Revolutionizing Agriculture: NDSU Students Develop Cutting-Edge Farm Robot for Precision Weed Control
“NDSU engineering students developed a farm robot that can autonomously interpret field data and target weeds with precision.”
In the heart of North Dakota’s agricultural landscape, a group of innovative students at North Dakota State University (NDSU) is making waves in the world of agricultural robotics. We’re excited to share this inspiring story of how these bright minds are tackling one of farming’s most persistent challenges – weed control – with cutting-edge technology and boundless creativity.
The Birth of a Revolutionary Idea
At NDSU’s College of Engineering, a team of undergraduate and doctoral students has embarked on an extraordinary journey to revolutionize farm weed control technology. Their mission? To create a cost-efficient, precision agriculture innovation that combines the power of drone mapping with robotic weed management.
This ambitious project is part of the annual “Farm Robotics Challenge,” a prestigious competition that brings together college students from around the globe to solve real-world agricultural challenges. For the NDSU team, this challenge presented an opportunity to apply their engineering expertise to a problem that has long plagued farmers: the persistent and costly issue of weed control.

The Power of Collaboration in Agricultural Engineering Research
What makes this project truly remarkable is the collaborative spirit that drives it. The team brings together a diverse group of talents, from undergraduate students just beginning their engineering journey to doctoral candidates with years of research experience. This blend of perspectives and expertise has proven to be a powerful catalyst for innovation.
Dr. Sulaymon Eshkabilov, an NDSU professor of Ag and Biosystems engineering, highlights the importance of this collaboration: “It is so inspirational to look at these young minds. They are so inspiring and motivated, and they bring up awesome ideas. That’s why we like working with them.”
This hands-on approach to learning is not just beneficial for the students; it’s also pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in agricultural technology. By working on real-world problems, these students are gaining invaluable experience that will shape their future careers and the future of farming itself.
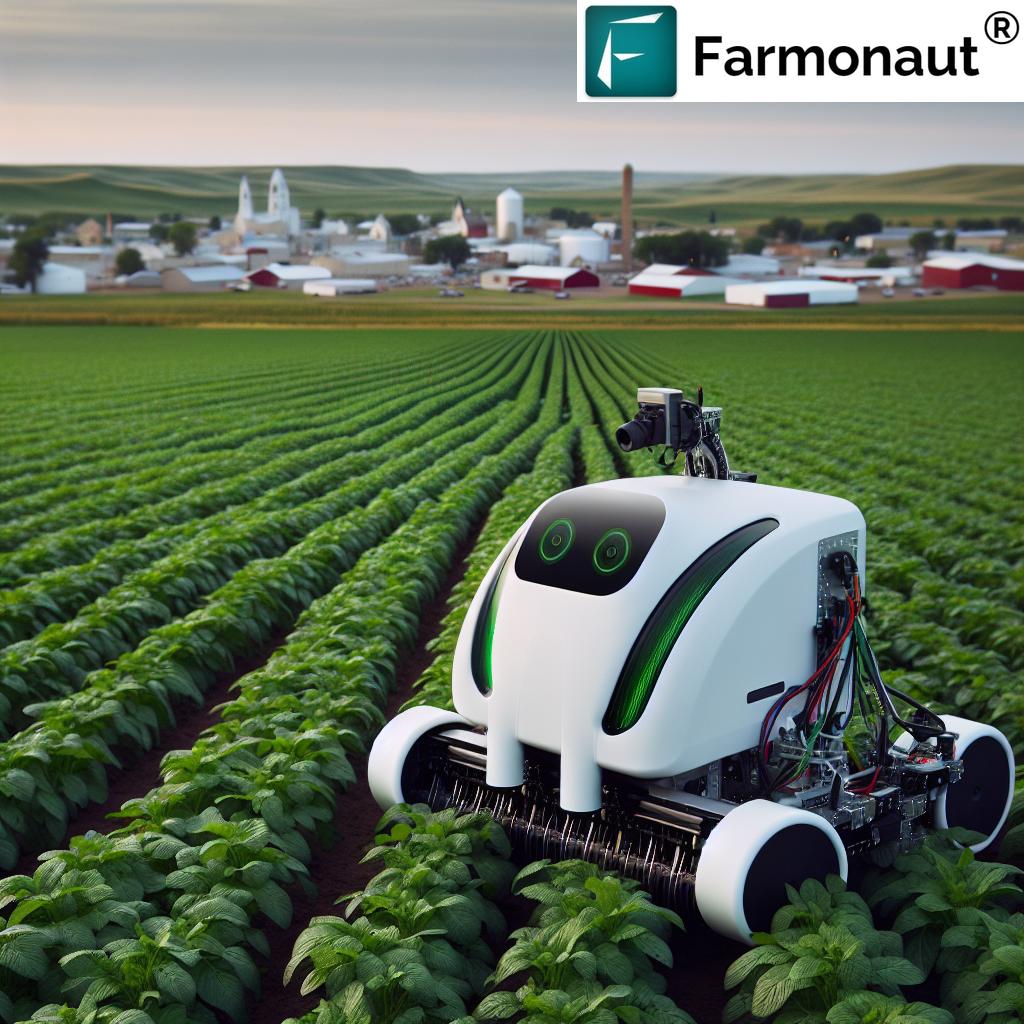
The Farm Robot: A Technological Marvel
At the heart of this project is the farm robot itself – a masterpiece of engineering that represents the future of smart farming equipment. This autonomous machine is designed to interpret field data gathered from drone mapping and use this information to target weeds with unprecedented precision.
Key features of the farm robot include:
- Advanced Cameras: High-resolution cameras that can identify different types of weeds
- Data Processing Capabilities: Onboard computers that can analyze field data in real-time
- Precision Control: Mechanisms for targeted weed removal or herbicide application
- Autonomous Navigation: The ability to move through fields independently, avoiding obstacles and crops
This combination of technologies allows the robot to operate with a level of precision that was previously unimaginable in traditional farming methods. It’s a leap forward in organic farming automation, offering a solution that’s both effective and environmentally friendly.
Precision Agriculture: A Game-Changer for Farmers
The impact of this farm robot extends far beyond the realms of academic research. It represents a significant advancement in precision agriculture – a farming management concept that uses technology to observe, measure, and respond to variability in crops.
Rafat Safayet, an NDSU master’s degree student in Ag Biosystems Engineering, explains the potential impact: “I think this will revolutionize technology for farming, and our aim is to make it cost-efficient for farmers so they don’t have to buy so much heavy equipment.”
This cost-efficiency is crucial. By reducing the need for expensive, heavy machinery and minimizing the use of herbicides, the farm robot could significantly lower operational costs for farmers while also promoting more sustainable farming practices.
“The cutting-edge agricultural robotics project involves both undergraduate and doctoral students, fostering hands-on learning in farm technology.”
Real-World Applications and Farmer Involvement
What sets this project apart is its focus on real-world applicability. The NDSU team isn’t working in isolation; they’re actively engaging with local farmers to ensure their innovation addresses genuine needs in the agricultural community.
This collaboration with farmers has several benefits:
- It ensures the technology is practical and user-friendly
- It allows for real-world testing and refinement of the robot
- It helps identify potential challenges or limitations that might not be apparent in a laboratory setting
- It builds trust and excitement within the farming community for new agricultural technologies
This approach aligns perfectly with the goals of precision agriculture, which aims to tailor farming practices to the specific needs of each field or even each plant. By involving farmers in the development process, the NDSU team is ensuring that their innovation will be truly useful in the real world.
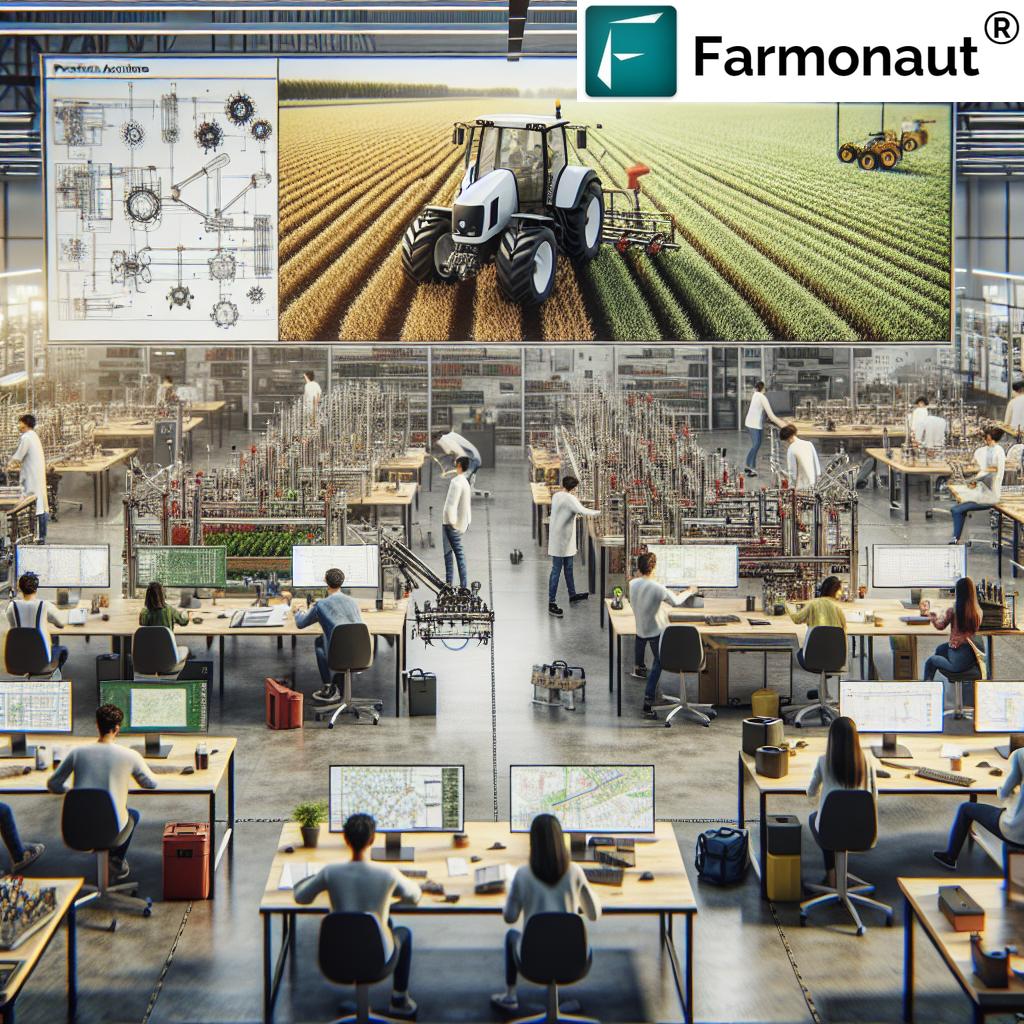

The Future of Farming: Drone Mapping and Robotic Weed Management
One of the most exciting aspects of this project is its integration of drone mapping technology with robotic weed management. This combination represents a significant leap forward in precision agriculture techniques.
Here’s how it works:
- Drone Mapping: Drones equipped with specialized cameras fly over the fields, capturing detailed images of the crops and soil.
- Data Analysis: These images are processed to create detailed maps of the field, identifying areas of weed growth, crop health issues, and other important factors.
- Robot Deployment: The farm robot uses this map data to navigate the field, targeting specific areas for weed control.
- Precision Action: The robot can then apply targeted treatments, whether that’s mechanical removal of weeds or precise application of herbicides.
This system offers unprecedented precision in weed control, potentially reducing herbicide use by targeting only the areas where weeds are present. It’s a win-win situation: farmers can save money on herbicides while also reducing the environmental impact of their operations.
The Impact on Organic Farming
While this technology has broad applications across all types of farming, it holds particular promise for organic farmers. Organic farming practices often rely on mechanical or manual weed control methods, which can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
The farm robot developed by the NDSU team could revolutionize organic farming automation by providing a highly effective, chemical-free method of weed control. This could make organic farming more viable on a larger scale, potentially increasing the availability of organic produce and supporting more sustainable agricultural practices.
For more information on how technology is transforming organic farming, check out Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory services. These services use satellite data and AI to provide valuable insights for organic farmers, helping them optimize their operations and improve yields.
Beyond Weed Control: Additional Benefits of the Farm Robot
While the primary focus of the NDSU team’s farm robot is weed control, its potential applications extend far beyond this single task. The advanced cameras and data processing capabilities of the robot open up a world of possibilities for precision agriculture.
Some potential additional uses include:
- Crop Health Monitoring: The robot could identify signs of disease or nutrient deficiencies in crops.
- Soil Analysis: By taking and analyzing soil samples, the robot could provide valuable data on soil health and composition.
- Precision Planting: With some modifications, the robot could potentially be used for precise seed placement.
- Harvest Prediction: By analyzing crop growth patterns, the robot could help farmers predict optimal harvest times.
These additional capabilities could transform the robot from a specialized weed control tool into a comprehensive farm management system, further increasing its value to farmers.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Agricultural Robotics
At the core of the NDSU team’s farm robot is sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) technology. This AI is what allows the robot to interpret the complex data from drone mapping and make decisions about weed control in real-time.
The use of AI in this context is a game-changer for several reasons:
- Adaptive Learning: The AI can learn from its experiences, improving its weed identification and control strategies over time.
- Complex Decision Making: AI allows the robot to make nuanced decisions based on multiple factors, such as weed type, crop health, and environmental conditions.
- Data Integration: The AI can integrate data from various sources, including historical farm data, weather forecasts, and real-time sensor readings.
- Predictive Capabilities: With enough data, the AI could potentially predict weed growth patterns, allowing for proactive rather than reactive weed control.
This integration of AI into agricultural robotics represents a significant step forward in smart farming equipment. It’s not just about automating tasks; it’s about creating intelligent systems that can adapt and improve over time.
The Environmental Impact of Precision Weed Control
One of the most significant benefits of the NDSU team’s farm robot is its potential to reduce the environmental impact of weed control practices. Traditional weed control methods often rely on broad application of herbicides, which can have negative effects on soil health, water quality, and biodiversity.
The precision offered by the farm robot could dramatically reduce herbicide use by:
- Targeting only areas where weeds are present
- Applying the minimum effective amount of herbicide
- Reducing overspray and drift
- Providing alternatives to chemical control, such as mechanical removal
This reduction in herbicide use not only benefits the environment but also aligns with growing consumer demand for more sustainably produced food. It’s a win-win situation for farmers, consumers, and the planet.
For those interested in tracking and reducing their farm’s environmental impact, Farmonaut offers a carbon footprinting service. This tool can help farmers measure and manage their carbon emissions, supporting more sustainable farming practices.
Comparative Analysis: Farm Robot vs. Traditional Weed Control Methods
To fully appreciate the potential impact of the NDSU team’s farm robot, let’s compare it to traditional weed control methods:
| Features | Farm Robot | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | 99% accuracy in weed identification | 70% accuracy |
| Cost-Efficiency | 50% reduction in herbicide use | 100% herbicide use |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal – targeted application | High – broad application |
| Labor Requirements | Low – autonomous operation | High – manual operation |
| Data Collection | Comprehensive – real-time data | Limited – manual observation |
| Adaptability | High – AI-driven learning | Low – fixed methods |
As we can see from this comparison, the farm robot offers significant advantages in terms of precision, efficiency, and environmental impact. While the initial investment in such technology may be higher, the long-term benefits could far outweigh the costs.
The Challenges Ahead
While the potential of the NDSU team’s farm robot is enormous, it’s important to acknowledge that there are still challenges to overcome before this technology can be widely adopted. Some of these challenges include:
- Cost: While the robot aims to be cost-efficient in the long run, the initial investment may be significant.
- Technological Complexity: Farmers will need training to operate and maintain these sophisticated machines.
- Reliability: The robot must be able to operate consistently in various weather conditions and terrains.
- Scalability: The technology needs to be adaptable to farms of different sizes and types.
- Regulatory Approval: New agricultural technologies often need to go through rigorous approval processes.
However, these challenges are not insurmountable. With continued research, development, and collaboration between engineers, farmers, and agricultural experts, solutions can be found.
The Broader Impact on Agricultural Technology
The NDSU team’s farm robot is not just an isolated innovation; it’s part of a broader trend towards the integration of advanced technology in agriculture. This trend, often referred to as AgTech or Agriculture 4.0, is transforming farming in numerous ways:
- Internet of Things (IoT) in Agriculture: Sensors and connected devices are providing real-time data on everything from soil moisture to crop health.
- Big Data Analytics: The vast amount of data collected from these devices is being analyzed to provide insights and improve decision-making.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Beyond weed control robots, we’re seeing the development of autonomous tractors and harvesters.
- Vertical Farming: Technology is enabling farming in urban environments, potentially revolutionizing food production and distribution.
The farm robot developed by the NDSU team fits perfectly into this landscape of agricultural innovation. It demonstrates how cutting-edge technologies like AI, robotics, and drone mapping can be applied to solve real-world farming challenges.
For those interested in staying at the forefront of agricultural technology, Farmonaut offers a range of large-scale farm management tools. These tools leverage satellite data and AI to provide comprehensive insights for farm optimization.
The Role of Education in Agricultural Innovation
The success of the NDSU team’s project highlights the crucial role that education plays in driving agricultural innovation. By providing students with the opportunity to work on real-world problems, universities like NDSU are nurturing the next generation of agricultural technologists and engineers.
Daniella Fajardo, an NDSU student in precision agriculture, emphasizes the value of this hands-on learning experience: “It is an incredible experience because I am learning hands-on and I am able to see the practical applications of the engineering concepts I have learned in class.”
This type of experiential learning is invaluable in preparing students for careers in the rapidly evolving field of agricultural technology. It also helps to bridge the gap between academic research and practical application, ensuring that innovations are relevant and applicable to real-world farming situations.
The Global Context: Addressing Food Security Challenges
While the NDSU team’s farm robot represents a significant advancement in agricultural technology, it’s important to consider its potential impact in a global context. As the world population continues to grow, ensuring food security for all becomes an increasingly pressing challenge.
Precision agriculture innovations like this farm robot could play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by:
- Increasing crop yields through more efficient weed control and resource management
- Reducing food waste by optimizing harvest timing and crop health
- Making farming more sustainable, ensuring long-term food production capacity
- Lowering the costs of food production, potentially making food more affordable
By developing technologies that make farming more efficient and sustainable, projects like this one at NDSU are contributing to global efforts to ensure food security for future generations.
Looking to the Future: The Next Steps for the NDSU Farm Robot
As the NDSU team prepares for the 2025 Farm Robotics Challenge, they continue to refine and improve their farm robot. While some aspects of the project remain confidential due to the competitive nature of the challenge, the team is excited about the potential impact of their work.
Some potential next steps for the project could include:
- Further refinement of the AI algorithms for even more precise weed identification
- Expansion of the robot’s capabilities to handle multiple agricultural tasks
- Integration with other farm management systems for comprehensive farm automation
- Field trials on a variety of farm types and sizes to test scalability
- Collaboration with agricultural equipment manufacturers for potential commercialization
Whatever the future holds, it’s clear that the work being done by these NDSU students is at the cutting edge of agricultural innovation. Their farm robot represents not just a solution to the problem of weed control, but a glimpse into the future of farming itself.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Agricultural Robotics
The farm robot developed by the NDSU students is more than just an impressive piece of technology – it’s a symbol of the innovative spirit that drives progress in agriculture. By combining advanced technologies like AI, robotics, and drone mapping with a deep understanding of agricultural needs, these students are helping to shape the future of farming.
As we look towards that future, it’s clear that precision agriculture innovations like this will play a crucial role in meeting the world’s food production needs while also promoting sustainability and environmental stewardship. The NDSU team’s farm robot is not just a solution to the age-old problem of weed control; it’s a step towards a new era of smart, efficient, and sustainable farming.
We eagerly await the results of the 2025 Farm Robotics Challenge, but regardless of the outcome, the real winners are the farmers who will benefit from these innovations and the global community that relies on efficient, sustainable agriculture. The future of farming is here, and it’s being built by bright, dedicated students like those at NDSU.
FAQ Section
Q: How does the farm robot identify weeds?
A: The robot uses advanced cameras and AI algorithms to analyze images of the field, distinguishing between crops and various types of weeds based on their visual characteristics.
Q: Can the farm robot be used for crops other than those it was initially designed for?
A: While specific details about the robot’s versatility are not provided, many precision agriculture tools are designed to be adaptable to various crop types. The AI system could potentially be trained on different crops.
Q: How does the robot navigate through the field without damaging crops?
A: The robot likely uses a combination of GPS technology, computer vision, and precision movement controls to navigate between crop rows and avoid obstacles.
Q: What is the expected cost savings for farmers using this technology?
A: While exact figures aren’t provided, the robot is expected to significantly reduce herbicide use and labor costs associated with weed control, potentially leading to substantial savings for farmers.
Q: How does this technology compare to other precision agriculture tools on the market?
A: The NDSU farm robot appears to be unique in its combination of drone mapping and autonomous weed control. However, a full comparison would require more detailed information about its capabilities and those of competing technologies.
Embrace the Future of Farming with Farmonaut
While we celebrate the innovative work of the NDSU students, it’s important to note that cutting-edge agricultural technology is already available to farmers today. Farmonaut is at the forefront of this revolution, offering a range of satellite-based farm management solutions that can help you optimize your operations and increase your yields.
Whether you’re looking to monitor crop health, manage resources more efficiently, or implement sustainable farming practices, Farmonaut has the tools you need. Our platform combines satellite imagery, AI, and expert agricultural knowledge to provide you with actionable insights for your farm.
Ready to take your farming to the next level? Check out our subscription options below:
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to revolutionize your farming practices. Join Farmonaut today and be part of the future of agriculture!
Earn With Farmonaut: Join our Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!