Washington’s Apple Industry: Navigating Water Management and Economic Challenges in the Yakima Basin
“Washington’s apple industry creates thousands of jobs and generates billions in economic output for the state.”
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of Washington’s apple industry and the intricate water management challenges faced in the Yakima Basin. As we delve into this crucial sector of Washington’s agriculture and economy, we’ll uncover the complex relationship between the region’s water resources and its thriving fruit orchards.
The Heart of Washington’s Apple Country
Washington state is renowned for its apple production, accounting for approximately 70% of the United States’ apple output. The Yakima River Basin plays a pivotal role in this agricultural success story, transforming semi-arid lands into lush, productive orchards through innovative irrigation techniques and water management strategies.
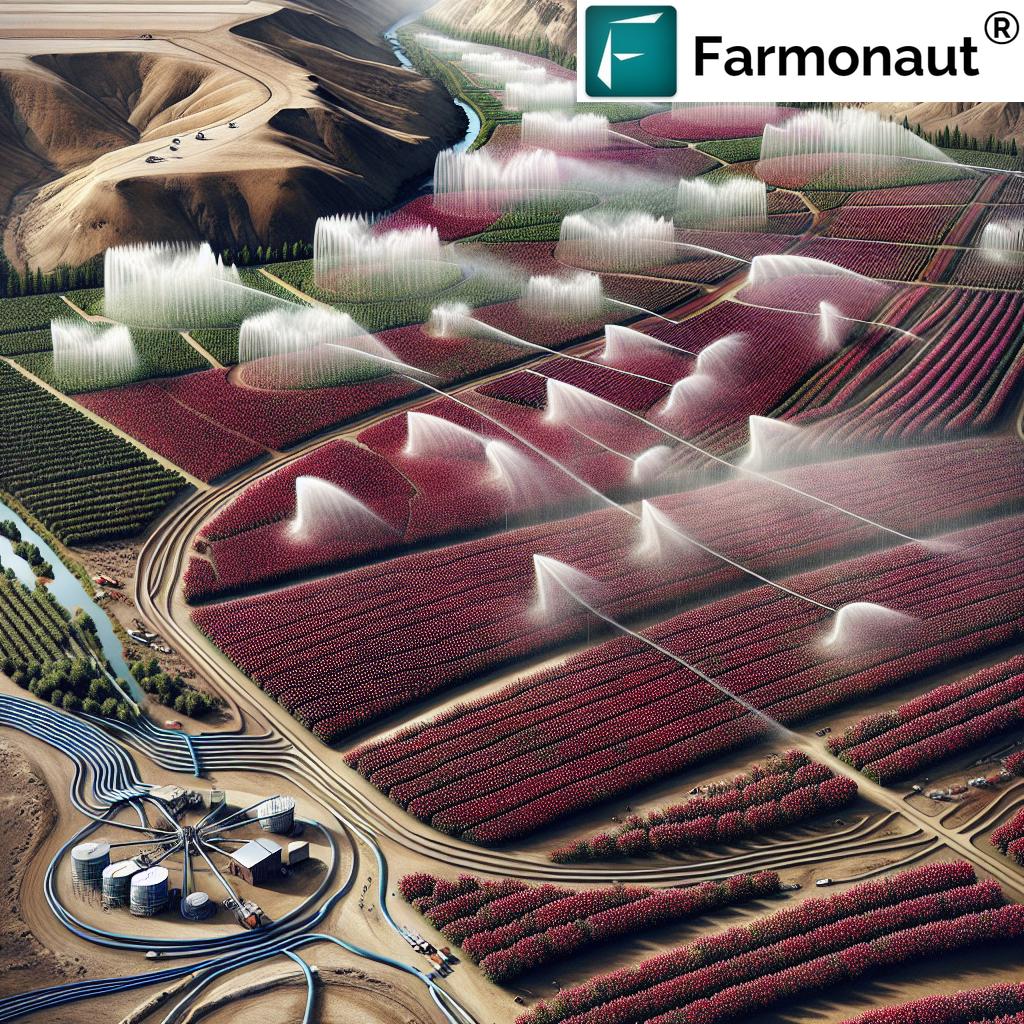

At the heart of this industry are growers like Tim Calhoun, whose family has been cultivating fruit in Wapato, Washington, since 1969. Their journey from a small family operation to a thriving 170-acre orchard exemplifies the growth and resilience of Washington’s apple industry.
Water: The Lifeblood of Yakima’s Orchards
The success of Washington’s apple industry hinges on one critical resource: water. The Yakima River and its network of irrigation canals, including the Wapato Irrigation Canal, provide the essential water supply that allows orchards to flourish in this otherwise semi-arid region.
Consider these staggering figures:
- Calhoun’s operation alone uses approximately 23 million gallons of irrigation water annually.
- The Yakima Project, established in 1910 by the Bureau of Reclamation, revolutionized agriculture in the region.
- The Columbia Basin Project, initiated in 1952, further expanded irrigated lands in Washington.
Together, these projects irrigate nearly two-thirds of Washington’s agricultural lands, dramatically reshaping the state’s economy and landscape.
Economic Impact of Washington’s Apple Industry
The economic significance of Washington’s apple industry cannot be overstated. Let’s break down the numbers:
| Economic Indicator | Value (Estimated) | Impact on State Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Apple Production | 125 million boxes | Major contributor to US apple supply |
| Total Economic Output | $6 billion direct, $9 billion including indirect | Over 1% of state GDP |
| Jobs Created | 46,000 direct, 22,000 indirect | Significant employment generator |
| Export Value | $850 million | Major contributor to state exports |
| Water Usage | 2.5 million acre-feet | Critical for regional water management |
| Acreage Under Apple Cultivation | 175,000 acres | Substantial land use for agriculture |
These figures underscore the apple industry’s role as a cornerstone of Washington’s agricultural sector and a significant contributor to the state’s overall economic health.
Sustainable Farming Practices in the Yakima Basin
The success of Washington’s apple industry is not just about volume; it’s also about sustainability. Growers in the Yakima Basin have adopted various sustainable farming practices to ensure long-term viability:
- Drip irrigation systems to conserve water
- Integrated pest management to reduce chemical use
- Cover cropping to improve soil health
- Precision agriculture techniques for optimal resource use
These practices not only help preserve the environment but also contribute to the production of high-quality apples that meet consumer demands for sustainably grown fruit.
Challenges Facing Washington’s Apple Growers
Despite the industry’s success, apple growers in Washington face several challenges:
- Market fluctuations and price volatility
- Rising operational costs
- Competition from global markets
- Climate change impacts on water availability and growing conditions
- Labor shortages during harvest seasons
These challenges require constant adaptation and innovation from growers to maintain profitability and sustainability.
The Role of Technology in Modern Orchards
Technology plays an increasingly important role in addressing the challenges faced by Washington’s apple industry. Advanced solutions like those offered by Farmonaut are transforming orchard management:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring
- AI-driven advisory systems for precision agriculture
- Blockchain-based traceability for supply chain transparency
- Resource management tools for optimizing water and input use
These technological advancements help growers make data-driven decisions, improving efficiency and sustainability in their operations.
The Seasonal Rhythm of Apple Orchards
The life of an apple orchard follows a distinct seasonal rhythm:
- Winter: Pruning and tree maintenance
- Spring: Blossoming and pollination
- Summer: Fruit development and pest management
- Fall: Harvest and distribution
Each season brings its own set of tasks and challenges, requiring growers to be constantly vigilant and adaptable.
The Future of Washington’s Apple Industry
Looking ahead, the future of Washington’s apple industry will likely be shaped by several factors:
- Advancements in water management and irrigation technology
- Development of new apple varieties to meet changing consumer preferences
- Adoption of more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices
- Increased use of data analytics and precision agriculture techniques
- Adaptation strategies to address climate change impacts
By embracing these changes and continuing to innovate, Washington’s apple industry can maintain its position as a global leader in apple production.
Explore Farmonaut’s API Solutions
Water Management: A Critical Component
Effective water management remains at the core of the industry’s sustainability. The Yakima Basin Integrated Plan is a prime example of collaborative efforts to ensure long-term water security for agriculture while also addressing environmental concerns. This comprehensive approach includes:
- Enhanced water storage capabilities
- Improved fish passages and habitat restoration
- Water market developments for more efficient allocation
- Groundwater recharge projects
These initiatives aim to balance the needs of agriculture, municipalities, and ecosystems, ensuring a sustainable future for all stakeholders in the basin.
Access Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs
The Global Context: Washington Apples in International Markets
Washington’s apple industry doesn’t operate in isolation; it’s part of a global market. Key aspects of its international presence include:
- Export markets in over 60 countries
- Competition from other major apple-producing nations
- Impact of international trade policies and tariffs
- Growing demand for organic and specialty apple varieties
Navigating these international waters requires strategic planning and adaptability from growers and industry organizations alike.
Innovation in Apple Varieties
Washington’s apple industry continually evolves through the development of new apple varieties. This innovation is crucial for:
- Meeting changing consumer preferences
- Improving disease resistance and crop yields
- Adapting to changing climate conditions
- Maintaining competitiveness in global markets
Varieties like Cosmic Crisp, developed at Washington State University, represent the cutting edge of this innovation, blending desirable traits for both growers and consumers.
Download Farmonaut’s Android App

The Role of Research and Education
Continued research and education play vital roles in the industry’s development:
- University research programs developing new cultivation techniques
- Extension services providing support to growers
- Industry-funded research initiatives addressing key challenges
- Educational programs training the next generation of apple growers
These efforts ensure that the industry remains at the forefront of agricultural innovation and sustainability.
Environmental Stewardship in Apple Production
Environmental stewardship is increasingly important in Washington’s apple industry. Key initiatives include:
- Reducing carbon footprints in orchard operations
- Implementing biodiversity-friendly practices
- Minimizing chemical inputs through integrated pest management
- Exploring renewable energy options for processing and storage facilities
These efforts not only benefit the environment but also align with consumer demands for sustainably produced food.
“The Yakima River Basin’s water resources support thriving fruit orchards in semi-arid lands, producing a significant portion of Washington’s apples.”
The Economic Ripple Effect
The impact of Washington’s apple industry extends far beyond the orchards:
- Supporting related industries like packaging and transportation
- Boosting rural economies through job creation and economic activity
- Contributing to tourism through agritourism initiatives
- Generating tax revenue that supports local and state services
This broader economic impact underscores the industry’s importance to Washington’s overall economic health.
Addressing Labor Challenges
Labor is a critical component of the apple industry, with challenges including:
- Seasonal labor shortages during harvest times
- Increasing labor costs impacting overall profitability
- The need for skilled workers to operate advanced agricultural technology
- Immigration policies affecting the availability of agricultural workers
Addressing these labor challenges is crucial for the industry’s long-term sustainability and competitiveness.
Climate Change and Its Impact
Climate change poses significant challenges to Washington’s apple industry:
- Changing precipitation patterns affecting water availability
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events
- Shifts in growing seasons and crop phenology
- Potential changes in pest and disease pressures
Adapting to these changes requires ongoing research, innovative practices, and collaborative efforts across the industry.
The Future of Water Management
Looking ahead, the future of water management in the Yakima Basin will likely involve:
- Advanced technologies for precise irrigation scheduling
- Increased water storage capacity to buffer against dry years
- Collaborative watershed management approaches
- Integration of climate change projections into long-term planning
These strategies will be crucial in ensuring the continued success of Washington’s apple industry in the face of changing environmental conditions.
Conclusion: A Resilient Industry Facing the Future
Washington’s apple industry, centered in the Yakima Basin, stands as a testament to the power of innovation, sustainable practices, and effective water management. Despite facing numerous challenges, from market fluctuations to climate change, the industry continues to thrive, adapting to new realities and embracing cutting-edge technologies.
As we look to the future, the resilience and adaptability demonstrated by growers like Tim Calhoun and countless others across the state provide confidence in the industry’s ability to navigate upcoming challenges. By continuing to focus on sustainable water management, adopting innovative technologies, and maintaining a commitment to quality, Washington’s apple industry is well-positioned to remain a leader in global apple production for generations to come.
The story of Washington’s apples is not just about fruit; it’s about the intricate dance between nature, technology, and human ingenuity. It’s a narrative of how careful stewardship of resources, particularly water, can transform semi-arid lands into productive agricultural powerhouses. As we face the challenges of the 21st century, the lessons learned from the Yakima Basin’s apple growers offer valuable insights for sustainable agriculture worldwide.
FAQs
- How much of the U.S. apple production comes from Washington state?
Washington state accounts for approximately 70% of the United States’ apple production. - What is the economic impact of Washington’s apple industry?
The apple industry in Washington generates about $6 billion in direct economic output and $9 billion when including indirect activities. - How many jobs does the Washington apple industry create?
The industry creates approximately 46,000 direct full-time jobs and 22,000 indirect jobs. - What are the main water sources for irrigation in the Yakima Basin?
The main water sources are the Yakima River and its network of irrigation canals, including the Wapato Irrigation Canal. - How are Washington apple growers adapting to climate change?
Growers are adopting water-efficient irrigation systems, exploring new apple varieties, and implementing sustainable farming practices to adapt to changing climate conditions. - What role does technology play in modern apple orchards?
Technology plays a crucial role through satellite-based crop monitoring, AI-driven advisory systems, and precision agriculture techniques for optimal resource use. - How is the Washington apple industry addressing labor challenges?
The industry is exploring automation, improving working conditions, and advocating for policies to ensure a stable workforce. - What are some of the sustainable practices used in Washington apple orchards?
Sustainable practices include drip irrigation, integrated pest management, cover cropping, and precision agriculture techniques. - How does the Yakima Basin Integrated Plan help the apple industry?
The plan ensures long-term water security for agriculture while addressing environmental concerns through enhanced water storage, habitat restoration, and efficient water allocation. - What are the main challenges facing Washington’s apple industry?
Key challenges include market fluctuations, rising operational costs, global competition, climate change impacts, and labor shortages.





