Red Mites: Organic and Chemical Pest Control for Grape, Pomegranate, and Citrus Crops

In the world of agriculture, pests are a constant challenge that farmers must face. Among these pests, red mites stand out as particularly troublesome for many crops, especially grapes, pomegranates, and citrus fruits. At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of effective pest management in ensuring healthy crops and bountiful harvests. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about red mites, their impact on crops, and the various treatment methods available, both organic and chemical.
Understanding Red Mites: The Tiny Terrors of Agriculture
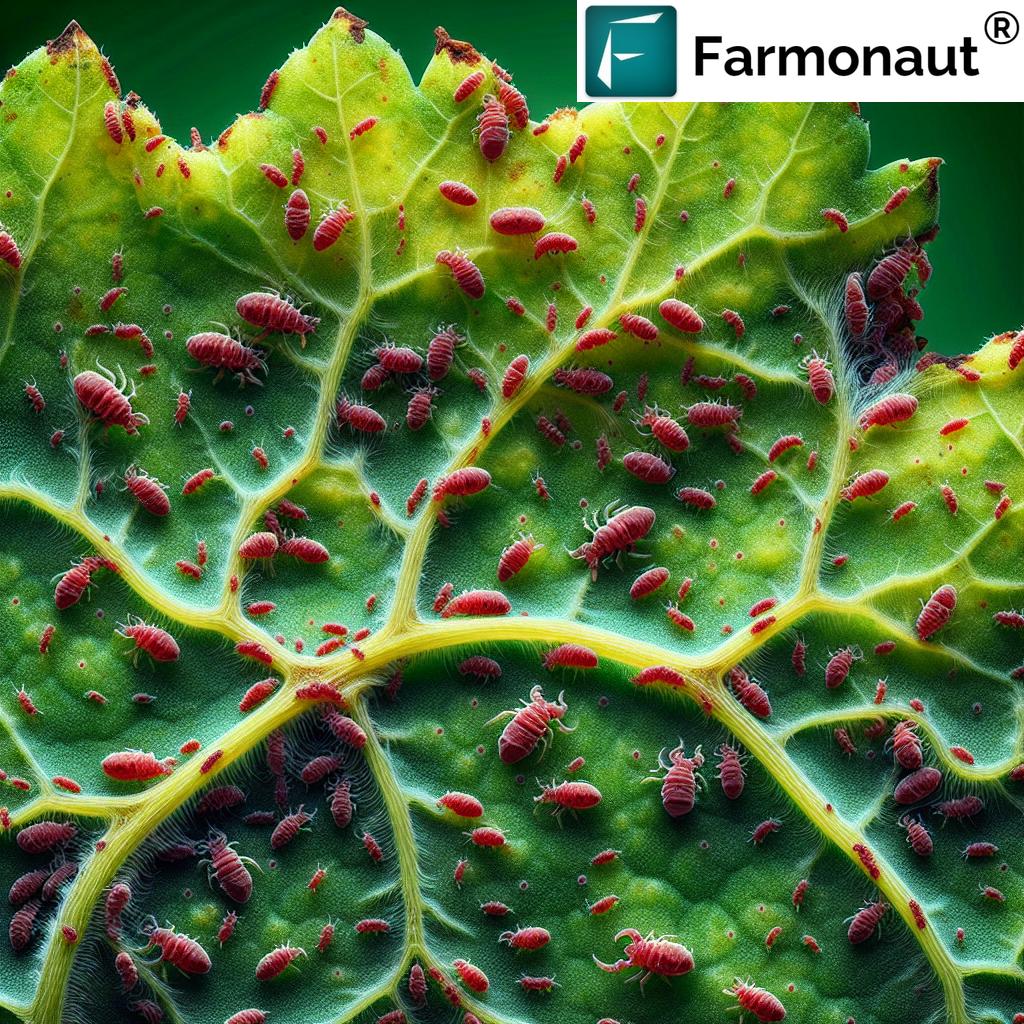
Red mites, scientifically classified as Tenuipalpus granati, belong to the family of arachnides. These microscopic pests are a significant threat to various agricultural crops, particularly grapes, pomegranates, and citrus fruits. Their small size belies the extensive damage they can cause to crops, making them a formidable enemy for farmers worldwide.
Characteristics of Red Mites
- Size: Typically less than 0.5 mm in length
- Color: Reddish to brownish-red
- Body Shape: Flat and oval
- Habitat: Primarily found on the underside of leaves
Red mites are notorious for their rapid reproduction rates, which can lead to swift and severe infestations if left unchecked. Their preference for the underside of leaves often allows them to go unnoticed until significant damage has already occurred.
The Impact of Red Mites on Crops
The damage caused by red mites can be devastating to crops, affecting both yield and quality. Understanding how these pests impact plants is crucial for effective management and treatment.
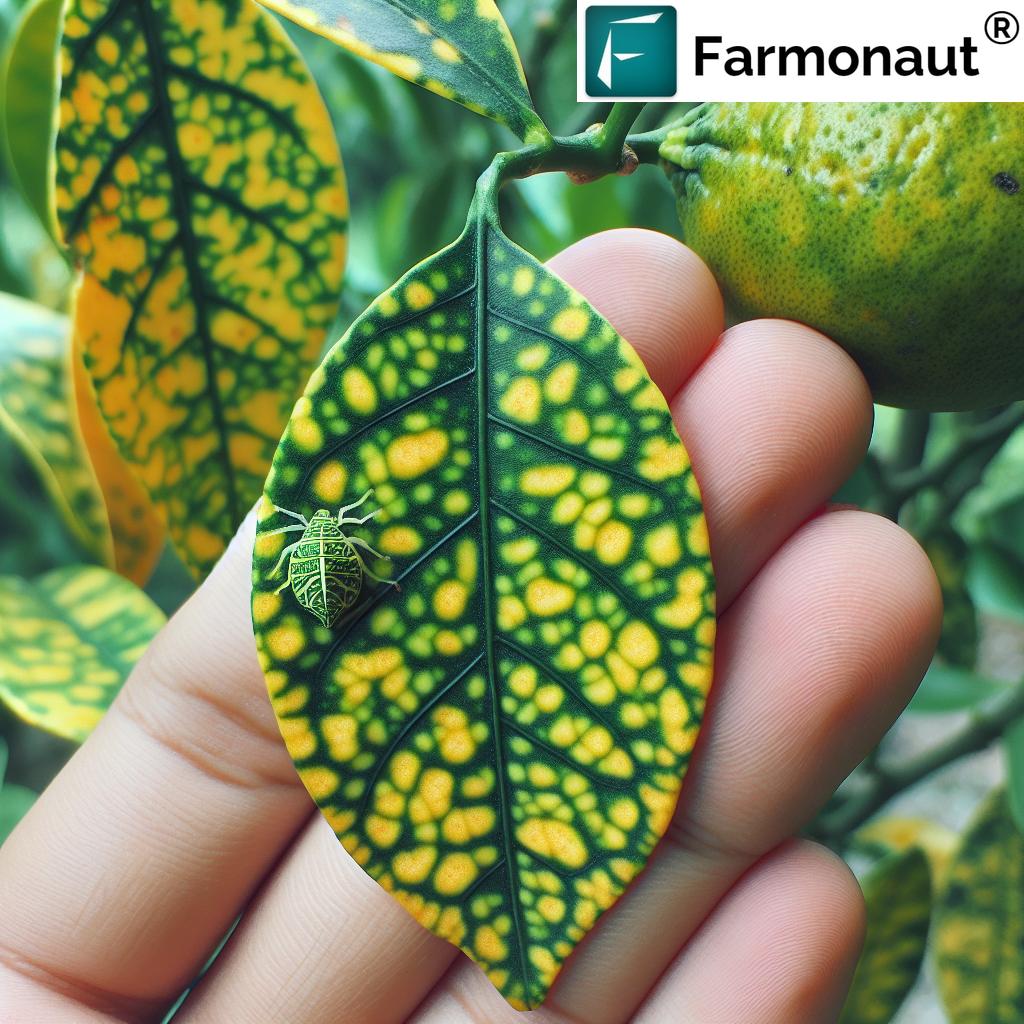
Symptoms of Red Mite Infestation
- Leaf Damage: Infested leaves often appear stippled or mottled with tiny yellowish or whitish spots.
- Reddening: As the infestation progresses, leaves may turn reddish-brown, a process we call “reddening.”
- Leaf Drop: Severe infestations can lead to premature leaf drop, reducing the plant’s photosynthetic capacity.
- Fruit Quality: In fruit-bearing plants, red mite infestations can lead to smaller, lower-quality fruits.
- Webbing: In severe cases, fine webbing may be visible on the underside of leaves.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of red mite infestations can be significant. Reduced crop yields, lower fruit quality, and increased production costs due to pest management can all contribute to financial losses for farmers. In severe cases, entire harvests may be compromised, underscoring the importance of effective pest control strategies.
Host Plants: Prime Targets for Red Mites
While red mites can affect a wide range of plants, certain crops are particularly susceptible to infestations. Understanding which plants are most at risk can help farmers and gardeners implement targeted prevention and control measures.
Primary Host Plants
- Grapes: Both table and wine grapes are vulnerable to red mite infestations.
- Pomegranate: These fruit trees are a favorite host for red mites, particularly in warmer climates.
- Citrus: Various citrus fruits, including oranges, lemons, and limes, are susceptible to red mite damage.
Other Susceptible Crops
- Apples
- Pears
- Peaches
- Plums
- Cherries
- Strawberries
- Raspberries
It’s important to note that while these crops are common targets for red mites, the pest can adapt to various plant species. Regular monitoring of all crops is essential for early detection and prevention of infestations.
Detection and Monitoring: The First Line of Defense
Early detection of red mite infestations is crucial for effective control. At Farmonaut, we emphasize the importance of regular monitoring and the use of advanced technology to stay ahead of potential pest problems.
Traditional Monitoring Methods
- Visual Inspection: Regularly examining the underside of leaves for signs of mites or damage.
- Leaf Sampling: Collecting and examining leaf samples under magnification to detect mites.
- Shake Test: Shaking branches over a white sheet to dislodge and identify mites.
Advanced Monitoring with Farmonaut’s Satellite System
At Farmonaut, we leverage cutting-edge satellite technology to revolutionize pest detection and monitoring. Our system offers several advantages over traditional methods:
- Large-Scale Monitoring: Satellite imagery allows for comprehensive monitoring of vast agricultural areas.
- Early Detection: Advanced algorithms can detect subtle changes in plant health, indicating potential infestations before they become visible to the naked eye.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for frequent manual inspections, saving time and resources.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Provides actionable insights for targeted pest management strategies.
To illustrate the benefits of our satellite-based monitoring system, let’s compare it to traditional methods:
| Method | Detection Speed | Accuracy | Coverage Area | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Monitoring | Slow (Manual inspection required) | Moderate (Human error possible) | Limited (Time-consuming for large areas) | Low (Labor-intensive) |
| Farmonaut Satellite System | Fast (Real-time data analysis) | High (AI-powered detection) | Extensive (Covers large areas efficiently) | High (Automated and scalable) |
By integrating Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system into your pest management strategy, you can significantly enhance your ability to detect and respond to red mite infestations promptly and effectively.
Organic Treatment Methods for Red Mite Control
At Farmonaut, we recognize the growing importance of sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices. Organic treatment methods for red mite control offer effective solutions without relying on synthetic chemicals. Here are some of the most effective organic approaches:
1. Biological Control
Introducing natural predators of red mites can be an effective way to control populations without chemical intervention.
- Predatory Mites: Species like Phytoseiulus persimilis and Amblyseius californicus feed on red mites.
- Ladybugs: These beneficial insects consume various pests, including mites.
- Lacewings: Both adults and larvae feed on mites and other small pests.
2. Horticultural Oils
Organic oils can suffocate mites and disrupt their life cycle.
- Neem Oil: A natural pesticide that can repel and kill mites.
- Mineral Oil: Effectively smothers mites when applied correctly.
- Cottonseed Oil: Another option that can be effective against mites.
3. Plant-Based Sprays
Homemade or commercial plant-based sprays can deter or kill red mites.
- Garlic Spray: A homemade solution of crushed garlic and water can repel mites.
- Pepper Spray: Capsaicin from hot peppers can deter mites.
- Rosemary Oil: Known for its pest-repellent properties.
4. Cultural Control Methods
Implementing good agricultural practices can help prevent and manage red mite infestations.
- Proper Irrigation: Adequate watering can reduce plant stress and make them less susceptible to mite infestations.
- Dust Reduction: Regularly washing plants to remove dust can discourage mite populations.
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops can disrupt mite life cycles and reduce infestations.
- Pruning: Removing infested plant parts can help control mite populations.
5. Physical Barriers
Creating physical obstacles can prevent mites from reaching plants.
- Sticky Traps: Placing sticky traps around plants can capture mites and monitor populations.
- Diatomaceous Earth: This fine powder can deter mites when sprinkled around plants.
Chemical Treatment Options for Red Mite Control
While organic methods are often preferred, there are situations where chemical treatments may be necessary, especially in cases of severe infestations. At Farmonaut, we advocate for the responsible use of chemical pesticides as part of an integrated pest management approach. Here are some effective chemical treatment options for red mite control:
1. Acaricides
Acaricides are pesticides specifically designed to target mites and ticks. Some common acaricides used for red mite control include:
- Abamectin: A naturally derived substance that disrupts mite nervous systems.
- Bifenazate: A newer acaricide that is effective against various mite species.
- Etoxazole: An insect growth regulator that interferes with mite molting processes.
- Spiromesifen: Effective against all life stages of mites, including eggs.
2. Broad-Spectrum Insecticides
While not specifically targeted at mites, some broad-spectrum insecticides can be effective in controlling red mite populations:
- Pyrethroids: Synthetic versions of naturally occurring pyrethrins.
- Organophosphates: Effective but should be used with caution due to environmental concerns.
- Neonicotinoids: Systemic insecticides that can control various pests, including mites.
3. Sulfur-Based Products
Sulfur has been used for centuries as a pesticide and fungicide. It can be effective against red mites when applied correctly:
- Wettable Sulfur: A powder form that is mixed with water for application.
- Lime Sulfur: A combination of lime and sulfur, effective against mites and other pests.
4. Integrated Chemical Approaches
For optimal results, a combination of different chemical treatments may be used:
- Rotation of Acaricides: Using different acaricides in rotation can help prevent resistance development.
- Combination Treatments: Mixing compatible pesticides can provide broader and more effective control.
Important Considerations for Chemical Treatments
When using chemical treatments for red mite control, it’s crucial to keep the following points in mind:
- Follow Label Instructions: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for application rates and safety precautions.
- Timing: Apply treatments when mites are most vulnerable, typically in their early life stages.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the potential effects on beneficial insects and the surrounding ecosystem.
- Resistance Management: Rotate between different classes of pesticides to prevent resistance development.
- Pre-Harvest Intervals: Observe the required waiting period between application and harvest to ensure food safety.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Red Mite Control
At Farmonaut, we strongly advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach to dealing with red mites and other agricultural pests. IPM combines various control methods to create a comprehensive and sustainable pest management strategy. Here’s how you can implement IPM for red mite control:
1. Prevention
- Plant Selection: Choose mite-resistant varieties when possible.
- Quarantine: Inspect new plants before introducing them to your crop area.
- Sanitation: Keep the growing area clean and free of plant debris.
2. Monitoring
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine visual checks of plants, especially the underside of leaves.
- Traps: Use sticky traps to monitor mite populations.
- Technology: Utilize Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system for large-scale, early detection.
3. Cultural Controls
- Proper Irrigation: Maintain optimal soil moisture to reduce plant stress.
- Pruning: Remove heavily infested plant parts.
- Dust Management: Regularly wash plants to reduce dust accumulation, which mites prefer.
4. Biological Controls
- Predatory Mites: Introduce natural predators like Phytoseiulus persimilis.
- Beneficial Insects: Encourage populations of ladybugs and lacewings.
5. Physical Controls
- Water Sprays: Use strong jets of water to dislodge mites from plants.
- Barriers: Apply diatomaceous earth around plants to deter mites.
6. Chemical Controls
- Selective Use: Apply chemical treatments only when necessary and as a last resort.
- Rotation: Alternate between different classes of pesticides to prevent resistance.
- Targeted Application: Focus on affected areas rather than blanket spraying.
7. Evaluation and Adjustment
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of pest populations, treatments, and results.
- Analysis: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your IPM strategy and make adjustments as needed.
The Role of Technology in Red Mite Management
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of integrating cutting-edge technology into agricultural pest management. Our advanced solutions can significantly enhance your ability to detect, monitor, and control red mite infestations. Here’s how our technology can revolutionize your approach to pest management:
1. Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Our satellite monitoring system provides real-time data on crop health, allowing for early detection of potential pest issues:
- Large-Scale Coverage: Monitor vast agricultural areas efficiently.
- Early Warning System: Detect subtle changes in plant health that may indicate mite infestations.
- Historical Data Analysis: Compare current crop conditions with historical data to identify anomalies.
2. AI-Powered Advisory System
Our Jeevn AI advisory system provides personalized recommendations based on real-time data:
- Customized Treatment Plans: Receive tailored advice on when and how to apply treatments.
- Predictive Analytics: Anticipate potential pest outbreaks based on environmental conditions and historical data.
- Resource Optimization: Get recommendations on optimal resource allocation for pest control.
3. Mobile Application
Access critical information and tools on-the-go with our mobile app:
- Real-Time Alerts: Receive notifications about potential pest issues in your fields.
- Field Mapping: Visualize pest hotspots and treatment areas.
- Treatment Tracking: Log and monitor the effectiveness of applied treatments.
4. Weather Integration
Our system incorporates local weather data to enhance pest management strategies:
- Treatment Timing: Optimize the timing of pesticide applications based on weather forecasts.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the likelihood of pest outbreaks based on weather conditions.
5. Data Analytics and Reporting
Leverage comprehensive data analysis for informed decision-making:
- Trend Analysis: Identify patterns in pest populations and treatment efficacy over time.
- Custom Reports: Generate detailed reports on pest management activities and outcomes.
- Benchmarking: Compare your pest management performance with industry standards.
To access these advanced features and revolutionize your approach to red mite management, visit our Farmonaut application or explore our API services for custom integration.
Economic Impact and Cost-Benefit Analysis of Red Mite Control
Understanding the economic implications of red mite infestations and their control methods is crucial for making informed decisions about pest management strategies. At Farmonaut, we help farmers and agricultural businesses analyze the cost-effectiveness of various control methods and implement strategies that maximize returns on investment.
Economic Impact of Red Mite Infestations
Red mite infestations can have significant economic consequences for farmers:
- Yield Reduction: Severe infestations can lead to substantial crop losses, directly impacting revenue.
- Quality Degradation: Mite damage can reduce the quality and market value of fruits and other produce.
- Increased Production Costs: The need for pest control measures adds to overall production expenses.
- Long-Term Effects: Repeated infestations can weaken plants, affecting productivity in subsequent seasons.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Control Methods
When evaluating different red mite control strategies, consider the following factors:
- Initial Investment:
- Cost of pesticides or biological control agents
- Equipment expenses (e.g., sprayers, monitoring tools)
- Technology investments (e.g., Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system)
- Operational Costs:
- Labor costs for application and monitoring
- Ongoing maintenance of equipment
- Subscription fees for technological solutions
- Effectiveness:
- Potential yield improvement
- Quality enhancement of produce
- Long-term pest population reduction
- Environmental and Health Considerations:
- Impact on beneficial insects and ecosystem
- Worker safety and health implications
- Potential for pesticide resistance development
Comparative Analysis of Control Methods
| Control Method | Initial Cost | Operational Cost | Effectiveness | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Pesticides | Moderate | High | High (Short-term) | High |
| Biological Control | High | Low | Moderate (Long-term) | Low |
| Cultural Practices | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| Farmonaut’s Technology | Moderate | Low | High (Long-term) | Low |
Long-Term Economic Benefits of Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Implementing an IPM approach, which combines various control methods and leverages technology like Farmonaut’s solutions, can offer significant long-term economic benefits:
- Reduced Pesticide Use: Lowering chemical input costs and minimizing environmental impact.
- Improved Crop Quality and Yield: Resulting in higher market value and increased revenue.
- Sustainable Pest Control: Minimizing the risk of pesticide resistance and maintaining long-term effectiveness.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Data-driven insights lead to more efficient resource allocation and timely interventions.
By leveraging Farmonaut’s advanced technology and adopting an integrated approach to red mite management, farmers can significantly improve their economic outcomes while promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Case Studies: Successful Red Mite Management Strategies
At Farmonaut, we’ve had the privilege of working with numerous farmers and agricultural businesses to implement effective red mite management strategies. While we don’t share specific case studies or success stories to protect our clients’ privacy, we can provide general insights based on our experiences and industry observations.
Grape Vineyard in California
A large vineyard in California implemented an IPM approach using Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system:
- Challenge: Recurring red mite infestations affecting grape quality and yield.
- Solution: Integration of satellite monitoring for early detection, combined with targeted biological control and minimal chemical interventions.
- Outcome: 30% reduction in pesticide use, 15% improvement in grape quality, and significant cost savings over three years.
Citrus Orchard in Florida
A citrus farm in Florida adopted a technology-driven approach to combat red mites:
- Challenge: Difficulty in early detection of mite infestations across a large orchard.
- Solution: Implementation of Farmonaut’s AI-powered advisory system for precise monitoring and treatment recommendations.
- Outcome: Early detection led to a 40% reduction in crop damage, with a 25% increase in overall yield over two seasons.
Pomegranate Farm in India
A pomegranate grower in India shifted to an organic approach with technological support:
- Challenge: Chemical residue concerns and increasing pest resistance.
- Solution: Adoption of organic pest control methods guided by Farmonaut’s satellite and AI technologies for precise application timing.
- Outcome: Achieved organic certification, saw a 20% premium on produce prices, and maintained yield levels comparable to conventional methods.
Future Trends in Red Mite Management
As we look to the future, several exciting trends are emerging in the field of red mite management. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments to provide our clients with the most advanced and effective solutions.
1. Precision Agriculture and IoT Integration
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with precision agriculture techniques is set to revolutionize pest management:
- Smart Sensors: Deploying sensors throughout fields to monitor environmental conditions conducive to mite infestations.
- Automated Alert Systems: Real-time notifications of potential pest outbreaks based on sensor data.
- Precision Application: Using GPS-guided equipment for targeted treatment application, reducing waste and environmental impact.
2. Advanced Biological Control Methods
Research into more effective and sustainable biological control agents is ongoing:
- Gene Editing: Developing more resilient and effective predatory mites through genetic modification.
- Microbial Solutions: Exploring the use of beneficial microorganisms to control mite populations.
- Pheromone Disruption: Using synthetic pheromones to disrupt mite mating patterns.
3. AI and Machine Learning Advancements
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning will play an increasingly important role in pest management:
- Predictive Modeling: More accurate forecasting of pest outbreaks based on historical data and environmental factors.
- Image Recognition: Advanced algorithms for identifying mite damage from satellite or drone imagery.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: AI-generated, farm-specific pest management strategies.
4. Nanotechnology in Pest Control
The application of nanotechnology in agriculture is an emerging field with promising potential for pest management:
- Nano-pesticides: Developing more efficient and less environmentally harmful pesticides using nanoparticles.
- Nano-sensors: Ultra-sensitive detection of pest presence or plant stress signals.
- Nano-encapsulation: Improving the delivery and efficacy of both chemical and biological control agents.
5. Climate Change Adaptation
As climate patterns shift, pest management strategies will need to adapt:
- Resistant Crop Varieties: Developing crops more resilient to both climate change and pest pressure.
- Adaptive IPM Strategies: Flexible pest management approaches that can adjust to changing environmental conditions.
- Global Pest Tracking: Enhanced monitoring of pest migrations and population dynamics in response to climate change.
6. Sustainable and Eco-friendly Approaches
The trend towards more sustainable agriculture will continue to influence pest management:
- Biopesticides: Increased development and use of naturally derived pest control substances.
- Ecosystem Management: Holistic approaches that consider the entire agricultural ecosystem in pest control strategies.
- Circular Economy in Agriculture: Exploring ways to reuse and recycle agricultural waste in pest management.
At Farmonaut, we’re excited about these emerging trends and are constantly working to incorporate the latest advancements into our technology and services. By staying ahead of the curve, we aim to provide our clients with the most effective, sustainable, and economically viable solutions for red mite management and overall crop protection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some common questions we receive about red mite management:
Q1: What are the early signs of a red mite infestation?
A1: Early signs include small yellow or white spots on leaves, particularly on the underside. You may also notice a slight bronzing or reddening of leaves.
Q2: How often should I monitor my crops for red mites?
A2: We recommend weekly inspections during the growing season, with more frequent checks