UK Wildfire Alert: Northern Ireland Battles Major Forest Fire Amid Rising Spring Fire Risks
“In spring 2023, Northern Ireland battled a major forest fire, with over 50 firefighters deployed to combat the blaze.”
As we delve into the pressing issue of wildfires in Northern Ireland and across the United Kingdom, it’s crucial to understand the far-reaching implications of these environmental disasters. The recent outbreak of forest fires has sparked major concerns, particularly as unseasonably warm and dry weather increases fire risks throughout the region. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll explore the causes, impacts, and prevention strategies related to these devastating blazes, with a focus on the recent major incident in Northern Ireland.
The Northern Ireland Blaze: A Wake-Up Call
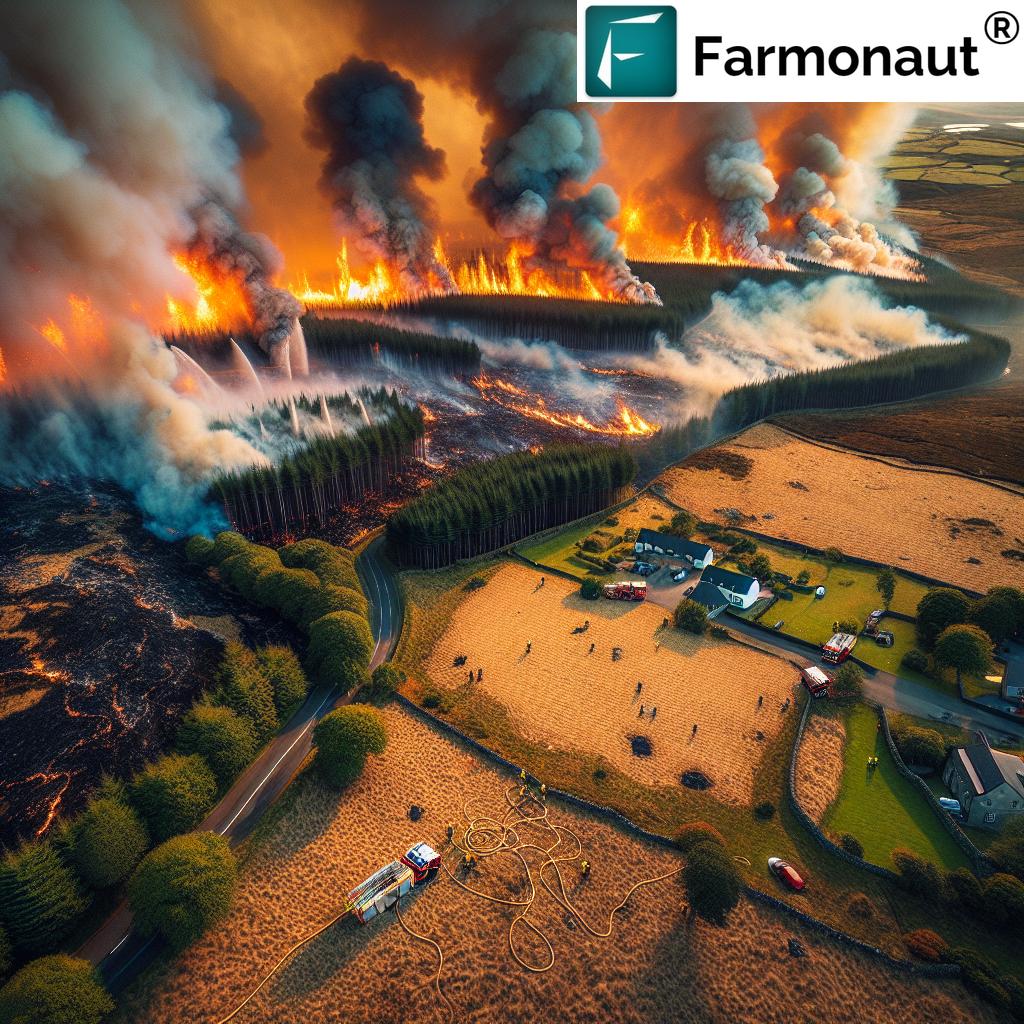
The southeastern corner of Northern Ireland recently witnessed a significant fire that swept through vast expanses of forest land. This incident serves as a stark reminder of the increasing wildfire threats faced by the United Kingdom, especially during periods of warm, dry weather. Let’s break down the key elements of this major event:
- Timing: The fire began late on a Saturday night, prompting an immediate response from emergency services.
- Scale: Over 100 firefighters were deployed to combat the blaze, highlighting the severity of the situation.
- Equipment: 14 pieces of specialized firefighting equipment were utilized in the operation.
- Location: The fire raged in a rural area outside the community of Hilltown, threatening both natural habitats and nearby settlements.
- Control: Firefighters managed to bring the blaze under control by the early hours of Sunday, showcasing their swift and effective response.
This incident underscores the critical need for heightened awareness and preparedness in the face of increasing wildfire risks across the UK. As we continue to experience warmer springs and drier conditions, the likelihood of such events occurring more frequently becomes a pressing concern for environmental experts and policymakers alike.

Understanding the Causes of Forest Fires in the UK
To effectively address the issue of wildfires in Northern Ireland and across the UK, it’s essential to understand their root causes. Several factors contribute to the increased risk of forest fires, particularly during the spring season:
- Unseasonably Warm Weather: As global temperatures continue to rise, the UK experiences more frequent periods of unusually warm weather, even during traditionally cooler seasons. This warmth accelerates the drying of vegetation, making it more susceptible to ignition.
- Dry Conditions: Prolonged periods without rainfall lead to decreased soil moisture and drier vegetation. This creates an ideal environment for fires to start and spread rapidly.
- Human Activities: Unfortunately, many wildfires in the UK are caused by human actions, whether intentional or accidental. These can include:
- Carelessly discarded cigarettes
- Unattended campfires
- Deliberate acts of arson
- Agricultural burning that gets out of control
- Natural Causes: While less common in the UK, natural phenomena such as lightning strikes can also ignite fires, especially in dry, forested areas.
Understanding these causes is crucial for developing effective wildfire prevention strategies and improving our response to these environmental threats.
The Environmental Impact of Wildfires
The consequences of forest fires extend far beyond the immediate destruction of vegetation. These events have profound and long-lasting effects on the environment:
- Biodiversity Loss: Fires can devastate local ecosystems, destroying habitats and potentially leading to the loss of rare or endangered species.
- Soil Degradation: Intense heat from fires can alter soil composition, affecting its ability to support plant life and increasing the risk of erosion.
- Air Quality: Smoke and particulate matter released during fires can significantly impact air quality, posing health risks to both humans and wildlife.
- Carbon Emissions: Wildfires release substantial amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
- Water Quality: Ash and debris from fires can contaminate water sources, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially impacting water supplies.
Given these severe environmental consequences, it’s clear that preventing and effectively managing wildfires is not just a matter of protecting property, but also of safeguarding our natural resources and ecosystems for future generations.
Wildfire Control Measures in the United Kingdom
In response to the growing threat of wildfires, the UK has implemented a range of control measures aimed at prevention, early detection, and rapid response. These include:
- Advanced Monitoring Systems: The use of satellite technology and AI-powered algorithms to detect potential fire hotspots. Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory services can play a crucial role in this aspect, providing real-time monitoring of vegetation health and potential fire risks in forested areas.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about fire safety, especially in rural and forested areas, to reduce the risk of human-caused fires.
- Controlled Burning: Implementing strategic, controlled burns to reduce fuel loads in high-risk areas, thus minimizing the potential for large-scale wildfires.
- Enhanced Firefighting Capabilities: Investing in specialized equipment and training for firefighters to improve their ability to combat forest fires effectively.
- Collaboration with Weather Services: Working closely with meteorological agencies to predict high-risk fire conditions and issue timely warnings.
These measures, when implemented effectively, can significantly reduce the risk of wildfires and mitigate their impact when they do occur.
“UK wildfire risks increased significantly, with incidents reported across three regions: Northern Ireland, Scotland, and southwestern England.”
Spring Wildfire Prevention: A Community Effort
Preventing wildfires during the spring season requires a concerted effort from all members of the community. Here are some key strategies that individuals and local authorities can adopt:
- Responsible Outdoor Activities: When enjoying outdoor activities, always follow fire safety guidelines, especially in dry, rural areas.
- Proper Waste Disposal: Ensure cigarettes and other flammable materials are disposed of safely and responsibly.
- Maintaining Fire Breaks: Create and maintain fire breaks around properties in high-risk areas to slow the spread of potential fires.
- Community Watchfulness: Encourage community members to stay vigilant and report any signs of fire or suspicious activities promptly.
- Supporting Local Fire Services: Participate in and support local fire prevention initiatives and training programs.
By working together, communities can significantly reduce the risk of wildfires and protect their local environments.

The Role of Technology in Wildfire Management
Advancements in technology are playing an increasingly important role in wildfire prevention and management. Here are some key technological innovations making a difference:
- Satellite Monitoring: High-resolution satellite imagery allows for real-time monitoring of forest conditions and early detection of potential fire hotspots. Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management solutions utilize such technology to provide valuable insights for agricultural and forestry management, which can be adapted for wildfire risk assessment.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to predict fire risks and optimize resource allocation during firefighting efforts.
- Drone Technology: Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are being used for aerial surveillance, mapping fire boundaries, and even assisting in firefighting operations in hard-to-reach areas.
- IoT Sensors: Networks of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors deployed in forests can monitor environmental conditions and provide early warnings of potential fire risks.
- Mobile Apps: Smartphone applications can provide real-time updates on fire risks and evacuation orders to local communities.
These technological advancements are enhancing our ability to prevent, detect, and respond to wildfires more effectively than ever before.
Climate Change and Its Impact on UK Wildfire Risks
The increasing frequency and severity of wildfires in the UK can be linked to broader climate change trends. As global temperatures rise, we’re experiencing:
- Longer Dry Spells: Extended periods without rainfall, leading to drier vegetation and increased fire risks.
- Higher Average Temperatures: Warmer conditions that accelerate the drying of soil and plant matter.
- Changing Vegetation Patterns: Shifts in plant species and distribution, potentially introducing more fire-prone vegetation to certain areas.
- Extreme Weather Events: More frequent occurrences of heat waves and droughts, creating ideal conditions for wildfires to start and spread.
Understanding these climate-related factors is crucial for developing long-term strategies to mitigate wildfire risks. It’s important to note that while we focus on immediate fire prevention and control measures, addressing the root causes of climate change is equally vital for long-term wildfire management.
In this context, technologies that help monitor and reduce environmental impact are becoming increasingly important. For instance, Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting solutions can assist organizations in measuring and managing their carbon emissions, contributing to broader efforts to combat climate change and, by extension, reduce wildfire risks.
Rural Fire Safety: Protecting Vulnerable Communities
Rural communities often face unique challenges when it comes to fire safety and wildfire prevention. These areas are typically more vulnerable due to their proximity to forested or grassland areas and may have limited access to firefighting resources. To enhance rural fire safety, we recommend the following strategies:
- Community Fire Plans: Develop and regularly update comprehensive fire safety plans tailored to the specific needs and risks of each rural community.
- Local Training Programs: Offer fire safety and prevention training to community members, empowering them to act as first responders in emergency situations.
- Improved Infrastructure: Invest in water storage facilities, fire breaks, and access roads to facilitate firefighting efforts in remote areas.
- Regular Risk Assessments: Conduct periodic evaluations of fire risks in rural areas, taking into account changing environmental conditions and land use patterns.
- Collaboration with Farmers: Work closely with agricultural communities to promote safe farming practices that minimize fire risks, such as proper management of crop residues and controlled burning techniques.
By focusing on these areas, we can significantly enhance the resilience of rural communities in the face of increasing wildfire threats.
The Economic Impact of Wildfires
While the environmental consequences of wildfires are often at the forefront of discussions, it’s crucial to also consider their significant economic impact. Wildfires can have far-reaching financial implications for communities, businesses, and governments:
- Property Damage: Destruction of homes, businesses, and infrastructure can lead to substantial financial losses and displacement of residents.
- Agricultural Losses: Fires can devastate crops and livestock, causing significant economic harm to farming communities. Crop loan and insurance services, such as those offered by Farmonaut, can help mitigate these risks by providing financial protection for farmers.
- Tourism Impact: Areas affected by wildfires may see a decline in tourism, affecting local businesses and economies that rely on visitors.
- Firefighting Costs: The resources required to combat large-scale wildfires can put significant strain on local and national budgets.
- Health Care Expenses: Smoke-related health issues can lead to increased medical costs and lost productivity.
- Ecosystem Services Loss: Damage to forests and natural areas can disrupt valuable ecosystem services, such as water purification and carbon sequestration.
Understanding these economic implications underscores the importance of investing in robust fire prevention and management strategies. It also highlights the need for comprehensive disaster preparedness and recovery plans that address both the immediate and long-term economic impacts of wildfires.
International Cooperation in Wildfire Management
As wildfires become an increasingly global concern, international cooperation in fire management and prevention is more important than ever. The UK, along with other nations, is actively engaged in several international initiatives:
- Knowledge Sharing: Participating in global forums to exchange best practices in wildfire prevention and management techniques.
- Joint Research Programs: Collaborating on international research projects to better understand fire behavior and develop innovative prevention strategies.
- Resource Sharing: Establishing agreements for sharing firefighting resources across borders during severe wildfire events.
- Global Monitoring Systems: Contributing to and utilizing international satellite monitoring networks for early fire detection.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Engaging in global efforts to address climate change, recognizing its role in increasing wildfire risks worldwide.
These collaborative efforts not only enhance the UK’s capacity to manage wildfires but also contribute to global resilience against this growing environmental threat.
The Future of Wildfire Management in the UK
Looking ahead, the UK must continue to evolve its approach to wildfire management to address the changing landscape of fire risks. Some key areas of focus for the future include:
- Adaptive Management Strategies: Developing flexible approaches that can respond to changing environmental conditions and fire behavior patterns.
- Integration of Advanced Technologies: Further incorporating AI, machine learning, and remote sensing technologies into fire prediction and management systems. Fleet management solutions like those offered by Farmonaut could be adapted to optimize the deployment of firefighting resources.
- Ecosystem-Based Approaches: Implementing fire management strategies that consider the ecological role of fire in certain ecosystems while protecting vulnerable areas.
- Community Engagement: Enhancing programs that involve local communities in fire prevention and preparedness efforts.
- Policy Adaptation: Regularly reviewing and updating policies related to land use, forest management, and fire safety to reflect current risks and best practices.
By focusing on these areas, the UK can build a more resilient and effective wildfire management system capable of addressing the challenges posed by changing climate conditions and land use patterns.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The recent wildfires in Northern Ireland and across the United Kingdom serve as a stark reminder of the increasing environmental challenges we face. As we’ve explored throughout this article, addressing these risks requires a multifaceted approach involving technological innovation, community engagement, policy adaptation, and international cooperation.
We must recognize that wildfire prevention and management are not just tasks for firefighters and forest managers—they are responsibilities shared by all members of society. By staying informed, supporting sustainable practices, and actively participating in local fire prevention efforts, each of us can contribute to safeguarding our forests, rural areas, and communities from the threat of wildfires.
As we move forward, let us commit to working together to build a more fire-resilient UK, protecting our natural heritage and ensuring a safer, more sustainable future for generations to come.
UK Wildfire Risk Factors and Prevention Measures
| Risk Factor | Impact | Prevention Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Unseasonably warm weather | Increases vegetation dryness by up to 30%, elevating fire risk | Implement early warning systems based on weather forecasts |
| Dry conditions | Reduces soil moisture by 40-60%, creating ideal fire conditions | Promote water conservation and implement irrigation strategies in high-risk areas |
| Rural/forested areas | Accounts for 70% of UK wildfire occurrences | Create and maintain fire breaks, conduct controlled burns |
| Human activities | Responsible for approximately 85% of wildfire ignitions | Enhance public education on fire safety, enforce stricter penalties for negligence |
FAQs
- Q: What causes most wildfires in the UK?
A: The majority of wildfires in the UK are caused by human activities, including careless disposal of cigarettes, unattended campfires, and deliberate acts of arson. Natural causes like lightning strikes are less common. - Q: How does climate change affect wildfire risks in the UK?
A: Climate change leads to warmer temperatures, longer dry spells, and changes in vegetation patterns, all of which increase the risk and potential severity of wildfires. - Q: What should I do if I spot a wildfire?
A: Immediately call the emergency services (999 in the UK). Do not attempt to fight the fire yourself unless it is very small and you have the proper equipment. - Q: How can communities prepare for wildfire risks?
A: Communities can prepare by developing fire safety plans, conducting regular risk assessments, maintaining fire breaks, and participating in fire safety training programs. - Q: Are wildfires beneficial in any way?
A: While uncontrolled wildfires are destructive, controlled burns can be beneficial for certain ecosystems by clearing out dead vegetation and promoting new growth. However, this must be carefully managed by experts.
For more information on how technology can assist in monitoring and managing environmental risks, including those related to wildfires, visit Farmonaut’s web application.
For developers interested in integrating satellite and weather data into their own systems, check out Farmonaut’s API and the API Developer Docs.
Download Farmonaut’s mobile apps for on-the-go access to crucial agricultural and environmental data:
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!




















Someone essentially help to make seriously articles I would state. This is the first time I frequented your web page and thus far? I surprised with the research you made to make this particular publish amazing. Great job!