Water Project Allocation | Varies annually based on precipitation | High – Directly affects crop planning | High – Influences water available for environmental flows |
| Drought Conditions | Ongoing concern with periodic severe droughts | High – Crop losses and increased water costs | High – Habitat loss and species stress |
| Wildfire Prevention Measures | Increased focus on forest management | Moderate – Indirect impact on water availability | High – Affects watershed health |
| Environmental Regulations | Strict policies to protect ecosystems | Moderate – Limits on water usage for agriculture | High – Critical for maintaining biodiversity |
The Future of California Water Policy
As we look to the future, it’s clear that California’s water policy must evolve to meet the challenges of a changing climate and growing population. Key considerations include:
- Investing in water infrastructure to improve efficiency and reduce waste
- Developing more sophisticated water storage and transfer systems
- Implementing advanced technologies for water conservation and management
- Fostering cooperation between different regions and stakeholders
In this context, innovative solutions like those offered by Farmonaut can play a crucial role. By leveraging satellite imagery and AI-driven insights, Farmonaut helps farmers optimize water usage and improve crop yields, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices.
The Role of Technology in Water Management
As California grapples with its water challenges, technology is emerging as a key ally in the quest for more efficient and sustainable water management. Advanced tools and platforms are revolutionizing how we monitor, allocate, and conserve water resources:
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Companies like Farmonaut are utilizing satellite imagery to provide real-time data on crop health and soil moisture levels. This technology allows for precise irrigation management, reducing water waste and optimizing crop yields.
- AI-Driven Advisory Systems: Artificial intelligence is being employed to analyze complex data sets and provide actionable insights for water management. These systems can predict water needs, suggest optimal irrigation schedules, and help in decision-making during drought conditions.
- Blockchain for Water Rights: Blockchain technology is being explored as a means to create more transparent and efficient systems for water rights allocation and trading, potentially revolutionizing how water is distributed among different users.
- IoT Sensors for Real-Time Monitoring: Internet of Things (IoT) sensors placed throughout water systems can provide real-time data on water levels, quality, and usage, enabling more responsive and efficient water management.
These technological advancements offer hope for more sustainable water management practices in California and beyond. By leveraging these tools, policymakers and water managers can make more informed decisions, balancing the needs of agriculture, urban areas, and the environment.
Challenges in Implementing Technological Solutions
While technology offers promising solutions, implementing these innovations across California’s vast and complex water system presents several challenges:
- Infrastructure Integration: Integrating new technologies with existing water infrastructure requires significant investment and planning.
- Data Privacy and Security: As more data is collected and analyzed, ensuring the privacy and security of this information becomes crucial.
- Equitable Access: Ensuring that all stakeholders, including small-scale farmers and rural communities, have access to these technologies is essential for fairness and overall effectiveness.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Current regulations may need to be updated to accommodate and encourage the use of new water management technologies.
Overcoming these challenges will require collaboration between technology providers, policymakers, and water management authorities. It’s a complex task, but one that’s essential for the future of California’s water resources.
The Economic Impact of Water Policy Decisions
Water policy decisions in California have far-reaching economic implications, affecting various sectors of the state’s economy:
- Agricultural Sector: As the largest user of water in the state, agriculture is particularly sensitive to water policy changes. Restrictions on water use can lead to reduced crop yields and economic losses for farmers.
- Urban Development: Water availability plays a crucial role in urban planning and development. Policies that limit water access can constrain growth in certain areas.
- Energy Production: Hydroelectric power, an important component of California’s energy mix, is directly affected by water levels in reservoirs and dams.
- Recreation and Tourism: Lakes, rivers, and other water bodies are vital for California’s tourism industry. Water scarcity can negatively impact this sector.
Balancing these economic interests with environmental concerns and long-term sustainability is a key challenge for policymakers. It requires a nuanced approach that considers both immediate economic needs and long-term resource management.
Public Perception and Education
One of the most significant challenges in California water policy is public perception and understanding. Misconceptions about water distribution, as seen in the recent controversy over dam releases, can lead to misguided policy demands and public frustration. To address this:
- There’s a need for more comprehensive public education about California’s water systems and the challenges they face.
- Transparency in decision-making processes can help build public trust and understanding.
- Regular communication from water management authorities can help dispel myths and provide accurate information.
By improving public understanding of water issues, we can foster more productive discussions and collaborations in addressing California’s water challenges.
Looking Ahead: Sustainable Solutions for California’s Water Future
As we conclude our analysis of California’s water policy and the recent controversies surrounding water management, it’s clear that the path forward requires a multifaceted approach. Here are key areas that need attention for a sustainable water future:
- Integrated Water Management: Developing comprehensive strategies that consider all aspects of water use, from agriculture to urban needs to environmental conservation.
- Technological Innovation: Continuing to invest in and implement advanced technologies for water monitoring, conservation, and distribution.
- Policy Reform: Updating water rights laws and regulations to reflect current realities and future challenges.
- Collaborative Governance: Fostering cooperation between different regions, stakeholders, and levels of government to create more cohesive water management strategies.
- Public Engagement: Improving public education and involvement in water policy decisions to ensure broader support and understanding.
By addressing these areas, California can work towards a more sustainable and equitable water future, balancing the needs of its diverse population with the realities of its water resources.
FAQ Section
Q: Why couldn’t the water released from Central Valley dams reach Los Angeles?
A: The dams are part of the federally run Central Valley Project, which is not connected to the State Water Project that serves Southern California. The water was released into the Tulare Basin, over 100 miles north of Los Angeles.
Q: How does California’s water policy affect agriculture in the Central Valley?
A: Water policy decisions directly impact water availability for irrigation in the Central Valley. Restrictions can lead to reduced crop yields and economic challenges for farmers, while sustainable management practices can help ensure long-term agricultural viability.
Q: What role do environmental regulations play in California’s water management?
A: Environmental regulations aim to protect ecosystems and ensure long-term water sustainability. They influence how water is allocated between human use and environmental needs, sometimes leading to conflicts between different stakeholders.
Q: How is technology being used to improve water management in California?
A: Technologies like satellite imagery, AI-driven advisory systems, and IoT sensors are being used to monitor water resources, optimize usage, and provide real-time data for decision-making. Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront of these innovations.
Q: What are the main challenges in implementing new water management technologies in California?
A: Key challenges include integrating new technologies with existing infrastructure, ensuring data privacy and security, providing equitable access to all stakeholders, and adapting regulations to accommodate technological innovations.
Conclusion
California’s water policy landscape is complex and often controversial, as evidenced by the recent misunderstandings surrounding water releases from Central Valley dams. By debunking myths and analyzing the true challenges facing water management in the state, we can move towards more informed and effective solutions.
The intricate relationships between water policy, agriculture, environmental conservation, and urban needs require nuanced approaches and innovative technologies. As we’ve seen, companies like Farmonaut are playing a crucial role in this landscape by providing advanced tools for water management and agricultural optimization.
Moving forward, it’s essential that policymakers, technologists, farmers, and urban planners work together to create sustainable water management strategies. These strategies must balance the diverse needs of California’s population while ensuring the long-term health of its ecosystems and water resources.
By embracing technological innovations, fostering public understanding, and developing integrated management approaches, California can navigate its water challenges and build a more sustainable future for all its residents.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Farmonaut Subscriptions
For more information on Farmonaut’s services and how they can help with water management and agricultural optimization, visit:
For developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s technology into their own applications, check out our API and API Developer Docs.








