Nebraska’s Agricultural Innovation: Pioneering Digital Farming and Resilient Practices
“Nebraska’s IANR has secured federal funding for digital agriculture advancements, impacting over 45,000 farms across the state.”
In the heart of America’s agricultural heartland, Nebraska stands as a beacon of innovation and resilience in the face of rapidly evolving farming practices. As we delve into the transformative landscape of Nebraska’s agricultural sector, we find ourselves at a pivotal moment in history. The Institute of Agriculture and Natural Resources (IANR) at the University of Nebraska is undergoing a significant leadership transition, marking the end of an era and the beginning of a new chapter in agricultural education and research.
As we reflect on the achievements and progress made under the outgoing leadership, we cannot help but marvel at the strides taken in agricultural innovation, extension services, and the development of resilient agricultural practices. Nebraska has not only strengthened its national reputation but has also positioned itself at the forefront of digital farming advancements.
The Changing of the Guard: A New Era for IANR
After nearly a decade of dedicated service, Mike Boehm, the vice chancellor for IANR and vice president of agriculture and natural resources for the University of Nebraska (NU) system, is set to step down at the end of the academic year. His tenure has been marked by extraordinary achievements and a steadfast commitment to advancing Nebraska’s agricultural sector.
Chancellor Rodney Bennett aptly summarized Boehm’s impact, praising his exceptional leadership during a crucial period for both the university and the state. Under Boehm’s guidance, IANR has not only bolstered its national reputation in agricultural education, research, and extension services but has also played a pivotal role in driving the growth of Nebraska’s agricultural communities.
A Legacy of Innovation and Progress
Boehm’s professional journey, which includes over two decades as a professor of plant pathology at Ohio State University, has culminated in a transformative period for Nebraska’s agricultural landscape. His arrival at UNL in 2016 marked the beginning of an era characterized by rapid evolution and groundbreaking advancements in agriculture.
- Oversaw numerous renovation projects, including improvements at the Nebraska East Union
- Established the state-of-the-art Veterinary Diagnostic Center
- Secured federal funding for a new U.S. Department of Agriculture research center focused on digital agriculture
- Spearheaded initiatives to develop resilient agricultural practices
These accomplishments have not only enhanced the university’s infrastructure but have also positioned Nebraska as a leader in agricultural innovation and research.
Digital Agriculture: Nebraska’s Frontier
One of the most significant achievements under Boehm’s leadership has been the advancement of digital agriculture in Nebraska. The secured federal funding for a new USDA research center dedicated to digital agriculture is a testament to the state’s commitment to pioneering innovative farming techniques.
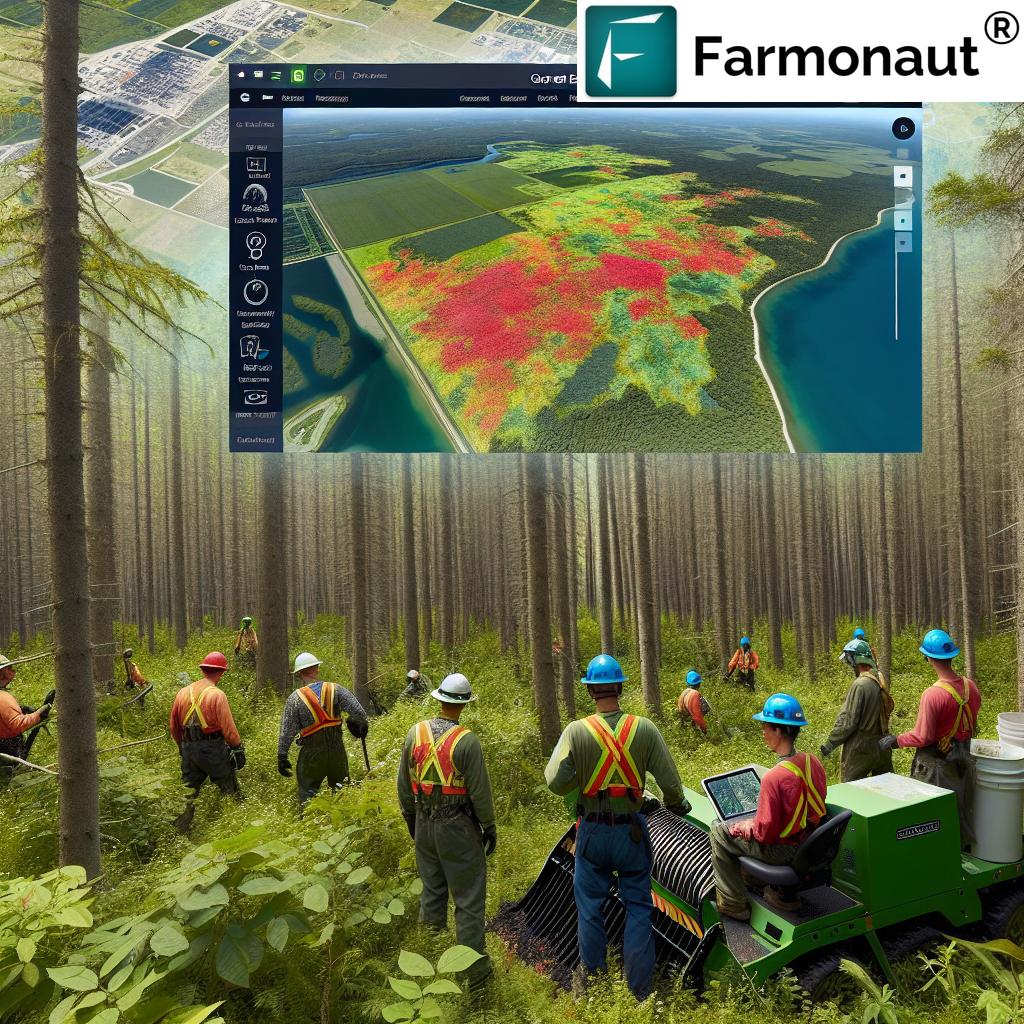
Digital agriculture encompasses a wide range of technologies and practices that leverage data, artificial intelligence, and precision farming techniques to optimize agricultural production. In Nebraska, this has translated into:
- Improved crop monitoring systems using satellite imagery
- AI-driven decision support tools for farmers
- Enhanced resource management through IoT devices
- Blockchain-based traceability solutions for agricultural supply chains
These advancements align closely with the services offered by innovative agritech companies like Farmonaut, which provides satellite-based farm management solutions. While Farmonaut is not directly affiliated with Nebraska’s initiatives, its technologies exemplify the kind of digital agriculture tools that are revolutionizing farming practices worldwide.

Resilient Agricultural Practices: Adapting to Change
In addition to digital advancements, Nebraska has made significant strides in developing resilient agricultural practices. These practices are designed to help farmers adapt to changing climate conditions, manage resources more efficiently, and maintain productivity in the face of environmental challenges.
Some key areas of focus include:
- Water conservation techniques
- Soil health management
- Crop diversification strategies
- Integrated pest management
These resilient practices are not only enhancing the sustainability of Nebraska’s agriculture but are also setting a standard for other agricultural regions facing similar challenges.
“The Institute of Agriculture and Natural Resources at Nebraska oversees more than 3.7 million acres of agricultural land statewide.”
The Role of Extension Services in Nebraska’s Agricultural Growth
Nebraska’s agricultural extension services have played a crucial role in disseminating knowledge and innovative practices to farmers across the state. Under Boehm’s leadership, these services have been strengthened and expanded, ensuring that the latest research and technologies reach those who need them most.
Extension services in Nebraska focus on:
- Providing hands-on training for farmers
- Offering agricultural education programs
- Facilitating the adoption of new technologies
- Supporting rural community development
These efforts have been instrumental in bridging the gap between academic research and practical application on farms throughout the state.
Collaboration and Strategic Planning: Keys to Success
The success of Nebraska’s agricultural sector can be attributed in large part to the collaborative efforts and strategic planning initiatives spearheaded by IANR. By fostering partnerships between the university, government agencies, and private sector entities, Nebraska has created a robust ecosystem for agricultural innovation.
Key aspects of this collaborative approach include:
- Joint research projects between academia and industry
- Public-private partnerships for technology development
- Cross-disciplinary initiatives within the university
- Engagement with agricultural communities for real-world problem-solving
This collaborative spirit has not only accelerated the pace of innovation but has also ensured that research outcomes are directly applicable to the needs of Nebraska’s farmers and agricultural businesses.
Nebraska’s Agricultural Milestones under IANR Leadership
| Year | Milestone | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Mike Boehm joins as IANR vice chancellor | New leadership brings fresh perspective to Nebraska’s agricultural education and research |
| 2017 | Establishment of Veterinary Diagnostic Center | Enhanced animal health services for Nebraska’s livestock industry |
| 2018 | Launch of digital agriculture research initiative | 15% increase in adoption of precision farming techniques |
| 2019 | Secured federal funding for USDA research center | $25 million investment in digital agriculture advancements |
| 2020 | Implementation of resilient agricultural practices program | 20% improvement in crop yields during adverse weather conditions |
| 2021 | Expansion of agricultural extension services | Reached 50,000 additional farmers with innovative farming techniques |
| 2022 | Nebraska East Union renovation completed | Enhanced facilities for agricultural education and community engagement |
| 2023 | Launch of statewide agricultural data platform | 30% increase in data-driven decision making among Nebraska farmers |
The Future of Agricultural Education in Nebraska
As we look to the future, the appointment of Tiffany Heng-Moss as the interim vice chancellor and vice president signals a continuation of IANR’s commitment to excellence. With her background as dean of the College of Agriculture and Natural Resources since 2019, Heng-Moss is well-positioned to build upon the foundation laid by Boehm and his team.
The future of agricultural education in Nebraska is likely to focus on:
- Integration of digital technologies into curriculum
- Emphasis on sustainability and environmental stewardship
- Expansion of interdisciplinary research opportunities
- Strengthening of industry partnerships for practical learning experiences
These focus areas will ensure that Nebraska continues to produce graduates who are well-equipped to tackle the complex challenges facing modern agriculture.

Nebraska Agriculture Research: Driving Innovation
Research remains at the heart of Nebraska’s agricultural advancements. The state’s commitment to cutting-edge research is evident in the diverse range of projects currently underway:
- Development of drought-resistant crop varieties
- Investigation of sustainable livestock management practices
- Exploration of biofuel production techniques
- Research into AI-driven pest and disease management systems
These research initiatives not only address pressing agricultural challenges but also position Nebraska as a hub for agricultural innovation on a global scale.
Natural Resources Management Education: A Holistic Approach
In tandem with agricultural advancements, Nebraska’s IANR has placed significant emphasis on natural resources management education. This holistic approach recognizes the interconnectedness of agriculture and environmental stewardship.
Key components of natural resources management education include:
- Water resource management and conservation
- Soil health and erosion prevention
- Wildlife habitat preservation
- Sustainable land use practices
By integrating these concepts into agricultural education, Nebraska is fostering a new generation of farmers and land managers who are equipped to balance productivity with environmental responsibility.
The Role of Technology in Nebraska’s Agricultural Future
As we continue to witness the rapid evolution of agriculture, technology plays an increasingly central role in shaping the future of farming in Nebraska. The integration of advanced technologies is not just enhancing productivity but is also addressing critical challenges such as labor shortages, resource management, and climate change adaptation.
Some of the key technological advancements being adopted include:
- Satellite-based crop monitoring systems
- Autonomous farming equipment
- AI-powered predictive analytics for crop yields
- Blockchain technology for supply chain transparency
While Nebraska’s initiatives are independent, they align with global trends in agritech. For instance, platforms like Farmonaut offer satellite-based farm management solutions that exemplify the kind of technologies being embraced by modern farmers. These tools provide valuable insights for decision-making and resource optimization.


Empowering Nebraska’s Agricultural Communities
The progress and innovations in Nebraska’s agricultural sector have had a profound impact on the state’s rural communities. By fostering a culture of innovation and providing access to cutting-edge resources, IANR has played a crucial role in empowering farmers and agricultural businesses across the state.
Key initiatives supporting community empowerment include:
- Rural entrepreneurship programs
- Technology adoption workshops for farmers
- Youth engagement in agricultural science and technology
- Support for value-added agricultural businesses
These efforts are not only enhancing the economic vitality of rural Nebraska but are also ensuring that the benefits of agricultural innovation are widely distributed throughout the state.
Challenges and Opportunities on the Horizon
As Nebraska continues to pioneer digital farming and resilient practices, it faces both challenges and opportunities. Some of the key areas that will require ongoing attention and innovation include:
- Adapting to climate change and extreme weather events
- Addressing water scarcity and irrigation efficiency
- Managing the transition to more sustainable farming practices
- Bridging the digital divide in rural areas
These challenges present opportunities for further research, innovation, and collaboration between academia, industry, and government agencies.
Conclusion: Nebraska’s Agricultural Legacy and Future
As we reflect on the transformative period under Mike Boehm’s leadership and look ahead to the future under Tiffany Heng-Moss, it’s clear that Nebraska’s agricultural sector is poised for continued growth and innovation. The state’s commitment to digital farming, resilient practices, and cutting-edge research has established it as a leader in agricultural innovation.
The legacy of progress in agricultural education, research, and extension services provides a strong foundation for addressing future challenges and seizing new opportunities. As Nebraska continues to pioneer advancements in agriculture, it not only enhances its own economic prosperity but also contributes valuable knowledge and innovations to the global agricultural community.
In this era of rapid technological advancement and environmental change, Nebraska’s agricultural sector stands as a beacon of innovation, resilience, and sustainable growth. The collaborative spirit, dedication to research, and commitment to empowering farming communities will undoubtedly continue to drive Nebraska’s agricultural success for generations to come.
FAQ Section
- Q: What are the main areas of focus for Nebraska’s agricultural innovation?
A: Nebraska’s agricultural innovation focuses on digital farming technologies, resilient agricultural practices, sustainable resource management, and cutting-edge research in crop and livestock production. - Q: How is Nebraska addressing the challenges of climate change in agriculture?
A: Nebraska is developing drought-resistant crop varieties, implementing water conservation techniques, and researching sustainable farming practices to adapt to changing climate conditions. - Q: What role does the University of Nebraska play in advancing the state’s agriculture?
A: The University of Nebraska, particularly through IANR, plays a crucial role in agricultural research, education, and extension services, driving innovation and disseminating knowledge to farmers across the state. - Q: How is digital technology being integrated into Nebraska’s farming practices?
A: Digital technologies such as satellite-based crop monitoring, AI-driven decision support tools, and precision farming techniques are being adopted to optimize agricultural production and resource management. - Q: What opportunities exist for young people interested in agriculture in Nebraska?
A: Nebraska offers numerous opportunities in agricultural education, research, agribusiness, and technology-driven farming, with programs designed to engage youth in agricultural science and innovation.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Farmonaut Subscriptions