Sustainable Cassava Farming: Mastering CMD Prevention and Control with Farmonaut’s Agritech Solutions
“Cassava mosaic virus can reduce crop yields by up to 90%, threatening food security in regions where cassava is a staple.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on sustainable cassava farming and the critical challenge of Cassava Mosaic Disease (CMD). As agricultural experts and representatives of Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping farmers and agricultural professionals tackle this devastating plant disease while promoting sustainable farming practices. In this blog post, we’ll explore the intricacies of CMD, its impact on cassava crops, and innovative strategies for prevention and control, including Farmonaut’s cutting-edge agritech solutions.
Understanding Cassava Mosaic Disease (CMD)
Cassava mosaic disease, caused by the cassava mosaic virus (CMV), is one of the most significant threats to cassava production worldwide. This plant disease can have devastating effects on crop yields, impacting food security in regions where cassava is a staple crop. Let’s delve into the key aspects of CMD to better understand its nature and impact.
What is Cassava Mosaic Virus?
Cassava mosaic virus (CMV) is a group of plant viruses that belong to the genus Begomovirus. These viruses specifically infect cassava plants, also known as yucca, manioc, or mandioca in various parts of the world. CMD is particularly prevalent in Africa and parts of Asia, including India, where cassava is an essential food source for millions of people.
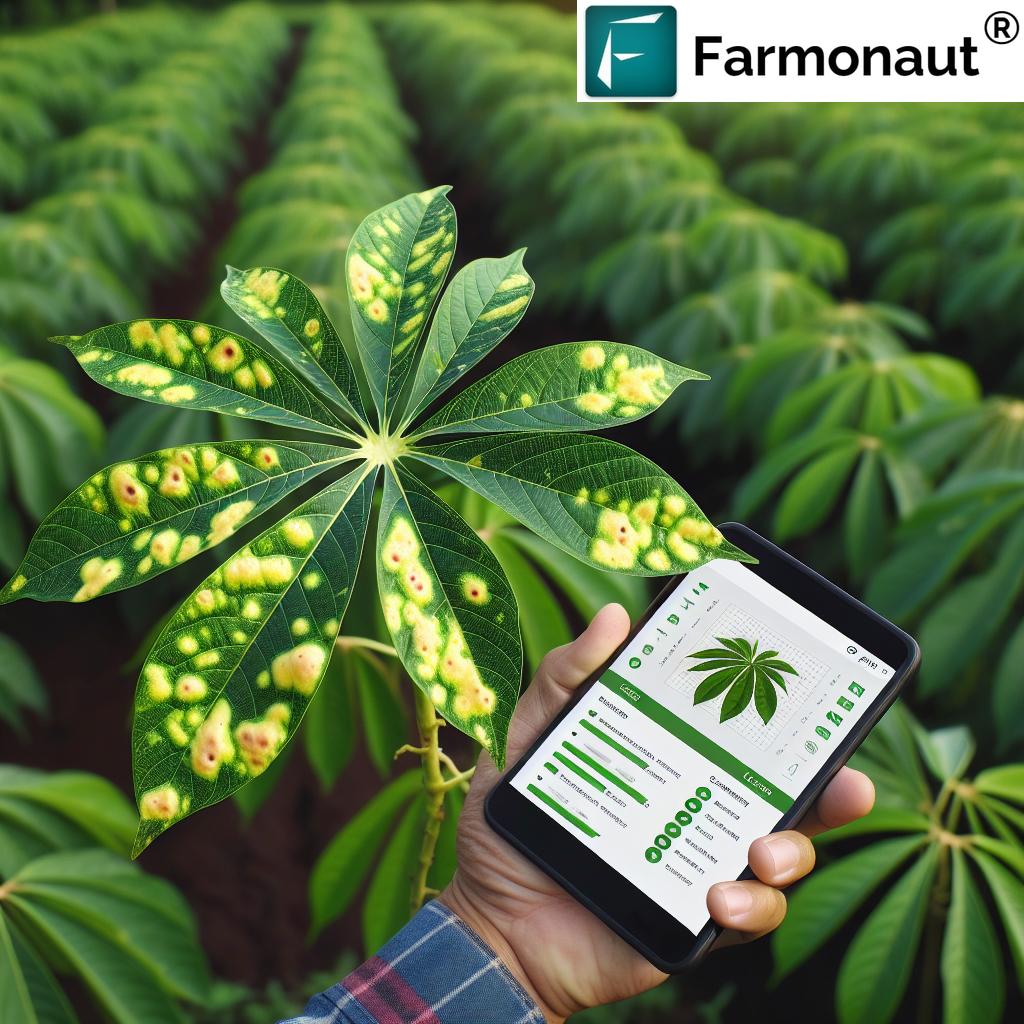

CMD Symptoms in Cassava
Recognizing the symptoms of CMD is crucial for early detection and management. The most common CMD symptoms in cassava include:
- Leaf mottling: Irregular patches of light green, yellow, or white areas on the leaves
- Leaf distortion: Curling, twisting, or other deformities of the leaves
- Stunting: Reduced plant growth and smaller leaves
- Reduced root development: Smaller and fewer tubers
- Chlorosis: Yellowing of leaves due to reduced chlorophyll production
These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the virus strain, plant variety, and environmental conditions. Early detection of these signs is crucial for implementing effective control measures.
The Role of Whiteflies in CMD Transmission
“Whiteflies, the primary vector for CMD, can transmit the virus to healthy cassava plants in as little as 10 minutes.”
Whitefly transmission of plant viruses plays a pivotal role in the spread of CMD. The whitefly species Bemisia tabaci is the primary vector for CMV. These tiny insects feed on the sap of infected plants and then transmit the virus to healthy cassava plants when they feed on them. Understanding this transmission mechanism is crucial for developing effective pest management strategies.
Key points about whitefly transmission:
- Whiteflies can acquire the virus in as little as 10 minutes of feeding on an infected plant
- Once a whitefly has acquired the virus, it can transmit it to healthy plants for the rest of its life
- Large whitefly populations can lead to rapid and widespread CMD infection in cassava fields
- Controlling whitefly populations is essential for limiting the spread of CMD
Impact of CMD on Cassava Production
The impact of CMD on cassava production can be severe, with significant economic and food security implications. Some of the major effects include:
- Yield reduction: CMD can cause yield losses of up to 90% in susceptible cassava varieties
- Quality degradation: Infected plants produce smaller, less nutritious tubers
- Economic losses: Reduced yields and quality lead to financial hardships for farmers
- Food insecurity: In regions where cassava is a staple food, CMD outbreaks can threaten local food supplies
Given these substantial impacts, it’s clear that effective CMD management is crucial for sustainable cassava farming and food security in affected regions.
Sustainable Cassava Farming Practices for CMD Prevention
Implementing sustainable cassava farming practices is essential for preventing and managing CMD effectively. Let’s explore some key strategies that farmers can adopt to protect their crops and promote long-term sustainability.
Selecting Resistant Cassava Varieties
One of the most effective ways to combat CMD is by planting resistant cassava varieties. These varieties have been developed through traditional breeding or genetic engineering to withstand or tolerate CMD infection. Benefits of using resistant cassava varieties include:
- Reduced susceptibility to CMD infection
- Higher yields even in the presence of the virus
- Decreased reliance on chemical pest control methods
- Improved food security and economic stability for farmers
When selecting resistant varieties, it’s important to consider local growing conditions and consult with agricultural experts or extension services for recommendations specific to your region.
Implementing Organic Pest Management for Crops
Organic pest management techniques can be highly effective in controlling whitefly populations and reducing CMD transmission. Some organic approaches include:
- Companion planting: Growing plants that repel whiteflies alongside cassava
- Biological control: Introducing natural predators of whiteflies, such as ladybugs or parasitic wasps
- Sticky traps: Using yellow sticky traps to monitor and reduce whitefly populations
- Neem oil: Applying neem-based organic pesticides to deter whiteflies
- Proper sanitation: Removing and destroying infected plants to prevent disease spread
These organic methods not only help control CMD but also promote overall ecosystem health and biodiversity in cassava fields.
Crop Rotation and Intercropping
Implementing crop rotation and intercropping practices can help reduce the incidence of CMD and improve overall soil health. Consider the following strategies:
- Crop rotation: Alternate cassava with non-host crops to break the disease cycle
- Intercropping: Plant cassava alongside crops that deter whiteflies or attract beneficial insects
- Cover crops: Use cover crops between cassava plantings to improve soil health and reduce pest pressure
These practices not only help manage CMD but also contribute to long-term soil fertility and sustainable farming.
Proper Field Sanitation and Hygiene
Maintaining good field sanitation is crucial for preventing the spread of CMD. Key practices include:
- Regularly inspecting fields for signs of CMD infection
- Promptly removing and destroying infected plants
- Cleaning tools and equipment between uses to prevent disease spread
- Controlling weeds that may serve as alternative hosts for whiteflies or the virus
By implementing these sanitation measures, farmers can significantly reduce the risk of CMD outbreaks in their cassava fields.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for CMD Control
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach to pest and disease control that combines various strategies to achieve long-term, sustainable results. For CMD control, an effective IPM program might include:
- Regular monitoring of cassava fields for CMD symptoms and whitefly populations
- Use of resistant cassava varieties
- Implementation of cultural practices like crop rotation and intercropping
- Application of organic pest control methods
- Judicious use of chemical controls when necessary
- Ongoing education and training for farmers on CMD management
By adopting an IPM approach, farmers can effectively manage CMD while minimizing environmental impact and promoting sustainable agriculture.

Farmonaut’s Agritech Solutions for CMD Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing innovative agritech solutions to help farmers combat plant diseases like CMD. Our advanced satellite-based farm management platform offers several tools that can aid in the prevention and control of CMD:
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Our satellite imagery technology allows farmers to monitor crop health in real-time, enabling early detection of potential CMD outbreaks. Key features include:
- Vegetation health index (NDVI) monitoring to detect changes in plant vigor
- Soil moisture analysis to optimize irrigation and reduce plant stress
- Early detection of crop anomalies that may indicate CMD infection
By leveraging this technology, farmers can take proactive measures to prevent the spread of CMD and protect their cassava crops.
AI-Powered Advisory System
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI advisory system provides personalized recommendations for CMD management based on real-time data and expert knowledge. This system offers:
- Customized crop management strategies tailored to local conditions
- Timely alerts for potential CMD outbreaks based on environmental factors
- Recommendations for integrated pest management practices
With these AI-driven insights, farmers can make informed decisions to protect their cassava crops from CMD and other threats.
Resource Management Tools
Efficient resource management is crucial for sustainable cassava farming and CMD control. Farmonaut’s platform includes tools for:
- Optimizing irrigation schedules to reduce plant stress and susceptibility to CMD
- Managing fertilizer application to promote plant health and resistance
- Tracking and analyzing farming practices to improve overall crop protection strategies
By optimizing resource use, farmers can create more resilient cassava crops that are better equipped to withstand CMD pressure.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Farmonaut’s platform aggregates and analyzes vast amounts of agricultural data, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions for CMD management. Benefits include:
- Historical crop performance analysis to identify trends and patterns
- Comparative analysis of different CMD management strategies
- Predictive modeling to anticipate potential CMD outbreaks
With these powerful data analytics tools, farmers can continuously improve their CMD prevention and control strategies.
To learn more about how Farmonaut’s agritech solutions can help you manage CMD and other agricultural challenges, visit our web app or download our mobile apps:
Comparison of CMD Management Strategies
To help you better understand the various approaches to CMD management, we’ve compiled a comprehensive comparison table of different strategies:
| Management Strategy | Effectiveness | Implementation Difficulty | Cost | Environmental Impact | Long-term Sustainability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant Cassava Varieties | High | Easy | Medium | Low | High |
| Whitefly Control Methods | Medium | Moderate | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Organic Pest Management | Medium | Moderate | Low | Low | High |
| Chemical Interventions | High | Easy | High | High | Low |
| Integrated Pest Management | High | Difficult | Medium | Low | High |
| Farmonaut’s Agritech Solutions | High | Moderate | Medium | Low | High |
This table provides a clear overview of the various CMD management approaches, allowing you to compare their effectiveness, practicality, and sustainability. As you can see, integrated approaches like IPM and Farmonaut’s agritech solutions offer a balanced combination of effectiveness and sustainability.
The Future of CMD Management: Emerging Technologies and Research
As we continue to battle CMD, researchers and agricultural technologists are developing new and innovative approaches to disease management. Some promising areas of research include:
- CRISPR gene editing: Developing cassava varieties with enhanced CMD resistance
- Nanotechnology: Creating novel pesticides and plant protection products
- Machine learning algorithms: Improving early detection and prediction of CMD outbreaks
- Drone technology: Enhancing field monitoring and targeted treatment application
These emerging technologies hold great promise for the future of CMD management and sustainable cassava farming.
Case Studies: Successful CMD Management in Different Regions
To illustrate the effectiveness of various CMD management strategies, let’s look at some success stories from different cassava-growing regions:
Uganda: Integrated Pest Management Success
In Uganda, a comprehensive IPM program combining resistant varieties, improved cultural practices, and community education led to a 60% reduction in CMD incidence over five years.
India: Technology-Driven Approach
Farmers in Tamil Nadu, India, using satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-powered advisory systems, reported a 40% decrease in CMD-related losses and a 25% increase in overall cassava yields.
Colombia: Biological Control Triumph
A biological control program in Colombia, focusing on the introduction of whitefly predators and parasitoids, resulted in a 70% reduction in whitefly populations and a corresponding decrease in CMD transmission.
These case studies demonstrate that with the right combination of strategies and technologies, effective CMD management is achievable across diverse agricultural contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
To address some common queries about CMD and its management, we’ve compiled this FAQ section:
- Q: Can CMD-infected cassava plants recover?
A: While infected plants rarely recover completely, proper management can help minimize yield losses and prevent further spread. - Q: How long does it take for CMD symptoms to appear after infection?
A: Symptoms typically appear 1-4 weeks after infection, depending on environmental conditions and plant variety. - Q: Are there any natural predators of whiteflies that can help control CMD spread?
A: Yes, several natural predators like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps can help control whitefly populations. - Q: How often should I monitor my cassava fields for CMD?
A: Regular monitoring, at least once a week during the growing season, is recommended for early detection of CMD symptoms. - Q: Can CMD be transmitted through cassava cuttings used for planting?
A: Yes, CMD can be transmitted through infected cuttings. Always use disease-free planting material from reliable sources.
For more information on CMD management and Farmonaut’s agritech solutions, please visit our web app or explore our API for developers.
Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Cassava Farming for a Resilient Future
As we’ve explored throughout this blog post, Cassava Mosaic Disease presents a significant challenge to cassava farmers worldwide. However, by embracing sustainable farming practices, integrated pest management strategies, and innovative agritech solutions like those offered by Farmonaut, we can effectively manage CMD and ensure the long-term viability of cassava production.
Key takeaways for sustainable cassava farming and CMD management include:
- Implementing a multi-faceted approach combining resistant varieties, cultural practices, and technological solutions
- Prioritizing early detection and prompt action through regular monitoring and data-driven decision making
- Adopting organic and integrated pest management strategies to minimize environmental impact
- Leveraging advanced technologies like satellite monitoring and AI-powered advisory systems
- Staying informed about emerging research and technologies in CMD management
By working together and implementing these strategies, we can create a more resilient and sustainable future for cassava farming, ensuring food security and economic stability for millions of people worldwide.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can support your sustainable cassava farming efforts, visit our web app or explore our API Developer Docs for custom integration options.