Colorado’s Agricultural Evolution: Innovative Solutions for Farm Labor and Sustainable Practices
“Colorado’s agricultural sector employs over 170,000 people, with immigrant workers making up a significant portion of the workforce.”

As we delve into the evolving landscape of Colorado’s agriculture, we find ourselves at a critical juncture where innovation meets tradition. The recent political shifts in our state’s congressional representation have brought to light the pressing challenges facing our agricultural sector, particularly in terms of farm labor shortages and the need for sustainable practices. In this comprehensive exploration, we at Farmonaut will guide you through the intricate web of agricultural policy, technological advancements, and the changing face of farming in the Centennial State.
The Changing Political Landscape and Its Impact on Agriculture
The recent congressional developments in Colorado have set the stage for significant changes in agricultural policy. U.S. Representative Greg Lopez’s brief but impactful tenure as one of the shortest-serving members of Congress from Colorado has highlighted the dynamic nature of our state’s political representation. This shift in leadership brings with it new perspectives on crucial issues such as national debt management, workers’ rights for immigrants, and public safety concerns.
While Lopez’s time in office was short, his advocacy for a “Red Card” system for immigrant workers directly addressed one of the most pressing issues in Colorado’s agricultural sector: farm labor shortages. This proposal underscores the critical role that immigrant workers play in our state’s agricultural workforce and the need for innovative solutions to address labor challenges.
Agricultural Labor Solutions: Bridging the Gap
The persistent shortage of farm labor in Colorado has pushed the agricultural industry to seek innovative solutions. We’re seeing a growing trend towards:
- Smart labor allocation systems: Utilizing data-driven approaches to optimize workforce distribution across farms.
- Mechanization and automation: Implementing advanced machinery to reduce reliance on manual labor for certain tasks.
- Seasonal worker programs: Developing more efficient and fair systems for bringing in temporary workers during peak seasons.
These solutions not only address the immediate labor needs but also pave the way for a more sustainable and efficient agricultural sector in Colorado.
The Role of Immigrant Workers in Agriculture
Immigrant workers have long been the backbone of Colorado’s agricultural workforce. Their contributions are invaluable, particularly in labor-intensive crops such as fruits and vegetables. The proposed “Red Card” system and similar initiatives aim to create a more streamlined and legal pathway for these essential workers, balancing the needs of the agricultural sector with fair labor practices.
Colorado Agricultural Policy: Adapting to New Realities
The evolution of Colorado’s agricultural policy is a reflection of both local needs and national trends. Key aspects include:
- Water conservation initiatives: Developing policies that encourage efficient water use in agriculture.
- Sustainable farming incentives: Creating programs that reward farmers for adopting environmentally friendly practices.
- Technology adoption support: Providing resources and incentives for farmers to implement precision agriculture techniques.
These policy directions are crucial in shaping a resilient and sustainable agricultural future for Colorado.
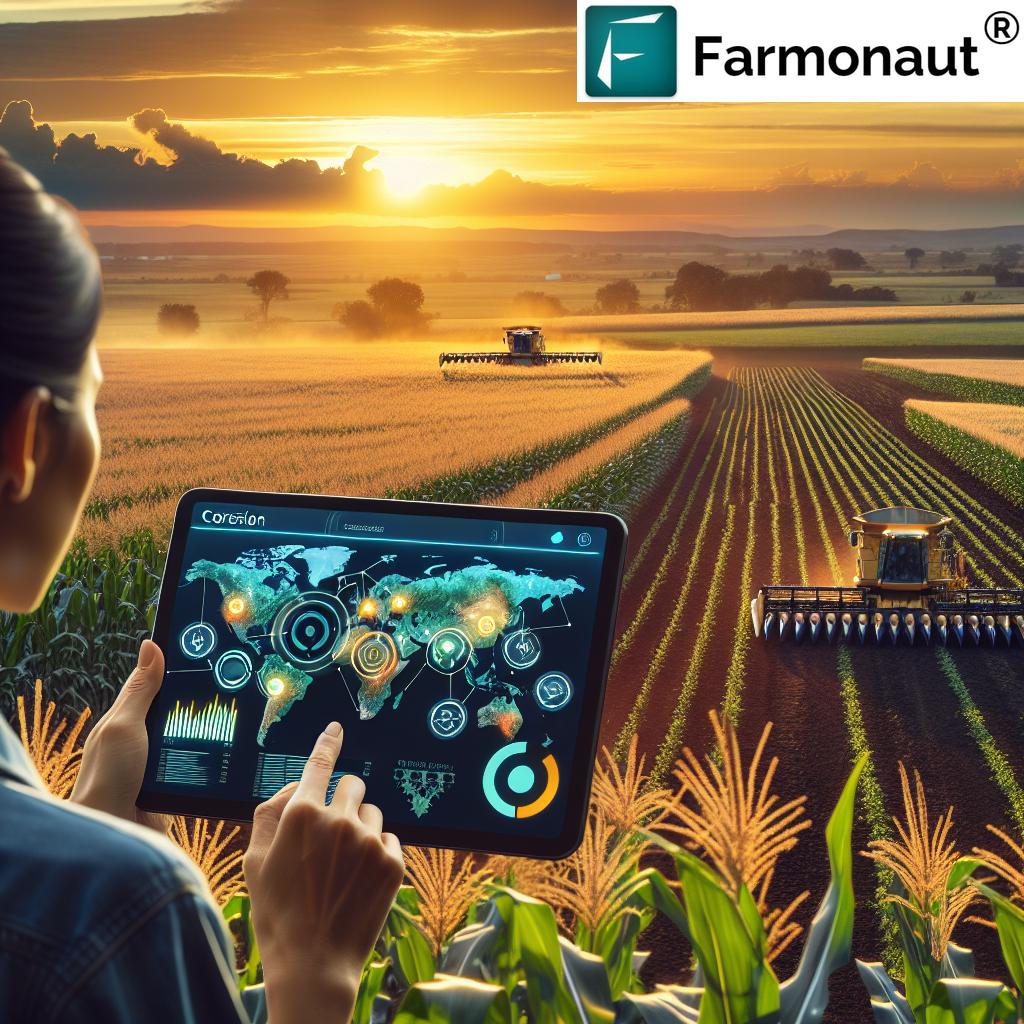
Precision Agriculture Techniques: The Future of Farming
“Precision agriculture techniques in Colorado have increased crop yields by up to 30% while reducing water usage by 20%.”
At the forefront of agricultural innovation are precision agriculture techniques. These advanced methods are transforming how we approach farming in Colorado:
- Satellite-based crop monitoring: Utilizing advanced imaging technology to assess crop health and growth patterns.
- Soil sensors and IoT devices: Deploying networks of sensors to gather real-time data on soil conditions and crop needs.
- Precision irrigation systems: Implementing water-efficient irrigation methods based on real-time data and weather forecasts.
These technologies not only boost productivity but also contribute significantly to resource conservation, aligning perfectly with Colorado’s sustainability goals.

Crop Monitoring Systems: Eyes in the Sky
One of the most revolutionary advancements in modern agriculture is the use of satellite-based crop monitoring systems. These systems provide farmers with unprecedented insights into their fields:
- Real-time vegetation health indices: Measuring crop vigor and identifying potential issues before they become visible to the naked eye.
- Yield prediction models: Using historical data and current crop conditions to forecast yields accurately.
- Pest and disease detection: Early identification of pest infestations or disease outbreaks for timely intervention.
By leveraging these technologies, Colorado farmers can make more informed decisions, optimizing their crop management strategies and resource allocation.
For those interested in exploring these cutting-edge technologies, Farmonaut’s web application offers a comprehensive suite of crop monitoring tools.
Agricultural Data Management: Empowering Informed Decision-Making
The influx of data from various sources has necessitated robust agricultural data management systems. These systems are crucial for:
- Integration of multiple data streams: Combining information from satellites, ground sensors, and weather stations.
- Historical trend analysis: Identifying patterns and long-term changes in crop performance and environmental conditions.
- Predictive analytics: Utilizing AI and machine learning to forecast future trends and potential challenges.
Effective data management is the cornerstone of modern precision agriculture, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions that optimize their operations.
Smart Farming Solutions: Integrating Technology into Traditional Practices
Smart farming solutions are bridging the gap between traditional agricultural practices and cutting-edge technology. In Colorado, we’re seeing an increasing adoption of:
- Automated farm equipment: GPS-guided tractors and drones for precise planting, spraying, and harvesting.
- Smart irrigation systems: Water management solutions that adjust based on real-time soil moisture and weather data.
- AI-powered decision support tools: Systems that provide recommendations on crop management based on vast datasets and machine learning algorithms.
These smart solutions are not just improving efficiency; they’re also making farming more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
For developers looking to integrate these advanced technologies into their own systems, Farmonaut’s API offers robust satellite and weather data capabilities.
Sustainable Farming Practices: A Greener Future for Colorado Agriculture
As we navigate the challenges of climate change and resource scarcity, sustainable farming practices are becoming increasingly crucial. Colorado farmers are adopting various strategies to ensure long-term viability:
- Cover cropping and crop rotation: Improving soil health and reducing the need for chemical inputs.
- Conservation tillage: Minimizing soil disturbance to preserve soil structure and reduce erosion.
- Integrated pest management: Using biological controls and targeted interventions to reduce reliance on pesticides.
- Renewable energy integration: Incorporating solar and wind power into farm operations to reduce carbon footprint.
These practices not only benefit the environment but also contribute to the long-term economic sustainability of farms across the state.
The Intersection of State and National Agricultural Policies
Colorado’s agricultural policies are inevitably influenced by national trends and decisions made in Washington. Key areas where state and national policies intersect include:
- Farm Bill implementation: Adapting national programs to meet the specific needs of Colorado farmers.
- Trade policies: Navigating the impact of international trade agreements on Colorado’s agricultural exports.
- Environmental regulations: Balancing federal environmental mandates with the practical realities of farming in Colorado.
Understanding this interplay is crucial for farmers and policymakers alike as we work towards a resilient and prosperous agricultural sector.
Agricultural Technology Innovations: Shaping the Future of Farming
The rapid pace of technological innovation is reshaping the agricultural landscape in Colorado and beyond. Some of the most promising advancements include:
- Blockchain for supply chain transparency: Enhancing traceability and consumer trust in agricultural products.
- Gene editing technologies: Developing crop varieties with enhanced resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses.
- Robotics and autonomous systems: Introducing robots for tasks like harvesting and weed control, reducing labor requirements.
These innovations are not just theoretical; they’re being implemented across Colorado, driving efficiency and sustainability in our agricultural sector.
For those interested in staying at the forefront of these technological advancements, Farmonaut’s Android app and iOS app offer cutting-edge tools for modern farmers.
From Denver to Washington: How Political Decisions Impact Agriculture
The decisions made in both Denver and Washington have far-reaching implications for Colorado’s farmers. We’re seeing this play out in several key areas:
- Water rights and management: Balancing urban growth with agricultural water needs.
- Labor policies: Addressing the complexities of agricultural labor, including immigration reform.
- Climate change adaptation: Developing strategies to help farmers cope with changing weather patterns and extreme events.
These political decisions shape the regulatory environment in which our farmers operate, influencing everything from crop choices to investment decisions.
Colorado’s Agricultural Innovation: A Comparative View
| Agricultural Aspect | Traditional Approach | Innovative Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Management | Manual seasonal hiring | Smart labor allocation systems |
| Crop Monitoring | Periodic visual inspections | Satellite-based crop health monitoring |
| Water Conservation | Fixed irrigation schedules | Precision irrigation based on real-time soil moisture data |
| Policy Impact | Limited engagement | Data-driven policy advocacy |
| Pest Management | Routine pesticide application | Integrated Pest Management (IPM) with AI predictions |
| Yield Forecasting | Historical averages | AI-powered predictive models |
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
As we look to the future of agriculture in Colorado, we face both challenges and opportunities:
- Climate resilience: Developing strategies to adapt to changing weather patterns and extreme events.
- Technological adoption: Ensuring that farmers of all scales can access and benefit from new technologies.
- Market diversification: Exploring new crops and value-added products to enhance farm income.
- Succession planning: Addressing the aging farmer population and attracting new generations to agriculture.
By embracing innovation and sustainable practices, Colorado’s agricultural sector is well-positioned to overcome these challenges and thrive in the years to come.
Conclusion: A New Era for Colorado Agriculture
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive overview, Colorado’s agricultural landscape is undergoing a significant transformation. From innovative labor solutions to cutting-edge precision agriculture techniques, the sector is adapting to meet the challenges of the 21st century. The interplay between state and national policies, coupled with technological advancements, is shaping a new era of farming that is more efficient, sustainable, and resilient.
We at Farmonaut are proud to be at the forefront of this agricultural revolution, providing farmers with the tools and insights they need to succeed in this dynamic environment. As we move forward, the collaboration between policymakers, technologists, and farmers will be crucial in ensuring a prosperous future for Colorado’s agricultural sector.
For those looking to be part of this exciting journey, we invite you to explore Farmonaut’s suite of agricultural technology solutions:
FAQ Section
Q: How are precision agriculture techniques benefiting Colorado farmers?
A: Precision agriculture techniques are helping Colorado farmers increase crop yields by up to 30% while reducing water usage by 20%. These techniques include satellite-based crop monitoring, soil sensors, and precision irrigation systems, which allow for more efficient resource use and better crop management.
Q: What role do immigrant workers play in Colorado’s agricultural sector?
A: Immigrant workers are a crucial part of Colorado’s agricultural workforce, particularly in labor-intensive crops. They help address farm labor shortages and contribute significantly to the state’s agricultural productivity.
Q: How is Colorado addressing the challenges of climate change in agriculture?
A: Colorado is addressing climate change challenges through various means, including the adoption of sustainable farming practices, water conservation initiatives, and the use of technology for better resource management. Additionally, there’s a focus on developing climate-resilient crop varieties and implementing adaptive farming strategies.
Q: What are some of the key agricultural technology innovations being implemented in Colorado?
A: Key agricultural technology innovations in Colorado include satellite-based crop monitoring systems, AI-powered decision support tools, smart irrigation systems, and the use of drones and robotics for various farming tasks. These technologies are helping to increase efficiency, reduce resource use, and improve overall farm management.
Q: How do state and national agricultural policies intersect in Colorado?
A: State and national agricultural policies intersect in Colorado through the implementation of federal programs like the Farm Bill, adaptation of national environmental regulations to local conditions, and the impact of federal trade policies on Colorado’s agricultural exports. This interplay shapes the regulatory environment for farmers and influences agricultural practices across the state.