Revolutionizing Urban Agriculture: How Vertical Farming is Transforming America’s Food Production Landscape
“The U.S. vertical farming market is projected to reach $2.55 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 18.2%.”
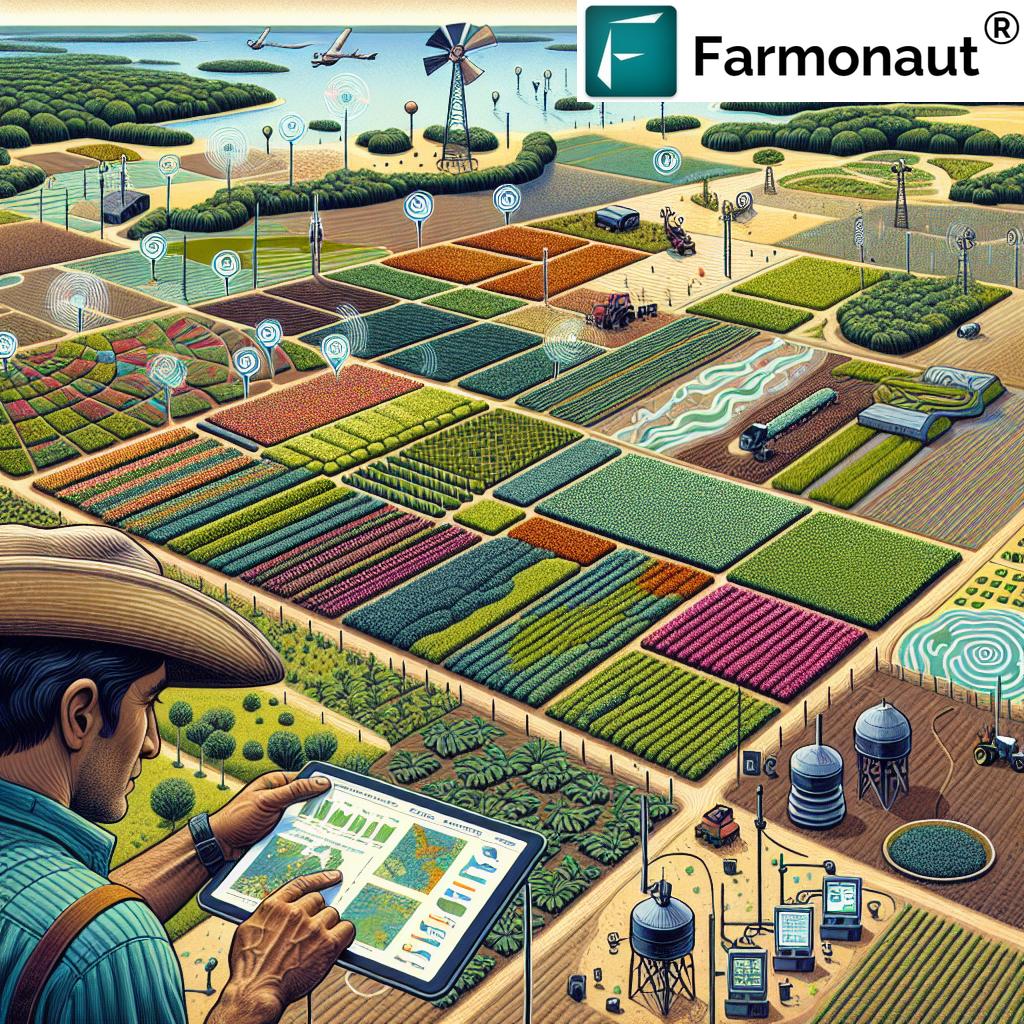
In the heart of America’s bustling cities, a green revolution is taking root – quite literally. As we navigate the challenges of decreasing arable land and increasing demand for fresh, local produce, vertical farming has emerged as a beacon of innovation in urban agriculture. This transformative approach to food production is not just changing how we grow our food; it’s reshaping the very landscape of American agriculture.
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of this agricultural renaissance, leveraging cutting-edge satellite technology and AI-driven insights to support the burgeoning vertical farming industry. Our mission aligns perfectly with the goals of vertical farming: to make precision agriculture accessible, sustainable, and highly efficient.
The Rise of Vertical Farming in America
The vertical farming market in the United States is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by a confluence of factors including urbanization, climate change, and technological advancements. As traditional farmland becomes scarcer and urban populations surge, the need for innovative farming solutions has never been more pressing.
Vertical farming, with its promise of year-round crop production and minimal land use, has emerged as a viable solution to these challenges. By 2029, the U.S. vertical farming market is projected to reach a staggering $2.55 billion, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.2%. This remarkable growth trajectory underscores the transformative potential of vertical farming in reshaping America’s food production landscape.

The Technology Driving Vertical Farming
At the heart of the vertical farming revolution lies a suite of advanced technologies that are transforming traditional agricultural practices. These innovations are not only increasing crop yields and efficiency but also addressing critical challenges such as water conservation and pesticide-free cultivation.
Building-Based Vertical Farms
Building-based vertical farms are leading the charge in the vertical farming industry. These state-of-the-art facilities maximize space efficiency through vertical stacking, allowing for significantly higher crop yields per unit area compared to conventional farming methods. The controlled environment within these structures enables year-round production, unaffected by external weather conditions or seasonal changes.
Key features of building-based vertical farms include:
- Advanced LED lighting systems that mimic natural sunlight
- Automated climate control for optimal growing conditions
- Precision nutrient delivery systems
- Vertical space utilization for maximum efficiency
These farms are particularly beneficial in urban areas where land is at a premium. By repurposing existing buildings or constructing purpose-built facilities, vertical farms can bring food production closer to consumers, reducing transportation costs and carbon emissions associated with long-distance food supply chains.
Hydroponic and Aeroponic Systems
At the core of many vertical farming operations are hydroponic and aeroponic systems, which represent a significant departure from traditional soil-based agriculture. These innovative growing methods offer superior resource efficiency and productivity, making them ideal for the controlled environments of vertical farms.
Hydroponic Systems: In hydroponics, plants are grown in nutrient-rich water solutions rather than soil. This method allows for precise control over nutrient delivery, resulting in faster growth rates and higher yields. Hydroponic systems are known for their water efficiency, using up to 90% less water than traditional farming methods.
Aeroponic Systems: Aeroponics takes water efficiency even further. In this system, plant roots are suspended in air and misted with a fine nutrient solution. Aeroponic farming shows the highest growth potential in the vertical farming sector, offering unparalleled resource efficiency and productivity.
According to our research at Farmonaut, aeroponic systems can use up to 98% less water than traditional farming methods and 30% less than hydroponic systems. This remarkable efficiency, coupled with faster growth rates and higher nutrient absorption, makes aeroponics a game-changer in urban agriculture.
Smart Farming Automation and AI
The integration of smart farming automation and artificial intelligence is revolutionizing vertical farming operations. These technologies enable precise control over every aspect of the growing environment, from lighting and temperature to nutrient delivery and harvesting.
AI-driven systems can:
- Analyze plant health in real-time
- Predict optimal harvesting times
- Adjust growing conditions to maximize yield and quality
- Manage resource use for optimal efficiency
At Farmonaut, we’re contributing to this technological revolution through our AI-powered Jeevn AI Advisory System. This advanced tool delivers real-time insights and personalized farm management strategies, helping vertical farmers optimize their operations and improve productivity.
Water-Efficient Crop Production: A Sustainable Solution
One of the most significant advantages of vertical farming is its water efficiency. In a world where water scarcity is becoming an increasingly pressing issue, the ability to produce food with minimal water usage is invaluable.
Vertical farming systems, particularly those utilizing hydroponic and aeroponic technologies, can achieve water savings of up to 95% compared to traditional agriculture. This efficiency is achieved through:
- Recirculating water systems that minimize waste
- Precision nutrient delivery that reduces runoff
- Controlled environments that minimize evaporation
Furthermore, the controlled environment of vertical farms allows for the cultivation of crops without the use of pesticides, addressing concerns about water pollution from agricultural runoff.
“Aeroponic farming, a subset of vertical farming, shows the highest growth potential in urban agriculture technology.”
Transforming Urban Food Production
The rise of vertical farming is fundamentally changing the landscape of urban food production. By bringing agriculture into the heart of cities, vertical farms are shortening supply chains, reducing transportation costs, and providing urban communities with access to fresh, locally grown produce year-round.
Benefits of Urban Vertical Farming:
- Reduced food miles and associated carbon emissions
- Year-round production regardless of climate conditions
- Improved food security for urban populations
- Creation of green jobs in urban areas
- Repurposing of unused urban spaces for food production
As urban populations continue to grow, the role of vertical farming in ensuring food security and sustainability will become increasingly crucial. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting this urban agricultural revolution through our advanced satellite-based farm management solutions and AI-driven advisory systems.
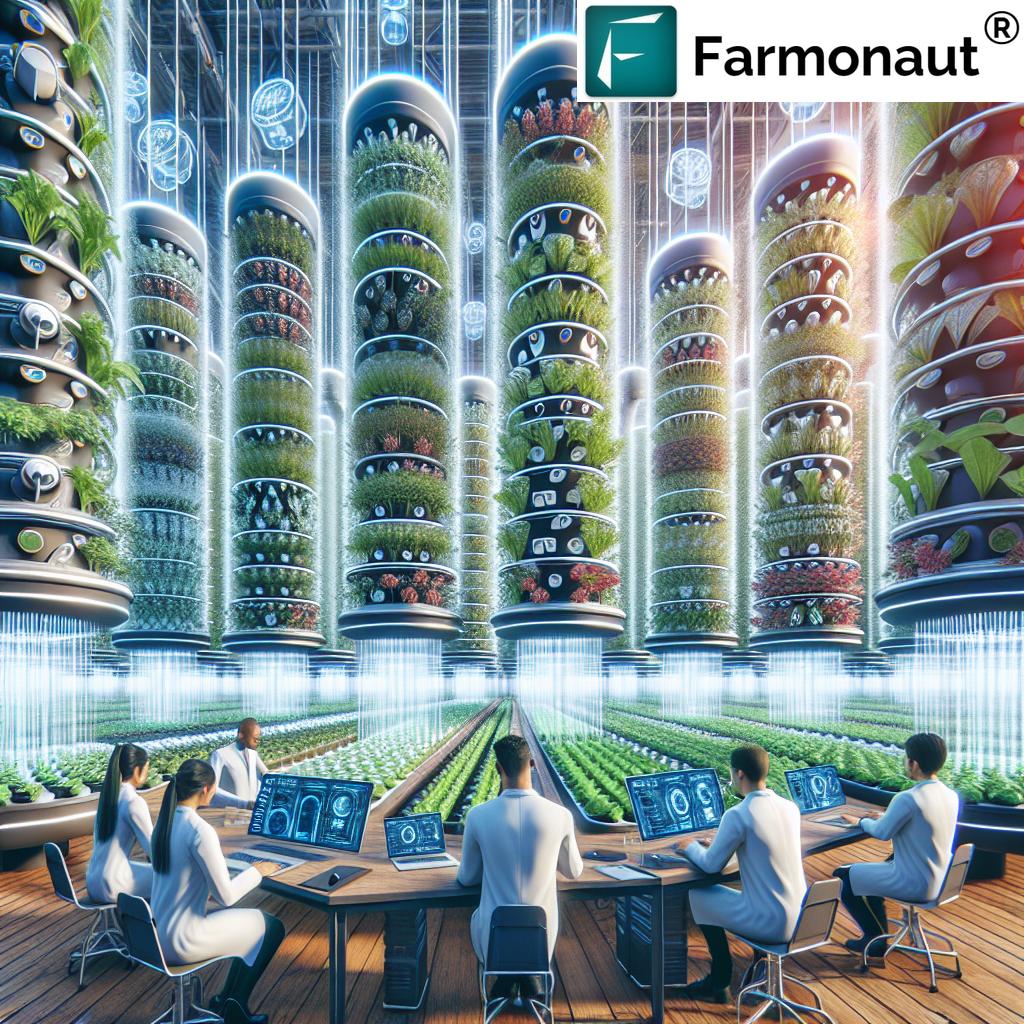

Vertical Farming Technologies Comparison
| Technology Type | Space Efficiency (1-10 scale) | Water Usage (gallons/lb of produce) | Estimated Yield (lbs/sq ft/year) | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building-based Vertical Farms | 9 | 1-2 | 50-80 | Maximizes urban space, year-round production |
| Aeroponic Systems | 10 | 0.1-0.5 | 70-100 | Highest water efficiency, rapid growth rates |
| Hydroponic Systems | 8 | 0.5-1 | 60-90 | Versatile, well-established technology |
| Traditional Greenhouse | 6 | 5-10 | 30-50 | Natural light utilization, lower initial costs |
The Role of Precision Agriculture in Vertical Farming
Precision agriculture plays a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency and productivity of vertical farming systems. By leveraging advanced technologies such as sensors, IoT devices, and data analytics, farmers can make informed decisions about every aspect of crop management.
At Farmonaut, we specialize in providing cutting-edge precision agriculture solutions that are particularly valuable for vertical farming operations. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system offers real-time insights into crop health, allowing farmers to detect and address issues before they become problematic.
Key benefits of precision agriculture in vertical farming include:
- Optimized resource use (water, nutrients, energy)
- Early detection of plant stress or disease
- Precise climate control for optimal growing conditions
- Data-driven decision making for improved yields
By integrating precision agriculture techniques, vertical farms can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and sustainability, further cementing their role in the future of food production.
Sustainable Farming Solutions: The Environmental Impact of Vertical Farming
As we confront the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, the sustainability of our food production systems has never been more critical. Vertical farming offers a range of environmental benefits that position it as a key player in sustainable agriculture.
Reduced Land Use
One of the most significant environmental advantages of vertical farming is its minimal land footprint. By growing crops vertically, these systems can produce the same amount of food as traditional farms using only a fraction of the land area. This efficiency is particularly crucial as we face increasing pressure on arable land due to urbanization and climate change.
Water Conservation
As mentioned earlier, vertical farming systems are incredibly water-efficient. By recycling and reusing water, these systems can reduce water usage by up to 95% compared to traditional agriculture. This conservation is vital in regions facing water scarcity and helps to preserve this precious resource for future generations.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Vertical farms, particularly those located in urban areas, can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with food production and distribution. By growing food closer to consumers, these systems minimize transportation distances, reducing fuel consumption and associated emissions.
At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of monitoring and reducing carbon emissions in agriculture. Our carbon footprinting tool helps vertical farmers and other agricultural businesses track their emissions and identify opportunities for reduction, supporting the industry’s sustainability goals.
Pesticide-Free Cultivation
The controlled environment of vertical farms allows for pesticide-free cultivation, eliminating the environmental impact of chemical pesticides. This not only produces healthier food but also protects surrounding ecosystems from the harmful effects of pesticide runoff.
Investment Opportunities in Vertical Farming
The rapid growth of the vertical farming market presents exciting investment opportunities across various sectors. As the industry continues to evolve and expand, investors are taking notice of its potential to revolutionize food production and address pressing global challenges.
Key Areas for Investment:
- Technology Development: Investments in advanced lighting systems, automation technologies, and AI-driven farm management solutions are driving innovation in the sector.
- Infrastructure: The construction of large-scale vertical farming facilities in urban areas represents a significant opportunity for real estate and infrastructure investors.
- Supply Chain and Logistics: As vertical farming reshapes urban food production, there’s growing demand for specialized supply chain and logistics solutions to support these operations.
- Sustainable Agriculture Funds: With increasing focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing, vertical farming offers an attractive option for sustainable agriculture investment funds.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting investors and entrepreneurs in the vertical farming space through our advanced agricultural technology solutions. Our large-scale farm management tools provide valuable insights and data-driven decision-making capabilities, essential for successful vertical farming operations.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While vertical farming offers tremendous potential, it’s not without its challenges. As we look to the future of this innovative industry, it’s important to address these obstacles and explore potential solutions.
Current Challenges:
- High Initial Costs: The setup of vertical farms, particularly large-scale operations, requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure and technology.
- Energy Consumption: The artificial lighting and climate control systems used in vertical farms can be energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of their environmental benefits.
- Limited Crop Variety: Currently, vertical farms are best suited for growing leafy greens and herbs. Expanding the range of crops that can be efficiently grown in these systems remains a challenge.
- Skilled Labor: Operating vertical farms requires specialized knowledge and skills, and there’s currently a shortage of trained professionals in this field.
Future Outlook and Potential Solutions:
Despite these challenges, the future of vertical farming looks promising. We anticipate several developments that will address current limitations and further enhance the viability of vertical farming:
- Renewable Energy Integration: Incorporating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can help offset the energy demands of vertical farms, improving their overall sustainability.
- Advanced AI and Automation: Continued developments in AI and automation technologies will increase efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enable the cultivation of a wider variety of crops.
- Genetic Research: Ongoing research into plant genetics could lead to the development of crop varieties specifically adapted for vertical farming environments.
- Policy Support: As governments recognize the potential of vertical farming to address food security and sustainability challenges, we expect to see increased policy support and incentives for this industry.
At Farmonaut, we’re actively working on solutions to support the growth and evolution of vertical farming. Our AI-driven advisory systems and precision agriculture tools are continually evolving to meet the changing needs of this dynamic industry.
Conclusion: The Future of Food Production
As we look to the future of agriculture in America, it’s clear that vertical farming will play an increasingly significant role. This innovative approach to food production offers a sustainable, efficient, and locally-focused solution to many of the challenges facing our food systems today.
From maximizing urban space and conserving water to reducing carbon footprints and providing year-round access to fresh produce, vertical farming is truly revolutionizing the landscape of American agriculture. As technology continues to advance and the industry matures, we can expect to see even greater innovations and efficiencies in this space.
At Farmonaut, we’re excited to be part of this agricultural revolution. Our commitment to providing cutting-edge satellite-based farm management solutions and AI-driven insights aligns perfectly with the goals of the vertical farming industry. We believe that by combining the power of technology with innovative farming practices, we can create a more sustainable and food-secure future for all.
As we continue to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by vertical farming, one thing is clear: the future of food production is vertical, and it’s happening right here in America’s cities.
FAQs
- What is vertical farming?
Vertical farming is an innovative agricultural method that involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in controlled environments like buildings or shipping containers. It maximizes space efficiency and allows for year-round crop production. - How does vertical farming compare to traditional agriculture in terms of water usage?
Vertical farming systems, particularly those using hydroponic or aeroponic methods, can use up to 95% less water than traditional agriculture. This is achieved through recirculating water systems and precise nutrient delivery. - What types of crops are typically grown in vertical farms?
Currently, vertical farms are best suited for growing leafy greens, herbs, and some fruits and vegetables. Common crops include lettuce, spinach, kale, basil, and strawberries. - How does vertical farming impact urban food security?
Vertical farming can significantly improve urban food security by bringing food production closer to consumers, reducing reliance on long-distance transportation, and providing fresh produce year-round, regardless of external weather conditions. - What role does AI play in vertical farming?
AI plays a crucial role in vertical farming by optimizing growing conditions, predicting crop health issues, managing resource use, and automating various aspects of farm management. This leads to improved efficiency and higher yields.
Earn With Farmonaut: Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Farmonaut Subscriptions
For more information on how Farmonaut can support your vertical farming operations or to explore our precision agriculture solutions, visit our website or download our app:
For developers interested in integrating our satellite and weather data into their own systems, check out our API and API Developer Docs.