Revolutionizing Coffee Farming in Kenya: How Sustainable Agroforestry Boosts Yields and Fights Climate Change

“Kenyan coffee farmers have planted millions of trees, creating carbon-sequestering ecosystems and boosting biodiversity.”
In the heart of East Africa, a quiet revolution is taking place that promises to transform the landscape of coffee farming and contribute significantly to the global fight against climate change. We’re witnessing a shift from traditional monoculture practices to innovative, sustainable agroforestry systems that are not only boosting coffee yields but also creating resilient, biodiverse ecosystems. This blog post delves into the fascinating world of sustainable coffee farming in Kenya, exploring how agroforestry practices are reshaping the industry and empowering local communities.
The Dawn of Sustainable Coffee Farming in Kenya
Coffee has long been a cornerstone of Kenya’s agricultural economy, with the country renowned for producing some of the world’s finest beans. However, traditional coffee farming methods have often come at a cost to the environment, leading to soil degradation, reduced biodiversity, and increased vulnerability to climate change. Recognizing these challenges, innovative farmers and agricultural experts in Kenya are now embracing sustainable agroforestry practices that promise to revolutionize the industry.
Sustainable coffee farming in Kenya is not just about producing high-quality beans; it’s about creating a harmonious relationship between agriculture and nature. By integrating trees and diverse crops into coffee plantations, farmers are fostering ecosystems that sequester carbon, enhance soil health, and provide habitats for a wide range of species. This approach is transforming degraded farmland into thriving, biodiverse landscapes that benefit both farmers and the environment.
The Power of Agroforestry Practices in Coffee Production
Agroforestry practices are at the heart of this agricultural revolution in Kenya. By strategically planting trees alongside coffee crops, farmers are creating multi-layered ecosystems that mimic natural forests. These systems offer numerous benefits:
- Improved Soil Health: Trees help prevent soil erosion, increase organic matter content, and enhance nutrient cycling.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: The diverse plant species attract a variety of insects, birds, and other wildlife, creating balanced ecosystems.
- Natural Pest Control: Increased biodiversity helps control pests naturally, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
- Climate Resilience: Trees provide shade and regulate temperature, protecting coffee plants from extreme weather events.
- Carbon Sequestration: The integration of trees significantly increases the amount of carbon stored in both soil and biomass.
These agroforestry systems are not just environmentally beneficial; they’re also proving to be more productive and economically viable for farmers. By diversifying their crops and integrating sustainable practices, farmers are seeing improved yields and accessing new revenue streams through carbon credits and eco-certified products.
Syntropic Farming: A Game-Changer for Coffee Production
One of the most exciting developments in sustainable coffee farming is the adoption of syntropic farming techniques. This innovative approach, pioneered by Swiss farmer and researcher Ernst Götsch, takes agroforestry to the next level by mimicking natural succession processes to create highly productive, self-sustaining agricultural systems.
In syntropic coffee farming, farmers strategically plant a diverse range of species that work together to create optimal growing conditions. This might include nitrogen-fixing trees, fruit trees, and various understory plants that complement the coffee crop. As the system matures, it becomes increasingly self-sufficient, requiring fewer inputs and providing multiple harvests throughout the year.
The benefits of syntropic farming for coffee production are numerous:
- Increased Productivity: Syntropic systems can produce higher yields per hectare compared to traditional monocultures.
- Improved Coffee Quality: The diverse ecosystem creates ideal microclimates for coffee plants, often resulting in better-tasting beans.
- Enhanced Resilience: The multi-layered canopy provides natural protection against extreme weather events and climate fluctuations.
- Continuous Harvests: Diversified planting allows for year-round harvests of various crops, improving income stability for farmers.
- Regeneration of Ecosystems: Syntropic farming actively restores degraded land, increasing biodiversity and ecosystem services.
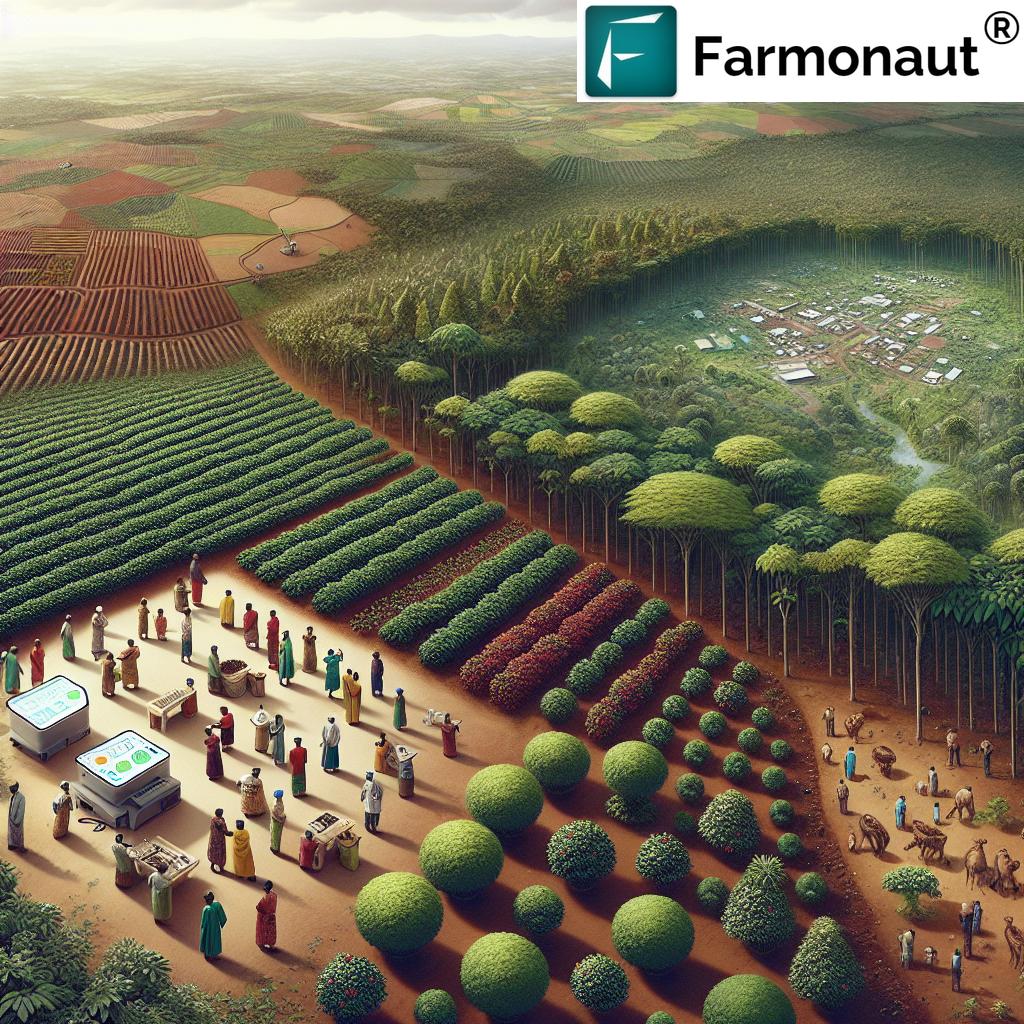

The Role of Technology in Sustainable Coffee Farming
As we embrace these innovative farming practices, technology plays a crucial role in optimizing their implementation and management. Agrotech solutions are empowering farmers with data-driven insights and precision agriculture techniques that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of sustainable farming practices.
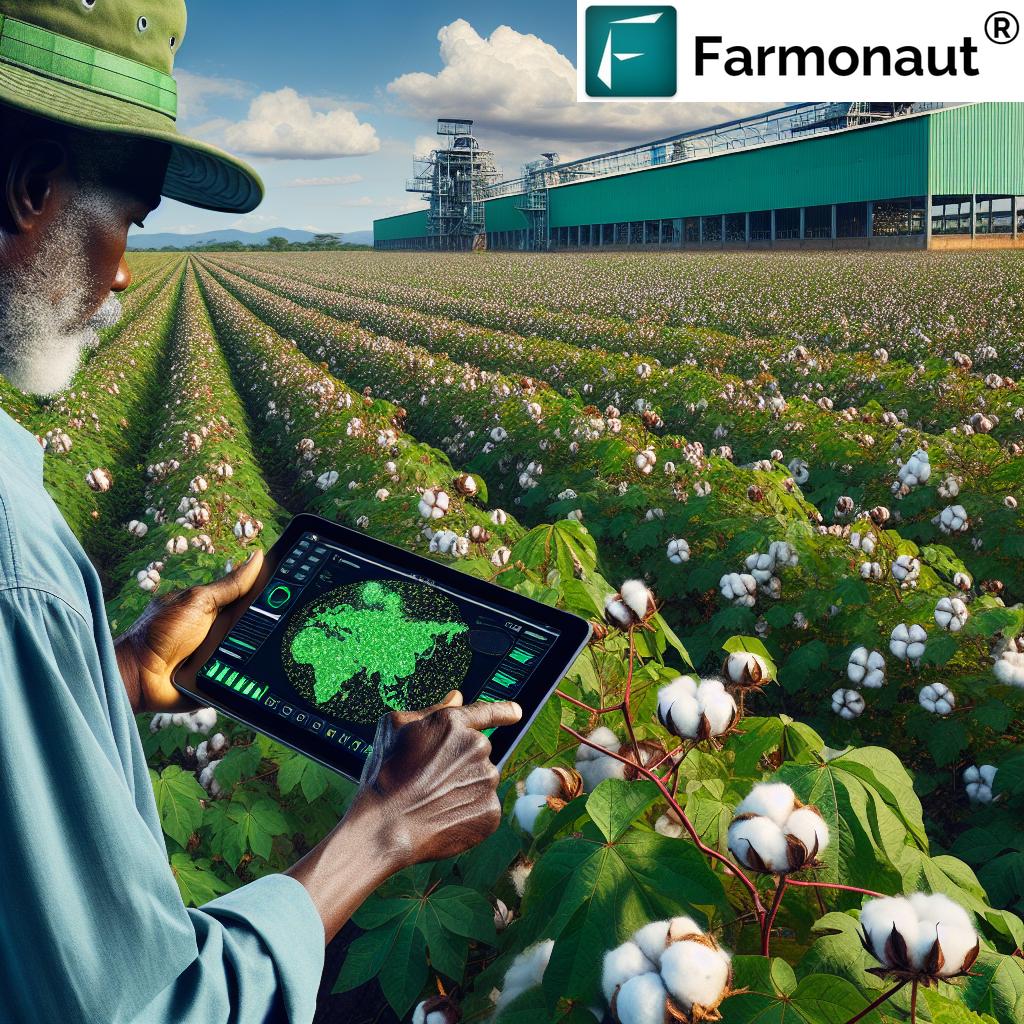
One such technology leader in this space is Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company that offers advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions. Through its comprehensive platform, Farmonaut provides valuable services such as real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisory systems, and resource management tools. These technologies are particularly beneficial for coffee farmers transitioning to agroforestry systems, allowing them to monitor crop health, optimize resource use, and make data-driven decisions.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring system, for instance, uses multispectral imagery to assess vegetation health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This information helps farmers identify areas that may need attention, optimize irrigation practices, and monitor the overall health of their agroforestry systems.
To learn more about how Farmonaut is supporting sustainable agriculture, you can explore their services through the following links:
Web App | API | API Developer Docs
Carbon Sequestration: A Key Benefit of Agroforestry
One of the most significant advantages of transitioning to agroforestry systems in coffee farming is the potential for carbon sequestration. As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, the role of agriculture in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions has come into sharp focus. Agroforestry practices offer a powerful solution by significantly increasing the amount of carbon stored in both soil and biomass.
In Kenya, coffee farmers adopting agroforestry techniques are not only improving their yields but also contributing to global climate action. Here’s how:
- Tree Integration: By planting millions of trees alongside coffee crops, farmers are creating substantial carbon sinks. Trees absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass and the soil.
- Soil Carbon Enhancement: Agroforestry practices improve soil health, increasing organic matter content and enhancing the soil’s capacity to store carbon.
- Reduced Emissions: Sustainable farming practices often require fewer chemical inputs and mechanization, reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions associated with coffee production.
- Long-term Carbon Storage: Unlike annual crops, the perennial nature of coffee plants and associated trees in agroforestry systems provides long-term, stable carbon storage.
The potential for carbon sequestration in agriculture is significant. According to recent studies, agroforestry systems can sequester up to 5 times more carbon compared to conventional agriculture. This not only contributes to climate change mitigation but also opens up new economic opportunities for farmers through carbon credit markets.
Economic Benefits for Farming Communities
“Sustainable agroforestry practices in East Africa have significantly improved coffee yields and increased farmer revenues.”
The transition to sustainable agroforestry practices is not just an environmental imperative; it’s also proving to be an economic boon for coffee farming communities in Kenya. By diversifying their crops and adopting innovative farming techniques, farmers are seeing tangible financial benefits:
- Improved Yields: Agroforestry systems often lead to increased coffee yields due to improved soil health and natural pest control.
- Diversified Income Streams: By integrating fruit trees and other crops, farmers can generate additional income throughout the year.
- Premium Prices: Sustainably grown coffee often commands higher prices in the market, especially when certified organic or fair trade.
- Carbon Credits: Farmers can potentially earn additional revenue by selling carbon credits generated through their agroforestry practices.
- Reduced Input Costs: Sustainable farming practices often require fewer chemical inputs, reducing overall production costs.
These economic benefits are crucial for the long-term viability of coffee farming in Kenya. By improving farmers’ livelihoods, sustainable agroforestry practices are helping to secure the future of coffee production while also contributing to rural development and poverty alleviation.
Comparison: Traditional vs. Agroforestry Coffee Farming
| Farming Method | Biodiversity Impact (species count) | Carbon Sequestration (tons CO2/ha/year) | Soil Health | Coffee Yield (kg/ha) | Economic Benefits (additional income %) | Climate Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Monoculture | 10-20 | 0.5-1 | Poor | 500-800 | 0% | Low |
| Agroforestry System | 50-100+ | 3-5 | Excellent | 800-1200 | 20-40% | High |
This comparison clearly illustrates the multiple benefits of transitioning from traditional monoculture to agroforestry systems in coffee farming. The improvements in biodiversity, carbon sequestration, soil health, and overall productivity make a compelling case for the adoption of sustainable practices.
Challenges and Opportunities in Scaling Sustainable Coffee Farming
While the benefits of sustainable agroforestry practices in coffee farming are clear, scaling these approaches across Kenya and East Africa presents both challenges and opportunities:
Challenges:
- Knowledge and Training: Many farmers require extensive training and support to transition to agroforestry systems effectively.
- Initial Costs: The upfront investment in trees and other resources can be a barrier for some farmers.
- Time to Maturity: Agroforestry systems take time to establish and reach full productivity, requiring patience and long-term planning.
- Market Access: Ensuring fair prices and market access for sustainably produced coffee remains a challenge in some regions.
Opportunities:
- Government Support: Increasing recognition of agroforestry’s benefits is leading to supportive policies and incentives.
- Technology Integration: The adoption of agrotech solutions like those offered by Farmonaut can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of sustainable farming practices.
- Carbon Markets: The growing global carbon market presents new revenue opportunities for farmers adopting sustainable practices.
- Consumer Demand: Increasing consumer preference for sustainably produced coffee is driving market demand and premium prices.
Addressing these challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities will be crucial for the widespread adoption of sustainable coffee farming practices across East Africa.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
As we continue to explore the potential of sustainable coffee farming in Kenya, it’s crucial to highlight the role of technology in facilitating this transition. Advanced agricultural technologies are playing a pivotal role in optimizing sustainable farming practices, improving efficiency, and providing farmers with valuable insights.
Farmonaut, a leader in agricultural technology, offers a range of solutions that are particularly relevant to sustainable coffee farming:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: This technology allows farmers to monitor the health of their coffee plants and associated crops in real-time, enabling early detection of issues and optimized resource allocation.
- AI-Powered Advisory Systems: Advanced algorithms analyze farm data to provide personalized recommendations on crop management, irrigation, and pest control, tailored to the specific needs of agroforestry systems.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: This technology ensures transparency in the coffee supply chain, allowing consumers to trace their coffee back to its sustainable origins and potentially commanding premium prices for farmers.
- Resource Management Tools: These help farmers optimize the use of water, fertilizers, and other inputs, reducing waste and improving the overall sustainability of their operations.
By leveraging these technologies, coffee farmers in Kenya can more effectively implement and manage their agroforestry systems, leading to improved yields, reduced environmental impact, and increased profitability.
The Future of Coffee Farming in Kenya
As we look to the future, the potential for sustainable coffee farming in Kenya is immense. The combination of innovative agroforestry practices, supportive policies, and advanced technologies is paving the way for a more resilient, productive, and environmentally friendly coffee industry.
Key trends shaping the future of coffee farming in Kenya include:
- Increased Adoption of Agroforestry: We expect to see a continued shift towards diverse, multi-layered farming systems that integrate coffee with other crops and trees.
- Technology Integration: The use of satellite monitoring, AI-powered advisory systems, and blockchain traceability will become increasingly common, enhancing farm management and market access.
- Climate-Resilient Varieties: Research into climate-resilient coffee varieties will continue, helping farmers adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Carbon Market Participation: More farmers are likely to participate in carbon markets, generating additional income through verified carbon credits.
- Sustainable Certification: The demand for sustainably certified coffee is expected to grow, incentivizing more farmers to adopt eco-friendly practices.
These trends point towards a future where Kenyan coffee is not only renowned for its quality but also for its positive environmental and social impact. By embracing sustainable agroforestry practices and leveraging cutting-edge technologies, Kenya’s coffee industry is positioning itself as a leader in sustainable agriculture, setting an example for coffee-growing regions worldwide.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Path Forward
The revolution in coffee farming taking place in Kenya represents a powerful model for sustainable agriculture in the face of climate change. By embracing agroforestry practices, leveraging innovative technologies, and focusing on long-term sustainability, Kenyan coffee farmers are not only improving their livelihoods but also contributing significantly to global climate action.
The transition to sustainable coffee farming is more than just an environmental imperative; it’s a pathway to economic resilience and community empowerment. As consumers, we have the power to support this transformation by choosing sustainably produced coffee and advocating for policies that support regenerative agriculture practices.
The future of coffee farming in Kenya is bright, rooted in practices that nourish the land, support biodiversity, and create thriving rural economies. As this model continues to evolve and expand, it offers hope not just for the coffee industry, but for sustainable agriculture worldwide.
FAQs about Sustainable Coffee Farming in Kenya
- What is agroforestry in coffee farming?
Agroforestry in coffee farming involves integrating trees and other crops alongside coffee plants, creating a diverse, multi-layered ecosystem that mimics natural forests. - How does sustainable coffee farming help fight climate change?
Sustainable coffee farming practices, particularly agroforestry, help sequester carbon in soil and biomass, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and create more resilient agricultural systems. - What are the economic benefits of sustainable coffee farming for Kenyan farmers?
Sustainable practices can lead to improved yields, diversified income streams, access to premium markets, potential carbon credit revenue, and reduced input costs. - How does technology support sustainable coffee farming?
Technologies like satellite monitoring, AI-powered advisory systems, and blockchain traceability help farmers optimize their operations, make data-driven decisions, and access new markets. - What is syntropic farming and how does it apply to coffee production?
Syntropic farming is an advanced agroforestry technique that mimics natural succession processes to create highly productive, self-sustaining agricultural systems. In coffee production, it involves strategically planting diverse species that work together to create optimal growing conditions.