Australian Biosecurity Alert: Protecting Tomato and Capsicum Crops from ToBRFV Spread
“ToBRFV affects 3 key crops: tomatoes, capsicums, and chillies, prompting biosecurity measures across 3 Australian states.”
In recent months, Australia’s agricultural sector has been on high alert due to the emergence of a significant threat to some of our most vital crops. The Tomato brown rugose fruit virus (ToBRFV) has sparked a nationwide response, prompting us to implement stringent biosecurity measures for agriculture across multiple states. As we navigate this critical situation, it’s essential for all stakeholders – from large-scale farmers to home gardeners – to understand the implications and contribute to the collective effort in safeguarding our produce industry.
Understanding ToBRFV: A Formidable Plant Virus
ToBRFV is a highly contagious plant virus that poses a significant threat to tomato, capsicum, and chilli crops. Its ability to spread rapidly and cause substantial damage to these economically important plants has raised concerns among agricultural experts and policymakers alike. The virus manifests through various symptoms, including:
- Browning and wrinkling of leaves
- Mosaic patterns on foliage
- Fruit discoloration and deformation
- Necrotic spots on stems and tendrils
These symptoms not only affect the aesthetic quality of the produce but also significantly impact crop yields, potentially leading to substantial economic losses for farmers and the broader agricultural industry.

The National Emergency Response
In response to the ToBRFV threat, Australia has mobilized a comprehensive national emergency response. This coordinated effort involves multiple layers of government, industry bodies, and agricultural experts working in unison to contain and manage the spread of the virus. Key components of this response include:
- Movement Restrictions: Implementation of strict controls on the movement of potentially infected plant materials across state borders, particularly in Queensland, Tasmania, and New South Wales.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Intensified surveillance and inspection protocols in greenhouses and open-field cultivation areas to detect early signs of ToBRFV infection.
- Import Suspensions: Temporary suspension of imports from countries with known ToBRFV outbreaks to prevent the introduction of new viral strains.
- Industry Collaboration: Close partnership with agricultural sectors to ensure widespread adoption of best practices in pest control and crop disease management.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating home gardeners and small-scale growers about the risks and preventive measures associated with ToBRFV.
These measures are crucial in our fight against ToBRFV, aiming to protect Australia’s agricultural health and maintain the quality and quantity of our produce.
State-Specific Measures and Their Impact
The response to ToBRFV has been tailored to meet the specific needs and conditions of different Australian states. Let’s examine the approaches taken by Queensland, Tasmania, and New South Wales:
Queensland (QLD)
As a major producer of tomatoes and capsicums, Queensland has implemented some of the most stringent measures:
- Mandatory testing of all incoming plant materials related to tomato and capsicum production
- Establishment of quarantine zones around suspected infection sites
- Increased funding for research into ToBRFV-resistant crop varieties
Tasmania
Tasmania’s island status has allowed for more stringent border controls:
- Complete suspension of tomato and capsicum imports from mainland Australia
- Enhanced screening procedures at ports and airports
- Support programs for local growers to increase self-sufficiency in tomato and capsicum production
New South Wales (NSW)
NSW has focused on a combination of preventive measures and rapid response capabilities:
- Implementation of a statewide monitoring system for early detection of ToBRFV
- Mandatory reporting requirements for suspected cases in commercial greenhouses
- Collaboration with neighboring states to create buffer zones along borders
These state-specific approaches demonstrate the adaptability and comprehensiveness of Australia’s biosecurity strategy in combating ToBRFV.
The Role of Technology in ToBRFV Detection and Management
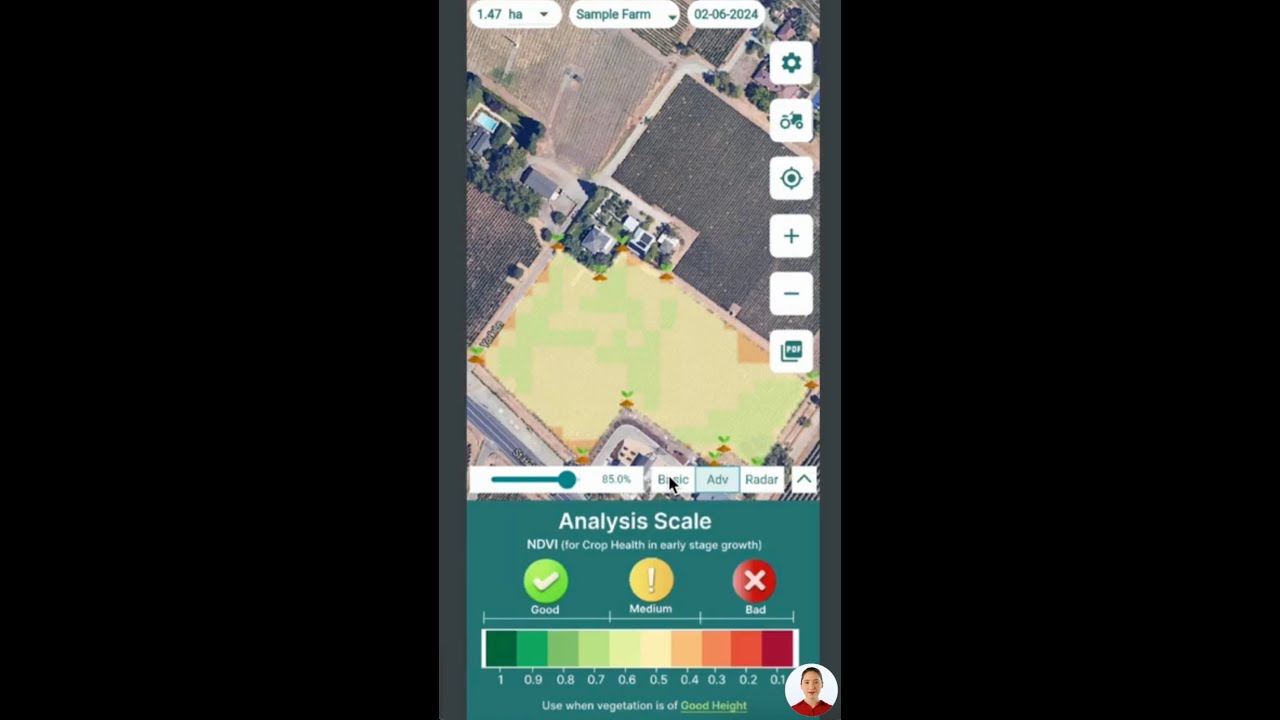
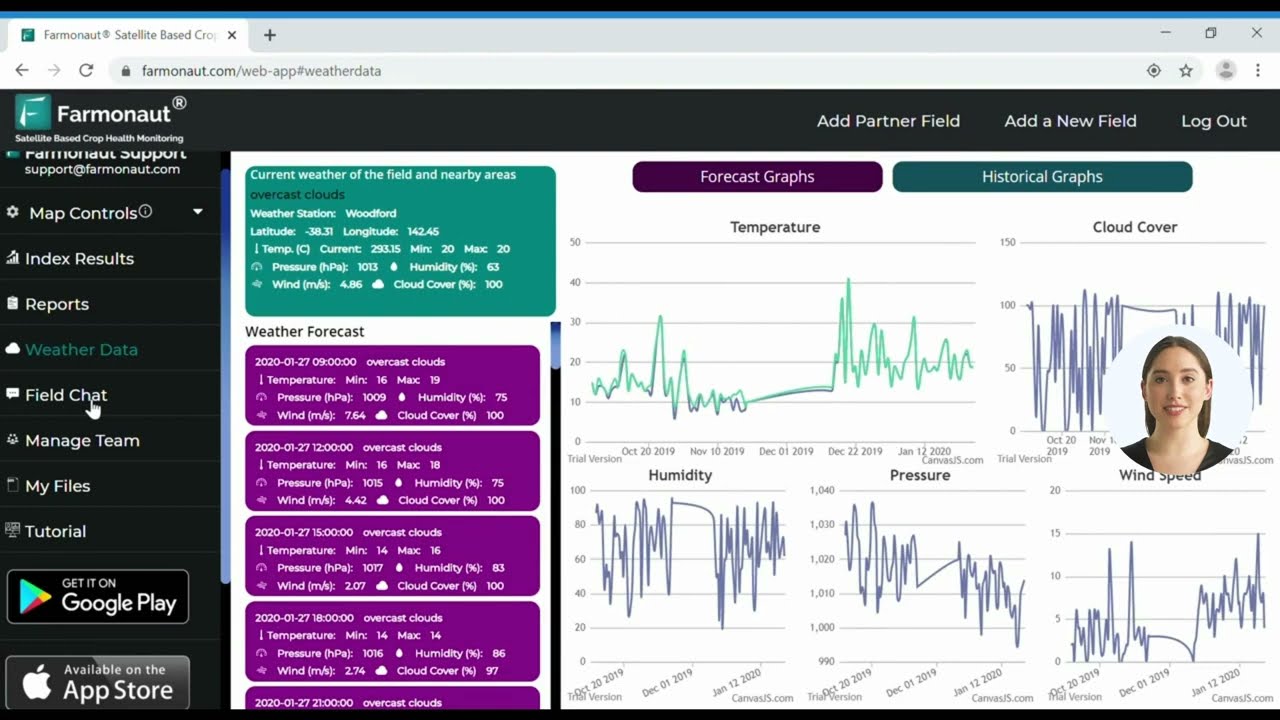
In our battle against ToBRFV, advanced technology plays a crucial role. Innovative solutions like those offered by Farmonaut can significantly enhance our ability to detect and manage the spread of this virus. Through satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-driven analysis, we can identify potential disease outbreaks earlier and more accurately than ever before.
Farmonaut’s advanced agritech solutions for virus detection offer several key benefits in the context of ToBRFV management:
- Early identification of stress patterns in crops that may indicate ToBRFV infection
- Large-scale monitoring capabilities, allowing for efficient surveillance of vast agricultural areas
- Data-driven insights to support decision-making in crop management and disease control
- Integration with existing agricultural practices to enhance overall plant health monitoring
By leveraging these technological advancements, we can create a more robust and responsive system for protecting our tomato and capsicum crops from ToBRFV and other potential threats.
Impact on Agricultural Exports and International Partnerships
The emergence of ToBRFV has not only affected domestic agricultural practices but has also had significant implications for Australia’s agricultural exports and international partnerships. As a major exporter of high-quality produce, maintaining the trust of our international partners is paramount.
Export Challenges and Opportunities
The ToBRFV outbreak has led to some immediate challenges for Australian exporters:
- Increased scrutiny and testing requirements from importing countries
- Temporary suspensions or restrictions on certain produce exports
- Higher costs associated with enhanced biosecurity measures and certifications
However, these challenges also present opportunities for Australia to strengthen its position as a leader in agricultural biosecurity:
- Development of new export protocols that set global standards for plant health
- Increased collaboration with international partners on disease prevention and management
- Opportunity to showcase Australia’s advanced agricultural technologies and practices
International Collaborations in ToBRFV Research
The global nature of the ToBRFV threat has spurred international cooperation in research and prevention strategies. Australia is actively engaging with partners worldwide to share knowledge and resources:
- Joint research initiatives with countries like New Zealand and New Caledonia on ToBRFV-resistant crop varieties
- Information exchange programs with European nations that have previously dealt with ToBRFV outbreaks
- Participation in global forums and conferences focused on plant virus control strategies
These international partnerships are crucial in developing a coordinated global response to ToBRFV and other emerging plant pathogens.
“Australia’s ToBRFV response involves multiple sectors: government, agriculture industry, and home gardeners, creating a comprehensive defense strategy.”
Greenhouse Pest Control and Crop Disease Management
Given the controlled environment they provide, greenhouses play a pivotal role in our defense against ToBRFV. However, they also present unique challenges in pest control and disease management. Here are some key strategies being implemented in Australian greenhouses:
- Enhanced Sanitation Protocols: Implementing rigorous cleaning and sanitizing procedures for all equipment, containers, and packaging materials.
- Restricted Access: Limiting entry to essential personnel only and requiring protective gear to minimize the risk of virus introduction.
- Vector Control: Implementing comprehensive pest management programs to control insects that may spread the virus.
- Environmental Optimization: Maintaining optimal temperature, humidity, and airflow conditions to reduce plant stress and enhance natural resistance.
- Regular Testing: Conducting frequent testing of plants and growing media to detect ToBRFV presence early.
These measures not only help in preventing ToBRFV but also contribute to overall improvement in greenhouse management practices, potentially leading to increased productivity and quality of produce.
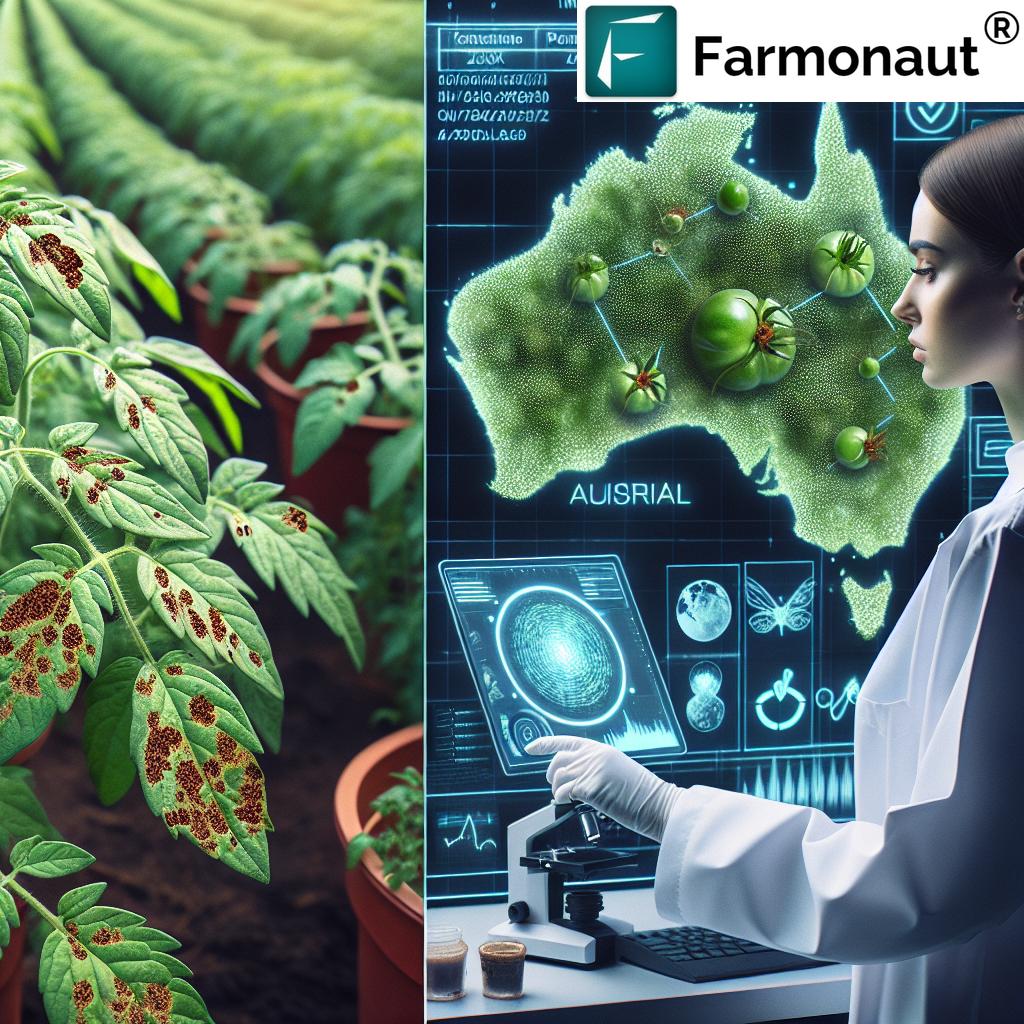
The Critical Role of Industry Professionals and Home Gardeners
The fight against ToBRFV is not limited to large-scale agricultural operations. Industry professionals and home gardeners play a crucial role in preventing the spread of this virus. Their involvement is essential for creating a comprehensive defense strategy that covers all aspects of plant cultivation in Australia.
Industry Professionals
Agricultural experts, nursery owners, and horticulturists are at the forefront of ToBRFV prevention. Their responsibilities include:
- Implementing and maintaining strict biosecurity protocols in their operations
- Educating staff and clients about ToBRFV risks and prevention measures
- Participating in early detection and reporting programs
- Collaborating with researchers to develop resistant plant varieties and effective control methods
Home Gardeners
Home gardeners, while often overlooked, can significantly impact the spread of plant diseases. Their role in ToBRFV prevention includes:
- Being vigilant for signs of ToBRFV in their gardens and reporting suspicious symptoms
- Practicing good garden hygiene, including proper tool sanitization and plant disposal
- Sourcing plants and seeds from reputable, certified disease-free suppliers
- Avoiding the movement of potentially infected plant material between different areas
By engaging both industry professionals and home gardeners in our biosecurity efforts, we create a more robust and comprehensive defense against ToBRFV.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Plant Health Monitoring
In the digital age, technology plays a crucial role in agricultural biosecurity. Advanced tools and platforms can significantly enhance our ability to monitor plant health and detect potential ToBRFV outbreaks early. Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring system is an excellent example of how technology can be leveraged in this fight.
Key benefits of using such advanced monitoring systems include:
- Real-time crop health assessment over large areas
- Early detection of stress patterns that may indicate disease presence
- Data-driven decision-making for targeted interventions
- Improved resource allocation in pest and disease management
By integrating these technological solutions into our biosecurity strategies, we can create a more responsive and efficient system for protecting our crops against ToBRFV and other threats.
Economic Impact and Support Measures
The ToBRFV outbreak has significant economic implications for Australia’s agricultural sector. To mitigate these impacts and support affected farmers, various measures have been put in place:
- Financial Assistance: Government-backed loans and grants to help farmers implement necessary biosecurity measures and recover from potential losses.
- Insurance Programs: Development of specialized crop insurance options to cover ToBRFV-related losses.
- Market Diversification Support: Assistance for farmers in exploring alternative markets or crop varieties to reduce economic vulnerability.
- Research Funding: Increased allocation of funds for ToBRFV research, including the development of resistant crop varieties.
These support measures are crucial in ensuring the long-term sustainability of Australia’s tomato and capsicum industries in the face of the ToBRFV threat.
Future Outlook and Ongoing Challenges
As we continue to grapple with the ToBRFV threat, several challenges and opportunities lie ahead:
- Evolving Virus Strains: The potential for ToBRFV to mutate, requiring ongoing research and adaptation of control strategies.
- Climate Change Impact: Changing climate patterns may affect the spread and severity of ToBRFV outbreaks, necessitating adaptive management approaches.
- International Coordination: The need for continued global collaboration in research, prevention, and control measures.
- Technological Advancements: Opportunities to develop and implement new technologies for more effective disease detection and management.
Addressing these challenges will require ongoing commitment from all stakeholders in the agricultural sector, as well as continued investment in research and technology.
Conclusion: A United Front Against ToBRFV
The Tomato brown rugose fruit virus presents a significant challenge to Australia’s agricultural sector, particularly our tomato and capsicum industries. However, through a combination of stringent biosecurity measures, advanced technology, and collaborative efforts across all levels of the industry, we are well-positioned to manage this threat effectively.
Key takeaways from our response to ToBRFV include:
- The importance of rapid, coordinated action in response to plant disease threats
- The value of integrating advanced technologies like satellite monitoring in agricultural biosecurity
- The critical role of both large-scale farmers and home gardeners in disease prevention
- The need for ongoing research and international collaboration in plant virus control
As we move forward, it’s crucial that we remain vigilant and continue to adapt our strategies to protect our vital agricultural resources. By working together and leveraging the best available technologies and practices, we can ensure the resilience and sustainability of Australia’s produce industry in the face of challenges like ToBRFV.
ToBRFV Impact and Prevention Measures
| Category | Impact | Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Crops | Tomatoes, capsicums, chillies | Crop rotation, use of resistant varieties |
| Affected States | Queensland, Tasmania, New South Wales | State-specific movement restrictions and monitoring |
| Economic Impact | Potential losses in millions of dollars | Financial assistance programs, crop insurance |
| Biosecurity Measures | Nationwide implementation | Enhanced sanitation, restricted access, vector control |
| Import Restrictions | Temporary suspensions from affected countries | Strict border controls, mandatory testing |
| Industry Role | Critical in prevention and management | Implementation of best practices, collaboration with researchers |
| Home Gardener Role | Important in preventing local spread | Vigilance, good garden hygiene, responsible sourcing |
| Detection Methods | Critical for early intervention | Satellite monitoring, regular testing, visual inspections |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is ToBRFV and how does it affect plants?
ToBRFV is a highly contagious plant virus that primarily affects tomatoes, capsicums, and chillies. It causes symptoms such as leaf discoloration, fruit deformation, and reduced yields. - How is ToBRFV spread?
The virus can spread through infected plant material, contaminated tools and equipment, and even on clothing. It can also be transmitted by certain insect vectors. - What measures are being taken to prevent ToBRFV in Australia?
Australia has implemented strict biosecurity measures including movement restrictions, enhanced monitoring, import suspensions, and collaboration with industry professionals. - Can home gardeners help prevent the spread of ToBRFV?
Yes, home gardeners play a crucial role by practicing good garden hygiene, sourcing plants from reputable suppliers, and being vigilant for signs of the virus. - How is technology being used to combat ToBRFV?
Advanced technologies like satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-driven analysis are being used for early detection and management of potential ToBRFV outbreaks. - What should I do if I suspect ToBRFV in my plants?
If you suspect ToBRFV, immediately isolate the affected plants and contact your local agricultural department or plant health authority for guidance. - Are there any ToBRFV-resistant crop varieties available?
Research is ongoing to develop resistant varieties, but currently, the focus is on prevention and management rather than resistance. - How is the ToBRFV outbreak affecting Australia’s agricultural exports?
The outbreak has led to increased scrutiny of exports and some temporary restrictions, but it has also spurred efforts to enhance Australia’s biosecurity reputation. - What support is available for farmers affected by ToBRFV?
Various support measures are in place, including financial assistance, specialized crop insurance, and market diversification support. - How long is the ToBRFV threat expected to last?
The duration of the threat is uncertain and depends on the effectiveness of control measures and ongoing research. Vigilance and adaptive management will be necessary for the foreseeable future.
For more information on how technology can assist in crop monitoring and disease detection, explore Farmonaut’s advanced agricultural solutions. Our satellite-based monitoring systems and AI-driven analytics can provide valuable insights for managing crop health and detecting potential disease outbreaks early.
For developers interested in integrating our agricultural monitoring capabilities into their own applications, check out our API and API Developer Docs.