Arizona’s Agricultural Boom: $30.9 Billion Economic Impact and Growing Trade with Mexico
“Arizona’s agriculture industry generates $30.9 billion in economic activity, significantly impacting the state’s economy.”
Welcome to our comprehensive analysis of Arizona’s thriving agricultural sector. In this blog post, we’ll explore the latest trends, challenges, and opportunities shaping the state’s farming landscape. From the booming winter vegetable production to the growing trade relationships with Mexico, we’ll delve into the factors contributing to Arizona’s impressive $30.9 billion economic impact from agriculture.
The Economic Powerhouse of Arizona Agriculture
Arizona’s agricultural industry has experienced remarkable growth in recent years, cementing its position as a vital contributor to the state’s economy. According to a recent study conducted by the University of Arizona’s Agriculture Cooperative Extension, the sector generated a staggering $30.9 billion in economic activity. This figure represents a significant 32% increase from 2017, as reported in the USDA’s agriculture census that occurs every five years.
Professor George Frisvold, a key contributor to the research, noted that while inflation has played a role in this rise, there has also been subtle industry growth across the state. This expansion is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of Arizona’s agricultural sector, which continues to thrive despite various challenges.

Breaking Down Arizona’s Agricultural Economic Impact
To better understand the composition of Arizona’s agricultural economy, let’s examine the contributions of various sectors:
| Agricultural Sector | Estimated Economic Impact (in billions) | Percentage of Total Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Wholesaling | $8.5 | 27.5% |
| Vegetable Farming | $6.2 | 20.1% |
| Agriculture Support Services | $4.3 | 13.9% |
| Bread and Bakery Manufacturing | $3.1 | 10.0% |
| Fluid Milk Production | $2.8 | 9.1% |
| Wineries | $1.5 | 4.9% |
| Tribal Agriculture | $1.2 | 3.9% |
| Other Sectors | $3.3 | 10.6% |
| Total | $30.9 | 100% |
This breakdown highlights the diversity of Arizona’s agricultural landscape, with wholesaling and vegetable farming leading the way in economic contributions. The emergence of wineries and the significant role of tribal agriculture also demonstrate the evolving nature of the state’s farming sector.
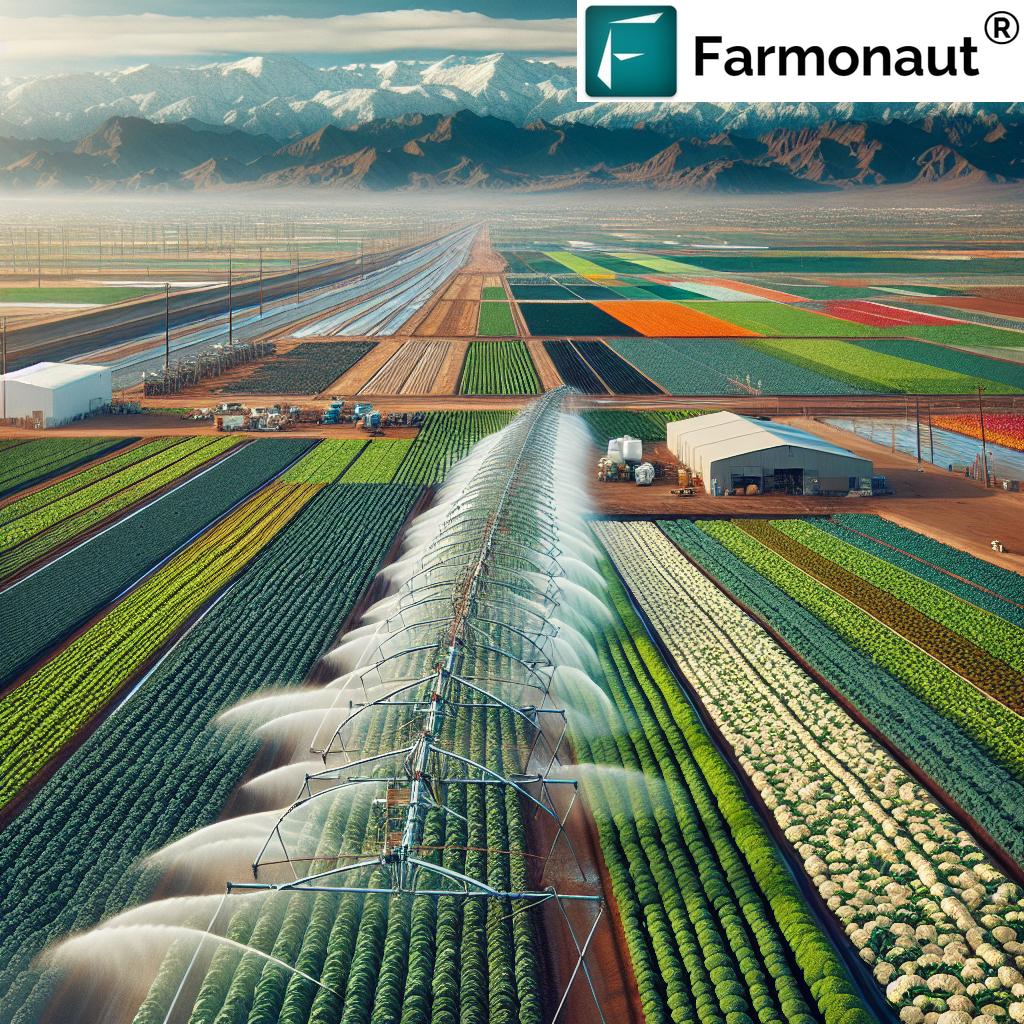
Winter Vegetable Production: Arizona’s Seasonal Advantage
One of the key drivers of Arizona’s agricultural success is its thriving winter vegetable production. The state’s unique climate allows for year-round farming, with a particular focus on supplying fresh produce during the colder months when many other regions struggle to meet demand.
Yuma, often referred to as the “Winter Lettuce Capital of the World,” plays a crucial role in this seasonal advantage. During the winter months, Yuma County produces approximately 90% of all leafy vegetables consumed in the United States and Canada. This impressive feat not only contributes significantly to the local economy but also ensures a steady supply of fresh produce to millions of consumers across North America.
The success of winter vegetable production in Arizona can be attributed to several factors:
- Optimal growing conditions with mild temperatures and abundant sunshine
- Advanced irrigation systems that maximize water efficiency
- Skilled workforce with expertise in specialized farming techniques
- Proximity to major transportation hubs for efficient distribution
As we continue to see an increasing demand for fresh, locally-sourced produce year-round, Arizona’s winter vegetable production is poised for continued growth and success.
Growing Trade Relations with Mexico
Another significant factor contributing to Arizona’s agricultural boom is the thriving trade relationship with Mexico. This cross-border commerce has become a vital source of employment in Southern Arizona, particularly in Nogales. The city has emerged as the largest private sector employer in the area, primarily fueled by the influx of produce from Mexico.
The benefits of this trade relationship are multifaceted:
- Economic Growth: The trade creates jobs in logistics, warehousing, and distribution sectors.
- Product Diversity: It enriches Arizona’s agricultural offerings, especially during winter months when demand for fresh vegetables is high.
- Market Expansion: Arizona farmers gain access to new markets in Mexico, fostering growth and innovation.
- Cultural Exchange: The trade fosters cross-cultural understanding and cooperation in the agricultural sector.
The success of this trade relationship highlights the importance of international cooperation in building a robust and resilient agricultural economy. As we look to the future, nurturing and expanding these trade ties will be crucial for sustaining Arizona’s agricultural growth.
Challenges Facing Arizona Agriculture
“Arizona’s agricultural sector faces challenges balancing economic growth with water scarcity from the Colorado River supply.”
While Arizona’s agricultural sector is thriving, it’s not without its challenges. Two primary concerns stand out: water availability and labor supply issues.
Water Availability and Sustainable Farming Practices
Water scarcity remains a critical issue for Arizona farmers, especially as the state grapples with potential cuts to its Colorado River water supply. This challenge has led to increased focus on sustainable farming practices and water conservation techniques. Some strategies being implemented include:
- Drip irrigation systems for more efficient water use
- Crop selection based on water requirements
- Soil moisture monitoring to optimize irrigation schedules
- Wastewater recycling for agricultural use
Innovative companies like Farmonaut are playing a crucial role in addressing these challenges. Through their satellite-based farm management solutions, farmers can access real-time data on soil moisture levels and crop health, enabling them to make informed decisions about irrigation and resource management.

Labor Supply Challenges in Agriculture
The agricultural labor market in Arizona presents a complex issue. While the influx of workers crossing the border is often viewed negatively in political discourse, Professor Frisvold argues that this labor supply is crucial for Arizona’s agricultural productivity. The sector directly employs around 160,000 individuals, with major contributors including:
- Wholesaling
- Vegetable and melon farming
- Agriculture support services
- Bread and bakery manufacturing
- Fluid milk production
There are concerns about potential disruptions to this labor source, highlighting the vulnerable balance the sector maintains between economic benefit and policy challenges. To address these issues, some agribusinesses are exploring solutions such as:
- Implementing precision agriculture technology to reduce labor requirements
- Offering competitive wages and benefits to attract and retain workers
- Investing in training programs to develop a skilled local workforce
- Advocating for comprehensive immigration reform to ensure a stable labor supply
Emerging Trends in Arizona Agriculture
Despite the challenges, Arizona’s agricultural landscape continues to evolve and adapt. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of farming in the state:
Precision Agriculture and Technology Adoption
Arizona farmers are increasingly turning to precision agriculture techniques to optimize crop yields and resource use. Technologies such as GPS-guided tractors, drone mapping, and IoT sensors are becoming more common on farms across the state. Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-powered advisory system are prime examples of how technology is revolutionizing farm management.

Diversification of Crops and Products
Arizona farmers are exploring new crop varieties and value-added products to increase profitability and resilience. The growing winery sector is a testament to this trend, with vineyards popping up in unexpected areas of the state.
Focus on Sustainability and Conservation
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, many Arizona farms are adopting sustainable practices. This includes implementing water-saving technologies, reducing chemical inputs, and exploring renewable energy options like solar power for farm operations.
The Role of Tribal Agriculture in Arizona’s Economy
An often overlooked but increasingly important aspect of Arizona’s agricultural landscape is tribal vegetable production. Native American communities across the state are revitalizing traditional farming practices while incorporating modern techniques to contribute significantly to the agricultural economy.
Key aspects of tribal agriculture in Arizona include:
- Preservation of heritage crop varieties
- Sustainable water management practices
- Integration of cultural traditions with modern farming methods
- Development of niche markets for unique, locally-grown products
The growth of tribal agriculture not only contributes to the state’s economic diversity but also plays a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage and promoting food sovereignty within Native American communities.
The Future of Arizona Agriculture: Balancing Growth and Sustainability
As we look to the future, the Arizona agricultural sector faces both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. The key to continued success lies in striking a balance between economic growth and sustainable practices. Here are some strategies that will be crucial in shaping the future of Arizona agriculture:
- Investing in Research and Development: Continued innovation in drought-resistant crops, water-saving technologies, and sustainable farming practices will be essential.
- Strengthening Trade Relations: Building on the successful trade partnership with Mexico while exploring new international markets can help diversify and strengthen the agricultural economy.
- Addressing Labor Challenges: Developing comprehensive policies that ensure a stable and skilled agricultural workforce will be critical for long-term growth.
- Embracing Technology: Wider adoption of precision agriculture tools, like those offered by Farmonaut, can help optimize resource use and increase productivity.
- Promoting Sustainable Water Use: Implementing innovative water conservation techniques and exploring alternative water sources will be crucial for long-term sustainability.

By focusing on these areas, Arizona’s agricultural sector can continue to thrive, contributing to the state’s economy while ensuring long-term sustainability and food security.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Arizona Agriculture
Arizona’s agricultural sector stands as a testament to the power of innovation, resilience, and adaptability. With its $30.9 billion economic impact and growing trade relations with Mexico, the industry continues to be a cornerstone of the state’s economy. While challenges such as water scarcity and labor issues persist, the sector’s ability to embrace new technologies, sustainable practices, and diverse crop production bodes well for its future.
As we move forward, the collaboration between farmers, policymakers, and technology providers like Farmonaut will be crucial in navigating the complex landscape of modern agriculture. By leveraging advanced tools for crop monitoring, resource management, and data-driven decision-making, Arizona’s farmers can continue to lead the way in sustainable and productive agriculture.
The story of Arizona’s agricultural boom is far from over. With continued innovation, strategic planning, and a commitment to sustainability, the sector is well-positioned to meet the challenges of the future while continuing to feed millions and drive economic growth in the Southwest and beyond.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the current economic impact of Arizona’s agricultural industry?
A: According to recent studies, Arizona’s agricultural industry generates $30.9 billion in economic activity, marking a 32% increase from 2017.
Q: How does winter vegetable production contribute to Arizona’s agriculture?
A: Winter vegetable production, particularly in regions like Yuma, is a significant contributor to Arizona’s agricultural success. During winter months, Yuma County produces about 90% of all leafy vegetables consumed in the US and Canada.
Q: What role does trade with Mexico play in Arizona’s agricultural economy?
A: Trade with Mexico is crucial for Arizona’s agricultural sector, providing a vital source of employment in Southern Arizona, especially in Nogales. It also enhances product diversity and expands market opportunities for Arizona farmers.
Q: What are the main challenges facing Arizona’s agricultural sector?
A: The two primary challenges are water availability, especially with potential cuts to Colorado River water supply, and labor supply issues, including the complexities surrounding cross-border workers.
Q: How is technology being used to address agricultural challenges in Arizona?
A: Arizona farmers are increasingly adopting precision agriculture techniques, including GPS-guided tractors, drone mapping, and satellite-based crop monitoring systems like those offered by Farmonaut, to optimize resource use and increase productivity.
Q: What is the significance of tribal agriculture in Arizona?
A: Tribal agriculture is an increasingly important aspect of Arizona’s agricultural landscape, contributing to economic diversity, preserving cultural heritage, and promoting food sovereignty within Native American communities.
Q: How is Arizona’s agricultural sector addressing sustainability concerns?
A: The sector is focusing on sustainable farming practices, including implementing water-saving technologies, reducing chemical inputs, exploring renewable energy options, and adopting precision agriculture techniques to optimize resource use.
For more information on how satellite-based farm management solutions can benefit your agricultural operations, visit Farmonaut’s web application or explore our API services. Stay updated with the latest in agricultural technology by checking out our API Developer Docs.