Maine Drought Monitor: Spring Rainfall Forecast and Soil Moisture Outlook for New England
“Maine’s drought monitor reveals varying degrees of dryness, with some areas experiencing moderate drought across 20% of the state.”
As we delve into the complex world of Maine’s drought conditions and soil moisture levels, we find ourselves at a crucial juncture where signs of improvement are emerging, yet caution remains the watchword. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll explore the intricate factors influencing Maine’s water resources and climate resilience, with a particular focus on the spring rainfall forecast and seasonal drought outlook for New England.
Understanding Maine’s Current Drought Situation
The latest data from the U.S. Drought Monitor paints a nuanced picture of Maine’s water status. Nearly 13% of the state, primarily along the southern coast and Down East regions, is currently experiencing moderate drought conditions. Meanwhile, almost two-thirds of Maine has been classified as “abnormally dry.” This persistent dry spell has been a concern since September, affecting various aspects of the state’s ecology and agriculture.

It’s worth noting that for most of 2025, a staggering 92% of Maine had been at least “abnormally dry,” with over 38% enduring moderate drought conditions. However, recent developments have brought some relief, as these numbers have decreased to their current levels.
Spring Rainfall Forecast: A Glimmer of Hope?
The arrival of spring brings with it the potential for change in Maine’s drought narrative. A recent storm system dropped approximately an inch of rain over southern Maine, with Greater Portland recording between half an inch to an inch of rainfall. While this precipitation offers a welcome respite, it’s essential to understand that short-term relief doesn’t necessarily erase the long-term impacts of prolonged drought.
Sarah Jamison, a senior hydrologist at the National Weather Service in Gray, aptly likens the situation to personal finance: “Think of today as you received your paycheck: ‘Boy we’ve got a lot of money.’ But in the background, there’s a bunch of credit card debt.” This analogy underscores the importance of sustained precipitation to truly alleviate drought conditions.
Seasonal Drought Outlook: What Lies Ahead?
The NOAA Climate Prediction Center’s seasonal drought outlook offers a cautiously optimistic view for Maine and much of New England. The forecast suggests that drought conditions may clear from Maine’s coastal communities by the end of June. This projection is based on near-normal precipitation levels observed so far, with expectations of more rain through the end of the month.
Brad Pugh, the forecast author, notes that cooler temperatures may also play a role in helping moisture absorb into the soil more effectively. However, it’s crucial to understand that forecast confidence remains low for the Northeast region, highlighting the inherent uncertainty in long-term weather predictions.
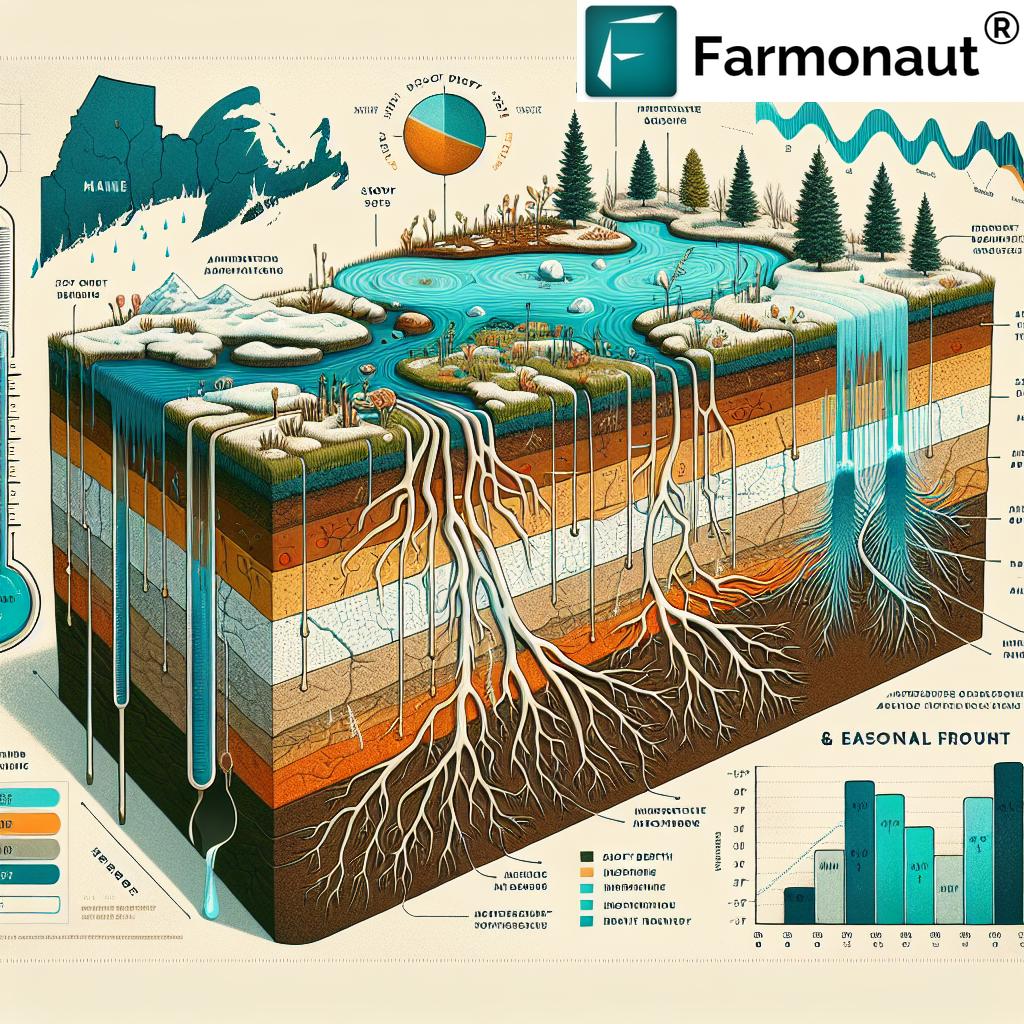
The Winter’s Impact: Frost Depth and Soil Moisture
To fully grasp Maine’s current drought situation, we must look back at the unique weather patterns experienced during the winter months. Rapid temperature fluctuations and deep frost penetration have complicated the usual moisture absorption processes in the soil.
Typically, Maine’s winters feature a thick layer of snow that acts as an insulator for the ground beneath. However, this past winter saw frequent oscillations between high and low temperatures, often leaving the ground bare. This exposure allowed frost to penetrate deep into the soil, creating what Jamison describes as “a floor of concrete” that’s thicker than it has been in about a decade.
The consequences of this deep frost are significant:
- Melting snow struggles to penetrate the frozen ground, leading to increased runoff.
- The natural process of soil moisture replenishment is disrupted.
- Early snowmelt (about two weeks earlier than usual) compounds runoff issues as the deep frost begins to soften.
These factors combine to create a challenging scenario for moisture retention and soil health as we transition into spring.
Agricultural Impacts and Runoff Concerns
The unusual winter conditions and ongoing drought have significant implications for Maine’s agricultural sector. Farmers and crop managers are particularly concerned about the following issues:
- Delayed soil moisture recovery may impact spring planting schedules.
- Increased runoff can lead to soil erosion and nutrient loss in fields.
- The potential for reduced water availability during critical growing periods.
To address these challenges, many agricultural professionals are turning to advanced technologies for monitoring and management. For instance, Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring system can provide valuable insights into vegetation health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This data-driven approach allows farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, ultimately optimizing crop yields and reducing resource wastage.
Climate Prediction Center Forecast: A Closer Look
The Climate Prediction Center’s forecast for New England offers some hope for drought relief, but it’s important to approach these projections with measured optimism. Here are the key points to consider:
- Near-normal precipitation levels are predicted for the region.
- There’s a 60% chance of near-normal precipitation for New England in the coming spring season.
- Cooler temperatures may aid in moisture retention and soil absorption.
- Forecast confidence remains low for the Northeast, indicating the need for continued monitoring and assessment.
As we navigate these uncertain weather patterns, tools like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System can prove invaluable. This AI-driven platform delivers real-time insights, weather forecasts, and expert crop management strategies, helping farmers adapt to changing conditions and optimize their operations.
Coastal Communities and Inland Areas: Varying Impacts
The drought’s effects are not uniform across Maine, with coastal communities and inland areas experiencing different challenges:
Coastal Regions
- More likely to benefit from incoming storm systems
- Potential for faster drought recovery due to proximity to moisture sources
- Concerns about saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers if drought persists
Inland Areas
- May take longer to recover from drought conditions
- Greater reliance on snowmelt and spring rains for water replenishment
- Increased risk of wildfires if dry conditions persist into summer
Understanding these regional variations is crucial for developing targeted drought mitigation strategies and resource management plans.
Monitoring Precipitation Trends: The Road Ahead
As we move further into spring, close attention to precipitation trends will be essential. Hydrologists and meteorologists will be focusing on several key factors:
- Frequency and intensity of rainfall events
- Distribution of precipitation across different regions of the state
- Soil moisture absorption rates as frost continues to thaw
- Runoff patterns and their impact on water resources
For those involved in agriculture or land management, tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system can provide valuable real-time data on these trends. By leveraging such technology, stakeholders can make more informed decisions about water usage, crop planning, and resource allocation.
Long-Term Effects on Water Resources and Climate Resilience
While immediate drought relief is a pressing concern, it’s equally important to consider the long-term implications of these weather patterns on Maine’s water resources and overall climate resilience. Some key areas of focus include:
- Groundwater recharge rates and aquifer health
- Ecosystem impacts, particularly on water-dependent flora and fauna
- Agricultural productivity and potential shifts in crop suitability
- Water conservation strategies and infrastructure improvements
Addressing these long-term concerns requires a multifaceted approach, combining traditional water management practices with innovative technologies. For instance, Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting feature can help agribusinesses monitor and reduce their environmental impact, contributing to broader sustainability goals.
Maine Drought Monitor Comparison Table
| Region | Current Drought Status | Spring Rainfall Forecast | Soil Moisture Outlook |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coastal | Moderate Drought | Near Normal | Improving |
| Southern | Abnormally Dry | Near Normal | Stable |
| Central | Abnormally Dry | Below Normal | Stable |
| Northern | None | Near Normal | Improving |
“Climate prediction center forecasts indicate a 60% chance of near-normal precipitation for New England in the coming spring season.”
The Role of Technology in Drought Monitoring and Management
As we continue to grapple with the challenges posed by drought conditions, it’s clear that technology will play an increasingly important role in monitoring, predicting, and managing water resources. Advanced tools and platforms offer several advantages:
- Real-time data collection and analysis
- Predictive modeling for more accurate forecasts
- Precision agriculture techniques for optimized water usage
- Improved decision-making support for farmers and water managers
Farmonaut’s suite of technologies exemplifies this innovative approach. From satellite-based crop health monitoring to AI-driven advisory systems, these tools provide valuable insights that can help stakeholders navigate the complexities of drought management and sustainable agriculture.
Community Engagement and Education
Addressing drought challenges effectively requires not only technological solutions but also community engagement and education. Here are some key areas where public awareness and participation can make a difference:
- Water conservation practices at home and in businesses
- Understanding the local watershed and its importance
- Supporting sustainable agricultural practices
- Participating in citizen science programs for drought monitoring
By fostering a community-wide understanding of drought issues and water resource management, we can build a more resilient and adaptive approach to these environmental challenges.
Looking Ahead: Preparing for Future Climate Variability
As we navigate the current drought situation in Maine, it’s crucial to consider how we can better prepare for future climate variability. Some key strategies include:
- Investing in water infrastructure improvements
- Developing drought-resistant crop varieties
- Implementing advanced irrigation technologies
- Creating comprehensive drought management plans at state and local levels
By taking a proactive approach to climate resilience, we can mitigate the impacts of future droughts and ensure the long-term sustainability of Maine’s water resources and agricultural sector.
Conclusion: A Call for Vigilance and Adaptation
As we conclude our in-depth exploration of Maine’s drought conditions, spring rainfall forecast, and soil moisture outlook, it’s clear that while there are signs of improvement, continued vigilance and adaptive strategies are essential. The complex interplay of winter weather patterns, soil conditions, and precipitation trends underscores the need for ongoing monitoring and data-driven decision-making.
We encourage all stakeholders – from individual farmers to policymakers – to stay informed about the evolving drought situation and to leverage available technologies and resources for effective water management. By working together and embracing innovative solutions, we can build a more resilient and sustainable future for Maine’s water resources and agricultural sector.
For those looking to enhance their agricultural practices with cutting-edge technology, consider exploring Farmonaut’s comprehensive suite of tools and services. From satellite-based crop monitoring to AI-driven advisory systems, Farmonaut offers solutions that can help you navigate the challenges of modern farming in an ever-changing climate.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced agricultural data integration
FAQ Section
- Q: How severe is the current drought situation in Maine?
A: Currently, about 13% of Maine is experiencing moderate drought conditions, primarily along the southern coast and Down East regions. Nearly two-thirds of the state is classified as “abnormally dry.” - Q: What is the spring rainfall forecast for Maine?
A: The Climate Prediction Center forecasts near-normal precipitation levels for New England, including Maine, in the coming spring season. However, forecast confidence remains low for the Northeast region. - Q: How has the winter weather affected soil moisture in Maine?
A: Unusual winter weather patterns, including rapid temperature fluctuations and deep frost penetration, have complicated soil moisture absorption. This has led to increased runoff and challenges in natural soil moisture replenishment. - Q: What are the potential impacts of the drought on agriculture in Maine?
A: The drought may lead to delayed soil moisture recovery, affecting spring planting schedules. There are also concerns about increased runoff leading to soil erosion and potential water availability issues during critical growing periods. - Q: How can farmers and land managers monitor drought conditions effectively?
A: Utilizing advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring systems can provide real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and other critical metrics. This allows for more informed decision-making in water management and crop planning.
Earn With Farmonaut: Join our Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Farmonaut Subscriptions