Texas Citrus Industry Faces Water Crisis: Innovative Solutions for Sustainable Farming in the Rio Grande Valley
“The Texas citrus industry in the Rio Grande Valley relies on irrigation from a single source: the Rio Grande river.”
As we delve into the heart of the Texas citrus industry, we find ourselves facing an unprecedented water crisis that threatens the very foundation of agriculture in the Rio Grande Valley. The lush orchards that have long been the pride of Texas are now grappling with the harsh realities of climate change, water scarcity, and the complex web of international water treaties. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll uncover the challenges, innovations, and resilience that define the future of sustainable farming in this vital agricultural region.

The Lifeblood of the Valley: Understanding the Rio Grande’s Role
The Rio Grande is more than just a river; it’s the lifeblood of the Texas citrus industry. Snaking its way through the heart of the Rio Grande Valley, this mighty waterway has historically provided the irrigation necessary for the region’s bountiful citrus harvests. However, recent years have seen a dramatic shift in this delicate balance between nature and agriculture.
- Drought conditions have severely impacted water levels in the Rio Grande
- Citrus trees require 40-50 inches of water annually, far exceeding natural rainfall
- The 1944 water treaty with Mexico complicates water allocation
As we face these challenges, it’s crucial to understand that the water crisis extends beyond just the citrus groves. It affects the entire agricultural landscape of the region, threatening food security and economic stability.
Climate Change: A Perfect Storm for Citrus Farmers
“Recent climate-related disasters have caused significant economic losses, with some citrus harvests experiencing up to 100% crop failure.”
The Texas citrus industry has been hit by a series of climate-related disasters that have left growers reeling. From devastating winter storms to hurricanes, these events have created a perfect storm of challenges for farmers in the Rio Grande Valley.
- Winter Storm Uri in 2021 caused widespread damage to citrus crops
- A 2020 hurricane further compounded the industry’s struggles
- Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent and severe
These climate-induced calamities have not only resulted in immediate crop losses but have also had long-term implications for the industry’s sustainability. As we navigate these turbulent times, it’s clear that adapting to climate change is no longer optional—it’s a necessity for survival.
Water Conservation: A Lifeline for Citrus Growers
In the face of dwindling water resources, Texas citrus growers are turning to innovative water conservation techniques to sustain their orchards. These methods not only help preserve precious water but also contribute to more sustainable farming practices.
| Water Conservation Technique | Water Savings | Implementation Cost | Adoption Rate in Rio Grande Valley | Impact on Crop Yield | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | 30-50% | High | 40% | Positive | Reduces water runoff and soil erosion |
| Mulching | 15-25% | Low | 60% | Neutral | Improves soil health and biodiversity |
| Drought-Resistant Varieties | 20-30% | Medium | 25% | Neutral | Reduces overall water demand |
| Precision Irrigation | 25-40% | High | 15% | Positive | Minimizes water waste and nutrient leaching |
| Soil Moisture Sensors | 10-20% | Medium | 30% | Positive | Optimizes water use based on plant needs |
As we can see from the table above, drip irrigation stands out as a highly effective water conservation technique. While the implementation cost is high, the potential water savings of 30-50% make it an attractive option for many growers. The positive impact on crop yield further justifies the investment.
However, it’s important to note that no single solution fits all farms. The adoption of these techniques often depends on factors such as farm size, financial resources, and the specific microclimate of each orchard.
The International Water Dilemma: Navigating Complex Treaties
The water crisis in the Rio Grande Valley is further complicated by international agreements that govern water allocation between the United States and Mexico. The 1944 water treaty, which stipulates water sharing from the Rio Grande and its tributaries, has come under strain due to prolonged drought conditions.
- Mexico has fallen behind on water deliveries mandated by the treaty
- Reservoirs on both sides of the border are at critically low levels
- Diplomatic tensions have risen over water allocation issues
These international complexities add another layer of uncertainty for citrus growers who depend on a reliable water supply. As we work towards solutions, it’s clear that international cooperation and flexible agreements will be crucial in addressing the water needs of the region.
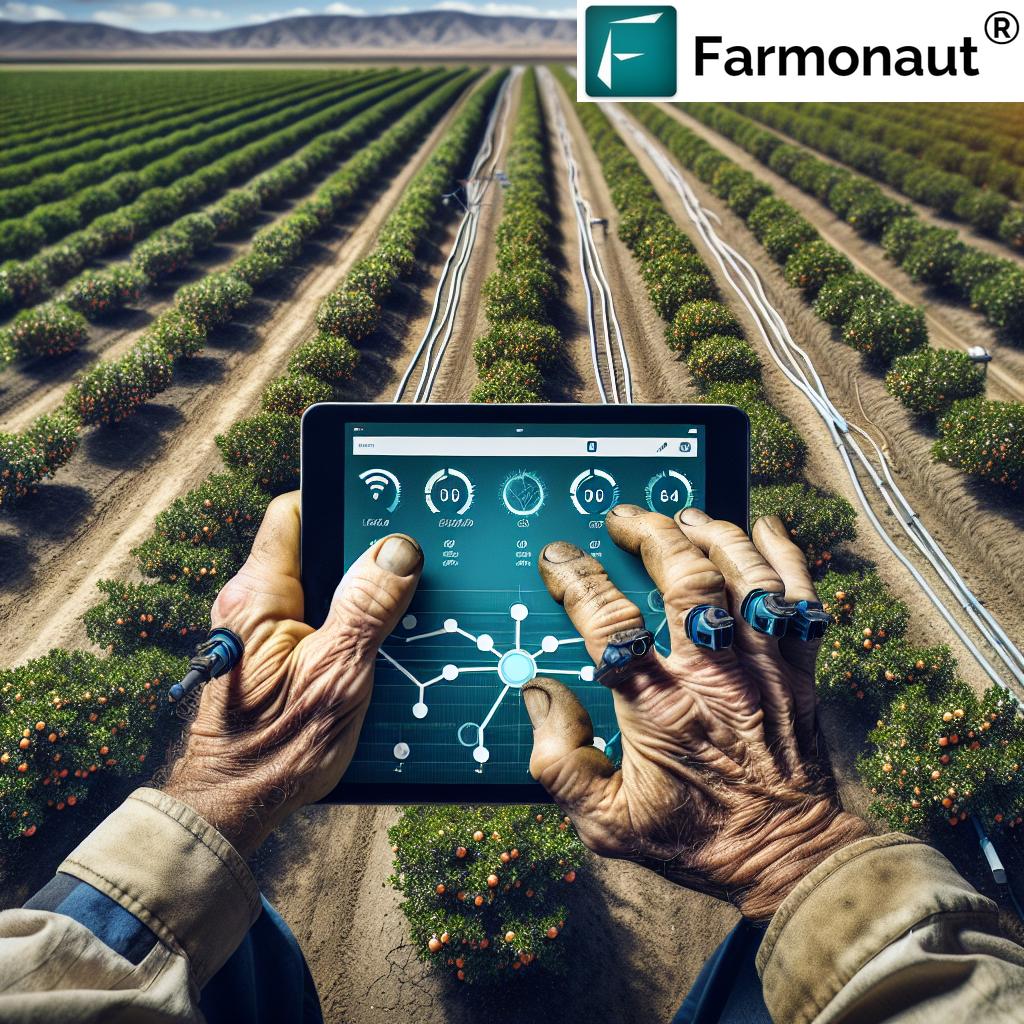

Technological Innovations: Precision Agriculture and Beyond
In the face of these challenges, technology is emerging as a powerful ally for citrus growers. Precision agriculture techniques, powered by satellite imagery and data analytics, are helping farmers make more informed decisions about water usage and crop management.
One such solution is offered by Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company that provides advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions. Through its platform, farmers can access real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisory systems, and resource management tools.
Here’s how Farmonaut’s technology is making a difference:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Provides insights into vegetation health and soil moisture levels
- AI Advisory System: Delivers personalized farm advice and weather forecasts
- Resource Management Tools: Helps optimize water usage and reduce waste
By leveraging these technologies, citrus growers can make data-driven decisions that not only conserve water but also improve overall farm productivity.
Explore Farmonaut’s solutions:
Economic Impact: The Ripple Effect of Water Scarcity
The water crisis in the Texas citrus industry has far-reaching economic implications. With an annual economic impact of $300 million, the industry’s struggles reverberate throughout the local and state economies.
- Citrus production has dropped from an average of 15 million cartons to just 7 million in the last year
- Many farmers are unable to plant new crops due to water uncertainty
- The closure of Texas’s last sugar mill highlights the broader agricultural impact
These economic challenges underscore the urgent need for sustainable solutions that can help stabilize the industry and protect the livelihoods of thousands of workers who depend on it.
Government Response and Policy Implications
As the water crisis deepens, there’s growing pressure on government officials at both the state and federal levels to address the issue. However, many local leaders express frustration with what they perceive as a lack of urgency in tackling the problem.
- Proposals for emergency financial assistance to farmers have been put forward
- Amendments to the international water treaty are being considered
- Calls for long-term water management strategies are gaining traction
While short-term relief measures are necessary, it’s clear that long-term, sustainable policies are needed to ensure the future viability of the Texas citrus industry.
The Human Face of the Crisis: Stories from the Valley
Behind the statistics and policy debates are the personal stories of those most affected by the water crisis. From multi-generation family farms to seasonal workers, the human impact of this situation is profound.
Take, for instance, the story of Elle Holbrook, set to be crowned Queen Citrianna in the upcoming Texas Citrus Fiesta. Her family’s farm, South Tex Organics, has struggled to recover from substantial crop losses, particularly in their lemon and lime production. These personal narratives remind us of the cultural and social significance of the citrus industry to the Rio Grande Valley.
Sustainable Farming Practices: Beyond Water Conservation
While water conservation is at the forefront of current efforts, sustainable farming in the Rio Grande Valley encompasses a broader range of practices. These include:
- Soil health management to improve water retention
- Integrated pest management to reduce chemical usage
- Cover cropping to prevent soil erosion and improve fertility
- Biodiversity enhancement to support beneficial insects and pollinators
By adopting these holistic approaches, citrus growers are not only addressing the immediate water crisis but also building more resilient and sustainable farming systems for the future.
The Role of Research and Innovation
As we face these unprecedented challenges, research and innovation play a crucial role in developing solutions. Institutions like Texas A&M AgriLife Research are at the forefront of efforts to breed drought-resistant citrus varieties and develop more efficient irrigation techniques.
Some key areas of research include:
- Developing citrus rootstocks that require less water
- Improving irrigation scheduling through advanced sensors and AI
- Exploring alternative water sources, such as treated wastewater for agriculture
These research efforts, combined with on-the-ground innovations by farmers, offer hope for a more sustainable future for the Texas citrus industry.
Looking to the Future: Adaptation and Resilience
As we look ahead, it’s clear that the Texas citrus industry must continue to adapt and build resilience in the face of ongoing water challenges and climate change. This will require a multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Continued investment in water-efficient technologies
- Strengthening international cooperation on water management
- Diversifying crop varieties to spread risk
- Enhancing farmer education and support programs
By embracing these strategies, the industry can work towards a more sustainable and secure future, ensuring that the rich tradition of Texas citrus continues for generations to come.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The water crisis facing the Texas citrus industry in the Rio Grande Valley is a complex challenge that requires immediate attention and long-term planning. As we’ve explored in this article, the solutions lie in a combination of innovative farming practices, technological advancements, policy reforms, and international cooperation.
We must recognize that the future of the citrus industry is intrinsically linked to the sustainable management of our water resources. By working together—farmers, researchers, policymakers, and consumers—we can create a more resilient and sustainable agricultural system that can withstand the challenges of a changing climate.
As we move forward, let’s remember the words of Elle Holbrook’s mother, who emphasized that Texas should be recognized for its exceptional citrus products. It’s up to all of us to ensure that this proud tradition continues, adapting and thriving in the face of adversity.
FAQs
- Q: How severe is the water shortage in the Rio Grande Valley?
A: The water shortage is critical, with reservoir levels at historic lows and citrus production dropping by more than 50% in recent years. - Q: What are the main causes of the water crisis?
A: The crisis is caused by a combination of prolonged drought, climate change, increased water demand, and complexities in international water agreements. - Q: How are citrus farmers adapting to water scarcity?
A: Farmers are adopting water-efficient irrigation systems, using drought-resistant crop varieties, and implementing precision agriculture techniques. - Q: What role does technology play in addressing the water crisis?
A: Technology, such as satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-driven advisory systems, helps farmers optimize water usage and improve overall farm management. - Q: How can consumers support the Texas citrus industry during this crisis?
A: Consumers can support the industry by choosing Texas citrus products, advocating for water conservation policies, and raising awareness about the challenges faced by farmers.
For more information on how technology can help address agricultural challenges, visit Farmonaut’s API and explore their API Developer Docs.