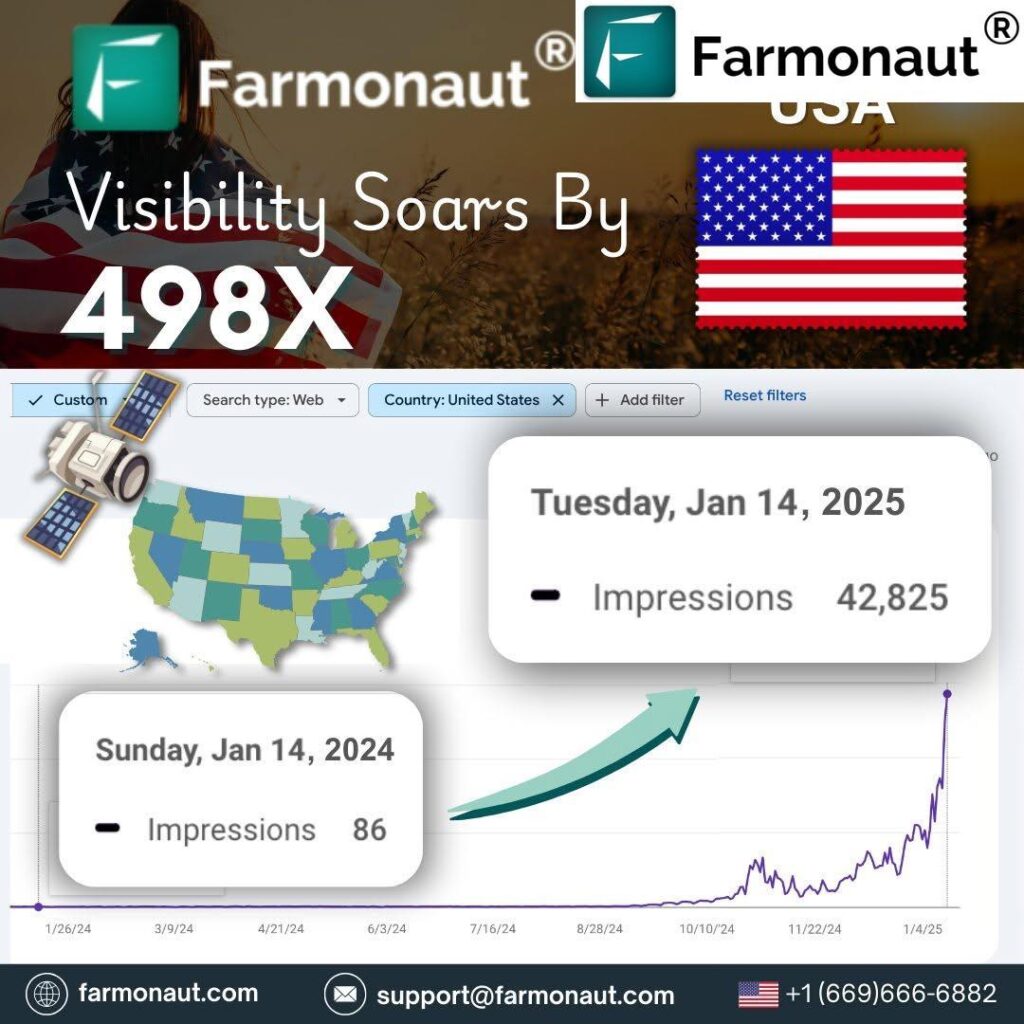
Revolutionizing Texas Border Land Management: Precision Agriculture Meets Immigration Policy
“Remote sensing and GIS technologies have increased agricultural productivity by up to 25% in Texas border counties like Starr.”
In the vast expanse of the Texas border region, a revolutionary transformation is taking place at the intersection of cutting-edge technology and agriculture. As we delve into this fascinating landscape, we’ll explore how precision agriculture is reshaping the management of border lands, addressing complex issues that span from crop yields to immigration policies. Join us on this journey as we uncover the innovative solutions that are changing the face of farming in one of America’s most challenging and dynamic regions.
The Changing Face of Texas Border Agriculture
The Texas-Mexico border, stretching along the meandering Rio Grande, has long been a focal point of national attention. However, beyond the headlines about immigration and border security lies a story of agricultural innovation that’s quietly reshaping the region’s economic and environmental landscape.
In counties like Starr, adjacent to the Rio Grande, farmers are embracing precision agriculture technology with open arms. These advancements are not just improving crop yields; they’re fundamentally altering how we approach land management in this unique geographical context.
[Image 1]
Remote Sensing: The Eyes in the Sky
At the heart of this agricultural revolution is remote sensing technology. Satellites orbiting high above the Earth are providing farmers with unprecedented insights into their land and crops. Here’s how remote sensing in agriculture is making a difference:
- Crop Health Monitoring: Multispectral imagery allows farmers to assess vegetation health (NDVI) across vast acreages without setting foot in the field.
- Soil Moisture Analysis: Advanced sensors can detect soil moisture levels, helping optimize irrigation schedules.
- Pest and Disease Detection: Early identification of crop stressors enables prompt intervention, reducing losses.
For Texas border farmers, this technology is a game-changer. With limited water resources and the constant challenge of maintaining productivity, remote sensing provides the data needed to make informed decisions quickly.
GIS: Mapping the Future of Border Agriculture
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are taking the data gathered through remote sensing and transforming it into actionable insights. In the context of Texas border land management, GIS applications are proving invaluable:
- Land Use Planning: Optimizing crop placement based on soil types and microclimates.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently distributing water and fertilizer based on precise field data.
- Yield Prediction: Analyzing historical and current data to forecast crop yields with greater accuracy.
These GIS tools are not just improving farm productivity; they’re also playing a crucial role in broader land management strategies along the border. By providing a comprehensive view of the landscape, GIS is helping policymakers make more informed decisions about land use, conservation, and even border security infrastructure.
Soil Analysis Techniques: Digging Deeper
Understanding the soil is fundamental to successful agriculture, and in the diverse terrain of the Texas border region, this knowledge is critical. Advanced soil analysis techniques are providing farmers with detailed insights into their land’s potential:
- Precision Soil Sampling: Using GPS-guided sampling to create detailed soil maps.
- Real-time Nutrient Analysis: Portable devices allowing on-the-spot soil testing for immediate action.
- Microbial Analysis: Assessing soil health at the microscopic level to optimize organic farming practices.
These techniques are particularly important in counties like Starr, where soil conditions can vary dramatically over short distances. By understanding the nuances of their soil, farmers can tailor their approach to each specific area of their land, maximizing productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
Crop Monitoring Systems: Vigilance from Seed to Harvest
In the challenging environment of the Texas border, where weather patterns can be unpredictable and resources scarce, crop monitoring systems are proving to be invaluable tools. These systems integrate various technologies to provide a comprehensive view of crop development:
- Drone Surveillance: Regular flyovers capture high-resolution imagery for detailed crop analysis.
- IoT Sensors: In-field devices monitor temperature, humidity, and soil conditions in real-time.
- AI-Powered Analytics: Machine learning algorithms process data to predict potential issues before they become problems.
For farmers in border counties, these monitoring systems offer peace of mind and the ability to respond quickly to changing conditions. Whether it’s adjusting irrigation in response to a heatwave or identifying the early signs of pest infestation, these tools are helping farmers stay one step ahead.
[Video: Farmonaut’s Advanced Agri Solutions: Precision Crop Area Estimation – Egypt Case Study]
Smart Irrigation Systems: Every Drop Counts
“Satellite imagery analysis has reduced water usage by 30% in smart irrigation systems along the Rio Grande.”
Water is a precious commodity in the arid landscape of the Texas border, and smart irrigation systems are revolutionizing how this resource is managed. These systems leverage data from various sources to optimize water usage:
- Weather-based Scheduling: Adjusting irrigation based on local weather forecasts and historical data.
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Delivering water only when and where it’s needed based on real-time soil conditions.
- Precision Application: Using variable-rate irrigation to apply different amounts of water to different parts of the field.
The impact of these systems extends beyond individual farms. By reducing overall water consumption, smart irrigation is helping to address broader concerns about water scarcity in the region, particularly in relation to the Rio Grande’s water levels.
Satellite Imagery: A Bird’s Eye View of Border Agriculture
Satellite imagery for farms has become an indispensable tool in the Texas border region. This technology provides farmers and land managers with a macro-level view of agricultural activities across vast areas:
- Crop Mapping: Identifying crop types and their distribution across the landscape.
- Change Detection: Monitoring land use changes over time, crucial for both agricultural and policy purposes.
- Disaster Assessment: Quickly evaluating the impact of natural disasters like floods or droughts.
In the context of border management, satellite imagery also plays a dual role. While primarily used for agricultural purposes, it also provides valuable data for border security agencies, highlighting the complex interplay between farming and national security in this region.
[Image 2]
Farm Data Analytics: Turning Information into Action
The abundance of data generated by precision agriculture technologies would be overwhelming without sophisticated analytics tools. Farm data analytics is the key to unlocking the full potential of this information:
- Predictive Modeling: Using historical and real-time data to forecast crop yields and potential issues.
- Performance Benchmarking: Comparing farm performance against regional and national standards.
- Decision Support Systems: Providing farmers with actionable recommendations based on comprehensive data analysis.
For Texas border farmers, these analytics tools are proving invaluable in navigating the unique challenges of their environment. By leveraging data-driven insights, they can make more informed decisions about everything from crop selection to resource allocation.
The Intersection of Agriculture and Immigration Policy
As we explore the technological advancements in Texas border agriculture, it’s impossible to ignore the broader context of immigration policy. The very land that’s being revolutionized by precision agriculture is also at the center of national debates about border security and immigration enforcement.
This intersection creates unique challenges and opportunities:
- Labor Considerations: Precision agriculture can reduce labor needs, potentially impacting immigrant workforce demand.
- Land Use Conflicts: Balancing agricultural development with border security infrastructure like walls or surveillance systems.
- Community Impact: How technological changes in farming affect border communities and local economies.
Understanding these complex dynamics is crucial for policymakers, farmers, and technology providers alike. As we continue to innovate in agricultural practices, we must also consider the broader implications for border communities and national policy.
[Video: Farmonaut’s Web App Tutorial: Comprehensive Guide for Interpreting Satellite Data]
Sustainable Farming Practices: A New Frontier
The adoption of precision agriculture technology along the Texas border isn’t just about increasing yields; it’s also opening new avenues for sustainable farming practices. These methods are particularly crucial in an area where environmental concerns intersect with agricultural needs:
- Reduced Chemical Use: Precision application of pesticides and fertilizers minimizes environmental impact.
- Water Conservation: Smart irrigation systems significantly reduce water waste.
- Soil Health Management: Data-driven approaches to crop rotation and cover cropping improve long-term soil viability.
By embracing these sustainable practices, Texas border farmers are not only improving their own operations but also contributing to the long-term environmental health of the region. This shift towards sustainability is creating a positive ripple effect, influencing agricultural policies and practices beyond the border area.
The Role of Federal Policies
The implementation of precision agriculture along the Texas border doesn’t occur in a vacuum. Federal policies play a significant role in shaping the landscape of agricultural innovation:
- USDA Programs: Initiatives supporting the adoption of precision agriculture technologies.
- Environmental Regulations: Policies that influence farming practices and resource management.
- Border Security Measures: How infrastructure projects and security policies impact agricultural land use.
Navigating this complex policy environment requires a delicate balance. Farmers and technology providers must stay informed about changing regulations and leverage available resources to support their transition to more advanced agricultural practices.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the benefits of precision agriculture in the Texas border region are clear, the path to widespread adoption is not without its challenges:
- Technology Access: Ensuring that smaller farms have access to advanced technologies.
- Data Privacy: Addressing concerns about the collection and use of farm data.
- Skills Gap: Training farmers and workers to effectively use new technologies.
- Infrastructure: Improving rural broadband access to support connected farming systems.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Public-private partnerships, educational initiatives, and targeted investments can help overcome these hurdles and unlock the full potential of precision agriculture in the region.
[Video: Farmonaut | How to Generate Time Lapse]
The Future of Texas Border Land Management
As we look to the future, the integration of precision agriculture technology with broader land management strategies holds immense promise for the Texas border region:
- Climate Resilience: Using advanced forecasting and adaptive farming techniques to mitigate climate change impacts.
- Cross-border Collaboration: Sharing data and best practices with Mexican farmers to improve regional agricultural sustainability.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Leveraging precision agriculture to support wildlife corridors and habitat preservation alongside productive farmland.
The future of land management in this unique region will likely see an even greater integration of technology, policy, and sustainable practices, creating a model for other border regions around the world.
Comparative Analysis of Precision Agriculture Technologies in Texas Border Counties
| County | Primary Crops | Remote Sensing Technology | GIS Applications | Smart Irrigation | Soil Analysis | Yield Improvement (%) | Water Conservation (%) | Challenges | Policy Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starr | Cotton, Sorghum | Satellite Imagery | Crop Mapping | Drip Irrigation | GPS Soil Sampling | 20 | 25 | Limited Broadband | Water Rights Disputes |
| Hidalgo | Citrus, Vegetables | Drone Surveillance | Yield Prediction | Precision Sprinklers | Real-time Sensors | 25 | 30 | Labor Shortages | Immigration Reform Impact |
| Cameron | Sugarcane, Rice | Multispectral Imaging | Flood Risk Mapping | Variable Rate Irrigation | Spectral Analysis | 18 | 28 | Salinity Issues | Coastal Management |
The Role of Farmonaut in Precision Agriculture
In the evolving landscape of precision agriculture, Farmonaut stands out as a pioneering force, offering cutting-edge solutions that align perfectly with the needs of Texas border agriculture. Let’s explore how Farmonaut’s technologies are contributing to this revolution:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Farmonaut’s advanced satellite imagery analysis provides farmers with crucial insights into vegetation health (NDVI) and soil moisture levels. This technology is particularly valuable in the vast and varied terrain of the Texas border region.
- AI-Driven Advisory System: The Jeevn AI system offers personalized farm advice, considering the unique challenges of border agriculture, from water scarcity to pest management.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: In a region where cross-border trade is significant, Farmonaut’s blockchain solutions ensure transparency and security in agricultural supply chains.
- Resource Management Tools: Farmonaut’s fleet and resource management features help large-scale operations optimize their logistics, crucial in the expansive border counties.
By leveraging these technologies, Texas border farmers can make more informed decisions, improve resource allocation, and ultimately increase their productivity while promoting sustainable practices.
[Video: Farmonaut Introduction – Large Scale Usage For Businesses and Governments]
Integrating Farmonaut Solutions in Border Agriculture
The integration of Farmonaut’s solutions into Texas border agriculture offers numerous benefits:
- Cost-Effective Precision Agriculture: Farmonaut’s satellite-based approach makes advanced farming techniques accessible to farms of all sizes, democratizing precision agriculture in the region.
- Enhanced Productivity: Real-time data on crop health and soil conditions enables farmers to make timely interventions, maximizing yields in the challenging border climate.
- Water Conservation: In an area where water rights are a contentious issue, Farmonaut’s smart irrigation insights help farmers optimize water usage, contributing to regional sustainability efforts.
- Policy Compliance: Features like carbon footprint tracking assist farmers in adhering to environmental regulations, an increasingly important aspect of border land management.
Farmers, agribusinesses, and even government agencies in the Texas border region can leverage Farmonaut’s comprehensive suite of tools to address the unique challenges they face. Whether it’s managing large-scale operations, implementing sustainable practices, or navigating complex regulatory environments, Farmonaut’s technology offers valuable support.
Accessing Farmonaut’s Solutions
For those interested in harnessing the power of Farmonaut’s precision agriculture technologies, there are several ways to get started:
Web Application: Access Farmonaut’s full suite of tools through their user-friendly web interface.
[App Button Image]
Mobile Apps: Stay connected on the go with Farmonaut’s mobile applications:
[Android App Button Image] [iOS App Button Image]
API Integration: For developers and businesses looking to incorporate Farmonaut’s data into their own systems, the Farmonaut API offers flexible integration options. Detailed documentation is available in the API Developer Docs.
Subscription Options
Farmonaut offers flexible subscription plans to suit various needs and scales of operation:
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does Farmonaut’s technology adapt to the unique challenges of Texas border agriculture?
A: Farmonaut’s solutions are highly customizable, taking into account factors like water scarcity, varied soil conditions, and the specific crops grown in the region. The AI-driven advisory system considers local climate patterns and agricultural practices to provide tailored recommendations.
Q: Can Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring help with border security concerns?
A: While Farmonaut’s primary focus is agricultural monitoring, the high-resolution satellite imagery and change detection capabilities can indirectly support land management decisions related to border security. However, it’s important to note that Farmonaut is not a security or surveillance tool.
Q: How does Farmonaut ensure data privacy for farmers in sensitive border areas?
A: Farmonaut takes data privacy seriously, employing robust encryption and secure data storage practices. Farmers have full control over their data, and Farmonaut does not share individual farm data with any third parties without explicit permission.
Q: Can Farmonaut’s solutions help small-scale farmers in the border region?
A: Absolutely. Farmonaut’s satellite-based approach makes precision agriculture accessible to farms of all sizes. The scalable subscription model allows small-scale farmers to access advanced technologies without significant upfront investments.
Q: How does Farmonaut contribute to sustainable farming practices in the Texas border region?
A: Farmonaut’s technology promotes sustainability by optimizing resource use, reducing chemical inputs through precise application, and helping farmers make data-driven decisions that minimize environmental impact while maximizing productivity.
Conclusion: A New Era for Texas Border Agriculture
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the integration of precision agriculture technology is ushering in a new era for land management along the Texas border. From remote sensing and GIS applications to advanced soil analysis and smart irrigation systems, these innovations are transforming how farmers operate in this unique and challenging environment.
The benefits extend far beyond increased crop yields. We’re seeing more sustainable farming practices, improved resource management, and a new level of data-driven decision-making that’s helping farmers navigate the complex interplay of agricultural needs, environmental concerns, and border policies.
Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront of this revolution, providing accessible, comprehensive solutions that empower farmers of all scales to embrace precision agriculture. As these technologies continue to evolve and become more integrated into daily farming operations, we can expect to see even greater advancements in productivity, sustainability, and resilience in Texas border agriculture.
The future of land management in this region is bright, filled with opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and sustainable growth. As we move forward, the lessons learned and successes achieved in the Texas border region could serve as a model for agricultural innovation in challenging environments around the world.
In embracing these technological advancements, we’re not just revolutionizing farming; we’re reshaping the very landscape of the Texas border, creating a more sustainable, productive, and resilient agricultural sector that’s prepared to meet the challenges of the 21st century and beyond.