California’s Regenerative Agriculture Revolution: Balancing Sustainability, Soil Health, and Carbon Sequestration
“California’s regenerative agriculture practices aim to sequester up to 20% more carbon in soil compared to conventional farming methods.”
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of California’s evolving agricultural landscape, where regenerative farming practices are taking center stage in the quest for sustainability, improved soil health, and effective carbon sequestration. As we delve into this topic, we’ll examine the challenges and opportunities that arise when implementing climate-smart agriculture techniques across the Golden State.
In recent years, California has emerged as a pioneer in sustainable farming practices, with regenerative agriculture gaining significant momentum across various counties and regions. From the fertile Central Valley to the coastal areas and even in urban farming initiatives, we’re witnessing a shift towards methods that prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration. This movement is not just a trend but a necessary evolution in our approach to food production and environmental stewardship.
The Rise of Regenerative Agriculture in California
Regenerative agriculture is rooted in indigenous farming practices and focuses on enhancing soil health rather than solely maximizing crop yields. This approach aligns perfectly with California’s ambitious environmental goals, including the shift of millions of acres to healthier soil practices by 2045, as reinforced by Governor Gavin Newsom’s executive orders aimed at promoting biodiversity and carbon neutrality.
However, the journey towards widespread adoption of regenerative practices is not without its challenges. One of the most significant hurdles is the lack of a universally accepted definition for regenerative agriculture. This ambiguity has led to ongoing debates and discussions among farmers, policymakers, and environmental advocates across the state.
Defining Regenerative Agriculture: A Complex Task
- The California Board of Food and Agriculture has deferred its decision on a draft definition until January 7, 2024
- Stakeholders are prioritizing a thoughtful and inclusive approach to ensure all voices are heard
- The debate centers around whether organic certification should be mandatory for regenerative practices
The complexity of defining regenerative agriculture stems from the diverse perspectives of various stakeholders. On one side, we have advocates pushing for stringent standards that include organic certification. They argue that this level of rigor is necessary to maintain the integrity of the term “regenerative” and ensure its effectiveness in the marketplace. On the other hand, critics warn that such strict requirements could create barriers for small and tribal farmers who may lack the resources for organic certification but still employ sustainable practices.
As we navigate these discussions, it’s crucial to recognize the potential of regenerative agriculture in addressing climate change and enhancing food security. Here at Farmonaut, we understand the importance of supporting farmers in their transition to more sustainable practices. Our satellite-based farm management solutions provide valuable insights that can help farmers make informed decisions about soil health, crop management, and resource allocation.
Soil Health: The Foundation of Regenerative Agriculture
At the heart of regenerative agriculture lies the concept of soil health improvement. Healthy soils are not only more productive but also serve as a crucial carbon sink, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. Let’s explore some of the key soil health improvement techniques that are gaining traction in California:
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops between growing seasons to protect and enrich the soil
- No-Till Farming: Minimizing soil disturbance to preserve soil structure and organic matter
- Crop Rotation: Diversifying crops to improve soil fertility and break pest cycles
- Composting: Adding organic matter to the soil to enhance its structure and nutrient content
- Reduced Chemical Inputs: Decreasing reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides
These practices not only improve soil health but also contribute significantly to carbon sequestration in agriculture. By implementing these techniques, California farmers are playing a crucial role in the state’s efforts to achieve agricultural carbon neutrality.
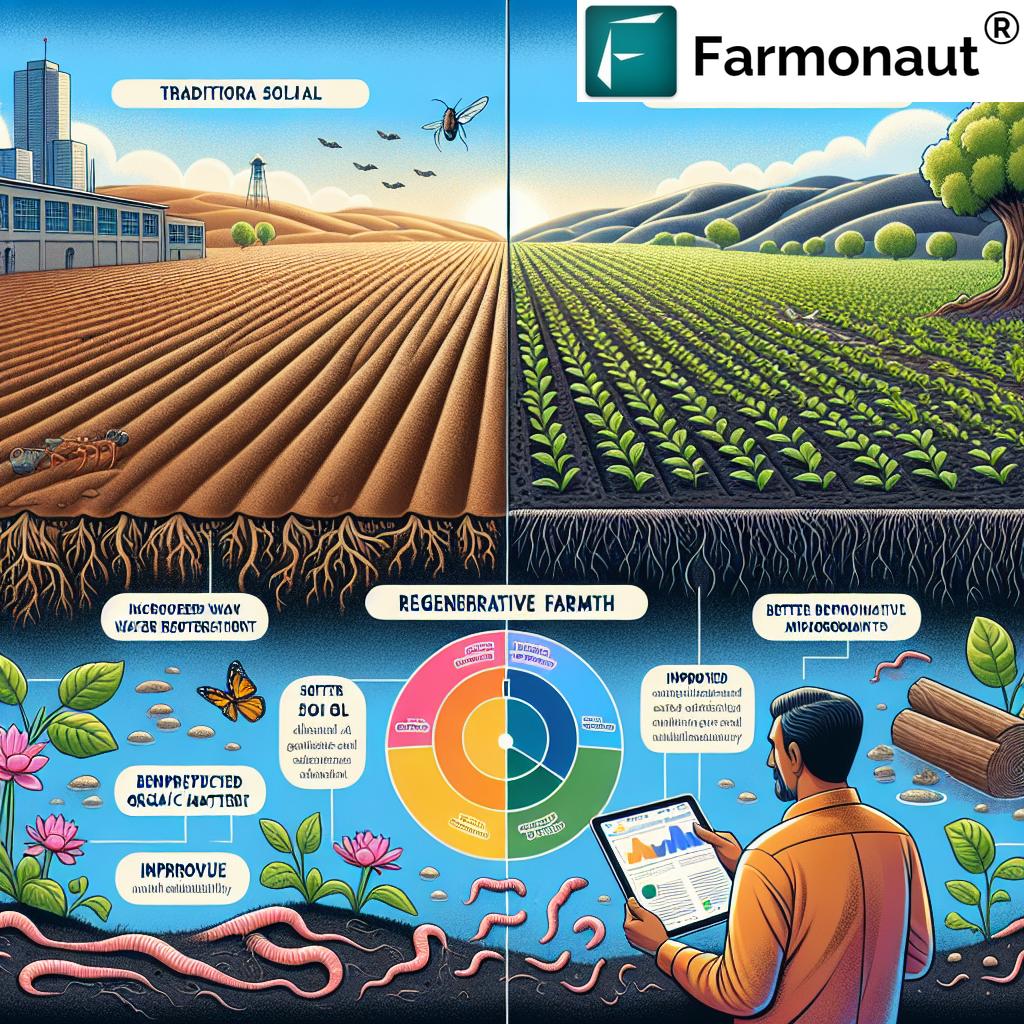
“Over 60% of California farmers are exploring at least one regenerative agriculture technique to improve soil health and sustainability.”
To support farmers in their transition to regenerative practices, technology plays a crucial role. Farmonaut’s API and API Developer Docs provide access to satellite imagery and AI-driven insights that can help farmers monitor soil health, track vegetation indices, and make data-driven decisions about their farming practices.
Carbon Sequestration: Agriculture’s Role in Climate Mitigation
Carbon sequestration in agriculture has become a focal point in California’s battle against climate change. By adopting regenerative practices, farmers can transform their fields into effective carbon sinks, pulling CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it in the soil. This not only helps mitigate climate change but also improves soil fertility and water retention capacity.
Let’s take a closer look at how different regenerative practices contribute to carbon sequestration:
| Regenerative Practice | Soil Health Impact | Carbon Sequestration Potential | Crop Yield Effect | Implementation Challenges | Adoption Rate in California |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cover Cropping | 30% improvement | 0.5-1.0 tons CO2/acre/year | 5-10% increase | Seed costs, timing of planting | 25% |
| No-Till Farming | 20% improvement | 0.3-0.5 tons CO2/acre/year | 0-5% increase | Initial yield dip, weed management | 15% |
| Crop Rotation | 15% improvement | 0.2-0.4 tons CO2/acre/year | 10-15% increase | Market demand for diverse crops | 40% |
| Composting | 25% improvement | 0.4-0.8 tons CO2/acre/year | 15-20% increase | Labor intensive, sourcing materials | 30% |
| Agroforestry | 35% improvement | 2.0-5.0 tons CO2/acre/year | Varied (depends on system) | Long-term investment, complex management | 5% |
As we can see from this comparative analysis, each practice offers unique benefits and challenges. The key to successful implementation lies in understanding the specific needs of each farm and tailoring the approach accordingly. This is where technologies like Farmonaut can make a significant difference, providing farmers with real-time data and insights to optimize their regenerative practices.
Balancing Environmental Regulations with Farmers’ Needs
One of the most significant challenges in implementing regenerative agriculture practices in California is striking the right balance between environmental regulations and the practical needs of farmers. The state’s ambitious climate goals, while necessary, can sometimes create tension with the realities of agricultural production.
Key considerations in this balancing act include:
- Ensuring that regulations are science-based and achievable for farmers of all scales
- Providing financial incentives and support for farmers transitioning to regenerative practices
- Recognizing and rewarding farmers for ecosystem services provided through regenerative agriculture
- Developing flexible frameworks that allow for regional and crop-specific variations in implementation
To address these challenges, California has been exploring various policy instruments and support mechanisms. For instance, the Healthy Soils Program, administered by the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA), provides financial assistance to implement conservation management practices that improve soil health, sequester carbon, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Organic Certification Debate
A central point of contention in the regenerative agriculture discussion is whether organic certification should be a mandatory component. This debate highlights the complex interplay between environmental ideals and practical realities:
- Pro-Organic Certification: Advocates argue that organic practices are fundamental to truly regenerative agriculture, ensuring the elimination of synthetic inputs that can harm soil health and biodiversity.
- Against Mandatory Certification: Critics point out that the cost and complexity of organic certification can be prohibitive for small farmers, potentially excluding them from the regenerative movement.
Finding a middle ground that promotes organic practices while remaining inclusive of diverse farming operations is crucial for the widespread adoption of regenerative agriculture in California.
Biodiversity in Farming: A Key Component of Regenerative Agriculture
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in regenerative agriculture, contributing to ecosystem resilience, pest management, and overall farm health. In California, farmers are increasingly recognizing the value of biodiversity in their operations. Some key strategies for enhancing biodiversity include:
- Planting diverse crop varieties and cultivars
- Maintaining hedgerows and buffer strips to provide habitat for beneficial insects and wildlife
- Integrating livestock into cropping systems
- Preserving and restoring native plant communities on and around farms
By promoting biodiversity, farmers can reduce their reliance on external inputs, improve natural pest control, and enhance pollination services. This not only benefits the environment but can also lead to more stable and resilient farming systems.
Sustainable Crop Yield Methods: Balancing Productivity and Sustainability
One of the primary concerns for farmers considering the transition to regenerative agriculture is the potential impact on crop yields. However, research and practical experience are showing that sustainable crop yield methods can maintain or even improve productivity while enhancing environmental outcomes. Some key approaches include:
- Precision Agriculture: Using technology to optimize resource use and target interventions
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Combining biological, cultural, and chemical methods to manage pests effectively
- Nutrient Management: Tailoring fertilizer applications to crop needs and soil conditions
- Water Conservation: Implementing efficient irrigation systems and improving soil water retention
These methods not only support sustainable yields but also contribute to the overall goals of regenerative agriculture by improving soil health and reducing environmental impacts.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in their journey towards more sustainable and productive farming practices. Our Android App and iOS App provide easy access to critical farm data, helping farmers make informed decisions about their regenerative practices.
California’s Path to Agricultural Carbon Neutrality
As California strives to achieve agricultural carbon neutrality, regenerative farming practices are playing an increasingly important role. The state’s ambitious climate goals include:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture
- Increasing carbon sequestration on agricultural lands
- Promoting climate-smart agriculture practices across the state
To support these goals, California has implemented various initiatives and programs, such as the Healthy Soils Program and the Alternative Manure Management Program. These efforts are complemented by research and extension services provided by institutions like the University of California Cooperative Extension, which help farmers implement and optimize regenerative practices.
The Role of Technology in Regenerative Agriculture
As we navigate the complexities of regenerative agriculture, technology plays a crucial role in supporting farmers and policymakers. Advanced tools and platforms, like those offered by Farmonaut, provide valuable insights that can help optimize regenerative practices and measure their impact.
Key technological advancements supporting regenerative agriculture include:
- Satellite-based crop monitoring for real-time assessment of vegetation health
- AI-driven advisory systems that provide personalized recommendations for soil management
- Precision agriculture tools for targeted resource application
- Blockchain-based traceability solutions for supply chain transparency
These technologies not only help farmers implement regenerative practices more effectively but also provide the data needed to measure and verify the environmental benefits of these approaches.
Looking to the Future: California’s Regenerative Agriculture Revolution
As we look to the future, California’s regenerative agriculture revolution holds immense promise for creating a more sustainable and resilient food system. By balancing the needs of farmers with environmental imperatives, the state is paving the way for a new era of agriculture that not only feeds the population but also nurtures the planet.
Key areas to watch in the coming years include:
- The evolution of regenerative agriculture definitions and standards
- Expansion of financial incentives and support programs for farmers adopting regenerative practices
- Advancements in technology and data analytics to support precision regenerative agriculture
- Integration of regenerative practices into broader climate change mitigation strategies
As these developments unfold, Farmonaut remains committed to supporting farmers and stakeholders in their journey towards more sustainable and regenerative agricultural practices. Our cutting-edge technology and data-driven insights will continue to play a crucial role in this transformative process.
Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Agricultural Future
California’s regenerative agriculture revolution represents a critical step towards a more sustainable and resilient food system. By balancing the needs of farmers with environmental imperatives, the state is setting a precedent that could influence agricultural practices nationwide and even globally.
As we continue to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by regenerative agriculture, collaboration between farmers, policymakers, researchers, and technology providers will be crucial. Together, we can create a future where agriculture not only feeds the world but also plays a pivotal role in mitigating climate change and preserving our planet’s resources for generations to come.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can support your journey towards regenerative agriculture, explore our comprehensive suite of tools and services:
Farmonaut Subscriptions
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is regenerative agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture is a farming approach that focuses on improving soil health, enhancing biodiversity, and sequestering carbon. It aims to restore and improve ecosystem functions while producing food sustainably. - How does regenerative agriculture differ from organic farming?
While organic farming focuses on avoiding synthetic inputs, regenerative agriculture goes further by actively working to improve soil health and ecosystem functions. However, many regenerative practices align with organic principles. - What are some key regenerative agriculture practices?
Key practices include cover cropping, no-till farming, crop rotation, composting, and integrating livestock into cropping systems. - How does regenerative agriculture contribute to carbon sequestration?
Regenerative practices enhance soil organic matter, which helps capture and store carbon from the atmosphere in the soil, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. - What challenges do farmers face when transitioning to regenerative agriculture?
Challenges include initial costs, potential yield fluctuations during transition, knowledge gaps, and market uncertainties for new crop rotations. - How can technology support regenerative agriculture?
Technology like satellite imaging, AI-driven advisory systems, and precision agriculture tools can help farmers implement and optimize regenerative practices more effectively. - What policies support regenerative agriculture in California?
California has programs like the Healthy Soils Program and Alternative Manure Management Program that provide financial and technical support for regenerative practices. - How does biodiversity contribute to regenerative agriculture?
Increased biodiversity improves ecosystem resilience, natural pest control, and pollination services, reducing the need for external inputs and enhancing overall farm health. - Can regenerative agriculture maintain crop yields?
While there may be short-term yield fluctuations during transition, many farmers report maintained or improved yields over time with regenerative practices. - How does Farmonaut support regenerative agriculture efforts?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based farm management solutions, AI-driven insights, and data analytics tools that help farmers implement and optimize regenerative practices effectively.